Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Neuroanatomy
Uploaded by
andreapurcanciolopezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is Neuroanatomy
Uploaded by
andreapurcanciolopezCopyright:
Available Formats
What is Neuroanatomy?
Neuroanatomy is the study of the structure of the nervous system, both at the macroscopic level, as well as tissu
es, cells, and neural connections.
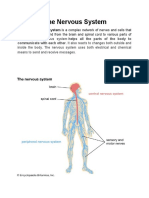
The nervous system
The nervous system transmits signals between the brain and the rest of the body, including internal organs.
In this way, nervous system activity controls the ability to move, breathe, see, think, and more. The basic unit of
the nervous system is a nerve cell, or neuron.
The central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord.
The peripheral nervous system is made up of all the nerves that branch from the spinal cord and extend to all
parts of the body.
Brain hemispheres
Left hemisphere: is responsible for producing language, numerical ability, reasoning, scientific ability, and
right hand control.
Right hemisphere: is responsible for three-dimensional perception, novel information processing, imagination,
functions of artistic ability and control of the left hand.
Brain lobes
Front: it is motor cut. It is responsible for reasoning, thinking and personality.
Parietal: it is somatosensory in nature. It is responsible for perception touch, pain and temperature, among
others.
Temporary: it is closely related to the processes of hearing, smell, language and memory.
Occipital: is responsible for processing visual information (perception).
Neurons
eurons are the functional cells of nervous tissue, they interconnect chemically and electrically (synapses), and
form networks of communication that transmit signals through defined areas of the system highly strung
Receive signals from sensory receptors.
Conduct these signals as nerve impulses.
Transmit the signals to other neurons or to effector cells.
Synapse
It is the process in which a neuron transmits the message or impulse nerve to another effector neuron,
interconnecting chemically or electric.
electrical: The transmission of the first neuron with the second is not produced by secretion of a
neurotransmitter
Chemistry: occurs through cells that are separated from each other by a space called the "synaptic cleft" and
the neural communication occurs through neurotransmission
You might also like
- Gale Researcher Guide for: Overview of Physiology and NeuropsychologyFrom EverandGale Researcher Guide for: Overview of Physiology and NeuropsychologyNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Nervous System NotesDocument8 pages3.1 Nervous System NotesabaybezawitNo ratings yet
- 3-Neural Basis of Cognition & Organization of Nervous SystemDocument36 pages3-Neural Basis of Cognition & Organization of Nervous Systemazharayesha64No ratings yet
- Nerve CellDocument17 pagesNerve CellCathy C DNo ratings yet
- Nervou S System:: NeuronsDocument16 pagesNervou S System:: NeuronsFizzah100% (4)
- CNS and PNSDocument4 pagesCNS and PNSDeepshikhaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab Disc 7Document44 pagesAnaphy Lab Disc 7BSLMS1D - Depasupil, Laurice Ann A.No ratings yet
- Neurons Elements of BehaviourDocument3 pagesNeurons Elements of Behaviourchantefraser8No ratings yet
- Structure of Brain Nervous System-20-04-2020Document3 pagesStructure of Brain Nervous System-20-04-2020Jethalal GadaNo ratings yet
- What Is The Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesWhat Is The Nervous SystemDavid ToledoNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument36 pagesThe Nervous SystemespirituronnierickNo ratings yet
- Human BrainDocument17 pagesHuman BrainAkbota KuanishkyzyNo ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviourDocument74 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviourytsrajalmaharjanNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - Summary NotesDocument9 pagesNervous System - Summary NotesHarshNo ratings yet
- ANATOMYDocument4 pagesANATOMYChristine IgnasNo ratings yet
- Questions and AnswersDocument15 pagesQuestions and AnswersTanveerAli01No ratings yet
- LomneuronotesDocument60 pagesLomneuronotesLibi FarrellNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesNervous Systemkitkat22phNo ratings yet
- Brain and NeuronDocument2 pagesBrain and NeuronMuhammad Ilham UtamaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesNervous SystemJavi OceansoulNo ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviourDocument34 pagesBiological Basis of Behaviouralizaakif3No ratings yet
