Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Winter School Maths Revision
Uploaded by
AthiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Winter School Maths Revision
Uploaded by
AthiCopyright:
Available Formats
Winter school revision booklet
Functions
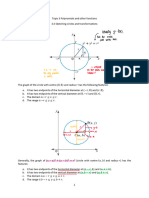
1.1 Graphs – Grade 11 Summary and examples
The Parabola
2.1 Sketching a parabola
2.2 Determine the equation of a parabola
The Hyperbola
3.1 Sketching a hyperbola
3.2 Determine the equation of a hyperbola
The Exponential Graph
4.1 Sketching a exponential graph
4.2 Determine the equation of a exponential graph
Inverse Functions
Consolidation
6.1 Algebra
6.2 Functions
Grade 12 Tutoring Programme: MATHEMATICS 2
1. GRAPHS – SUMMARY AND EXAMPLES
1.1 Summary of the GR11 Graphs
GRAPH NAME Parabola Hyperbola Exponential Graph
EQUATION 𝑦𝑦 = 𝑎𝑎𝑥𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑏𝑏𝑏 + 𝑐𝑐 𝑘𝑘 𝑦𝑦 = 𝑎𝑎 𝑥𝑥+𝑝𝑝 + 𝑞𝑞
𝑦𝑦 = + 𝑞𝑞
𝑥𝑥 + 𝑝𝑝
WHAT YOU 𝑥𝑥 −intercepts 𝑥𝑥 −intercepts 𝑥𝑥 −intercepts
NEED to sketch
the graph. • 𝑦𝑦 = 0 𝑦𝑦 = 0 𝑦𝑦 = 0
𝑦𝑦 −intercepts 𝑦𝑦 −intercepts 𝑦𝑦 −intercepts
• 𝑥𝑥 = 0 𝑥𝑥 = 0 𝑥𝑥 = 0
TURNING POINT ASYMPTOTES ASYMPTOTE
Axes of Symmetry
𝑏𝑏
• 𝑥𝑥 = − • 𝑥𝑥 = −𝑝𝑝 • 𝑦𝑦 = 𝑞𝑞
2𝑎𝑎
• 𝑓𝑓 ′ (𝑥𝑥) = 0 • 𝑦𝑦 = 𝑞𝑞
EXAMPLE of the
SKETCH of the
graph
Grade 12 Tutoring Programme: MATHEMATICS 3
2. THE PARABOLA
2.1 Sketching a parabola
EXAMPLE 1:
Equations in the TURNING POINT form 𝒚𝒚 = (𝒙𝒙 + 𝒑𝒑)𝟐𝟐 + 𝒒𝒒
Given: 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) = (𝑥𝑥 + 1)2 − 4
1.1 Write down the turning point of 𝑓𝑓.
1.2 Determine the 𝑥𝑥-intercepts of f.
1.3 Determine the coordinates of the 𝑦𝑦-intercept of f.
1.4 Draw the graph of f. Clearly show the turning point and intercepts with the axes.
1.5 Use your graph to answer the following questions:
1.5.1 Give the range of 𝑓𝑓.
1.5.2 For which values of 𝑥𝑥 will
(a) 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) > 0
(b) 𝑓𝑓 ′ (𝑥𝑥) > 0
1.5.3 Determine the equation of ℎ where ℎ is the graph after 𝑓𝑓 moved 1 unit to
the right.
1.5.4 Write down the turning point for 𝑔𝑔 if 𝑔𝑔 is the reflection of 𝑓𝑓 in the 𝑥𝑥 −axis.
Grade 12 Tutoring Programme: MATHEMATICS 4
EXAMPLE 2:
Equations in the STANDARD FORM 𝑦𝑦 = 𝑎𝑎𝑥𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑏𝑏𝑏 + 𝑐𝑐
Given: 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) = −2𝑥𝑥 2 + 8𝑥𝑥 + 10
2.1 Determine the coordinates of the turning point of 𝑓𝑓.
2.2 Determine the 𝑥𝑥-intercept of f.
2.3 Write down the coordinates of the 𝑦𝑦-intercept of f.
2.4 Draw the graph of f. Clearly show the turning point and intercepts with the axes.
2.5 Use your graph to answer the following questions:
2.5.1 Give the range of 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) − 3.
2.5.2 For which values of 𝑥𝑥 will
(a) 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) ≤ 0
(b) 𝑓𝑓 ′ (𝑥𝑥) < 0
2.5.3 Determine the equation of the axis of symmetry of 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥 − 1)
2.5.4 Does the graph – 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) have a maximum or minimum value? Give this
value.
Grade 12 Tutoring Programme: MATHEMATICS 5
2.2 Determine the equation of a parabola.
EXAMPLE 3:
𝑥𝑥–INTERCEPTS GIVEN 𝑦𝑦 = 𝑎𝑎(𝑥𝑥 − 𝑟𝑟1 )(𝑥𝑥 + 𝑟𝑟2 )
The graph of 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) = 𝑎𝑎𝑥𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑏𝑏𝑏 + 𝑐𝑐 and 𝑘𝑘(𝑥𝑥) = 2𝑥𝑥 + 10 is drawn below.
• The parabola cuts the 𝑥𝑥-axis at A and B and the 𝑦𝑦-axis at P.
• B and P are also the intercepts of 𝑘𝑘.
• T is the turning point of f.
3.1 Write down:
3.1.1 the coordinates of P.
3.1.2 the equation of the axis of symmetry.
3.2 Determine the numerical values of 𝑎𝑎, 𝑏𝑏 and 𝑐𝑐 .
3.3 For which values of 𝑥𝑥 is,
3.3.1 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) ≤ 0
3.3.2 𝑓𝑓 ′ (𝑥𝑥) = 0
3.4 Give the range of 𝑓𝑓.
3.5 Determine the values of 𝑘𝑘 for which 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) = 𝑘𝑘 will have no real roots.
