Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Repro Ssystem
Uploaded by
Guen0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views6 pagesOriginal Title
REPRO SSYSTEM - Copy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views6 pagesRepro Ssystem
Uploaded by
GuenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
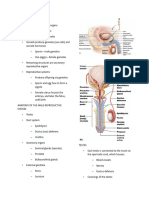
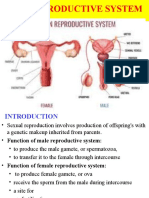
• Sex cells- gametes • Membranous urethra- spanning
• Reproductive system- reproduce distance from prostatic urethra to the
offspring penis
• Male gametes- sperm • Spongy (penile) urethra- running
• Female gametes- ova within the length of penis and opening to
• Fertilized egg- zygote body exterior
• From embryo to fetus • Seminal vesicle (paired)
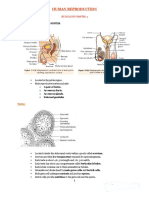
• Testes- size: 4 cm (1.5 inches) long and - located at the base of the bladder
2.5 cm (1inch) wide - size: 6-7 cm
• Spermatic cord- connective tissue - produce 60% of seminal fluid
sheath that encloses blood vessels, - thick yellowish secretion rich in
nerves and ductus deferens fructose
• Tunic albuginea- connective tissue • Prostate(single)
capsule that surrounds each testis - Single doughnut-shaped gland
• Septa- extension of each capsule - About size of peach pit
• Seminiferous tubules- the actual - Milky and plays a role in activating
sperm-forming factors sperm
• Rete testis- locate one side of the testis • Bulbourethral glands(paired)
- Tiny pea-sized glands
• Interstitial cells- functionally distinct cells
- Secretion that is first to pass when
that produce androgens- testosterone
sexual excitement
• Duct system
- Cleanses urethral of trace acidic
- Epididymis
urine prior to ejaculation
- Ductus deferens
- Acts as lubricants
- Urethra
• Cystitis- bladder inflammation
• Epididymis
• Prostatitis- inflammation of the prostate
- highly convoluted tube about 6 cm
(20 feet). Hugs posterior side of • Prostate cancer- 3rd most prevalent
testis. First part of male duct system cancer in men
- provide temporary storage site of • Semen- milky white somewhat sticky
immature sperm mixture of sperm and accessory gland
• ejaculates- shoot forth secretions
• Ductus deferens • Acidic condition- below Ph 6
- Vas deferens • Alkalinity of semen- pH 7.2-7.6
- Propel live sperm from their storage • Female’s vagina acidity- pH 3.5-4
sites • 2-5mL(a teaspoon)- semen propelled
• Ampulla- end of ductus deferens that out during ejaculation
expands • 50-150 million sperm in each millimeter
• Ejaculatory duct • Male infertility- inability to conceive a
• Vasectomy- birth control that have child
small incision into the scrotum and then • Semen analysis- test done when
cuts through and ties off the ducts of couple has been unable to conceive
deferens • Scrotum- a divided sac of skin with
• Urethra- terminal part of duct system sparse hairs that hangs outside
(males) • 3 C(5.4F)- a temperature provided by
• Prostatic urethra- surrounded by scrotum for production of healthy sperm
prostate gland
• Penis- deliver sperm into the female • Secondary sex characteristics- are
reproductive tract features induced in nonreproductive
• Shaft- body of penis organs by sex hormones
• Glans penis- enlarged tip end of penis • Sexual infantilism- secondary sex
• Prepuce/foreskin- skin covering the characteristics never appear, and other
penis that is loose and folds downward reproductive organs remain childlike
from a sleeve of skin • Castration- inability of interstitial cells to
• Circumcision- foreskin is surgically produce testosterone
removed • Sterility- occurs because testosterone
• Erectile tissue- spongy tissue that fills is necessary for final stages of sperm
with blood during sexual excitement production
• Erection- help penis serve as male • Ovaries
organ of copulation to deliver semen - primary female reproductive organ
into female reproductive tract - shape of almonds but twice large
• Copulation- sexual intercourse • Ovarian follicles- tiny saclike structures
• Spermatogenesis- sperm production • Oocyte- immature egg
• Spermatogonia- primitive stem cells • Antrum- fluid-filled central region of
• Primary spermatocyte- destined to follicle
undergo meiosis • Vesicular follicle or Graafian follicle-
• Meiosis- special type of nuclear division mature and developing egg ready to be
