Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dp200 Pump Timing Instructions
Uploaded by
infoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dp200 Pump Timing Instructions
Uploaded by
infoCopyright:
Available Formats
New 1000 Series 20
Lucas DP 200 Series fuel injection pump
1
To remove to fit 20-10
Special tools: 2
3
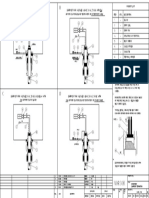
Timing pin PD.246, Lucas fuel injection pumps
General description
Caution: Do not release the nut (C2) from the fuel
injection pump. Illustration (C) shows the nut in
position when the fuel pump is fitted to the engine. A A0299
The fuel pump hub is fitted to the shaft in the factory
to ensure that the fuel pump is in the correct position
for timing. If the nut is removed and the hub moves,
the hub will need to be accurately fitted to the pump 1
by use of specialist equipment before the pump can
be fitted to the engine.
The manufacturer fits the hub (A2) to the pump to
ensure very accurate timing. Engines that have this 2
arrangement have the drive gear fastened to the hub
instead of to the shaft of the pump.
The hub is permanently mounted onto the drive shaft
by the pump manufacturer to allow the pump timing to
be set accurately when the engine is in service. 3
B C 0 07 3 /2
To prevent incorrect adjustments to the engine timing
by rotation of the fuel pump, the mounting flange (B1)
has holes instead of slots.
Accurate timing of the pump to the engine is by a pin
(C1) used to align the fuel pump gear and the the hub
(C4), with a hole in the body (C3) of the fuel pump.
The gear is passed over the pin and fastened to the 1
hub with four fasteners (C6). 2
6
Note: On the latest engines with belt driven coolant
pumps, four tamper proof fasteners retain the fuel
5
pump gear. Special tools to remove these fasteners
are available at your Perkins distributor.
4 3
Caution: A new fuel injection pump may be supplied C A03 7 4
with the pump shaft in the locked position. The drive
shaft of the pump must not be turned without the
spacer (B2) in position under the locking screw (B3).
The fuel injection pump has a locking screw (A3) and
(B3) and a spacer (B2). The locking screw prevents
the rotation of the drive shaft.
An "O" ring (A1) is fitted into a groove in the pump
flange. This "O" ring is fitted instead of a joint between
the pump flange and the timing case.
Workshop Manual, TPD 1350, issue 3 203
20 New 1000 Series
To remove
Before the crankshaft is turned or the pump is fitted,
put the spacer (A1) into position under the locking
screw (A2) to ensure that the pump drive shaft is
released.
1 Disconnect the battery before the fuel injection
pump is removed from the engine. 1
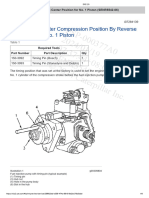
2 Set the engine to TDC on the number 1 cylinder on
the compression stroke, see operation 17-1 or , see
operation 17-2.
3 Remove the gear cover from the cover of the timing
case. For gear driven coolant pumps: Remove the 2
coolant pump, see operation 21-3. A C 0 07 3 /1
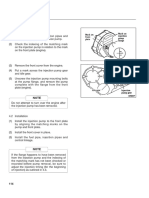
4 Insert the timing pin (B1) through the hole (B5) in
the fuel pump gear and the slot of the hub (B4). Push
the pin fully into the hole (B3) in the body of the fuel
pump. If the pin can be fully inserted then the pump
timing is correct. There should be no resistance when
the pin is inserted.
Caution: Use a second spanner to prevent 1
movement of the high-pressure outlet when the union 2
nut for each high-pressure pipe is released. 6
5 Remove the pipes, the cables and the connections
5
for the cold start device and the electrical stop
solenoid from the fuel pump.