Grade 12 Tutoring Programme: MATHEMATICS 6
EXAMPLE 4:
TURNING POINT GIVEN 𝑦𝑦 = 𝑎𝑎(𝑥𝑥 + 𝑝𝑝)2 + 𝑞𝑞
The graph of 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) = 𝑎𝑎𝑥𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑏𝑏𝑏 + 𝑐𝑐 is drawn below. W, P and Q are the intercepts of 𝑓𝑓.
R(1 ; −8) is the turning point of f. S(2 ; −6) is a point on f.
4.1 Write down the coordinates of Q if S and Q are reflections in the axis of symmetry.
4.2 Write down the range of 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) + 8.
4.3 Determine the numerical values of 𝑎𝑎, 𝑏𝑏 and 𝑐𝑐 .
4.4 Determine the length of WP
4.5 For which values of 𝑥𝑥 will
4.5.1 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) ≤ 0
4.5.2 𝑓𝑓 ′ (𝑥𝑥) > 0
4.6 Write down the equation of the axis of symmetry for 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥 + 3)
4.7 Determine the coordinates of the turning point for 𝑓𝑓(−𝑥𝑥).
4.8 Determine the values of 𝑘𝑘 for which 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) = 𝑘𝑘 will have two unequal, positive real
roots.
Grade 12 Tutoring Programme: MATHEMATICS 7
3. THE HYPERBOLA
3.1 Sketching a hyperbola
EXAMPLE 5:
𝑘𝑘
𝑦𝑦 = + 𝑞𝑞
𝑥𝑥 + 𝑝𝑝
6
Given: 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) = +4
𝑥𝑥−3
5.1 Write down:
5.1.1 the equation of the horizontal asymptote of f.
5.1.2 the equation of the vertical asymptote of f.
5.1.3 the domain of f.
5.2 Determine:
5.2.1 the 𝑥𝑥-intercept of f.
5.2.2 the coordinates of the 𝑦𝑦-intercept of f.
5.3 Draw the graph of f. Clearly show ALL the asymptotes and intercepts with the axes.
5.4 Use your graph to answer the following questions:
5.4.1 Write down the range of f.
5.4.2 For which values of 𝑥𝑥 will
(a) 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) ≥ 0
(b) 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) < 0
(c) 𝑓𝑓 ′ (𝑥𝑥) < 0
5.5 Determine the equation of ℎ where ℎ is the graph after 𝑓𝑓 moved 1 unit to the right.
5.6 Determine the equation(s) of the axis of symmetry of 𝑓𝑓.
Grade 12 Tutoring Programme: MATHEMATICS 8
3.2 Determine the equation of a hyperbola.
𝑘𝑘
EXAMPLE 6: 𝑦𝑦 = + 𝑞𝑞
𝑥𝑥+𝑝𝑝
𝑘𝑘
In the diagram is the graph of: 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) = + 𝑞𝑞. C and D are the intercepts of 𝑓𝑓.
𝑥𝑥+𝑝𝑝
The asymptotes of 𝑓𝑓 intercept at B(−3; −4) . A (−1; −5) is a point on f.
6.1 Write down:
6.1.1 the equations of the asymptotes of f.
6.1.2 the range of f.
6.1.3 the domain of 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥 + 3).
6.2 Determine:
6.2.1 the numerical values of 𝑘𝑘, 𝑝𝑝 𝑎𝑎nd 𝑞𝑞.
6.2.2 the coordinates of the 𝑦𝑦-intercept of f.
6.2.3 the coordinates of the 𝑥𝑥-intercept of f.
6.2.4 the equation of the axis of symmetry of 𝑓𝑓 that has a negative gradient.
6.3 For which values of 𝑥𝑥 will:
6.3.1 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) ≥ 0
6.3.2 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) < 0
6.4 Is the graph increasing or decreasing?
Grade 12 Tutoring Programme: MATHEMATICS 9
4. THE EXPONENTIAL GRAPH
4.1 Sketching an exponential graph.
EXAMPLE 7: 𝑦𝑦 = 𝑎𝑎. 𝑏𝑏 𝑥𝑥+𝑝𝑝 + 𝑞𝑞
Given: 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) = 2−𝑥𝑥 − 4
7.1 Write down the equation of the asymptote of f.
7.2 Determine:
7.2.1 the 𝑥𝑥-intercept of f.
7.2.2 the coordinates of the 𝑦𝑦-intercept of f.
7.3 Draw the graph of f. Clearly show ALL the asymptote(s) and intercepts with the axes.
7.4 Use your graph to answer the following questions:
7.4.1 Write down the range of f.
7.4.2 For which values of 𝑥𝑥 will
(a) 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) ≥ 0
(b) 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) < 0
7.5 Determine the equation of ℎ where ℎ is the graph after 𝑓𝑓 moved 2 unit to the right and
1 unit up.
7.6 Is the graph increasing or decreasing?
Grade 12 Tutoring Programme: MATHEMATICS 10
4.2 Determine the equation of an exponential graph.
Example 8: 𝒚𝒚 = 𝒂𝒂. 𝒃𝒃𝒙𝒙+𝒑𝒑 + 𝒒𝒒
In the diagram is the graph of: 𝒇𝒇(𝒙𝒙) = 𝟐𝟐𝒙𝒙+𝒑𝒑 + 𝒒𝒒 . A(3;0) and B are the intercepts of 𝒇𝒇.
The asymptote of 𝑓𝑓 is at 𝑦𝑦 = −8
8.1 Write down:
8.1.1 the range of f.
8.1.2 the range of 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) + 3
8.2 Determine:
8.2.1 the numerical values of 𝑝𝑝 and 𝑞𝑞.
8.2.2 the coordinates of B, the 𝑦𝑦-intercept of f.
8.3 For which values of 𝑥𝑥 will:
8.3.1 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) ≥ 0
8.3.2 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) < 0
8.4 Is the graph increasing or decreasing?
1 𝑥𝑥
8.5 Describe the transformation from 𝑓𝑓 to ℎ(𝑥𝑥) = � �
2
Grade 12 Tutoring Programme: MATHEMATICS 11
5. INVERSE FUNCTIONS
BACKGROUND KNOWLEDGE
FUNCTIONAL NOTATION
𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) = 2𝑥𝑥 − 1 Given: 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) = 3𝑥𝑥
𝑓𝑓(3) = 2(3) − 1 Determine 𝑓𝑓(−2) and write down the coordinates.