that occurs for most part only in gonads. ejected
It results four daughter cells instead of • Corpus luteum- ruptured follicle
two • Ovulation occurs every 28 days
• Spermatids- gametes during • Suspensory ligaments- secured the
spermatogenesis organs to the lateral walls of pelvis
• Spermiogenesis- all excess cytoplasm • Ovarian ligaments- anchor organs to
is sloughed off and what remains is the uterus medially
compacted three regions of mature • Uterine tubes
sperm - Also called fallopian tube
• Acrosome- anterior to the nucleus and - Receive ovulated oocyte and
is helmetlike. Produce by Golgi provide site where fertilization occur
apparatus and similar to lysosome - About 10 cm (4 inches)
• Filaments- form the long tail arise from • Infundibulum- distal end of each
proximal centriole in the midpiece uterine tube expands as funnel-shaped
• Mitochondria- wrapped tightly around • Fimbriae- fingerlike projections that
these filaments provide ATP partially surround ovary
• 64-72 Days: entire process of formation • 3-4 days: journey to uterus
of primary spermatocyte • Most 24 hours- viability of oocyte
• Testosterone- produced by interstitial • Gonorrhea- a sexually transmitted
cells and most important hormonal bacteria sometimes infect peritoneal
product of testes cavity
• Luteinizing hormone (LH)- activates • Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)-
the interstitial cells and is released by can cause scarring and closure of the
anterior pituitary gland narrow uterine tubes
• Uterus • Labia minora- two delicate hair-free
- a hollow organ that functions to folds
receive, retain and nourish fertilized • Vestibule- contains external openings
egg of urethra
- about the size and shape of a pear • Clitoris- small protruding structure that
• Major parts of uterus corresponds to male penis. It is sensible
✓ Fundus erectile tissue that swollen with blood
✓ Body • Greater vestibular glands- pair of
✓ Cervix mucus-producing glands that flank
• Body- major portion of uterus vagina. Lubricates distal end of vagina
• Fundus- rounded region superior to the during intercourse
entrance of the uterine tubes • Perineum- the diamond-shaped region
• Cervix- narrow outlet that protruded between anterior end of labial folds
inferiorly • Oogenesis- a process where ova or
• Endometrium- inner layer of uterus gametes are produced
• Myometrium- bulky middle layer of • Oogonia- female stem cell
uterus. It is composed of bundles of • Primary oocytes- daughter cells
smooth muscles • FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone)-
• Perimetrium(visceral peritoneum)- stimulate small number of follicles to
outermost layer of uterus grow and mature each month
• Implantation- fertilized egg burrows into • There is only ONE ovulation event
the endometrium PER MONTH
• Menstruation- endometrial lining • Fewer than 500 ova out of potential
sloughs off periodically usually about 300,000 are released during lifetime
every 28 days • Larger cell- secondary oocyte
• Cervical cancer- common among • Very tiny cell- polar body
women ages 30-50 • Corona radiata- follicle-cell capsule that
• HPV (human papillomavirus) surrounds secondary oocyte
infection- major cause of cervical • Mittelschmerz (middle pain)- pain in
cancer the lower abdomen when ovulation
• Pap smear- diagnostic test for detecting occurs. Caused by intense stretching of
slow-growing cancer ovarian wall during ovulation
• Gardasil: a 3-dose vaccine that • Meiosis in females yield only one
provides protection for most common functional ovum and three tiny polar
types of HPV induced cervical cancer bodies
• Vagina- thin-walled tube to 10 cm (3-4 • Estrogens- produced by follicle cells of
inches long. Often called birth canal. It growing and mature follicles . It causes
provides passageway for delivery of the appearance of secondary sex
infant and for menstrual flow characteristic of young woman
• Hymen- very vascular that it bleeds • Sperm: tiny and equipped with tails and
when ruptured during first sexual locomotion
intercourse • Egg: large and nonmotile cell
• Mons pubis- a fatty rounded area
overlying pubic symphysis
• Labia majora- two elongated hair-
covered skin folds
• Progesterone • Breast cancer- hereditary defects and
- second ovarian hormone could be from dangerous mutations.