4 3
Cautions: B A0 3 74 /2
! Do not rotate the crankshaft when the pump is not
on the engine; the loose fuel pump gear may
damage the timing case. If it is necessary to rotate
the crankshaft, fit the fuel pump temporarily to
ensure that the gear is in the correct position. If the
fuel pump is fitted temporarily in order to rotate the
crankshaft, the locking screw (A2) must be
released and a spacer (A1) fitted.
! Do not release the nut (B2) from the fuel injection
pump. The fuel pump hub is fitted to the shaft in
the factory to ensure that the fuel pump is in the
correct position for timing. If the hub is removed,
the hub will need to be accurately fitted to the
pump by use of special equipment available to
Perkins distributors.
6 Remove the four fasteners (B6) and release the
fuel pump gear from the hub of the fuel injection
pump.
7 Remove the nuts from the flange of the fuel pump
and remove the pump.
204 Workshop Manual, TPD 1350, issue 3
New 1000 Series 20
To fit
Cautions:
! The engine must be set to TDC number 1 cylinder,
compression stroke before the pump is fitted. If the
crankshaft needs to be rotated, the pump must be
fitted temporarily, or the loose gear could damage
1
the timing case.
! The drive shaft of the pump must not be rotated
without the spacer (A1) in position under the
locking screw (A2). If the drive shaft is rotated with
the locking screw tightened on to the shaft, the
drive shaft will be damaged. 2
A C 0 07 3 /1
1 Inspect the "O" ring (B1) in the pump flange and, if
necessary, fit a new "O" ring.
2 Lightly lubricate the "O" ring with clean engine 1
lubricating oil and put the pump into position on the
timing case.
3 Put the fuel pump in position on the three studs and
fit the flange nuts. 2
3
4 Fit the setscrew and nut of the support bracket.
Ensure that force is not applied to the fuel pump when
the support bracket is fitted.
5 Tighten the flange nuts of the fuel pump to 28 Nm
(20 lbf ft) 2,8 kgf m.
Caution: Do not remove the nut (C2) from the shaft
of the fuel injection pump. The fuel pump hub is fitted B A0299
to the shaft in the factory to ensure that the fuel pump
is in the correct position for timing. If the hub is
removed, the hub will need to be accurately fitted to
the pump by use of special equipment available to
Perkins distributors.
6 Put the fuel pump gear onto the hub of the fuel
pump. The fasteners (C6) for the fuel pump gear 1
should be in the centre of the slots to allow for the 2
removal of the backlash. Tighten the setscrews finger 6
tight.
Note: The fuel pump gear will only fit in one position. 5
The gear is fitted with the letters C and M at the front.
4 3
7 Insert the timing pin (C1) through the hole (C5) of
C A03 7 4
the fuel pump gear and the slot of the hub (C4) until it
can be pushed fully into the hole (C3) in the body of
the fuel pump. If the timing pin cannot be pushed into
the pump body, check that the engine is correctly set
at TDC on the number 1 cylinder, see operation 17-1
or , see operation 17-2.
Continued
Workshop Manual, TPD 1350, issue 3 205
20 New 1000 Series
Caution: The fuel pump gear must be fitted to the
engine before the crankshaft is rotated. 1
8 Carefully turn the gear counter-clockwise, by hand
(A1), to remove the backlash between the idler gear
and the fuel pump gear. Do not rotate the crankshaft
or the fuel pump shaft. Tighten the setscrews for the
fuel pump gear to 28 Nm (20 lbf ft) 2,8 kgf m.
9 Remove the timing pin.
10 Fit the gear cover to the cover of the timing case.
For gear driven coolant pumps: Fit the coolant pump,
see operation 21-3.
Caution: Do not tighten the union nuts of the high-
pressure pipes more than the recommended torque A A0 3 7 4/1
tension. If there is a leakage from the union nut,
ensure that the pipe is correctly aligned with the
atomiser inlet. Do not tighten the atomiser union nut
more, as this can cause a restriction at the end of the
pipe. This can affect the fuel delivery.
