Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CO1 (3) Families of Curves
CO1 (3) Families of Curves
Uploaded by
dimarananxyz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views6 pagesThis document outlines the academic week of October 4th through 8th for the MATHA43 course. It will cover Course Outcome 1 which includes definitions of differential equations, elimination of arbitrary constants, and solutions to first-order ordinary differential equations including separable differential equations. Course Outcome 2 topics include homogeneous differential equations, linear differential equations, and exact differential equations. It also provides examples of obtaining the differential equation of families of plane curves described, such as circles with centers on the x-axis, parabolas with axes parallel to the x-axis, and more.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines the academic week of October 4th through 8th for the MATHA43 course. It will cover Course Outcome 1 which includes definitions of differential equations, elimination of arbitrary constants, and solutions to first-order ordinary differential equations including separable differential equations. Course Outcome 2 topics include homogeneous differential equations, linear differential equations, and exact differential equations. It also provides examples of obtaining the differential equation of families of plane curves described, such as circles with centers on the x-axis, parabolas with axes parallel to the x-axis, and more.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views6 pagesCO1 (3) Families of Curves
CO1 (3) Families of Curves
Uploaded by
dimarananxyzThis document outlines the academic week of October 4th through 8th for the MATHA43 course. It will cover Course Outcome 1 which includes definitions of differential equations, elimination of arbitrary constants, and solutions to first-order ordinary differential equations including separable differential equations. Course Outcome 2 topics include homogeneous differential equations, linear differential equations, and exact differential equations. It also provides examples of obtaining the differential equation of families of plane curves described, such as circles with centers on the x-axis, parabolas with axes parallel to the x-axis, and more.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Academic Week 3: (Oct 4 – Oct 8)
MATHA43 Course Outcome 1
• Definition of Differential Equation
• Elimination of Arbitrary Constants
• Families of Curves
• Solutions of First-Order Ordinary Differential Equation:
• Separable Differential Equations
MATHA43 Course Outcome 2
• Homogeneous Differential Equations
• Linear Differential Equations
• Exact Differential Equations
MATHA43 Differential Equations
michelangelo.sucaldito@gsfe.tupcavite.edu.ph
05/10/2021 1
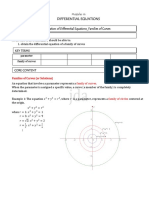
Families of Curves
An equation involving a parameter, as well as one or both of the
coordinates of a point in a plane, may represent a family of curves,
one curve corresponding to each value of the parameter. For instance,
the equation
2 2
𝑥−𝑐 + 𝑦−𝑐 = 2𝑐 2
or
𝑥 2 + 𝑦 2 − 2𝑐 𝑥 + 𝑦 = 0
may be interpreted as the equation of a family of circles, each having
its center on the line 𝑦 = 𝑥 and each passing through the origin.
MATHA43 Differential Equations
michelangelo.sucaldito@gsfe.tupcavite.edu.ph
05/10/2021 2
In each exercise, obtain the differential equation of 2. Straight lines with algebraic sum of the intercepts fixed
the family of plane curves described. as k.
1. Straight lines through the origin.
MATHA43 Differential Equations
michelangelo.sucaldito@gsfe.tupcavite.edu.ph
05/10/2021 3
MATHA43 Differential Equations
michelangelo.sucaldito@gsfe.tupcavite.edu.ph
05/10/2021 4
3. Circles with center on the x-axis. 4. All circles.
MATHA43 Differential Equations
michelangelo.sucaldito@gsfe.tupcavite.edu.ph
05/10/2021 5
5. Parabolas with vertex on the x-axis, with axis 6. Parabolas with axis parallel to the x-axis and with
parallel to the y-axis, and with distance from focus to distance from vertex to focus fixed as 𝑎.
vertex fixed as 𝑎.