- Coordinated Function of Nervous, Endocrine, and Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesCoordinated Function of Nervous, Endocrine, and Reproductive SystemPosionous SubstancesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document8 pagesChapter 2itxkazimNo ratings yet
- Neurons: Cells of The Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesNeurons: Cells of The Nervous SystemItpixels OfficebackdoorNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Neuroscience and BehaviourDocument7 pages1.2 Neuroscience and BehaviourDiya MehtaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesNervous SystemShinar EsparteroNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - Overview: FunctionDocument11 pagesNervous System - Overview: FunctionAadil JuttNo ratings yet
- Human Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesHuman Nervous Systemzainab umerNo ratings yet
- Physiological Basis of Behaviour: Neurons: Structure and Function, Synapse and NeurotransmittersDocument12 pagesPhysiological Basis of Behaviour: Neurons: Structure and Function, Synapse and NeurotransmittersKiran TradeNo ratings yet
- NeuropsychologyDocument28 pagesNeuropsychologyFarhan AkhtarNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument41 pagesThe Nervous Systemclnquita9No ratings yet
- Nervous System PresentationDocument24 pagesNervous System Presentationv8569zm58gNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesThe Nervous SystemAkheyla GarciaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument46 pagesNervous SystemMac Gab100% (3)
- Chapter SummaryDocument2 pagesChapter SummaryrogelynlumasagNo ratings yet
- Control and CoordinationDocument4 pagesControl and CoordinationdeveshigiricontactNo ratings yet
- Weekly AssignmentDocument7 pagesWeekly AssignmentBajwa AyeshaNo ratings yet
- Presentation Biology in Healthcare Stage4Document29 pagesPresentation Biology in Healthcare Stage4alanmauriciohdzNo ratings yet
- Preparation in Psychology: Bicol University College of Engineering East Campus LegazpiDocument8 pagesPreparation in Psychology: Bicol University College of Engineering East Campus LegazpiKielNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesThe Nervous SystemKristiene Kyle AquinoNo ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviorDocument57 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviorJAMES ALDRIN CALVEZ PAMPOSANo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination, PPT, Module-1.3Document22 pagesControl and Coordination, PPT, Module-1.3Khushi GuptaNo ratings yet
- BIOAA1BSP221E - Neutral Conduction - MendozaDocument6 pagesBIOAA1BSP221E - Neutral Conduction - MendozaCassandraNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System in CatsDocument2 pagesThe Nervous System in CatsadierinNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesNervous SystemIhtisham Ul haqNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument24 pagesNervous SystemJeus BatadlanNo ratings yet
- Form 3 History BookDocument21 pagesForm 3 History BookDISHONNo ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviourDocument21 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviourSufian Khan100% (1)
- ASSIGNMENT 2 in ScienceDocument1 pageASSIGNMENT 2 in Sciencezionselegna012808No ratings yet
- Coordinated Functions Nervoys SDocument3 pagesCoordinated Functions Nervoys SGwency Ross Alvarez (Gwen)No ratings yet
- Molina, Zciedie FDocument2 pagesMolina, Zciedie FZeny Ann MolinaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 Finals ExamDocument32 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Finals ExamJohn Lloyd BallaNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Nervous SystemDocument18 pagesModule 7 Nervous SystemMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument28 pagesNervous SystemPhoebe dane M PandayNo ratings yet
- PY1101 Lecture 3 NotesDocument9 pagesPY1101 Lecture 3 NotesSeah Fu MeiNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument86 pagesThe Nervous SystemNatukunda Dianah100% (1)
- Bilology XII 2014 Ch-17 Nervous CoordinationDocument26 pagesBilology XII 2014 Ch-17 Nervous CoordinationMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument24 pagesNervous SystemaldensolaNo ratings yet
- Mind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.From EverandMind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.No ratings yet