11 Fit all the pipes. Connect the control rod of the fuel
injection pump. Fit the cables and connection for the
cold start device and electrical stop solenoid to the
pump. Ensure that a spanner is used to prevent
movement of the pump outlets when the high-
pressure pipes are fitted and tighten the union nuts to
22 Nm (16 lbf ft) 2,2 kgf m.
12 Eliminate air from the fuel system, see operation
20-12.
13 Fit the cylinder head rocker cover.
14 Operate the engine and check for leakage. With
the engine at the normal temperature of operation,
check that the idle speed and the maximum no-load
speed are correct, see operation 20-11.
206 Workshop Manual, TPD 1350, issue 3
New 1000 Series 20
To adjust 20-11
1
The engine conforms with USA (EPA/CARB) stage 1 2
and EEC stage 1 emissions legislation for agricultural
and industrial applications.
The idle or maximum speed settings must not be
changed by the engine operator, because this can
damage the engine or the transmission.
Specialist equipment, which is available at your
Perkins Distributor, is needed to adjust the idle or
maximum speed settings. The warranty of the engine
can be affected if the seals on the fuel injection pump
are broken during the warranty period by a person A A0299
who is not approved by Perkins.
1 Operate the engine until it reaches its normal
temperature of operation and check the idle speed. If
necessary, adjustment can be made by the outer
adjustment screw (A2). Release the lock nut and
rotate the adjustment screw clockwise to increase the
speed, or counter-clockwise to decrease the speed.
When the speed is correct, tighten the lock nut. The
setting of the idle speed can change for different
applications. Normally the correct speed will be given
in the manufacturer's handbook for the application. If
it is not given, refer to your nearest Perkins distributor.
Caution: The setting for the maximum no load speed
can change for different applications. For the correct
maximum no-load speed, check the emissions data
plate fitted to the left side of the cylinder block before
any adjustment is made to the maximum no load
speed.
2 With the engine at its normal temperature of
operation, check the maximum no load speed. A
typical maximum no load speed is 2860 rev/min. If
necessary, this speed can be adjusted by the inner
adjustment screw (A1). Release the lock nut and
rotate the adjustment screw counter-clockwise to
increase the speed or clockwise to decrease the
speed. When the speed is correct, tighten the lock nut
and seal the screw.
The person who fits the pump must ensure that the
adjustment screw is suitably sealed against
interference after it has been set initially.
Workshop Manual, TPD 1350, issue 3 207
You might also like
- Manual TransmissionDocument33 pagesManual TransmissionEmad Satari100% (1)
- LQ4 LQ9 Engine Manual L510016Document229 pagesLQ4 LQ9 Engine Manual L510016Kyle Dubay100% (3)
- Puma Diesel Engine Camshaft Removal & Installation GuideDocument9 pagesPuma Diesel Engine Camshaft Removal & Installation GuideJam Bab100% (1)
- 2014-02-21 020021 Fuel Injection Pump - Install c4.4 PDFDocument4 pages2014-02-21 020021 Fuel Injection Pump - Install c4.4 PDFGanda PrajaNo ratings yet
- Cat C-13 Valve LashDocument6 pagesCat C-13 Valve LashEwgeny100% (5)
- Fuel Injection Pump Timing - AdjustDocument6 pagesFuel Injection Pump Timing - AdjustRonald Yucra Cadena100% (2)
- Plymouth and Chrysler-built cars Complete Owner's Handbook of Repair and MaintenanceFrom EverandPlymouth and Chrysler-built cars Complete Owner's Handbook of Repair and MaintenanceNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - John Deere Powertech 68l Diesel Engines Mechanical Fuel Systems Component Service Repair Technical Manual ctm207Document15 pagesDokumen - Tips - John Deere Powertech 68l Diesel Engines Mechanical Fuel Systems Component Service Repair Technical Manual ctm207Valeriy Valkovets100% (1)
- Installation Procedure: Fuel Injection Pump - InstallDocument4 pagesInstallation Procedure: Fuel Injection Pump - InstallPe ArvasliNo ratings yet
- Stanadyne DB2 and DB4 Pump Removal and InstallationDocument3 pagesStanadyne DB2 and DB4 Pump Removal and InstallationJoseph100% (1)
- Volvo Penta Workshop Manual Part BDocument60 pagesVolvo Penta Workshop Manual Part BMišo Vučko100% (1)
- Spring and Shock AbsorberDocument16 pagesSpring and Shock AbsorberAzim AzlanNo ratings yet
- Volvo D13H Shop Armed Vol2Document34 pagesVolvo D13H Shop Armed Vol2Juan José AldanaNo ratings yet
- VW 1.9L TURBO DIESELDocument26 pagesVW 1.9L TURBO DIESELfloresf5100% (1)
- 216B 226B 232B 242B Skid Steer Loader BXM00001-04224 (MACHINE) POWERED BY 3024C Engine (SEBP3770 - 65) - Systems & Components 15 UBA PDFDocument6 pages216B 226B 232B 242B Skid Steer Loader BXM00001-04224 (MACHINE) POWERED BY 3024C Engine (SEBP3770 - 65) - Systems & Components 15 UBA PDFubaldo caraballoNo ratings yet
- Iveco Engine T3Document33 pagesIveco Engine T3Marian Taras100% (1)
- 3208 Pump Install Timing InstructionsDocument4 pages3208 Pump Install Timing InstructionsUliAlejandroRodriguezCorianga100% (1)
- CCR Catalogiseki Parts PDFDocument45 pagesCCR Catalogiseki Parts PDFKemal Lisnik ArnautovicNo ratings yet
- Fuel Pump Replacement ManualDocument7 pagesFuel Pump Replacement Manualapi-542121636No ratings yet
- Fuel Injection Pump - Install - Type 2 Engines and 7BJ EnginesDocument4 pagesFuel Injection Pump - Install - Type 2 Engines and 7BJ EnginesDaniel AndradeNo ratings yet
- Finding Top Center Position For No. 1 PistonDocument14 pagesFinding Top Center Position For No. 1 PistonTuan Anh100% (1)
- Fuel Injection Pump - InstallDocument8 pagesFuel Injection Pump - Installedwin100% (1)
- The Book of the Singer Junior - Written by an Owner-Driver for Owners and Prospective Owners of the Car - Including the 1931 SupplementFrom EverandThe Book of the Singer Junior - Written by an Owner-Driver for Owners and Prospective Owners of the Car - Including the 1931 SupplementNo ratings yet
- ADJUST FUEL TIMINGDocument3 pagesADJUST FUEL TIMINGSanjay MadakaNo ratings yet
- IntruderDocument98 pagesIntruderRushabh DoshiNo ratings yet
- Jack Erjavec Auto Tech BookDocument33 pagesJack Erjavec Auto Tech BookSantiago UrgilesNo ratings yet
- Basicos de Caterpillar 3208Document20 pagesBasicos de Caterpillar 3208Hector Herrera100% (6)
- Cummins Engine InfoDocument13 pagesCummins Engine Infovictor villaseñor garciaNo ratings yet
- Service Bulletin: Phaser/1000 Series 1 New Water Seal/water Pump February 1988Document2 pagesService Bulletin: Phaser/1000 Series 1 New Water Seal/water Pump February 1988Jacques Van NiekerkNo ratings yet