MATHA43 Differential Equations
michelangelo.sucaldito@gsfe.tupcavite.edu.ph
05/10/2021 6
You might also like
- Schemes For Partial Differential EquationsDocument453 pagesSchemes For Partial Differential Equationsgabo2008100% (3)
- Maths - 2B Imp QuestionsDocument93 pagesMaths - 2B Imp QuestionsBandaru Chiranjeevi100% (1)
- PreCal ReviewerDocument13 pagesPreCal ReviewerJan Clyde Cortez100% (1)
- Analytical GeometryDocument93 pagesAnalytical GeometryBensonNo ratings yet
- Infinity Optional Mathematics Book 9 Final For CTP 2077Document352 pagesInfinity Optional Mathematics Book 9 Final For CTP 2077Aakriti PoudelNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument280 pagesUntitledmanju kumariNo ratings yet
- SPM AddMath IntegrationDocument21 pagesSPM AddMath IntegrationLeneNo ratings yet
- Definition of Differential Equations Elimination of Arbitrary ConstantsDocument5 pagesDefinition of Differential Equations Elimination of Arbitrary ConstantsdimarananxyzNo ratings yet
- Elimination of Arbitrary ConstantsDocument5 pagesElimination of Arbitrary ConstantsdimarananxyzNo ratings yet
- Orthogonal TrajectoriesDocument14 pagesOrthogonal TrajectoriesSalvador TiñoNo ratings yet
- MELC's: Identify What Is Being Asked (Knowledge /skill/ Process/ Understanding)Document18 pagesMELC's: Identify What Is Being Asked (Knowledge /skill/ Process/ Understanding)Marife Faustino GanNo ratings yet
- Fedosov Quantization of Fractional Lagrange Spaces: Dumitru BaleanuDocument14 pagesFedosov Quantization of Fractional Lagrange Spaces: Dumitru BaleanuvahidNo ratings yet
- Nueva Vizcaya State UniversityDocument5 pagesNueva Vizcaya State UniversityAndrea Rabago AlejandrinoNo ratings yet
- Date: May 17, 2024. Key Words and Phrases. Plane Branch, Approximate Roots, Moduli, K Ahler DifferDocument52 pagesDate: May 17, 2024. Key Words and Phrases. Plane Branch, Approximate Roots, Moduli, K Ahler DifferreubleNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - 2Document18 pagesModule 2 - 2Jr BagaporoNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Module 2: Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs) Unpacking The MelcsDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education: Module 2: Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs) Unpacking The MelcsJhun MarkNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Quadratic Equations and InequalitiesDocument49 pagesModule 1 Quadratic Equations and InequalitiesKatherine Joy CruzNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Concept of Analytic GeometryDocument28 pagesFundamental Concept of Analytic Geometryzyna elilahNo ratings yet
- LC Math 8 1ST - 4THDocument4 pagesLC Math 8 1ST - 4THkaren takasaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Math Unit 5 10-2012Document11 pagesGrade 8 Math Unit 5 10-2012Luth AmmarNo ratings yet
- Deleted Part of Class 11-MathsDocument3 pagesDeleted Part of Class 11-MathssidrxshrafNo ratings yet
- 1708 03298 PDFDocument52 pages1708 03298 PDFseplacajenneNo ratings yet
- Precalculus Week 4Document10 pagesPrecalculus Week 4Kim Paulene ElepNo ratings yet
- 2023 DLL Mathematics 7 Q1 W 1Document6 pages2023 DLL Mathematics 7 Q1 W 1JOLITA INWAY LISBOGNo ratings yet
- MTHN31E - Topic 2.2 - Families of CurvesDocument8 pagesMTHN31E - Topic 2.2 - Families of CurvesAndreaNo ratings yet
- Q1 Week 8 9 SLK 4Document30 pagesQ1 Week 8 9 SLK 4Aileen Joyce EscasinasNo ratings yet
- Review For Final ExamDocument2 pagesReview For Final Exammagical_trevorNo ratings yet
- 1) Linearization and Iteration: Contributions by B. Kirby, R. Bhaskaran, and S. SantanaDocument2 pages1) Linearization and Iteration: Contributions by B. Kirby, R. Bhaskaran, and S. SantanaCehanNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations: (3.1. Definition and Characteristics of The Roots of A Quadratic Equation)Document8 pagesQuadratic Equations: (3.1. Definition and Characteristics of The Roots of A Quadratic Equation)Sally ManyongahNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Illustrating System of Linear Equations in Two Variables - M8AL-Ih-1Document11 pagesMathematics: Illustrating System of Linear Equations in Two Variables - M8AL-Ih-1ROMEO JR RAMIREZNo ratings yet