∴ (3; 5)
DEFINITION OF A FUNCTION
For every 𝑥𝑥-value, there is at most one 𝑦𝑦-value.
INVERSE
1. The inverse of a function takes the 𝑦𝑦-values (range) of the function to the corresponding 𝑥𝑥-
values (domain) and vice versa. Therefore, the 𝑥𝑥 and 𝑦𝑦 values are interchanged.
2. The function is reflected along the line 𝑦𝑦 = 𝑥𝑥 to form the inverse.
3. The notation for the inverse of a function is 𝑓𝑓 −1 .
Grade 12 Tutoring Programme: MATHEMATICS 12
INVERSE GRAPHS THAT YOU HAVE TO KNOW
THE INVERSE OF A STRAIGHT LINE 𝒚𝒚 = 𝒎𝒎𝒎𝒎 + 𝒄𝒄
INVERSE FUNCTION BY SWOPPING 𝒙𝒙 AND 𝒚𝒚
Example 1:
𝑦𝑦 = 2𝑥𝑥 − 4 𝑓𝑓
Interchange 𝑥𝑥 and 𝑦𝑦
Make 𝑦𝑦 the subject of the formula
𝑓𝑓 −1
Example 2:
If 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) = 2𝑥𝑥 + 6
2.1 Determine 𝑓𝑓 −1 , that is the inverse of 𝑓𝑓.
2.2 Sketch the graphs of 𝑓𝑓, 𝑓𝑓 −1 and 𝑦𝑦 = 𝑥𝑥 on the same system of axes.
Grade 12 Tutoring Programme: MATHEMATICS 13
WRITING IN LOG FORM
We know that:
If 𝑦𝑦 = 𝑎𝑎 𝑥𝑥
21 = 2 then log 𝑎𝑎 𝑦𝑦 = 𝑥𝑥
22 = 4
• But what will the answer Example 1 Example 2
be if: 2𝑥𝑥 = 3 2𝑥𝑥 = 3 5𝑥𝑥 = 3
• To answer this question,
we need to understand
logarithms.
Example 3 Example 4
2𝑥𝑥 = 8 10𝑥𝑥 = 100
• The answer to a logarithm
is an exponent.
NOTE that we do not have to
write the base if it is 10.
Grade 12 Tutoring Programme: MATHEMATICS 14
Writing from exponent form to log form:
Example 1 Example 2
52 = 25 34 = 81
Note that the answer
of a logarithm can be
Example 3 Example 4 negative, but
1
102 = 100 2−2 = • base of a log cannot
4
be negative and
• you cannot take the
log of a negative.
Write the following from log form to exponent form:
If log 𝑎𝑎 𝑦𝑦 = 𝑥𝑥
then 𝑦𝑦 = 𝑎𝑎 𝑥𝑥
Example 1 Example 2
2 = log 5 25 4 = log 3 81
Example 3 Example 4
1
−2 = log 2 2 = log 100
4
Grade 12 Tutoring Programme: MATHEMATICS 15
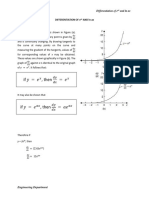
THE INVERVES OF AN EXPONENTIAL FUNCTION 𝒚𝒚 = 𝒂𝒂𝒙𝒙
AND
LOG FUNCTION 𝒚𝒚 = 𝐥𝐥𝐥𝐥𝐥𝐥 𝒂𝒂 𝒙𝒙
Example 3:
Let’s investigate the exponential graph and its inverse:
Given: 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) = 2𝑥𝑥
See the completed table for 𝑦𝑦 = 2𝑥𝑥 :
𝑥𝑥 −2 −1 0 1 2
𝑓𝑓: 𝑦𝑦 = 2𝑥𝑥
1 1
𝑦𝑦 1 2 4
4 2
Let’s swop the 𝑥𝑥 and 𝑦𝑦-values: 𝑓𝑓 −1 :
𝑥𝑥
𝑦𝑦
Grade 12 Tutoring Programme: MATHEMATICS 16
NOVEMBER 2019
QUESTION 5
Sketched below is the graph of 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) = 𝑘𝑘 𝑥𝑥 ; 𝑘𝑘 > 0. The point (4; 16) lies on 𝑓𝑓.
5.1 Determine the value of 𝑘𝑘. (2)
5.2 Graph 𝑔𝑔 is obtained by reflecting graph 𝑓𝑓 about the line 𝑦𝑦 = 𝑥𝑥.
Determine the equation of 𝑔𝑔 in the form 𝑦𝑦 = … (2)
5.3 Sketch the graph 𝑔𝑔. Indicate on your graph the coordinates of two points on 𝑔𝑔. (4)
Grade 12 Tutoring Programme: MATHEMATICS 17
NOVEMBER 2021
QUESTION 6
The graph of 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) = log 4 𝑥𝑥 is drawn below. B(𝑘𝑘; 2) is a point on 𝑓𝑓.
6.1 Calculate the value of 𝑘𝑘. (2)
6.2 Determine the values of 𝑥𝑥 for which −1 ≤ 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) ≤ 2. (2)
6.3 Write down the equation of 𝑓𝑓 −1 , the inverse of 𝑓𝑓, in the form 𝑦𝑦 = … (2)
6.4 For which values of 𝑥𝑥 will 𝑥𝑥. 𝑓𝑓 −1 (𝑥𝑥) < 0? (2)
Grade 12 Tutoring Programme: MATHEMATICS 18
THE INVERSE OF A PARABOLA 𝒚𝒚 = 𝒂𝒂𝒙𝒙𝟐𝟐
Example 4:
1
Given:𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) = − 𝑥𝑥 2
2
4.1 Determine the equation of the inverse function in the form 𝑓𝑓 −1 (𝑥𝑥) = …
4.2 Sketch the graph of the function and its inverse on the same set of axes
4.3 Now restrict the domain of the original function in two different ways to form new
one-to-one functions.
