Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Experimental Report 6
Experimental Report 6
Uploaded by
Minh Huệ TôOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Experimental Report 6
Experimental Report 6
Uploaded by
Minh Huệ TôCopyright:
Available Formats
Experimental Report 6
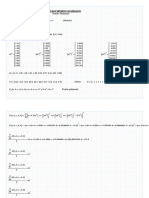
DETERMINATION OF SPECIFIC HEAT RATIO OF AIR
BASED ON CLEMENT DESORME’S METHOD
Student name: Nguyễn Hải Phong
Student ID: 20222797
Class: EE – E8 02 K67
Group: 05
Verification of the instructor
I. EXPERIMENT MOTIVATION
Cp
- To determine the specific heat ratio γ = C for air.
v
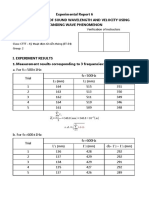
II. EXPERIMENT RESULTS
L1 = 410 (mm), L2 = 165 (mm), H = L1 – L2
H = 245 (mm)
Trial L1 (mm) L2 (mm) h = L2 – L1 (mm)
1 315 255 60
2 315 254 61
3 317 254 63
4 316 254 62
5 315 254 61
6 317 256 61
7 314 251 63
8 316 254 62
9 316 255 61
10 315 254 61
III. DATA PROCESSING
1. Calculation of the mean value of h:
10
1
h= ∑ h =6 1.5 ( mm )
10 i=1 i
2. Calculation of the uncertainty of h:
√∑
10
2
(hi−h)
s .d i=1
∆ h= = =0. 3(mm)
√10 10
Hence: h=6 1.5 ±0. 3(mm)
3. Calculation of the specific heat ratio γ
H
The formula: γ = H−h
H 245
γ= = =1.3 4
H−h 245−6 1.5
∆ γ =γ
√( h )
∆h 2
=1.3 4 ×
√( )
0. 3 2
6 1.5
≈ 0.0 1
Hence,
γ = 1.34 ± 0.01
IV.
COMPARISON AND CONCLUSION
Theoretically, we can calculate the specific heat ratio of air by using
i+ 2
the formula γ = i , where i = 5 which is the Degree of Freedom (DOF)
of ideal gas (in this case it is air). Hence, we get:
i+ 2 5+ 2
γ= = =1.40
i 5
The experiment result has a small difference from the
theoretical result due to instrumental uncertainty, observational
uncertainty and environment uncertainty.
You might also like
- Moonlight On Manila Bay by Fernando MDocument4 pagesMoonlight On Manila Bay by Fernando MAlex Zaragoza100% (1)
- Experiment 3-Fixed End Moment For A Fixed End BeamDocument7 pagesExperiment 3-Fixed End Moment For A Fixed End BeamIsmail Right67% (6)
- Information Booklet 22nd UCMAS Abacus & Mental Arithmetic International Competition 2017Document52 pagesInformation Booklet 22nd UCMAS Abacus & Mental Arithmetic International Competition 2017Viet NguyenHoang50% (2)
- Flexibility Method (Truss and Composite Structure)Document38 pagesFlexibility Method (Truss and Composite Structure)Roif Samsul0% (1)
- MMME2053-AsymBend Lab Report TemplateDocument7 pagesMMME2053-AsymBend Lab Report TemplateShuhang ChenNo ratings yet
- Wheelen Smbp13 PPT 06Document21 pagesWheelen Smbp13 PPT 06rikky adiwijayaNo ratings yet
- Amdahl LawDocument2 pagesAmdahl Lawsuresh012No ratings yet
- BÁO CÁO BÀI 6đã qua chỉnh sửa lần 1Document3 pagesBÁO CÁO BÀI 6đã qua chỉnh sửa lần 1Đỗ Quốc ViệtNo ratings yet
- Ex6 1Document2 pagesEx6 1Mạnh Duy TrầnNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6Document4 pagesExperiment 6Kiệt Như LêNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6 VMT đã chuyển đổi 1Document2 pagesExperiment 6 VMT đã chuyển đổi 1Geralt VesemirNo ratings yet
- Determination of Specific Heat Ratio of Air Based On Clement Desorme'S MethodDocument2 pagesDetermination of Specific Heat Ratio of Air Based On Clement Desorme'S MethodnamNo ratings yet
- Determination of Specific Heat Ratio of Air Based On Clement Desorme'S MethodDocument4 pagesDetermination of Specific Heat Ratio of Air Based On Clement Desorme'S MethodNguyễn Đức MạnhNo ratings yet
- Report 6Document4 pagesReport 6Đình TrườngNo ratings yet
- Econometrics For Finance Assignment 2 2023 12-07-12!14!23Document3 pagesEconometrics For Finance Assignment 2 2023 12-07-12!14!23Binyam Taye100% (1)
- thí nghiệm lý 2 06Document2 pagesthí nghiệm lý 2 06Hoang Anh PhamNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 PDFDocument4 pagesLab 4 PDFAisha NurymgaliNo ratings yet
- Experimental-Report-3 FixDocument7 pagesExperimental-Report-3 FixNguyễn Quốc HưngNo ratings yet
- D111171014 - Rickhardo W. Kasim - GEOTEKNIK TAMBANG - TUGAS 3 PDFDocument6 pagesD111171014 - Rickhardo W. Kasim - GEOTEKNIK TAMBANG - TUGAS 3 PDFwahyu KasimNo ratings yet
- Experimental Report 1 Measurement of Basic LengthDocument3 pagesExperimental Report 1 Measurement of Basic LengthCuber HCNo ratings yet
- Báo Cáo Lý 1Document31 pagesBáo Cáo Lý 1Việt HoàngNo ratings yet
- Basic Integration FormulasDocument17 pagesBasic Integration FormulasVincent DL TngNo ratings yet
- CC19 Group 1 Lab Report 10Document6 pagesCC19 Group 1 Lab Report 10PHƯỚC DƯƠNG THANHNo ratings yet
- Experiment Report 1Document5 pagesExperiment Report 1Kien Kieu GiaNo ratings yet
- Experiment Report 1 - DoneDocument4 pagesExperiment Report 1 - Donemaianh123vuNo ratings yet
- Open Ended LAB: Name: Ayyan AhmadDocument7 pagesOpen Ended LAB: Name: Ayyan AhmadMaheenNo ratings yet
- ECMT1020 - Week 02 Workshop Answers PDFDocument4 pagesECMT1020 - Week 02 Workshop Answers PDFperthwashington.j9t23No ratings yet
- Uji Hipotesis Statistika IndustriDocument15 pagesUji Hipotesis Statistika IndustriAdikka FatimahNo ratings yet
- The Method of Least Squares: Lectures INF2320 - P. 1/80Document80 pagesThe Method of Least Squares: Lectures INF2320 - P. 1/80stevecraigNo ratings yet
- Sample Applied Statistics and Probability For EngineersDocument7 pagesSample Applied Statistics and Probability For EngineersALBERT DAODANo ratings yet
- Problem Set No. 3Document16 pagesProblem Set No. 3MayNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio Con Pipe FlowDocument6 pagesEjercicio Con Pipe FlowInes Prado AceboNo ratings yet
- Physical Experiment 6 ViệtDocument3 pagesPhysical Experiment 6 ViệtLâm NgôNo ratings yet
- Problems Chap5Document2 pagesProblems Chap5Mohamed TahaNo ratings yet
- Experiment Report 3 Ban ChinhDocument9 pagesExperiment Report 3 Ban ChinhNgô Quang TúNo ratings yet
- NSTSE Class 05 Solution 449 2018 UpdatedDocument3 pagesNSTSE Class 05 Solution 449 2018 UpdatedG KumarNo ratings yet
- Bản sao của Experimental Report 3Document10 pagesBản sao của Experimental Report 3Kiệt Như LêNo ratings yet
- Reprot 1Document49 pagesReprot 1ntuanhung322No ratings yet
- LC+OL+Physics+Solutions 2015Document10 pagesLC+OL+Physics+Solutions 2015Mohamad NabihNo ratings yet
- Curiosities On The Monotone Preserving Cubic SplineDocument10 pagesCuriosities On The Monotone Preserving Cubic SplineRMolina65No ratings yet
- Statistical Notations and OperationsDocument9 pagesStatistical Notations and OperationsKrizell Jane Ojarliza Acha100% (1)
- 2 ReportDocument9 pages2 Reportsvzdv asdqNo ratings yet
