Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PARABOLA
Uploaded by
Daniel Solicito0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesThis document defines the key parts of a parabola - the vertex, focus, directrix, and latus rectum. It provides the general and standard forms of the parabolic equation and formulas to determine the vertex, focus, directrix, and endpoints of the latus rectum given a standard or general form equation. Examples are given to demonstrate how to determine these parts of a parabola from its equation. Exercises are also included to allow the reader to practice finding the standard equation, sketching the graph, and determining the vertex, focus, directrix, and latus rectum of parabolas.
Original Description:
GRADE 11 STEM 1ST SEM
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document defines the key parts of a parabola - the vertex, focus, directrix, and latus rectum. It provides the general and standard forms of the parabolic equation and formulas to determine the vertex, focus, directrix, and endpoints of the latus rectum given a standard or general form equation. Examples are given to demonstrate how to determine these parts of a parabola from its equation. Exercises are also included to allow the reader to practice finding the standard equation, sketching the graph, and determining the vertex, focus, directrix, and latus rectum of parabolas.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesPARABOLA
Uploaded by
Daniel SolicitoThis document defines the key parts of a parabola - the vertex, focus, directrix, and latus rectum. It provides the general and standard forms of the parabolic equation and formulas to determine the vertex, focus, directrix, and endpoints of the latus rectum given a standard or general form equation. Examples are given to demonstrate how to determine these parts of a parabola from its equation. Exercises are also included to allow the reader to practice finding the standard equation, sketching the graph, and determining the vertex, focus, directrix, and latus rectum of parabolas.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
PARABOLA
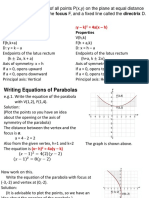
Parts of Parabola
a) Vertex (V)
b) Focus (F)
c) Latus Rectum (LR)
d) Directrix (D)
Equations
General Form: Standard Form:
y= ax2+ bx + c Vertical: (x-h)2 = 4a (y-k)
x = ay2 + by + c Horizontal: (y-k)2 = 4a (x-h)
Formulas
Vertex
(h, k)
Focus Endpoints of the LR (Horizontal)
Vertical (upward or downward): (h, k+a) ELR1 (h+a, k+2a)
Horizontal (left or right): (h+a, k) ELR2 (h+a, k-2a)
Directrix Endpoints of the LR (vertical)
Vertical: y = (k-a) ELR1 (h+2a, k+a)
Horizontal: x = (h-a) ELR2 (h-2a, k+a)
Graphing a Parabola with V (0,0) can be determined if:
Vertical
Horizontal Upward if x2 = 4ay (positive)
Right if y2 = 4ax (positive)
Equation example:
Equation example:
x2 = 12y
y2 = 12x
Downard if x2 = -4ay (negative)
Left fs y2 = -4ax (negative)
Equation example:
Equation example:
x2 = -16y
y2 = -16x
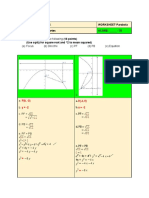
Determining the V, F, D & ELRs of an Equation
Standard Equation
(x-2)2 -= -12 (y-2) F : (h, k+a): (2, -2)
V (h, k): (2, 2) D: y = k-a; y = 4
4a = -12 ELR1 (h+2a, k+a): [2 + 2(-4), 2 + (-4)]: (-6, -2)
-12 divided by 4 a = -4 ELR1 (h-2a, k+a): [2 - 2(-4), 2 + (-4)]: (10, -2)
General Equation
y2 – 6y + 8x + 25 = 0
1. arrange
y2 – 6y = -8x – 25
2. factor
y2 – 6y = -8x – 25 +9 = -16 ÷ -8 = 2
÷2
(y – 3)2 = -8 (x + 2)
(y-3) (y-3) = y2 – 6y + 9
(y – 3)2 = -8 (x + 2) standard form
You can now get the V, F, D & ELRs by following the same
method from standard form.
V (-2, 3)
4a = -8; a = -2
F (-4, 3)
D: x = -0
ELR1 (-4, -1)
ELR2 (-4, 7)
Exercises
a. Find the standard equation and sketch the parabola given its V and F.
1. V (4, -4); F (4, -2)
2. V (0, -1); F (-2, -1)
b. Find the general equation.
1. (y – 4)2 = 8 (x + 2)
2. (x + 4)2 = 20 (y - 3)
c. Find the standard equation, V, F, D, ELRs and sketch.
1. x2 – 2x – 6y + 25 = 0
2. y2 – 6x + 2y – 17 = 0
You might also like
- Introduction and Review Differential CalculusbDocument32 pagesIntroduction and Review Differential CalculusbRalph Piolo BuanNo ratings yet
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsFrom EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 3.0 Conic Sections Ellipses FCIT CompatDocument29 pages3.0 Conic Sections Ellipses FCIT CompatMykhaela Louize Gumban100% (1)
- Ellipse: Intercepts. The Endpoints of The Minor Axis Are (0, B) and (0, - B) and Are Referred To AsDocument18 pagesEllipse: Intercepts. The Endpoints of The Minor Axis Are (0, B) and (0, - B) and Are Referred To AseL LeahNo ratings yet
- 6.6 Analyzing Graphs of Quadratic FunctionsDocument22 pages6.6 Analyzing Graphs of Quadratic FunctionsCikgu Shaiful Kisas100% (1)
- Precalculus Reviewer PDFDocument5 pagesPrecalculus Reviewer PDFAnnel Christine RamosNo ratings yet
- Precalculus Midterm ExamDocument7 pagesPrecalculus Midterm ExamRai100% (1)
- First Quarter Examination: PrecalculusDocument4 pagesFirst Quarter Examination: Precalculuswalden habanaNo ratings yet
- First Quarter Grade 11 Pre-CalculusDocument7 pagesFirst Quarter Grade 11 Pre-CalculusGary VargasNo ratings yet
- Jovic G. Rullepa: SST - Iii, Shs StemDocument36 pagesJovic G. Rullepa: SST - Iii, Shs StemMykhaela Louize GumbanNo ratings yet
- Parabola 3Document6 pagesParabola 3Aly FayeNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Parabola at VertexDocument1 pageParts of The Parabola at VertexFiedacan, Sherwin Jr.No ratings yet
- Math 9 ReviewerDocument23 pagesMath 9 ReviewerLorica John LuisNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1-Pre CalDocument5 pagesQuiz 1-Pre CalCynette Danielle Florentino CaseresNo ratings yet
- 1stQtr Pre Calculus ReviewerDocument3 pages1stQtr Pre Calculus ReviewerGanyu da SecretaryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Conic SectionsDocument8 pagesChapter 4 Conic SectionsILEENVIRUSNo ratings yet
- Equations of Conics - InfoDocument6 pagesEquations of Conics - Infoty trackNo ratings yet
- The ParabolaDocument1 pageThe ParabolaShiella Mae A. JimenezNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Conics NotesDocument8 pagesModule 2 Conics NotesFons Roxas-ChuaNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections 1Document41 pagesConic Sections 1Chaz grant borromeoNo ratings yet
- 1 Parabolas 2 Circles 3 Ellipses 4 Hyperbolas 5 ExerciesDocument6 pages1 Parabolas 2 Circles 3 Ellipses 4 Hyperbolas 5 ExerciesKyle VuNo ratings yet
- Formulas 1Document3 pagesFormulas 1BetooHernándezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Circles: Finding The Equation of The CircleDocument4 pagesLesson 1: Circles: Finding The Equation of The CircleLumpa RamosNo ratings yet
- Soalan 4-Circle and ElipseDocument6 pagesSoalan 4-Circle and ElipseHaooonNo ratings yet
- 2D Part 04 Conic SectionDocument13 pages2D Part 04 Conic Sectiongouravagrawal309No ratings yet
- PRECALCULUS FORMULAS DetailedDocument2 pagesPRECALCULUS FORMULAS DetailedJessa Mae Dechavez DumalagNo ratings yet