- Produced by glandular corpus Symptoms: change in skin texture,
luteum puckering and leakage from the nipple
- It helps to maintain the pregnancy • Mammography- x-ray examination that
and prepare breast for milk detects breast cancer (less than 1 cm)
production • Pregnancy- refers to events that occur
• Uterine cycle (menstrual cycle)- form the time fertilization (conception)
series of cyclic changes that the until birth
endometrium (mucosa of the uterus) • Conceptus- pregnant woman’s
goes thru each month as it responds to developing offspring
changing blood levels of ovarian • Gestation period (to carry)- extends
hormones by convention from last menstrual
• Both ovarian and uterine cycles are period until birth. Approx 280 days
about 28 days long • Fertilization- Week 8(embryonic
• Ovulation typically occurs midway period) : Embryo
• 3 Menstrual cycle Phases • Week 9 through birth (fetal period):
✓ Day 1-5: Menstrual phase Fetus
✓ Day 6-14: Proliferative phase • 1-2 hours for the sperm to complete the
✓ Day 15-28: Secretory phase journey up to female duct system
• Menstrual phase- functional layer of • Acrosomal reaction- acrosome
endometrial lining is sloughing off and membranes breakdown releasing
detached tissues and blood pass enzymes that digest holes in the
through vagina as menstrual flow surrounding oocyte membrane
• 3-5DAYS: duration of period • Fertilization- occurs at the moment the
• 50-150mL (1/4 to ½ cup)- blood loss genetic material of a sperm combines
during menstrual period with that of an ovum to form fertilized
• Proliferative phase: rising level of egg or zygote
estrogen and regeneration of functional • Cleavage-rapid mitotic-cell divisions
layers. Endometrium becomes velvety, forming first two cells then four
thick and well vascularized again • Morula- tiny ball of 16 cells that looks
• 14-15 days: time from ovulation to the like a microscopic raspberry
beginning of menses • Blastocyst- a ball-like structure
• Mammary glands(modified sweat • Human chorionic gonadotropin
glands)- produce milk to nourish a (HCG)- an LH hormone that prods
newborn baby corpus luteum of ovary to continue
• Areola- pigmented are of center of each producing its hormones
breast • Trophoblast- form the large fluid-filled
• Nipple- central protruding sphere
• Alveolar glands- produce milk when • Inner cell mass- a small cluster of cells
woman is lactating on one side
• Lactiferous ducts- open to the outside • Day 7 of ovulation, blastocyst attached
of the nipple to the endometrium
• Lactiferous sinus- where milk • Ectoderm- which will become nervous
accumulates during nursing system and epidermis of skin
• Endoderm- forms mucosae and • Stages of Labor:
associated glands ✓ Dilation stage
• Mesoderm- will become everything else ✓ Expulsion stage
• Day 14: Implantation is done ✓ Placental stage
• Chorionic villi- elaborate projections that • Appearance of true contractions where
combine with the tissues of mother’s cervix is fully dilated by baby’s head
uterus to form placenta (about 10 cm)
• Amnion- fluid-filled sac and is attached • Water breaking- when amnion raptures
to the placenta by umbilical cord and amniotic fluid flows out
• Umbilical cord- a blood vessel- • Dilation stage- is the longest stage in
containing stalk of tissue laboring and usually last for 6-12 hours
• 8th week of embryonic development • Expulsion stage- the period from full
all groundwork has been completed dilation to delivery of the infant. Last for
• 55 cm or 22 inches: total body length at 2 hours
birth • Placental stage- delivery of placenta
• Approximately 270 days after (15 minutes done)
fertilization, the fetus is said to be “full- • Vertex position- head-first presentation
termed” of the baby
• Relaxin- a placental production that • Breech position- buttock- first
causes pelvic ligaments and pubic presentation. Sometimes require
symphysis to relax, widen, and become forceps or vacuum extractor
more flexible • Dystocia- oxygen delivery to the infant
• 300 additional calories- daily to sustain is inadequate leading to fetal brain
proper fetal growth damage
• Miscarriage- natural termination of • C-section (cesarian section)- delivery
pregnancy of infant through the surgical incision
• Abortion- medical termination of made through abdominal and uterine
pregnancy walls
• GI System; • Afterbirth- placenta and its attached
✓ Morning sickness fetal membranes
✓ Heartburn • Pseudohermaphrodites- individuals
✓ Constipation with external genitalia that don’t match
• Urinary system; their gonads
✓ Urination becomes frequent • True hermaphrodites- rare individuals
• Parturition- childbirth, is the culmination who possess both ovarian and testicular
of pregnancy tissues
• Labor- series of events that expel the • XO female appear normal but lacks
infant from uterus ovaries
• Baraxton Hicks- a weak, irregular • YO males die during development
uterine contractions that have cause • Phimosis- a narrowing of the foreskin of
many to go hospital but told to go home the penis and misplaced urethral
due to FALSE LABOR openings
• Oxytocin and Prostaglandins- • Cryptorchidism- failure of testes to
hormones that stimulate more frequent make their normal descent
and powerful contractions. Needed to • Puberty- the period of life, ages
initiate labor between 10-15 years when reproductive
organs grow to their adult size and
become functional
• Escherichia coli- spread from digestive
tract
• Sexually transmitted microorganism;
• Yeast- type of fungus
• Common inflammatory conditions in
men; Urethritis, prostatitis,
epididymitis
• Orchitis- inflammation of the testes
• Menopause- ending childbearing ability.
Ages 46-54
• Hot flashes- intense vasodilation of
skin’s blood vessels
• HRT estrogen-containing hormone
therapy
• Andropause- steady decline in
testosterone secretion and a longer
latent period after orgasm
You might also like
- Innocent Words That Make Her HornyDocument14 pagesInnocent Words That Make Her HornyH69% (13)
- Installation of Submarine PE PipesDocument84 pagesInstallation of Submarine PE Pipeswaseemiqbal133100% (2)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Female Reproductive SystemDocument34 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Female Reproductive Systemruthpebbles100% (2)
- Literature Review - Part Time Job Among StudentDocument3 pagesLiterature Review - Part Time Job Among StudentMarria65% (20)
- 2020 - Reproductive System - Lecture NotesDocument18 pages2020 - Reproductive System - Lecture Notesinsight scienceNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive System The Reproductive System: © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. 1Document19 pagesThe Reproductive System The Reproductive System: © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. 1lourd nabNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive System The Reproductive System: © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. 1Document19 pagesThe Reproductive System The Reproductive System: © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. 1valjulene monteNo ratings yet
- MF009 6B Human Reproduction System James LDocument26 pagesMF009 6B Human Reproduction System James LPikuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Male and Female Reproductive SystemDocument13 pagesAnatomy of The Male and Female Reproductive SystemThrecia RotaNo ratings yet
- Safe Environment ContractDocument37 pagesSafe Environment Contractdipanjang panjanginNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionDocument16 pagesLesson 4 Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionAngel AsisNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument94 pagesHuman ReproductionDivya AgarawalNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument92 pagesMale Reproductive SystemYunandhika RizkiNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproductive SystemDocument46 pagesSexual Reproductive Systemred JimNo ratings yet
- Human Male Reproductive SystemDocument45 pagesHuman Male Reproductive Systemcyber secNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 STARS REVIEWERDocument12 pagesGrade 10 STARS REVIEWERjulianna startNo ratings yet
- Male SubfertilityDocument41 pagesMale SubfertilityIshaThapaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction SystemDocument81 pagesReproduction SystemGabrielle GreyNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System Male and FemaleDocument61 pagesReproductive System Male and FemaleAsad KHAN100% (1)
- Basic Steps in Human ReproductionDocument14 pagesBasic Steps in Human ReproductionMauz KhanNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument30 pagesMale Reproductive SystemRaisashimi M.S.100% (1)
- Histologi Reproduksi PriaDocument45 pagesHistologi Reproduksi Priablack junoNo ratings yet
- 04 Reproductive Anatomy - Physiology - Fetal Structure 1Document10 pages04 Reproductive Anatomy - Physiology - Fetal Structure 1Gwen CastroNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemnotesDocument26 pagesThe Reproductive SystemnotesJared Bien TagolimotNo ratings yet
- 5a. Male & Female Reproductive AnatomyDocument119 pages5a. Male & Female Reproductive AnatomyvictorNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of ReproductionheavenNo ratings yet
- Biology 2 Lecture 10 - Reproductive SystemDocument42 pagesBiology 2 Lecture 10 - Reproductive SystemRYLE IBANEZNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System: Endocrinology of ReproductionDocument40 pagesReproductive System: Endocrinology of ReproductiongerginNo ratings yet
- 11 Reproductive SystemDocument51 pages11 Reproductive Systemamare mitkuNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument5 pagesHuman ReproductionHimanshu Harsh 12th ANo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Human Reproduction - STUDY RATEDocument14 pagesChapter 3 - Human Reproduction - STUDY RATEsriharshitha darapuNo ratings yet
- 3Q Module 1 Male and Female Reproductive Systems 1Document29 pages3Q Module 1 Male and Female Reproductive Systems 1Pau BluzaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 2nd-U-6 Reproductive SystemDocument134 pagesAnatomy 2nd-U-6 Reproductive Systemsinte beyuNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper Rizal PlumaDocument33 pagesReaction Paper Rizal PlumaJazzd Sy Gregorio0% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Male Reproductive SystemDocument81 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Male Reproductive SystemMj BrionesNo ratings yet
- Q4 Lesson 4 Plant and Animal ReproductionDocument38 pagesQ4 Lesson 4 Plant and Animal ReproductionPhan MhiveNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument11 pagesHuman ReproductionAdesh BhullarNo ratings yet
- Part 8 - Human Male Reproductive SystemDocument19 pagesPart 8 - Human Male Reproductive SystemAmal Naeem JHNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System - Anatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive SystemDocument47 pagesReproductive System - Anatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive SystemGeorge MunyendoNo ratings yet
- MCHNDocument6 pagesMCHNAine Jermaine GatchalianNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction: 3.1: Male Reproductive SystemDocument27 pagesHuman Reproduction: 3.1: Male Reproductive SystemAvik BhaumikNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Nursing NotesDocument7 pagesMaternal and Child Nursing NotesVillanueva, Jony Miaca O.No ratings yet
- Human Sexuality Unit: Reproductive SystemsDocument38 pagesHuman Sexuality Unit: Reproductive SystemsMary Grace CacalNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument43 pagesHuman Reproductive Systembabaaijaz01No ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument38 pagesReproductive Systemkhairul rizkiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy For DocmmiesDocument41 pagesAnatomy For DocmmiesMartinez_DONo ratings yet
- Enhanced Notes 3 Reproductive SystemDocument5 pagesEnhanced Notes 3 Reproductive SystemLyle CasulNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument32 pagesReproductive SystemZephie100% (1)
- Reproductive Function: Physiology Department Medical School, University of Methodist IndonesiaDocument21 pagesReproductive Function: Physiology Department Medical School, University of Methodist IndonesiaAlex Syaputra SihalohoNo ratings yet
- Y11 Hum - Rep1 20 3 17Document8 pagesY11 Hum - Rep1 20 3 17Rabia RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Contents of PelvisDocument38 pagesContents of Pelvisdr_asalehNo ratings yet
- W2 - Human Reproductive SystemDocument35 pagesW2 - Human Reproductive Systemleo manalonNo ratings yet
- 8 - Reproductive SystemDocument29 pages8 - Reproductive SystemDance TagleNo ratings yet
- Basic Human AnatomyDocument43 pagesBasic Human AnatomyZirah Lee ValledorNo ratings yet
- Sistem Reproduksi PriaDocument87 pagesSistem Reproduksi PriaAnonymous uLcvBr5ywNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument30 pagesMale Reproductive SystemChinju Jose SajithNo ratings yet
- Department of Zoology Govt Hss Mylachal: PresentsDocument69 pagesDepartment of Zoology Govt Hss Mylachal: PresentsBiju MylachalNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Reproductive SystemDocument32 pagesScience 10 - Reproductive SystemHanabi Scarlet ShadowNo ratings yet
- HumanreproductionpptDocument59 pagesHumanreproductionpptsugi sivamNo ratings yet
- Repro A 2017Document94 pagesRepro A 2017Ruvarashe MutadzaNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive System: Anatomy and Physiology of The Male and Female Reproductive SystemsDocument55 pagesThe Reproductive System: Anatomy and Physiology of The Male and Female Reproductive SystemsJeffrey Roy Adlawan LopezNo ratings yet
- Science Lesson 1 G5 1Document31 pagesScience Lesson 1 G5 1Sarah JumalonNo ratings yet
- Chapter8-12 NotesDocument15 pagesChapter8-12 NotesGuenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - SKELETALSYSTEMDocument22 pagesChapter 5 - SKELETALSYSTEMGuenNo ratings yet
- Chapters 1 and 2Document20 pagesChapters 1 and 2GuenNo ratings yet
- Digestive and Body MetabolismDocument25 pagesDigestive and Body MetabolismGuenNo ratings yet
- Overview (Advance)Document8 pagesOverview (Advance)GuenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 (Skin&membranes)Document12 pagesChapter 4 (Skin&membranes)GuenNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument1 pageAnatomyGuenNo ratings yet
- Drugs PregnancyDocument9 pagesDrugs PregnancyPamelaS9No ratings yet
- Pharmacy Guidelines For Dispensing of MedicinesDocument9 pagesPharmacy Guidelines For Dispensing of MedicinesAngelica Lee Acebuche PalmeroNo ratings yet
- Composition of Meat JoanDocument7 pagesComposition of Meat JoanGuenNo ratings yet
- Composition of Meat JoanDocument7 pagesComposition of Meat JoanGuenNo ratings yet
- Cheese ProductionDocument11 pagesCheese ProductionGuenNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER I Lesson II Seven Environmental PrinciplesDocument17 pagesCHAPTER I Lesson II Seven Environmental PrinciplesTrixie jade DumotNo ratings yet
- MSDS Leadframe (16 Items)Document8 pagesMSDS Leadframe (16 Items)bennisg8No ratings yet
- Buddha Mind PDFDocument32 pagesBuddha Mind PDFVishal GadeNo ratings yet
- Assessment - UK Forestry Data ICT THEORY For CAT1Document13 pagesAssessment - UK Forestry Data ICT THEORY For CAT1Joanna AchemaNo ratings yet
- Data Mining in IoTDocument29 pagesData Mining in IoTRohit Mukherjee100% (1)
- ANTINEOPLASTICSDocument21 pagesANTINEOPLASTICSGunjan KalyaniNo ratings yet
- Swift As A MisanthropeDocument4 pagesSwift As A MisanthropeindrajitNo ratings yet
- Very Hungry Caterpillar Clip CardsDocument5 pagesVery Hungry Caterpillar Clip CardsARTGRAVETO ARTNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Newtonian and Non-Newtonian Fluid and Give Example For Each Case?Document11 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Newtonian and Non-Newtonian Fluid and Give Example For Each Case?MOHAMED ABD ELGHANYNo ratings yet
- (Bruno Bettelheim) Symbolic Wounds Puberty RitesDocument196 pages(Bruno Bettelheim) Symbolic Wounds Puberty RitesAmbrose66No ratings yet
- Adigwe J. C.: ATBU, Journal of Science, Technology & Education (JOSTE) Vol. 3 (1), January, 2015 ISSN: 2277-0011Document16 pagesAdigwe J. C.: ATBU, Journal of Science, Technology & Education (JOSTE) Vol. 3 (1), January, 2015 ISSN: 2277-0011AnnyNo ratings yet
- QSasDocument50 pagesQSasArvin Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- XXXX96 01 01 2023to28 08 2023Document18 pagesXXXX96 01 01 2023to28 08 2023dabu choudharyNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect and Present Perfect ProgressiveDocument5 pagesPresent Perfect and Present Perfect ProgressiveKiara Fajardo matusNo ratings yet
- Anykycaccount Com Product Payoneer Bank Account PDFDocument2 pagesAnykycaccount Com Product Payoneer Bank Account PDFAnykycaccountNo ratings yet
- Chromatographic Separation PDFDocument7 pagesChromatographic Separation PDFNicolle CletoNo ratings yet
- Lahore Waste Management CompanyDocument45 pagesLahore Waste Management CompanyHadia NasirNo ratings yet
- LT3845ADocument26 pagesLT3845Asoft4gsmNo ratings yet
- PV Power To Methane: Draft Assignment 2Document13 pagesPV Power To Methane: Draft Assignment 2Ardiansyah ARNo ratings yet
- 1 AlarmvalveDocument9 pages1 AlarmvalveAnandNo ratings yet
- Class 1 KeyDocument3 pagesClass 1 Keyshivamsingh.fscNo ratings yet
- Collins Ks3 Science Homework Book 3Document5 pagesCollins Ks3 Science Homework Book 3g3pz0n5h100% (1)
- Royal British College Dancesport TeamDocument10 pagesRoyal British College Dancesport TeamAnna rose CabatinganNo ratings yet
- AIP 2020 FINAL JuneDocument5 pagesAIP 2020 FINAL JuneVINA ARIETANo ratings yet
- 835 (Health Care Claim PaymentAdvice) - HIPAA TR3 GuideDocument306 pages835 (Health Care Claim PaymentAdvice) - HIPAA TR3 Guideअरूण शर्माNo ratings yet
- Full Download University Physics With Modern Physics 14th Edition Young Test Bank PDF Full ChapterDocument13 pagesFull Download University Physics With Modern Physics 14th Edition Young Test Bank PDF Full Chapterpoetrycloudyzjm12q100% (19)
- CBC DrivingDocument74 pagesCBC DrivingElonah Jean ConstantinoNo ratings yet