0% found this document useful (0 votes)
156 views5 pagesDigestive System Exam Review
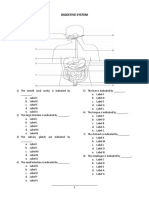
The document is a science exam for 8th grade students covering topics in digestive system anatomy and physiology. It contains 50 multiple choice questions and 12 matching questions testing knowledge of the digestive tract organs and their functions, digestive enzymes, and processes like peristalsis. The questions cover the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, liver, pancreas and large intestine. Students are asked to identify structures, their locations and roles in digestion.
Uploaded by
ALYSSA MAE DAPADAPCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
156 views5 pagesDigestive System Exam Review
The document is a science exam for 8th grade students covering topics in digestive system anatomy and physiology. It contains 50 multiple choice questions and 12 matching questions testing knowledge of the digestive tract organs and their functions, digestive enzymes, and processes like peristalsis. The questions cover the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, liver, pancreas and large intestine. Students are asked to identify structures, their locations and roles in digestion.
Uploaded by
ALYSSA MAE DAPADAPCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd