Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Day 4 Lesson Plan
Uploaded by
Billy Joe GodoyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Day 4 Lesson Plan
Uploaded by
Billy Joe GodoyCopyright:
Available Formats
Day 8 Lesson Plan
In erratic motion, we are going to talk about three types of graphs - the s-t graph (position versus time),
the v-t graph (velocity versus time), and the a-t graph (acceleration versus time).
Sample Problems:
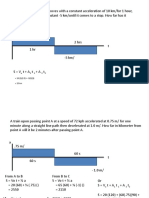
1. A bicycle moves along a straight road such that its position is described by the graphs shown. Construct the v-t
and a-t graphs from 0 < t < 30s.
Solutions:
From 0 to 10 and Since s=t2,
Differetiate position to get the Velocity
v = 2t
Differetiate velocity to get the acceleration
a=2
From 10 to 30 and Since s=20t - 100,
Differentiate position to get the Velocity
v = 20
Differentiate velocity to get the acceleration
a=0
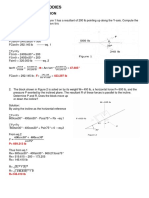
2. The car below starts from rest and travels along a straight track such that it accelerates at 10 m/s2 for 10s and then
decelerates at 2 m/s2. Draw the v-t and s-t graphs and determine the time t’ needed to stop the car. Also, how far has
the car traveled?
Solution:
A10 = 10m/s²
Integrate acceleration to get velocity
V10 = 10t
Integrate velocity to get position
S10 = 5t²
A10>t = -2m/s²
Integrate acceleration to get velocity
v t
∫ dv = ∫ −2 dt
100 m/ s 10 s
|v| v = |−2 t| t
100 10
V-100 = -2t + 20
V =( 2t + 120 ) m/s
To find for the t when the velocity is zero(because it stop)
0 = -2t + 120
-120 = -2t
t = 60 s
Integrate velocity to get position
V = 2t + 120
When the initial t= 10 s, then s=5t² = 5 (10)² = 500 m
s t
∫ ds = ∫ (−2 t+120)dt
5 00 m/ s 10 s
|s| s = |−t 2 +120 t| t
5 00 10
S - 500 = -t² + 120t – (-(10)² + 120(10))
S – 500 = -t² + 120t -1100
S =( -t² + 120t – 600) m
The time the car stop is at 60 s
S = -(60)² + 120(60) – 600
S = -3600 + 7200 – 600
S = 3000 m
You might also like
- Day 2 Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesDay 2 Lesson PlanBilly Joe GodoyNo ratings yet
- Final MechanicsDocument94 pagesFinal Mechanicsreyann0% (1)
- Laboratory Exercises in Astronomy: Solutions and AnswersFrom EverandLaboratory Exercises in Astronomy: Solutions and AnswersNo ratings yet
- Ch12 Kinematics - of - A - ParticleDocument46 pagesCh12 Kinematics - of - A - ParticletarntodNo ratings yet
- Applications of Derivatives Rate of Change (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandApplications of Derivatives Rate of Change (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Rectilinear Kinematics Erratic Motion PDFDocument28 pagesRectilinear Kinematics Erratic Motion PDFThibankumar Arumugam0% (1)
- A-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (10)
- Ass N 2 SolutionDocument7 pagesAss N 2 SolutionTorenToerntenoNo ratings yet
- Chapter1_kinematics_mabborang, Mary Kristelle uDocument6 pagesChapter1_kinematics_mabborang, Mary Kristelle uyram LetsirkNo ratings yet
- Dynamics GLA-1c PDFDocument9 pagesDynamics GLA-1c PDFAhmad IrfanNo ratings yet
- JamiehorizontalDocument7 pagesJamiehorizontalJamie Amanda FaderonNo ratings yet
- HWK 12Document24 pagesHWK 12Arron Vetus SablanNo ratings yet
- Dyna ProjectDocument58 pagesDyna ProjectCarlo Domanais0% (3)
- Kinematic EquationsDocument10 pagesKinematic EquationsYoAmoNYCNo ratings yet
- HWK 12Document24 pagesHWK 12subash1111@gmail.com67% (3)
- Acceleration: The Change Velocity Ms Thetime Taken For That Change Occur (S) V U TDocument8 pagesAcceleration: The Change Velocity Ms Thetime Taken For That Change Occur (S) V U TDaniel BerryNo ratings yet
- MODUL OF SCIENCE 2 Uniformly Accelerated MotionDocument4 pagesMODUL OF SCIENCE 2 Uniformly Accelerated MotionDiana SariNo ratings yet
- ETEEAP student guide to rigid body mechanicsDocument4 pagesETEEAP student guide to rigid body mechanicsRick Paulo ManalloNo ratings yet
- Variable acceleration and motion curve problemsDocument2 pagesVariable acceleration and motion curve problemsKent Edve Neil Rabe0% (2)
- VelovityDocument3 pagesVelovityRajesh TipnisNo ratings yet
- Calculus Word Problems IDocument20 pagesCalculus Word Problems IPatricia SioNo ratings yet
- Particle motion analysis and jet plane braking distanceDocument11 pagesParticle motion analysis and jet plane braking distanceSaad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Examples Solutions Answers Section1 01Document5 pagesExamples Solutions Answers Section1 01biligalaNo ratings yet
- Distance and Displacement ExplainedDocument37 pagesDistance and Displacement ExplainedHany ElGezawyNo ratings yet
- Kinematics problems with acceleration, velocity, and position calculationsDocument10 pagesKinematics problems with acceleration, velocity, and position calculationsNickolas RogersNo ratings yet
- Motion 220729 031748Document29 pagesMotion 220729 031748Imam Akbar RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Capítulo 2 (5th Edition)Document35 pagesCapítulo 2 (5th Edition)Kevin KumarNo ratings yet
- uniformlyacceleratedmotion-130924010203-phpapp02Document35 pagesuniformlyacceleratedmotion-130924010203-phpapp02Shierry Amor G. LangoteNo ratings yet
- Sol 04 Distance Speed and Time PDFDocument12 pagesSol 04 Distance Speed and Time PDFlinaNo ratings yet
- Solutions of Kinematics HC Verma Chapter 3Document16 pagesSolutions of Kinematics HC Verma Chapter 3Wave Education100% (1)
- Phy - Motion Graph AnalysisDocument63 pagesPhy - Motion Graph AnalysisGkid GkidNo ratings yet
- PHY10T2KINEMATICSDocument57 pagesPHY10T2KINEMATICSLuke CruzNo ratings yet
- Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia: Mechanical Engineering Dynamics DDE2063 BY En. Khairulnizam Bin OthmanDocument24 pagesUniversiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia: Mechanical Engineering Dynamics DDE2063 BY En. Khairulnizam Bin OthmanSuhayl AzminNo ratings yet
- Linear Motion Formulas: Acceleration of A CarDocument1 pageLinear Motion Formulas: Acceleration of A CarVishwajeet SinghNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument65 pagesKinematicsGarlapati Srinivasa Rao100% (1)
- Integrals As General and Particular Solutions: Section 1.2Document3 pagesIntegrals As General and Particular Solutions: Section 1.2Liz AñazcoNo ratings yet
- HW02 SolutionsDocument5 pagesHW02 Solutionshansony_2100% (3)
- Chapter2Kinematics With Constant Accelerationin1dDocument12 pagesChapter2Kinematics With Constant Accelerationin1dnsbaruaoleNo ratings yet
- Linear MotionDocument21 pagesLinear MotionHafiz AnshariNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Dynamic Bedford ch13Document197 pagesEngineering Mechanics Dynamic Bedford ch13Ozkhar AF100% (4)
- Igcse 11 Movement&PositionDocument36 pagesIgcse 11 Movement&PositionHany ElGezawy100% (1)