Grade 12 Tutoring Programme: MATHEMATICS 19
Example 5:
Given 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) = 2𝑥𝑥 2
5.1 Determine the inverse of 𝑓𝑓. Hence rewrite the equation of the inverse function in the
form 𝑓𝑓 −1 (𝑥𝑥) = …
5.2 Sketch the graphs of the new function and its inverse function and 𝑦𝑦 = 𝑥𝑥 on the same
set of axes.
5.3 Is 𝑓𝑓 −1 a function? Give a reason for your answer.
Grade 12 Tutoring Programme: MATHEMATICS 20
NOVEMBER 2018
QUESTION 4
In the diagram below, the graph of 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) = 𝑎𝑎𝑥𝑥 2 is drawn in the interval 𝑥𝑥 ≤ 0. The graph 𝑓𝑓 −1 is
also drawn. P(−6; −12) is a point on 𝑓𝑓 and R is a point on 𝑓𝑓 −1 .
4.1 Is 𝑓𝑓 −1 a function? Motivate your answer. (2)
4.2 If R is the reflection of P in the line 𝑦𝑦 = 𝑥𝑥, write down the coordinates of R. (1)
4.3 Calculate the value of 𝑎𝑎. (2)
4.4 Write down the equation of 𝑓𝑓 −1 in the form 𝑦𝑦 = … (3)
Grade 12 Tutoring Programme: MATHEMATICS 21
6. Consolidation
6.1 Algebra
QUESTION 1 [Q1 – DBE/Nov 2020]
1.1 Solve for 𝑥𝑥:
1.1.1 𝑥𝑥 2 − 6𝑥𝑥 = 0 (2)
1.1.2 𝑥𝑥 2 + 10𝑥𝑥 + 8 = 0 (correct to TWO decimal places) (3)
1.1.3 (1 − 𝑥𝑥)(𝑥𝑥 + 2) < 0 (3)
1.1.4 √𝑥𝑥 + 18 = 𝑥𝑥 − 2 (5)
1.2 Solve for 𝑥𝑥 and 𝑦𝑦 simultaneously:
𝑥𝑥 + 𝑦𝑦 = 3 and 2𝑥𝑥 2 + 4𝑥𝑥𝑥𝑥 − 𝑦𝑦 = 15 (6)
1.3 If 𝑛𝑛 is the largest integer for which 𝑛𝑛200 < 5300 , determine the value of 𝑛𝑛. (3)
[22]
QUESTION 2 [Q1 – DBE/Nov 2022]
2.1 Solve for 𝑥𝑥:
2.1.1 (3𝑥𝑥 − 6)(𝑥𝑥 + 2) = 0 (2)
2.1.2 2𝑥𝑥 2 − 6𝑥𝑥 + 1 = 0 (correct to TWO decimal places) (3)
2.1.3 𝑥𝑥 2 − 90 > 𝑥𝑥 (4)
2.1.4 𝑥𝑥 − 7√𝑥𝑥 − 12 (4)
2.2 Solve for 𝑥𝑥 and 𝑦𝑦 simultaneously:
2𝑥𝑥 − 𝑦𝑦 = 2 and 𝑥𝑥𝑥𝑥 = 4 (5)
2.3 Show that 2.5𝑛𝑛 − 5𝑛𝑛+1 + 5𝑛𝑛+2 is even for all positive integer vales of 𝑛𝑛. (3)
2.4 Determine the values of 𝑥𝑥 and 𝑦𝑦 if:
3𝑦𝑦+1
= √96𝑥𝑥 (4)
32
[25]
Grade 12 Tutoring Programme: MATHEMATICS 22
QUESTION 3 [Q1 – DBE/May-Jun 2022]
3.1 Solve for 𝑥𝑥:
3.1.1 𝑥𝑥 2 + 2𝑥𝑥 − 15 = 0 (3)
3.1.2 5𝑥𝑥 2 − 𝑥𝑥 − 9 = 0 (Leave your answer correct to TWO decimal places.) (3)
3.1.3 𝑥𝑥 2 ≤ 3𝑥𝑥 (4)
64
3.2 Given: 𝑎𝑎 + = 16
𝑎𝑎
3.2.1 Solve for 𝑎𝑎. (3)
3.2.2 Hence, solve for 𝑥𝑥: 2𝑥𝑥 + 26−𝑥𝑥 = 16 (3)
21002 +21006 (4)
3.3 Without using a calculator, calculate the value of �
17(2)998
3.4 Solve for 𝑥𝑥 and 𝑦𝑦 simultaneously:
2𝑥𝑥 − 𝑦𝑦 = 2 and
1
− 3𝑦𝑦 = 1 (6)
𝑥𝑥
[26]
QUESTION 4 [Q1 – DBE/Nov 2021]
4.1 Solve for 𝑥𝑥:
4.1.1 𝑥𝑥 2 − 2𝑥𝑥 − 24 = 0 (3)
4.1.2 2𝑥𝑥 2 − 3𝑥𝑥 − 3 = 0 (correct to TWO decimal places) (3)
4.1.3 𝑥𝑥 2 + 5𝑥𝑥 ≤ −4 (4)
4.1.4 √𝑥𝑥 + 28 = 2 − 𝑥𝑥 (4)
4.2 Solve simultaneously for 𝑥𝑥 and 𝑦𝑦 in:
2𝑦𝑦 = 3 + 𝑥𝑥 and 2𝑥𝑥𝑥𝑥 + 7 = 𝑥𝑥 2 + 4𝑦𝑦 2 (6)
−𝑛𝑛±�𝑛𝑛2 −4𝑚𝑚𝑚𝑚
4.3 The roots of an equation are 𝑥𝑥 = where 𝑚𝑚, 𝑛𝑛 and 𝑝𝑝 are positive real
2𝑚𝑚
numbers. The numbers 𝑚𝑚, 𝑛𝑛 and 𝑝𝑝 , in that order, form a geometric sequence.
(4)
Prove that 𝑥𝑥 is a non-real number.
