Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Purcom Midterm
Uploaded by
Nene Ocampo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageA reviewer for PurComm
Original Title
purcom-midterm (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA reviewer for PurComm
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pagePurcom Midterm
Uploaded by
Nene OcampoA reviewer for PurComm
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
LESSON 1: Communication Processes, Principles, and Ethics Uses of non-verbal communication:
Used to repeat the verbal message,
COMMUNICATION Often used to accent a verbal message.
"with", munus which means "a business", communis which means "common" Often complements the verbal message but may also contradict.
and communico which means "to confer". Regulate interactions.
-It is therefore defined as the process of accomplishing a goal May substitute for the verbal message, especially if it is blocked by noise or
-is the most critical component of total quality management. interruption.
-described as the transfer of information, thoughts or ideas to create a
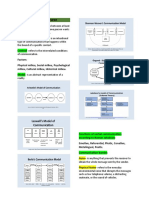
shared understanding between a sender and a receiver. ELEMENTS OF THE COMMUNICATION PROCESS
- It is a dynamic, two-way process Sender - a person, group or organization who initiates communication. Also
- Therefore, communication is the process of transferring information from called as encoder, source, Speaker, writer or communicator. The sender is
one point to another where the receiver responsible for the success of the communication. The sender's experiences,
attitudes, knowledge, skills, perceptions, and culture influence the message.
TYPES OF COMMUNICATION Message - is the element transmitted in the communication process. The
1. Verbal Communication - Uses words or symbols. It is done through message should be coded by the sender in a way that it will be easily
speaking or writing. understood by the receiver.
Spoken communication can be done through face-to-face interaction, Channel - pathway or medium through which the message travels to reach
through mobiles or computers, public speaking, etc. its destination. It may be oral, written or visual, Each kind of channel has a
Written communication can be written, digitized or printed. specific use depending on the message.
Examples: Face-to-face, through writing letters, social media, mobile phone
Factors that affect verbal communication: call, etc
Tone of voice Noise - a form of distortion, barrier or obstacle that occurs in any of the
Use of descriptive words phases of the oral communication process. It may be visual, aural, physical or
Emphasis on certain phrases psychological in forms.
Volume of voice Examples: inappropriate channel, incorrect grammar, inflammatory words,
jargon,
Non-verbal cues - make the message clearer and give the listener an Receiver - the person who receives, understands, analyzes and interprets the
indication in what way the Information should be received. message, Also called as decoder, reader or listener
These are similar to nonverbal type of communication; but these are used to Feedback - the receiver's response that provides information to the sender. It
accompany verbal communication. shows whether the receiver understood the message or not.
Adjustment - it is done if the message Is not clearly understood by the
Examples of Non verbal Cues: receiver.
Intonation
Facial expressions ASPECTS OF COMMUNICATION
Pause The importance of communication is related to various aspects.
Hand gestures 1. Communication is integrated in all parts of our lives.
Use of visuals We communicate every minute and every second of our lives. And as we go
Body movement through life every day, we use communication in all places we go to, in
Eye contact different parts of our lives.
2. Non-verbal Communication - sending of message using methods other Academics
than spoken language, It may be intentional or unintentional According to research, students who are good in writing and speaking
According to Tidwell (2016) there are two kinds of non-verbal perform better not only in the English class, but also in other learning areas.
communication: Professional
Non-verbal messages produced by the body Employees who are better in communicating have the higher chance of
Non-verbal messages produced by the broad setting such as time, space and getting hired.
silence Personal
Having a vocabulary to name the communication phenomena in our lives
Examples of non-verbal communication: increases our ability to alter consciously our communication in order to
touch achieve our goals and avoid miscommunication.
facial expressions Civic
dress Civic engagement refers to working to make a difference in our communities
glance by improving the quality of life of community members.
posture
eye contact 2. Communication meets needs
volume Communication is more than the transmission of information. We also
smell communicate in order to survive our day-to-day activities.
vocal nuance Physical Needs - keep our brain and body functioning
pause (silence) Instrumental Needs - instructing people, giving directions
context Relational Needs - initiate, maintain or end a relationship
proximity Identity Needs • people present their image through the way they
intonation communicate
formality
3. Communication is guided by culture and context
*In high-context cultures, the manner of saying the word is more important Culture - as defined by O'Neil (2006), it is the full range of learned human
than the word itself. behavior patterns. It
includes knowledge, belief, art, law, morals, customs, etc.