- PhysicsDocument6 pagesPhysicsAnonymous F8ejLpFD4No ratings yet
- Mechanos 1 CH 2Document8 pagesMechanos 1 CH 2Darlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- Final Velocity FormulaDocument7 pagesFinal Velocity FormulakarimNo ratings yet
- Solucionario Capitulos 1 & 2 Ing. Mecanica - Dinamica, Robert Soutas LittleDocument211 pagesSolucionario Capitulos 1 & 2 Ing. Mecanica - Dinamica, Robert Soutas LittleGeraldo De Los Santos100% (2)
- Rectilinear Kinematics (Continuous Motion)Document12 pagesRectilinear Kinematics (Continuous Motion)Nik RuqiyahNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of MechanicsB at time t be rABBrABADocument95 pagesFundamentals of MechanicsB at time t be rABBrABAalienx60582% (22)
- Phyf4 Chap2Document179 pagesPhyf4 Chap2Mohd AzlanNo ratings yet
- MotionDocument6 pagesMotionNikka FerrerNo ratings yet
- Equiz #2 (Automotive)Document5 pagesEquiz #2 (Automotive)Secret SecretNo ratings yet
- Take g-10m/s - 2 Give Answers To 2 Significant Figures. Formulas and Calculations Required For All AnswersDocument10 pagesTake g-10m/s - 2 Give Answers To 2 Significant Figures. Formulas and Calculations Required For All Answersisgigles157No ratings yet
- KINEMATICS ErnelDocument26 pagesKINEMATICS Erneljaalobiano100% (1)
- 14 2052012Assignments1and2SolutionDocument11 pages14 2052012Assignments1and2SolutionAbdullrahman Ahmed100% (1)
- Physic chapter 3 numricalsDocument12 pagesPhysic chapter 3 numricalsZafar Habib ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Physics Probs With Answers CompleteDocument9 pagesPhysics Probs With Answers CompleteKP DizonNo ratings yet
- hwk12 PDFDocument24 pageshwk12 PDFRick PongiNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus: 1.1 Areas Under Curves - Introduction and ExamplesDocument6 pagesIntegral Calculus: 1.1 Areas Under Curves - Introduction and Exampleskali capitalNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document83 pagesModule 1Billy Joe GodoyNo ratings yet
- Defining Construction ManagementDocument17 pagesDefining Construction ManagementBilly Joe GodoyNo ratings yet
- Bes 025-Statics of Rigid Bodiess PERIODICAL GRADE-2 ASSIGNMENT 1 (Total of 200 Points)Document4 pagesBes 025-Statics of Rigid Bodiess PERIODICAL GRADE-2 ASSIGNMENT 1 (Total of 200 Points)Billy Joe GodoyNo ratings yet
- Construction MethodsDocument7 pagesConstruction MethodsBilly Joe GodoyNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 1 SolutionDocument3 pagesAssignment - 1 SolutionBilly Joe GodoyNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 1 SolutionDocument3 pagesAssignment - 1 SolutionBilly Joe GodoyNo ratings yet
- QUANTITY SURVEYING DETAILED HVACDocument6 pagesQUANTITY SURVEYING DETAILED HVACBilly Joe GodoyNo ratings yet
- Quantity Surveying-Sanitary & Plumbing WorksDocument59 pagesQuantity Surveying-Sanitary & Plumbing WorksBilly Joe Godoy100% (1)
- Quantity Surveying-EarthworksDocument27 pagesQuantity Surveying-EarthworksBilly Joe Godoy0% (1)
- Quantity Surveying - Electrical WorksDocument57 pagesQuantity Surveying - Electrical WorksBilly Joe GodoyNo ratings yet
- List of Students 1st Semester, S.Y. 2021-2022 Bsce 4 A2-4BSCE-07 CIE 126 Quantity Surveying 07:30AM-10:30AM T Billy Joe Garcia GodoyDocument1 pageList of Students 1st Semester, S.Y. 2021-2022 Bsce 4 A2-4BSCE-07 CIE 126 Quantity Surveying 07:30AM-10:30AM T Billy Joe Garcia GodoyBilly Joe GodoyNo ratings yet