[24]
Grade 12 Tutoring Programme: MATHEMATICS 23
QUESTION 5 [Q1 – DBE/May-Jun 2021]
5.1 Solve for 𝑥𝑥:
5.1.1 𝑥𝑥 2 − 𝑥𝑥 − 20 = 0 (3)
5.1.2 3𝑥𝑥 2 − 2𝑥𝑥 − 6 = 0 (correct to TWO decimal places) (4)
5.1.3 (𝑥𝑥 − 1)2 > 9 (4)
5.1.4 2√𝑥𝑥 + 6 + 2 = 𝑥𝑥 (4)
5.2 Solve simultaneously for 𝑥𝑥 and 𝑦𝑦:
4𝑥𝑥 + 𝑦𝑦 = 2 and 4𝑥𝑥 + 𝑦𝑦 2 = 8 (5)
5.3 If it is given that 2𝑥𝑥 × 3𝑦𝑦 = 246 , determine the numerical value of 𝑥𝑥 − 𝑦𝑦. (4)
[24]
Grade 12 Tutoring Programme: MATHEMATICS 24
6.2 Functions
QUESTION 1 [Q5 – DBE/Feb-Mar 2010]
2
Given: 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) = +1
𝑥𝑥−3
1.1 Write down the equation of the asymptotes of 𝑓𝑓 (2)
1.2 Calculate the coordinates of the 𝑥𝑥 − and 𝑦𝑦 −intercepts of 𝑓𝑓. (3)
1.3 Sketch 𝑓𝑓 and show all intercepts with the axes and the asymptotes. (3)
[8]
QUESTION 2 [Q6 – DBE/Feb-Mar 2010]
The graphs of 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) = −𝑥𝑥 2 + 7𝑥𝑥 + 8 and 𝑔𝑔(𝑥𝑥) = −3𝑥𝑥 + 24 are sketched below.
𝑓𝑓and 𝑔𝑔 intersect in D and B. A and B are the 𝑥𝑥 − intercepts of 𝑓𝑓.
2.1 Determine the coordinates of A and B. (4)
2.2 Calculate 𝑎𝑎, the 𝑥𝑥 −coordinate of D. (4)
2.3 S(𝑥𝑥; 𝑦𝑦) is a point on the graph of 𝑓𝑓, where 𝑎𝑎 ≤ 𝑥𝑥 ≤ 8. (2)
ST is drawn parallel to the 𝑦𝑦 −axis with T on the graph of 𝑔𝑔.
Determine ST in terms of 𝑥𝑥.
2.4 Calculate the maximum length of ST. (2)
[12]
Grade 12 Tutoring Programme: MATHEMATICS 25
QUESTION 3 [Q7 – DBE/Feb-Mar 2010]
The graphs of 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) = 3𝑥𝑥 is drawn below.
3.1 Write 𝑓𝑓 −1 in the form 𝑦𝑦 =. .. (1)
3.2 Sketch the graph of 𝑦𝑦 = 𝑓𝑓 −1 (𝑥𝑥) and 𝑦𝑦 = 𝑓𝑓 −1 (𝑥𝑥 − 2). (4)
3.3 Use your graphs to solve for 𝑥𝑥 if log 3 (𝑥𝑥 − 2) < 1. (2)
[7]
Grade 12 Tutoring Programme: MATHEMATICS 26
QUESTION 4 [Q4 – DBE/Feb-Mar 2018]
Below are the graphs if 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) = (𝑥𝑥 − 4)2 − 9 and a straight line 𝑔𝑔.
• A and B are the 𝑥𝑥 −intercepts of 𝑓𝑓 and E is the turning point of 𝑓𝑓.
• C is the 𝑦𝑦 −intercept of both 𝑓𝑓 and 𝑔𝑔.
• The 𝑥𝑥 −intercept of 𝑔𝑔 is D. DE is parallel to the 𝑦𝑦 −axis.
4.1 Write down the coordinates of E. (2)
4.2 Calculate the coordinates of A. (3)
4.3 M is the reflection of C in the axis of symmetry of 𝑓𝑓. Write down the coordinates of (2)
M.
4.4 Determine the equation of 𝑔𝑔 in the form 𝑦𝑦 = 𝑚𝑚𝑚𝑚 + 𝑐𝑐. (3)
4.5 Write down the equation of 𝑔𝑔−1 in the form 𝑦𝑦 =. .. (3)
4.6 For which values of 𝑥𝑥 will, 𝑥𝑥�𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥)� ≤ 0? (4)
[18]
Grade 12 Tutoring Programme: MATHEMATICS 27
QUESTION 5 [Q5 – DBE/Feb-Mar 2018]
The graph of 𝑔𝑔(𝑥𝑥) = 𝑎𝑎 𝑥𝑥 is drawn in the sketch below. The point S(2; 9) lies on 𝑔𝑔.
T is the 𝑦𝑦 −intercept of 𝑔𝑔.
5.1 Write down the coordinates of T. (2)
5.2 Calculate the value of 𝑎𝑎. (2)
5.3 The graph ℎ is obtained by reflecting 𝑔𝑔 in the 𝑦𝑦 −axis. Write down the equation of ℎ. (2)
5.4 Write down the values of 𝑥𝑥 for which, 0 < log 3 𝑥𝑥 < 1. (2)
[8]
QUESTION 6 [Q6 – DBE/Feb-Mar 2018]
𝑎𝑎
The function 𝑓𝑓, defined by 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) = + 𝑞𝑞, has the following properties:
𝑥𝑥+𝑝𝑝
• The range of 𝑓𝑓 is 𝑦𝑦 ∈ ℝ, 𝑦𝑦 ≠ 1.
• The graph 𝑓𝑓 passes through the origin.
• P(√2 + 2; √2 + 1) lies on the graph 𝑓𝑓.