- NC 750 X Manual de TallerDocument86 pagesNC 750 X Manual de TallerDiego Rodini100% (1)
- 2013 OPEL INSIGNIA - Engine Mechanical - 2.0L (LTG) - Repair Instructions - Off VehicleDocument317 pages2013 OPEL INSIGNIA - Engine Mechanical - 2.0L (LTG) - Repair Instructions - Off VehicleGedas GvildysNo ratings yet
- Perkins Boletin MotorDocument7 pagesPerkins Boletin MotorWilliams Araya100% (1)
- Remove & Install Oil Cooler - Step-by-Step GuideDocument15 pagesRemove & Install Oil Cooler - Step-by-Step GuideFredy QuistialNo ratings yet
- R065E2Document7 pagesR065E2Mk MakyNo ratings yet
- Fuel SystemDocument3 pagesFuel SystemHenriqueNo ratings yet
- Top 1Document6 pagesTop 1Dedy hermawanNo ratings yet
- 200 CC6Document14 pages200 CC6Edward KaranjaNo ratings yet
- Pistons and Connecting Rods - AssembleDocument5 pagesPistons and Connecting Rods - Assembleeshopmanual limaNo ratings yet
- Sci Mop Bombas Espuma Cgp80 - ChemguardDocument13 pagesSci Mop Bombas Espuma Cgp80 - Chemguarddiuska13No ratings yet
- Remove Injection Pump c4. 4 SN s1mDocument2 pagesRemove Injection Pump c4. 4 SN s1mBadrus AqmarNo ratings yet
- U009E1Document5 pagesU009E1381tutNo ratings yet
- Scion XBDocument18 pagesScion XBLucien Wright0% (1)
- Engine DesignDocument43 pagesEngine DesignANTONIO CRUZNo ratings yet
- Correa Reparticion FORD F150 - FULL MOTORES CHECKDocument11 pagesCorrea Reparticion FORD F150 - FULL MOTORES CHECKciroNo ratings yet
- Disassembly and AssemblyDocument100 pagesDisassembly and AssemblybagoesNo ratings yet
- TELEDYNE CONTINENTAL AIRCRAFT ENGINE MANDATORY SERVICE BULLETINDocument6 pagesTELEDYNE CONTINENTAL AIRCRAFT ENGINE MANDATORY SERVICE BULLETINBarry MohrNo ratings yet
- Instalar Bomba 430DDocument5 pagesInstalar Bomba 430Drjan7peNo ratings yet
- AFC06901 (Balancines)Document12 pagesAFC06901 (Balancines)salvador montenegroNo ratings yet
- PumpDocument3 pagesPump薛泽绵No ratings yet
- Disassemble pistons and connecting rodsDocument9 pagesDisassemble pistons and connecting rodsbagoesNo ratings yet
- HONDA2Document8 pagesHONDA2Taller PNCNo ratings yet
- Engine Brakes PDFDocument18 pagesEngine Brakes PDFMitchelle GonouyaNo ratings yet
- Inline Cummins Pump Removal and InstallationDocument5 pagesInline Cummins Pump Removal and Installationlukman sodiqNo ratings yet
- 3Document6 pages3George GuerreroNo ratings yet
- SelectionDocument20 pagesSelectionJoséEnriqueSosaNo ratings yet
- Carburador Toyota 1991Document23 pagesCarburador Toyota 1991William Martínez B.No ratings yet
- 060 - Engine Mechanical - 2.4L (LEA LUK) - Repair Instructions - Off VehicleDocument320 pages060 - Engine Mechanical - 2.4L (LEA LUK) - Repair Instructions - Off VehicleGedas GvildysNo ratings yet
- Service BulletinDocument12 pagesService BulletinEdward Adrian Moreno FernandezNo ratings yet
- R9M Bottom Engine Crankshaft DetailsDocument11 pagesR9M Bottom Engine Crankshaft Detailszmatij24No ratings yet
- Engine Valve Lash - Inspect/AdjustDocument4 pagesEngine Valve Lash - Inspect/AdjustHrvoje ŠkaricaNo ratings yet
- Fuel Injection Pump - Install - Delphi DP210Document4 pagesFuel Injection Pump - Install - Delphi DP210bagoesNo ratings yet
- Notice: Table 1Document3 pagesNotice: Table 1Soluciones Costa CaribeNo ratings yet