High context cultures - those who communicate in ways that are implicit and Context - the circumstances that form the setting for an event
rely heavily on context. Culture and context influence how we deliver and how we understand
These are the collectivistic in nature. messages.
Low context cultures - those who communicate in ways that are explicit. 4. Communication is learned.
These are the individualistic in nature. The need to communicate and the ability to learn a language Is innate.
However, our manner of communication varies from person to person.
You might also like
- Communis Which Means "Common" and Communico Which Means "To Confer"Document8 pagesCommunis Which Means "Common" and Communico Which Means "To Confer"Angelica TañedoNo ratings yet
- Sanchez (2017) : Non-Verbal Cues - Make TheDocument11 pagesSanchez (2017) : Non-Verbal Cues - Make TheLei Yunice NorberteNo ratings yet
- Communication: Communis Which Means "Common," and Communico Which Means "To Confer" or "To RelateDocument9 pagesCommunication: Communis Which Means "Common," and Communico Which Means "To Confer" or "To RelateKc Kirsten Kimberly MalbunNo ratings yet
- CommunicationDocument5 pagesCommunicationEman D. PangcatanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-4Document16 pagesChapter 1-4SJ SuingNo ratings yet
- PurposiveCommunication ModuleDocument5 pagesPurposiveCommunication Modulequeenie opelioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Communication Processes, Principles and EthicsDocument7 pagesChapter 1 Communication Processes, Principles and EthicsCuttie Anne Galang83% (6)
- The Concepts and Nature of Communication 2Document11 pagesThe Concepts and Nature of Communication 2Cristina GomezNo ratings yet
- Choosing Methods of CommunicationDocument6 pagesChoosing Methods of CommunicationAvery Jan SilosNo ratings yet
- Communication ReviewerDocument3 pagesCommunication ReviewerJESTON AMBUNANNo ratings yet
- Reviewer CommunicationDocument2 pagesReviewer CommunicationJaimNo ratings yet
- Purposive Com ReviewerDocument5 pagesPurposive Com Reviewerljn32179No ratings yet
- Purposive ComDocument16 pagesPurposive ComGhleedel Mhae AquinoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Oral CommDocument20 pagesLesson 1 Oral CommRaymond CorreaNo ratings yet
- Note Taking Cor 001Document14 pagesNote Taking Cor 001Clitz Myle Ochea YmbongNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Introduction To CommunicationDocument10 pagesModule 1 Introduction To CommunicationchailixlixanneNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication PrelimDocument2 pagesOral Communication PrelimAngelika ParungaoNo ratings yet
- PC Prelims 1Document3 pagesPC Prelims 1Jennifer DimaporoNo ratings yet
- Group 1Document32 pagesGroup 1Joe MoeNo ratings yet
- Oral ComDocument5 pagesOral ComVenise RevillaNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy Midterm-Module 1: Week 1Document12 pagesMedia and Information Literacy Midterm-Module 1: Week 1Jake GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Oral Comms - Reviewer For Oral Test 1Document7 pagesOral Comms - Reviewer For Oral Test 1Ken Juliana Fe IsaacNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Purposive CommunicationDocument5 pagesModule 1 - Purposive CommunicationKiko BernardinoNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication 1st PartDocument73 pagesOral Communication 1st PartJazmille Marie GlumalidNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Sep 12, 2021Document21 pagesAdobe Scan Sep 12, 2021Tushar AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Eng 3a - Chapter 1Document20 pagesEng 3a - Chapter 1Gerald GuiwaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Communication Processes Principles and EthicsDocument8 pagesChapter 1 Communication Processes Principles and EthicsDave BanquerigoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Oral Com 22 23Document4 pagesReviewer in Oral Com 22 23Melody BatoNo ratings yet