6.1 Write down the value of 𝑞𝑞. (1)
6.2 Calculate the value of 𝑎𝑎 and 𝑝𝑝. (5)
6.3 Sketch a neat graph of this function. Your graph must include the asymptotes, if any.
(4)
[10]
Grade 12 Tutoring Programme: MATHEMATICS 28
QUESTION 7 [Q4 – DBE/Nov 2012]
7.1 Consider the function 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) = 3.2𝑥𝑥 − 6.
7.1.1 Calculate the coordinates of the 𝑦𝑦 −intercept of the graph of 𝑓𝑓. (1)
7.1.2 Calculate the 𝑥𝑥 −intercept of the graph of 𝑓𝑓. (2)
7.1.3 Sketch the graph of 𝑓𝑓 in your ANSWER BOOK. (3)
Clearly show ALL asymptotes and intercepts with the axes.
7.1.4 Write down the range of 𝑓𝑓. (1)
7.2 S(−2; 0) and T(6; 0) are the 𝑥𝑥 −intercepts of the graphs of 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) = 𝑎𝑎𝑥𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑏𝑏𝑏 + 𝑐𝑐
and R is the 𝑦𝑦 −intercept. The straight line through R and T represents the graph of
𝑔𝑔(𝑥𝑥) = −2𝑥𝑥 + 𝑑𝑑.
7.2.1 Determine the value of 𝑑𝑑. (2)
7.2.2 Determine the equation of 𝑓𝑓 in the form 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) = 𝑎𝑎𝑥𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑏𝑏𝑏 + 𝑐𝑐. (4)
7.2.3 If 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) = −𝑥𝑥 2 + 4𝑥𝑥 + 12, calculate the coordinates if the turning point of 𝑓𝑓. (2)
7.2.4 For which values of 𝑘𝑘, will 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) = 𝑘𝑘 have two distinct roots? (2)
7.2.5 Determine the maximum value of ℎ(𝑥𝑥) = 3 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥)−12 . (3)
[20]
Grade 12 Tutoring Programme: MATHEMATICS 29
QUESTION 8 [Q5 – DBE/Nov 2012]
The graph of 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) = −√27𝑥𝑥 for 𝑥𝑥 ≥ 0 is sketch below.
The point P(3; −9) lies on the graph if 𝑓𝑓.
8.1 Use the graph to determine the values of 𝑥𝑥 for which 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) ≥ −9. (2)
8.2 Write down the equation of 𝑓𝑓 −1 in the form 𝑦𝑦 =. .. Include ALL restrictions. (3)
8.3 Sketch 𝑓𝑓 −1 , the inverse of 𝑓𝑓, in your ANSWER BOOK.
Indicate the intercept(s) with the axes and the coordinates of ONE other point. (3)
8.4 Describe the transformation from 𝑓𝑓 to 𝑔𝑔 if 𝑔𝑔(𝑥𝑥) = √27𝑥𝑥, where 𝑥𝑥 ≥ 0. (1)
[9]
QUESTION 9 [Q6 – DBE/Nov 2012]
The graph of a hyperbola with the equation 𝑦𝑦 = 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥) has the following properties:
• Domain: 𝑥𝑥 ∈ ℝ, 𝑥𝑥 ≠ 5
• Range: 𝑦𝑦 ∈ ℝ, 𝑦𝑦 ≠ 1
• Passes through point (2; 0)
Determine 𝑓𝑓(𝑥𝑥).
[4]
Grade 12 Tutoring Programme: MATHEMATICS 30
QUESTION 10 [Q5 – DBE/Nov 2022]
The graphs of 𝑔𝑔(𝑥𝑥) = 2𝑥𝑥 + 6 and 𝑔𝑔−1 , the inverse of 𝑔𝑔, are shown in the diagram below.
• D and B are the 𝑥𝑥 − and 𝑦𝑦 − intercepts respectively of 𝑔𝑔.
• C is the 𝑥𝑥 − intercept of 𝑔𝑔−1 .
• The graphs of 𝑔𝑔 and 𝑔𝑔−1 intersect at A.
10.1 Write down the 𝑦𝑦 − coordinate of B. (1)
10.2 Determine the equation of 𝑔𝑔−1 in the form 𝑔𝑔−1 (𝑥𝑥) = 𝑚𝑚𝑚𝑚 + 𝑛𝑛. (2)
10.3 Determine the coordinates of A. (3)
10.4 Calculate the length of AB. (2)
10.5 Calculate the area of ∆ABC (5)
[13]
Grade 12 Tutoring Programme: MATHEMATICS 31
You might also like
- Analytical Geometry Grade 12Document6 pagesAnalytical Geometry Grade 12Paula Fana0% (1)
- Basic Algebra PDFDocument12 pagesBasic Algebra PDFUyen Tran100% (1)
- Instant Download Ebook PDF Foundation Maths 7th Edition PDF ScribdDocument41 pagesInstant Download Ebook PDF Foundation Maths 7th Edition PDF Scribdjudith.haley157100% (38)
- Gr12 Ighs Maths Functions 2024Document18 pagesGr12 Ighs Maths Functions 2024ngqambioNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 - InversesDocument26 pagesTopic 5 - Inversesmpfumawulomaluleke78No ratings yet
- March Practice Control Test - Qp - 2023-1Document5 pagesMarch Practice Control Test - Qp - 2023-1rashidemaan07No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 BookletDocument20 pagesChapter 4 Bookletgabriel loNo ratings yet
- Ch1 - Algebraic and Non-Algebraic Functions and Their InverseDocument37 pagesCh1 - Algebraic and Non-Algebraic Functions and Their InverseRafi SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Transformation of A Straight Line: MathematicsDocument10 pagesTransformation of A Straight Line: MathematicsWilma Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Seeta High School Post - 2023 S.6 Pure Mathematics Paper 1Document3 pagesSeeta High School Post - 2023 S.6 Pure Mathematics Paper 1vanessablessed999100% (1)
- Gra de 11 Functions WorksheetDocument4 pagesGra de 11 Functions WorksheetLincoln Munashe KaparadzaNo ratings yet
- PRECAL 1st PT Answer KeyDocument5 pagesPRECAL 1st PT Answer KeyhinsNo ratings yet
- 3 - 5 Sketching Circles and TransformationsDocument6 pages3 - 5 Sketching Circles and Transformationsyi lingNo ratings yet
- D33116505 - Muh Halilul Rohman - TGS Matek 4Document12 pagesD33116505 - Muh Halilul Rohman - TGS Matek 4muh halilul rohmanNo ratings yet
- W4 CH 1-4 Mixed QuestionsDocument6 pagesW4 CH 1-4 Mixed QuestionsJessicaNo ratings yet