- Engine Valve Lash - Inspect/Adjust: Testing and AdjustingDocument6 pagesEngine Valve Lash - Inspect/Adjust: Testing and AdjustingAngelica VergaraNo ratings yet
- Fuel Injection Pump - Install - With Electronic GovernorDocument5 pagesFuel Injection Pump - Install - With Electronic Governoreshopmanual limaNo ratings yet
- Caterpillar Cat 216B3 Skid Steer Loader (Prefix HR2) Service Repair Manual (HR200001 and Up)Document25 pagesCaterpillar Cat 216B3 Skid Steer Loader (Prefix HR2) Service Repair Manual (HR200001 and Up)rpoy9396615No ratings yet
- Installation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitFrom EverandInstallation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitNo ratings yet
- Screws With External Hexalobular Driving Feature: Mercedes-Benz MBN 10 142Document6 pagesScrews With External Hexalobular Driving Feature: Mercedes-Benz MBN 10 142achin123No ratings yet
- BRCDocument237 pagesBRCHitachiNo ratings yet
- ZF AVS Automatic Gearbox Manual PDFDocument67 pagesZF AVS Automatic Gearbox Manual PDFDardan HusiNo ratings yet
- Thermo Lab 5Document12 pagesThermo Lab 5Zain ul AbideenNo ratings yet
- Engine, Dismantling D11MDocument23 pagesEngine, Dismantling D11MAMIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- 13 6181 33 Stiga Park Diesel 4WD 2007Document51 pages13 6181 33 Stiga Park Diesel 4WD 2007Michael worthmannNo ratings yet
- Caterpillar Parts Manual 3304Document6 pagesCaterpillar Parts Manual 3304Jovie GrohlNo ratings yet
- Engine MechanicalDocument42 pagesEngine MechanicalHarry HavocNo ratings yet
- iCR 3600 Flat Gear and Motor Replacement: WarningDocument13 pagesiCR 3600 Flat Gear and Motor Replacement: WarningEliana Caceres TorricoNo ratings yet
- Training Material DANA TCON - Full Flow - 6196.528Document21 pagesTraining Material DANA TCON - Full Flow - 6196.528aybchb20No ratings yet
- Esquema PIN OUT Haltech NSXDocument4 pagesEsquema PIN OUT Haltech NSXDavid Infante HernandezNo ratings yet
- BPW axle and suspension maintenance guideDocument92 pagesBPW axle and suspension maintenance guideAnton Van NiekerkNo ratings yet
- Mech DocDocument81 pagesMech Docjosealejandro martinezlaraNo ratings yet
- Installation Instructions: Spring Brake Chamber and Service Brake Chamber Installation and Clocking (Air Disc Brake)Document8 pagesInstallation Instructions: Spring Brake Chamber and Service Brake Chamber Installation and Clocking (Air Disc Brake)Elmer Tintaya MamaniNo ratings yet
- Wire, 10 AWG, 5000 V, Tefzel - Focal 3393Document1 pageWire, 10 AWG, 5000 V, Tefzel - Focal 3393Marilton SiqueiraNo ratings yet
- Norsok: NotesDocument1 pageNorsok: NotestxagusNo ratings yet
- 1997 Toyota Corolla 1.8L 4-cylinder engine control module diagramDocument45 pages1997 Toyota Corolla 1.8L 4-cylinder engine control module diagramDarimar CorredorNo ratings yet
- 50 ZVDocument376 pages50 ZVDedy setiawanNo ratings yet
- Engine Overhauling Inspection ReportDocument8 pagesEngine Overhauling Inspection ReportAlaeldin AlhennawyNo ratings yet
- LESCO Category Wise Equipment 11 33kVDocument3 pagesLESCO Category Wise Equipment 11 33kVfddf0% (1)
- General Specifications: TorqueDocument2 pagesGeneral Specifications: TorqueTheWrenchNo ratings yet
- SB 238Document38 pagesSB 238Amit KumarNo ratings yet