- One Way AnovaDocument5 pagesOne Way AnovaJeff Rey Casiño DalubatanNo ratings yet
- A) Dados de Entrada : Méto Dos Mínimos Quadrados Funções PolinomiasDocument8 pagesA) Dados de Entrada : Méto Dos Mínimos Quadrados Funções PolinomiasLucas MartinsNo ratings yet
- Binomial - 4Document7 pagesBinomial - 4priyesatyamNo ratings yet
- Math Pages Did Not WriteDocument1 pageMath Pages Did Not WritebbNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICSDocument3 pagesMATHEMATICSoforiamponsahdaniel970No ratings yet
- Diffraction at A Slit and Heisenberg'S Uncertainty PrincipleDocument10 pagesDiffraction at A Slit and Heisenberg'S Uncertainty PrincipleĐào Lương Duy AnhNo ratings yet
- Experiment Report 6Document4 pagesExperiment Report 6Cuber HCNo ratings yet
- Informe 5 Pendulo FisicoDocument6 pagesInforme 5 Pendulo FisicoJohan Sebastian Niño UribeNo ratings yet
- Instructions: This Paper Consists of FIVE (5) Questions. Answer Any FOUR (4) Questions in TheDocument6 pagesInstructions: This Paper Consists of FIVE (5) Questions. Answer Any FOUR (4) Questions in TheZain Mirxa ChughtaiNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio 44 de La Guía de EstudioDocument1 pageEjercicio 44 de La Guía de EstudioJavier MogrovejoNo ratings yet
- Nghien Ray TronDocument13 pagesNghien Ray TronNguyễn Kiều Kim ThiNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology: Course Name: Chemical Engineering Laboratory-VDocument9 pagesBangladesh University of Engineering and Technology: Course Name: Chemical Engineering Laboratory-VMd Abid AfridiNo ratings yet
- SumFormulaFQ1985234380 381Document8 pagesSumFormulaFQ1985234380 381Mahmoud SabryNo ratings yet
- A Review of Basic Statistical Concepts: Answers To Odd Numbered Problems 1Document32 pagesA Review of Basic Statistical Concepts: Answers To Odd Numbered Problems 1Rafidul IslamNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document7 pagesLab 2shakcodproNo ratings yet
- University of Kirkuk College of Engineering Civil Engineering Dep Fluid LaboratoryDocument8 pagesUniversity of Kirkuk College of Engineering Civil Engineering Dep Fluid Laboratoryali najatNo ratings yet
- Trigo-Worksheet Class-11Document1 pageTrigo-Worksheet Class-11dodiumyashasNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 CLAYNO DOCUMENTATIONDocument4 pagesActivity 2 CLAYNO DOCUMENTATIONstephaniejeancortez522No ratings yet
- Be Computer Engineering Semester 3 2017 December Digital Logic Design and Analysis CbcgsDocument25 pagesBe Computer Engineering Semester 3 2017 December Digital Logic Design and Analysis CbcgsMadhura KanseNo ratings yet
- Report: Assignment 1: Compute Definite Integral Using C Code 1. ProblemDocument8 pagesReport: Assignment 1: Compute Definite Integral Using C Code 1. ProblemYosua Heru IrawanNo ratings yet
- HeatDocument7 pagesHeatSharonNo ratings yet
- Modular Forms and Special Cycles on Shimura Curves. (AM-161)From EverandModular Forms and Special Cycles on Shimura Curves. (AM-161)No ratings yet
- Measurements Lab Manual, Mechanical Engineering, MG UniversityDocument29 pagesMeasurements Lab Manual, Mechanical Engineering, MG Universitypramodkb_cusat100% (1)
- Exam-Style Paper A - Pure 1Document2 pagesExam-Style Paper A - Pure 1Syeda Asra AkhterNo ratings yet