- Customer Relationship ManagementDocument55 pagesCustomer Relationship ManagementBALASARAVANANNo ratings yet
- Purcom Midterm Exam NotesDocument18 pagesPurcom Midterm Exam NotesShaina TelenNo ratings yet
- Engg MGMTDocument26 pagesEngg MGMTAlex NavalNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document8 pagesModule 4Florian Ecalner100% (1)
- Purcom ReviewerDocument4 pagesPurcom ReviewerBianca Jane AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Purcom ReviewerDocument15 pagesPurcom ReviewerJhae Zharie Delasan PanosoNo ratings yet
- Notes-What Is CommunicationDocument4 pagesNotes-What Is CommunicationSheena ChanNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication (GE 02) : First Semester Academic Year 2020-2021Document11 pagesPurposive Communication (GE 02) : First Semester Academic Year 2020-2021Criza Mae Castor Padernal100% (1)
- Purposive Communication - Second Sem - Midterms: Community. They Share Same Set of Rules in TheDocument7 pagesPurposive Communication - Second Sem - Midterms: Community. They Share Same Set of Rules in TheDA SulitNo ratings yet
- Purp Com Reviewer 1Document5 pagesPurp Com Reviewer 1Janica Pauline DaydayNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 (GNED05)Document3 pagesLesson 1 (GNED05)Ralph ChavezNo ratings yet
- FinalsDocument3 pagesFinalslapNo ratings yet
- Rev 1 (GNED05)Document3 pagesRev 1 (GNED05)Ralph ChavezNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument6 pagesPurposive CommunicationLEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Principles of Business CorrespondenceDocument15 pagesPrinciples of Business CorrespondenceRoberto Velasco MabulacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Communication Processes, Principles and EthicsDocument73 pagesChapter 1: Communication Processes, Principles and EthicsDeniell Kahlil Kyro GabonNo ratings yet
- GMRC Notes MidtermssDocument4 pagesGMRC Notes Midtermssmain.23001392No ratings yet
- Types of CommuDocument2 pagesTypes of CommuFATIMA AYRAA SALIHNo ratings yet
- J. Paul LeaganDocument15 pagesJ. Paul LeaganAries C. GavinoNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication Class Reading #1Document7 pagesOral Communication Class Reading #1Assiah AndreaNo ratings yet
- ENG Short NotesDocument23 pagesENG Short Notesb423069No ratings yet
- COMMUNICATIONDocument2 pagesCOMMUNICATIONwannabeeurzNo ratings yet
- MIL 1ST QUARTER REVIEWERDocument11 pagesMIL 1ST QUARTER REVIEWERoliveNo ratings yet
- AECC EnglishDocument31 pagesAECC Englishkavya70% (33)
- Non-Verbal Communication: DiscussionDocument10 pagesNon-Verbal Communication: DiscussionChriscell Gipanao EustaquioNo ratings yet
- Gec 5 ReviewerrDocument13 pagesGec 5 ReviewerrAllaika Zyrah FloresNo ratings yet
- Purp CommDocument5 pagesPurp CommKrisha Mabel TabijeNo ratings yet
- P119 - Module 3Document4 pagesP119 - Module 3Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Communication Processes, Principles and EthicsDocument26 pagesWeek 2 Communication Processes, Principles and EthicsMIGUEL BUHAINNo ratings yet
- 2 Nature Elements Types of CommunicationDocument27 pages2 Nature Elements Types of CommunicationNoemie DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Oral Com 2Document5 pagesOral Com 2Kieli JimjimNo ratings yet