- Parabola 2Document9 pagesParabola 2Aly FayeNo ratings yet
- r y x=h− p Σ (Summation Symbol/ Sigma) xDocument1 pager y x=h− p Σ (Summation Symbol/ Sigma) xAlkallain Brands CompanyNo ratings yet
- Section ConicDocument22 pagesSection ConicRishab Kumar100% (1)
- Project in Precal: Mary Joyce MolinesDocument11 pagesProject in Precal: Mary Joyce MolinesJaja KeykNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1 PBDocument2 pagesSheet 1 PBAaRaV KuShWaHaNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections: - Circle - Parabola - Ellipse - HyperbolaDocument11 pagesConic Sections: - Circle - Parabola - Ellipse - Hyperbolajohn tanNo ratings yet
- Precal - Lesson 4Document4 pagesPrecal - Lesson 4alayca cabatanaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document13 pagesLecture 8Solomon BinutuNo ratings yet
- Math Unit 2Document14 pagesMath Unit 2Jessica MehraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Quadratic FunctionDocument20 pagesLesson 8 Quadratic FunctionNicole Daphnie LisNo ratings yet
- Math 285 Formula SheetDocument2 pagesMath 285 Formula SheetjosiahgerberNo ratings yet
- Bicol University College of Engineering Civil Engineering DepartmentDocument2 pagesBicol University College of Engineering Civil Engineering DepartmentMa Ella Mae LogronioNo ratings yet
- Parabolas: Topic 7.2Document8 pagesParabolas: Topic 7.2Judicar AbadiezNo ratings yet
- Parabolas: Topic 7.2Document8 pagesParabolas: Topic 7.2Judicar AbadiezNo ratings yet
- Translating Conic SectionsDocument15 pagesTranslating Conic SectionsNikhil KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Analytic Geometry: Discovering ParabolaDocument4 pagesUnit 1: Analytic Geometry: Discovering ParabolaBilly Jasper DomingoNo ratings yet
- Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates 11.6. Conic SectionsDocument10 pagesParametric Equations and Polar Coordinates 11.6. Conic SectionsKing CreativeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Coordinate Geometry and Conic SectionsDocument17 pagesChapter 1 Coordinate Geometry and Conic SectionsAik0% (1)
- Introduction To Conic SectionDocument41 pagesIntroduction To Conic SectionJessa Jane SanchezNo ratings yet
- EQUATIONSDocument2 pagesEQUATIONStotoej10No ratings yet
- Introduction To Conic SectionsDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Conic SectionsG10. Llagas, Jana Micaella GubatonNo ratings yet
- 07 Parabola and Ellipse - Handouts PDFDocument28 pages07 Parabola and Ellipse - Handouts PDFMark ReyesNo ratings yet
- Parabola WorksheetDocument5 pagesParabola WorksheetEdzel FrinceNo ratings yet
- Parabola Week 2: Content StandardsDocument9 pagesParabola Week 2: Content StandardsJackylyn FalejoNo ratings yet
- Parabola (TN)Document27 pagesParabola (TN)Raju Singh100% (1)
- Lesson 2 ParabolaDocument57 pagesLesson 2 ParabolaJohn Paul Recopuerto ParachaNo ratings yet
- Fs Pab1Document8 pagesFs Pab1Vipul Jain100% (1)
- Parabolas: Topic 7.2Document8 pagesParabolas: Topic 7.2John Philip ReyesNo ratings yet
- Parabolas: Topic 7.2Document8 pagesParabolas: Topic 7.2John Philip ReyesNo ratings yet
- Shortcuts For Ellipses and HyperBolaDocument3 pagesShortcuts For Ellipses and HyperBolaChristian Simon D. SOLINAPNo ratings yet
- Learning Competencies: Discovering EllipseDocument5 pagesLearning Competencies: Discovering EllipseBilly Jasper DomingoNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 EllipseDocument5 pagesUNIT 1 EllipseBilly Jasper DomingoNo ratings yet