- Differentiation of e Ax and LN (Ax)Document5 pagesDifferentiation of e Ax and LN (Ax)Jericho CunananNo ratings yet
- Q1 LAS1 IllustratingSolvingQEDocument12 pagesQ1 LAS1 IllustratingSolvingQEHarry PotterNo ratings yet
- GR 10 Maths Term 2 Week 2 FinalDocument2 pagesGR 10 Maths Term 2 Week 2 Finalmartinajoan1No ratings yet
- P1.ed - CH.8 Part 2Document25 pagesP1.ed - CH.8 Part 2math magicNo ratings yet
- EXPONENTIAL GRAPHDocument19 pagesEXPONENTIAL GRAPHPaula FanaNo ratings yet
- CIRCLES Grade 12Document13 pagesCIRCLES Grade 12Paula FanaNo ratings yet
- GRAPH EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONSDocument9 pagesGRAPH EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONSKirsten Shayne ManingasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Review of The The Straight Lines (Week 1 and 2)Document22 pagesChapter 1 - Review of The The Straight Lines (Week 1 and 2)Angelo ResuelloNo ratings yet
- STPM 2016 T2 Maths Revision UlanganDocument2 pagesSTPM 2016 T2 Maths Revision UlanganOb oNo ratings yet
- P1 Chapter 6 Circles Equations Tangents IntersectionsDocument29 pagesP1 Chapter 6 Circles Equations Tangents IntersectionsSudeep100% (1)
- Rondebosch Boys' High School: Senior CertificateDocument11 pagesRondebosch Boys' High School: Senior CertificateChey1242No ratings yet
- Q1 W2 PrecalculusDocument11 pagesQ1 W2 PrecalculusArianne MolinaNo ratings yet
- IB Official MAA ExamplesDocument65 pagesIB Official MAA ExamplesnkvfdvdfNo ratings yet
- Bridge 2 Linear and Quadratic EquationsDocument6 pagesBridge 2 Linear and Quadratic EquationsDearly Niña OsinsaoNo ratings yet
- S.6 Pure Mathematics Assignment (1)Document3 pagesS.6 Pure Mathematics Assignment (1)DenisNo ratings yet
- Essential Skills Whole BookletDocument44 pagesEssential Skills Whole BookletJo PatrickNo ratings yet
- 2022 Functions and GraphsDocument16 pages2022 Functions and GraphsmvelonhlemsimangoNo ratings yet
- Class IX Mathematics CH-3 and 4 AsignmentDocument3 pagesClass IX Mathematics CH-3 and 4 AsignmentPriyankAhujaNo ratings yet
- GCSE GraphTransformationsDocument4 pagesGCSE GraphTransformationsdshsj djkdghsdgysudNo ratings yet
- G11 Pre Cal W2 LASDocument12 pagesG11 Pre Cal W2 LASStreaming Lalisa03100% (1)
- Linear RegressionDocument4 pagesLinear RegressionDeadly ChillerNo ratings yet
- AASL Calculus 1 Review PDFDocument10 pagesAASL Calculus 1 Review PDFJosh Student - MeiiselNo ratings yet
- Notes in SMAT 01Document16 pagesNotes in SMAT 01Xiel John BarnuevoNo ratings yet
- MATH 9 Module 2 Week 6Document13 pagesMATH 9 Module 2 Week 6Henry Kahal Orio Jr.No ratings yet
- PRECAL_LESSON 4Document4 pagesPRECAL_LESSON 4alayca cabatanaNo ratings yet
- Day-11: Section 13.7 Tangent Planes and Normal VectorsDocument13 pagesDay-11: Section 13.7 Tangent Planes and Normal VectorsFaizaNo ratings yet
- Math 9-Q1-Week-1Document14 pagesMath 9-Q1-Week-1Pinky FaithNo ratings yet
- Math - Term 2 Test 2Document4 pagesMath - Term 2 Test 2zainNo ratings yet
- Finding the turning point by completing the squareDocument12 pagesFinding the turning point by completing the squareHoang NgoNo ratings yet
- Exam 3 Fall 22Document9 pagesExam 3 Fall 22BennyNo ratings yet
- Deriving Quadratic Functions From Graphs and InterceptsDocument11 pagesDeriving Quadratic Functions From Graphs and InterceptsKen BalaneNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations: Teacher: Wendy M. SelgasDocument55 pagesQuadratic Equations: Teacher: Wendy M. SelgasMagnetismPlayz YtNo ratings yet
- LESSONS 7 AND 8 ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS I PRODUCTION OPTIONDocument25 pagesLESSONS 7 AND 8 ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS I PRODUCTION OPTIONRobert K OtienoNo ratings yet
- Calculating Distances and Slopes in a Coordinate PlaneDocument68 pagesCalculating Distances and Slopes in a Coordinate PlaneDimple DizonNo ratings yet
- Class XII Top 10 Sample Papers Mathematics With SolutionDocument128 pagesClass XII Top 10 Sample Papers Mathematics With Solutionanushkabisht2006No ratings yet
- Lesson 13 Transformation and Graphs of QFDocument5 pagesLesson 13 Transformation and Graphs of QFMarion Nico EspiloyNo ratings yet
- MATHS P1 QP GR12 SEPT 2019 DBE - English2Document9 pagesMATHS P1 QP GR12 SEPT 2019 DBE - English2Kean Van TonderNo ratings yet
- Slope FieldDocument7 pagesSlope FieldŞilayNo ratings yet
- 2.2-quadratic-equations-graphs-quadratic-functionsDocument52 pages2.2-quadratic-equations-graphs-quadratic-functionsMbocaBentoNo ratings yet
- CALCULUS TUTORIAL TANGENTS AND DERIVATIVESDocument10 pagesCALCULUS TUTORIAL TANGENTS AND DERIVATIVESNazurah Kamaruzzaman KamariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Geometric TransformationsDocument12 pagesChapter 4 Geometric TransformationsJan Mar MateoNo ratings yet
- SPM Form 4 Add Maths Final ExamDocument5 pagesSPM Form 4 Add Maths Final ExamPatrick PhuahNo ratings yet