- Personal Best B1 Unit 1 Grammar Test PDFDocument2 pagesPersonal Best B1 Unit 1 Grammar Test PDFNguyệt NgânNo ratings yet
- Scriptlet NLDocument3 pagesScriptlet NLtepaneroashlynNo ratings yet
- Anh 6-HK IiDocument16 pagesAnh 6-HK IiXuân Xuân PhạmNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 22-Apr-2023 PDFDocument2 pagesAdobe Scan 22-Apr-2023 PDFakhilesh kumar mishra Akhilesh Kumar mishraNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument13 pagesParts of Speechsandosa renoNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Mapping LlarenaDocument14 pagesCurriculum Mapping LlarenaBenedict LlarenaNo ratings yet
- Cover Letter For Trainee Bus DriverDocument4 pagesCover Letter For Trainee Bus Driverafdmjphtj100% (1)
- Chess-Results Server Chess-Results - Com - KEJOHANAN CATUR MSS KELANTAN 2023 5Document1 pageChess-Results Server Chess-Results - Com - KEJOHANAN CATUR MSS KELANTAN 2023 5MOHD ROSLAN BIN ARIFFIN MATRIFIN KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- GE 2 - Learning Manual - For PrintDocument52 pagesGE 2 - Learning Manual - For PrintKianggNo ratings yet
- Audio-Lingual Method - WikipediaDocument9 pagesAudio-Lingual Method - WikipediaToqeer TumraniNo ratings yet
- Introduction Discourse AnalysisDocument28 pagesIntroduction Discourse Analysissivi619450% (2)
- Duolingo French Scope and SequenceDocument6 pagesDuolingo French Scope and SequenceJosephine RoperNo ratings yet
- Resa Novian Dwi Saputra - Grammar D - Week 2Document2 pagesResa Novian Dwi Saputra - Grammar D - Week 2Reza SaputraNo ratings yet
- Classroom Observation ReportDocument10 pagesClassroom Observation ReportALAMSYAH ALAMSYAHNo ratings yet
- The Project Gutenberg Ebook of The New Atlantis, by Sir Francis BaconDocument33 pagesThe Project Gutenberg Ebook of The New Atlantis, by Sir Francis BaconTeoNo ratings yet
- How Culture Is Important in Language LearningDocument3 pagesHow Culture Is Important in Language Learning28mj8bfzc5No ratings yet
- Morphemes ProjectDocument5 pagesMorphemes ProjectRezpect QueenNo ratings yet
- Language Lab Assignments 2023Document2 pagesLanguage Lab Assignments 2023Anusriya MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Easy Steps To Chinese Pinyin - Text PDFDocument68 pagesEasy Steps To Chinese Pinyin - Text PDFbmNo ratings yet
- Vinateach English: Trial Class Feedback FormDocument2 pagesVinateach English: Trial Class Feedback FormCharmaine Rose TrocinoNo ratings yet
- LP in Compound Words English 5Document7 pagesLP in Compound Words English 5Aleza PearlNo ratings yet
- Centros Medicos AsociadosDocument19 pagesCentros Medicos AsociadosCris RiveraNo ratings yet
- Singular / Plural in EnglishDocument2 pagesSingular / Plural in EnglishDaniel VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Elln Digital TsnaDocument2 pagesElln Digital TsnaRodnel MonceraNo ratings yet
- 554 - Conditional Mood MCQ Test With Answers If Clause Type 1 2 3Document4 pages554 - Conditional Mood MCQ Test With Answers If Clause Type 1 2 3Chanako DaneNo ratings yet
- Applied Linguistics and Language UseDocument4 pagesApplied Linguistics and Language UseSalome ChachibaiaNo ratings yet
- Proverbs Website ArticleDocument2 pagesProverbs Website ArticleTash FaganNo ratings yet
- Daily Test-8 - Simple PastDocument2 pagesDaily Test-8 - Simple PastAji SakaNo ratings yet
- VisemicsDocument11 pagesVisemicsmilanhramNo ratings yet
- American English File 5 2nd-TB PDFDocument235 pagesAmerican English File 5 2nd-TB PDFTatiane Da Silva78% (91)