- Pre Cal Lesson NotesDocument23 pagesPre Cal Lesson Notesnunezreneboy1No ratings yet
- Saksakin Mo Nalang Ako VonzkiDocument2 pagesSaksakin Mo Nalang Ako VonzkiJohn Ernest MarcoNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Conic Sections Part 1Document54 pages1.1 Conic Sections Part 1Robie Vasquez CamposanoNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections-A Figure Formed by Intersection of A Plane and A Right Circular ConeDocument20 pagesConic Sections-A Figure Formed by Intersection of A Plane and A Right Circular ConeJron Keith TuazonNo ratings yet
- Tables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27From EverandTables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27No ratings yet
- Quarter 1Document55 pagesQuarter 1Mikaela Julianne EradaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - EllipseDocument30 pagesLesson 4 - EllipseMattheus Marcus ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Mini Quiz 1 - Hyperbolics FunctionsDocument2 pagesMini Quiz 1 - Hyperbolics Functionsirfananda hutomoNo ratings yet
- Ellipse TheoryDocument36 pagesEllipse TheorypadmaNo ratings yet
- Pre Calculus Conic Section Around Us, Project PDFDocument17 pagesPre Calculus Conic Section Around Us, Project PDFAlly OcbianNo ratings yet
- PreCal Q1 Mod5Document32 pagesPreCal Q1 Mod5PororoNo ratings yet
- Illustrate The Different Type of Conic SectionDocument8 pagesIllustrate The Different Type of Conic SectionCry BeroNo ratings yet
- Circumference and Area of CirclesDocument41 pagesCircumference and Area of CirclesDarven OfficialNo ratings yet
- Conic SectionDocument66 pagesConic SectionVansh MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Dinah Fe T. Olitan Instructor I College of Engineering and Technology Civil Engineering ProgramDocument52 pagesAnalytic Geometry: Dinah Fe T. Olitan Instructor I College of Engineering and Technology Civil Engineering ProgramMae MateoNo ratings yet
- MATHS Revision DPP No 2Document8 pagesMATHS Revision DPP No 2ashutosh100% (2)
- Pre Calculus: Lesson 1: Knowing The Conic SectionsDocument33 pagesPre Calculus: Lesson 1: Knowing The Conic SectionsGENEEN LOUISE F. GELVOLEONo ratings yet
- A2 ch10 04 Edit HyperbolasDocument25 pagesA2 ch10 04 Edit HyperbolasRicka ValinoNo ratings yet
- Precalculus Q1 Mod4 Hyperbola v5Document24 pagesPrecalculus Q1 Mod4 Hyperbola v5Andrea NicoleNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections OverviewDocument93 pagesConic Sections OverviewAkihiko SuzukiNo ratings yet
- Midpoint Ellipse AlgorithmDocument7 pagesMidpoint Ellipse AlgorithmThilina MadhushaniNo ratings yet
- Class 11 MathDocument355 pagesClass 11 MathAryanNo ratings yet
- Ncert Exemplar Math Class 11 Chapter 11 Conic-SectionDocument33 pagesNcert Exemplar Math Class 11 Chapter 11 Conic-SectionDhairy KalariyaNo ratings yet
- CH#5 Elliptic IntegralsDocument15 pagesCH#5 Elliptic IntegralsTaha ZakaNo ratings yet
- CircleDocument10 pagesCircleRokaya fouadNo ratings yet
- Ellipse + Qee QuizDocument2 pagesEllipse + Qee QuizGitanshu AroraNo ratings yet
- Analytical Geometry Previous Year Questions From 2020 To 1992Document12 pagesAnalytical Geometry Previous Year Questions From 2020 To 1992SHAHIL KUMAR SHRIWASTAVNo ratings yet
- Math 2 PDFDocument1 pageMath 2 PDFJads CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Cycle Test-I (19.05.22) Sec - A & FDocument4 pagesCycle Test-I (19.05.22) Sec - A & FculvertsNo ratings yet