- P1 Revision Worksheet for April 2021 BatchDocument2 pagesP1 Revision Worksheet for April 2021 BatchLe Jeu LifeNo ratings yet
- AQA IGCSE Further Maths Predicted PaperDocument8 pagesAQA IGCSE Further Maths Predicted PapermrudulaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 - Graph of A Function: Two-Dimensional Coordinate PlaneDocument8 pagesLesson 8 - Graph of A Function: Two-Dimensional Coordinate PlanemcNo ratings yet
- Math Review: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandMath Review: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Analytical Techniques Final OSADocument15 pagesAnalytical Techniques Final OSAAthiNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting Final OSADocument9 pagesManagement Accounting Final OSAAthiNo ratings yet
- GENERIC Economics 1B Final-1Document8 pagesGENERIC Economics 1B Final-1AthiNo ratings yet
- Economics 1B Final OSA_231104_182657 (1) - With NotesDocument8 pagesEconomics 1B Final OSA_231104_182657 (1) - With NotesAthiNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Project Management Final OSADocument3 pagesIntroduction to Project Management Final OSAAthiNo ratings yet
- Analytical Techniques Final OSADocument15 pagesAnalytical Techniques Final OSAAthiNo ratings yet
- Business Communication Prep 2Document7 pagesBusiness Communication Prep 2AthiNo ratings yet
- Business Communication Prep 3Document5 pagesBusiness Communication Prep 3AthiNo ratings yet
- Business Mathematics Final OSADocument10 pagesBusiness Mathematics Final OSAAthiNo ratings yet
- Business Communication Exam PrepDocument6 pagesBusiness Communication Exam PrepAthiNo ratings yet
- Business Communication Final OSADocument3 pagesBusiness Communication Final OSAAthiNo ratings yet
- The Mathematical Model and Direct Kinematics Solution Analysis of Delta Parallel RobotDocument5 pagesThe Mathematical Model and Direct Kinematics Solution Analysis of Delta Parallel Robotfilipe o toscoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics T 954/2 (2012/2013) solutionsDocument2 pagesMathematics T 954/2 (2012/2013) solutionslingbooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (John H. Mathews)Document29 pagesChapter 3 (John H. Mathews)Alan WangNo ratings yet
- Grade 10-Portions For Pre Model Examination 1 - 2023-2024Document8 pagesGrade 10-Portions For Pre Model Examination 1 - 2023-2024Faraz AhmadNo ratings yet
- 121Document39 pages121Hendra RuhunussaNo ratings yet
- SFDVSVDCfor Olympiads & NTSE 2025 - Class IXDocument22 pagesSFDVSVDCfor Olympiads & NTSE 2025 - Class IXAtul KunduNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Q1 Week 4-6Document10 pagesMath 9 Q1 Week 4-6John Nino DoligolNo ratings yet
- Hongkong Secondary School Math CurriculumDocument53 pagesHongkong Secondary School Math CurriculumCHENXI DONGNo ratings yet
- Sample Algebra CourseDocument68 pagesSample Algebra Courseapi-264733744No ratings yet
- BSEd Major in MathematicsDocument10 pagesBSEd Major in MathematicsChoi YuriNo ratings yet
- Book - Mathematical Methods For EngineersDocument860 pagesBook - Mathematical Methods For EngineersFazle HaiderNo ratings yet
- Business Mathematics Quadratic EquationsDocument6 pagesBusiness Mathematics Quadratic EquationsEida Hidayah100% (1)
- New Century Mathematics 8 SyllabusDocument12 pagesNew Century Mathematics 8 SyllabusDee Jay Monteza Cabungan100% (1)
- Agarwal and Lang-Solutions-237Document1 pageAgarwal and Lang-Solutions-237JokerTHNo ratings yet
- M.Tech Thermal Engineering Teaching SchemeDocument19 pagesM.Tech Thermal Engineering Teaching SchemeNavneet KumarNo ratings yet
- 100 Calculus Based Physics Examples by Chris McMullen PDFDocument296 pages100 Calculus Based Physics Examples by Chris McMullen PDFNadeem Nasir MalikNo ratings yet
- Recent Research Advances in The Dynamic Behavior of Shells: 1989-2000, Part 2: Homogeneous ShellsDocument20 pagesRecent Research Advances in The Dynamic Behavior of Shells: 1989-2000, Part 2: Homogeneous Shellsadel8888No ratings yet
- Resonance QuadraticDocument25 pagesResonance Quadratickaeshav manivannanNo ratings yet
- PDF - SolverDocument7 pagesPDF - SolverRAJKUMAR CHATTERJEE. (RAJA.)No ratings yet
- B SC - II-10Document84 pagesB SC - II-10vishal jamnekarNo ratings yet
- PRO E Tips N TricksDocument33 pagesPRO E Tips N TricksGraham MooreNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 AnswersDocument8 pagesUnit 8 Answerspyropop3No ratings yet
- Gen Math Week 6 ModuleDocument5 pagesGen Math Week 6 ModuleJazka Abegail NavaNo ratings yet
- ODE Simulink PDFDocument92 pagesODE Simulink PDFcristianNo ratings yet
- 6 Exam Paper - IB HL - Separable Differential EquationsDocument19 pages6 Exam Paper - IB HL - Separable Differential EquationsYang WangNo ratings yet
- Solving SlesDocument1 pageSolving Slesapi-234725699No ratings yet
- Co - Po & Pso Mapping: Shree Venkateshwara Hi-Tech Engineering College, GobiDocument1 pageCo - Po & Pso Mapping: Shree Venkateshwara Hi-Tech Engineering College, GobiJeevitha SanthoshNo ratings yet