- CoMAE - Yang Et Al - 2023Document10 pagesCoMAE - Yang Et Al - 2023xuhangmkNo ratings yet
- ANTHE-2020 - (X Studying) - Code-BDocument15 pagesANTHE-2020 - (X Studying) - Code-BG.K UpGradeNo ratings yet
- R.D. Nelson Et Al - A Linear Pendulum Experiment: Effects of Operator Intention On Damping RateDocument19 pagesR.D. Nelson Et Al - A Linear Pendulum Experiment: Effects of Operator Intention On Damping RateDominos021No ratings yet
- First Order OdeDocument43 pagesFirst Order OdeAkshat KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Progression Sequence DDocument4 pagesProgression Sequence DAyush ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Digital Electronics - Logic GatesDocument13 pagesFundamentals of Digital Electronics - Logic Gatesabhi soniNo ratings yet
- Lagrangian Relaxation With Gams PDFDocument5 pagesLagrangian Relaxation With Gams PDFCESARPINEDANo ratings yet
- Civil Service Commission Professional or Sub DwawdawdawdreviewerDocument99 pagesCivil Service Commission Professional or Sub DwawdawdawdreviewerHarey PatarNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus MMWDocument5 pagesCourse Syllabus MMWLysa DeeNo ratings yet
- PNL and Risk Analysis For Credit DerivativesDocument36 pagesPNL and Risk Analysis For Credit DerivativesTheodor MunteanuNo ratings yet
- ME - Computer - Engg 2017 - 20-6-17Document70 pagesME - Computer - Engg 2017 - 20-6-17ashwini wajeNo ratings yet
- Itae006 ExamDocument9 pagesItae006 ExamNageshwar Singh100% (1)
- Experience in The Application of Iec-Tr 61000-3-6 To Harmonic Allocation in Transmission SystemsDocument8 pagesExperience in The Application of Iec-Tr 61000-3-6 To Harmonic Allocation in Transmission Systemsrad1962No ratings yet
- Litterick Register FinalDocument12 pagesLitterick Register Finalpinakin4uNo ratings yet
- ETME205TS2Document1 pageETME205TS2Dishant KumarNo ratings yet
- CE 137 ReportDocument8 pagesCE 137 ReportKaren LovedorialNo ratings yet
- Determining The Relationship of The Volume of The Solid Figures Relationship of The Volume Between Rectangular Prism and PyramidDocument3 pagesDetermining The Relationship of The Volume of The Solid Figures Relationship of The Volume Between Rectangular Prism and PyramidChel CalejaNo ratings yet
- Multiplication of Fractions 2.1A Multiplication of A Proper Fraction by A Whole Number Chapter 2: FractionsDocument5 pagesMultiplication of Fractions 2.1A Multiplication of A Proper Fraction by A Whole Number Chapter 2: Fractionsparam1No ratings yet
- Full Solutions Manual To Accompany Introduction To Management Science 4Th Edition PDF Docx Full Chapter ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Solutions Manual To Accompany Introduction To Management Science 4Th Edition PDF Docx Full Chapter Chapterbibberbombycid.p13z100% (14)
- Trib Us 1961Document684 pagesTrib Us 1961niltonbispoNo ratings yet
- New Method To Compute The Determinant of A 4x4 Matrix: Conference PaperDocument9 pagesNew Method To Compute The Determinant of A 4x4 Matrix: Conference PaperKene KasimanNo ratings yet
- PROCEQ - PROFOMETER 5 (V2.3.1, 57.8004) Rebar Locator Title: Date: Name: RemarksDocument1 pagePROCEQ - PROFOMETER 5 (V2.3.1, 57.8004) Rebar Locator Title: Date: Name: RemarksJannes PandianganNo ratings yet