- Math 8 3rd Quarter SubtasksDocument2 pagesMath 8 3rd Quarter SubtasksHoneylyn TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Towards Natural and Realistic E Guts in F-Theory: Prepared For Submission To JhepDocument52 pagesTowards Natural and Realistic E Guts in F-Theory: Prepared For Submission To Jheputam555No ratings yet
- MATH 270 Master SyllabusDocument2 pagesMATH 270 Master SyllabusmariolabestiaNo ratings yet
- ELECTIVE-MATHEMATICS-10-Module-2-Equation-of-Parabola Part 2Document17 pagesELECTIVE-MATHEMATICS-10-Module-2-Equation-of-Parabola Part 2FVERON, JESSICA FABELLORENo ratings yet
- Math 376 Prealgebra Textbook: Department of Mathematics College of The Redwoods June 23, 2010Document32 pagesMath 376 Prealgebra Textbook: Department of Mathematics College of The Redwoods June 23, 2010ismael63322No ratings yet
- What Are Differential Equations A Review of Curve FamiliesDocument5 pagesWhat Are Differential Equations A Review of Curve FamiliesBenjhon S. ElarcosaNo ratings yet
- Bernstein-Sato Polynomials in Commutative AlgebraDocument64 pagesBernstein-Sato Polynomials in Commutative AlgebraTudor MicuNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Solving System of Linear EquationsDocument14 pages1.4 Solving System of Linear EquationselshourbagynadaNo ratings yet
- Pauli Matrices - WikipediaDocument9 pagesPauli Matrices - WikipediaAdefope OwojoriNo ratings yet
- 62f896029b19ea001261ce5f-1660465185-Math 8 - Q2W1Document15 pages62f896029b19ea001261ce5f-1660465185-Math 8 - Q2W1Elmer HabloNo ratings yet
- Reasoning With Equations Inequalities Unit MapDocument2 pagesReasoning With Equations Inequalities Unit Mapapi-343090158No ratings yet
- Rmya Math8Document27 pagesRmya Math8John Ashley FernandezNo ratings yet
- Date Key Words and PhrasesDocument17 pagesDate Key Words and Phrasesrhab13No ratings yet
- Pre Calc Q1 W2Document15 pagesPre Calc Q1 W2Hamza MinongNo ratings yet
- First Quarter Assessment: Ax by C y MX B X yDocument4 pagesFirst Quarter Assessment: Ax by C y MX B X yNino WangiwangNo ratings yet
- Module 1.3-1.5 Lecture Video NotesDocument11 pagesModule 1.3-1.5 Lecture Video NotesCyam DashNo ratings yet
- Budget of WorkDocument7 pagesBudget of WorkPatrick Dag-um MacalolotNo ratings yet
- 2023 Y8 Core AT2 NotificationDocument2 pages2023 Y8 Core AT2 NotificationCamloc LuNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 Analytic GeometryDocument14 pagesMODULE 2 Analytic Geometrysimonjohn spanglerNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document1 pageProblem Set 1soft dumplingNo ratings yet
- AIAA ASM2009 UQ StochExp PDFDocument20 pagesAIAA ASM2009 UQ StochExp PDFAlfredo Gonzalez SoteloNo ratings yet
- 2nd QTR Week 1 Module 3 Linear Equations in Two Variables (Part 1)Document12 pages2nd QTR Week 1 Module 3 Linear Equations in Two Variables (Part 1)Erwin dela PuntaNo ratings yet
- Higher-Order Beta-Functions in The Standard ModelDocument8 pagesHigher-Order Beta-Functions in The Standard Modelespirituapril19No ratings yet
- Quarter 3 - Week 1Document5 pagesQuarter 3 - Week 1Valein PrincenaNo ratings yet
- ADVANCED ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS FOR CpEDocument1 pageADVANCED ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS FOR CpEJeff LaycoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: George L. Ekol, BSC, MSCDocument67 pagesMathematics: George L. Ekol, BSC, MSCMohamed AbdiNo ratings yet
- Fractional Splines and WaveletsDocument26 pagesFractional Splines and WaveletsAbidNo ratings yet
- MathsylDocument3 pagesMathsylDionne TheirinNo ratings yet
- 25HomeworkSolutions 1 PDFDocument7 pages25HomeworkSolutions 1 PDFLordje Divine EmotinNo ratings yet
- Fractional Sobolev Inequalities - Symmetrization Isoperimetry and InterpolationDocument114 pagesFractional Sobolev Inequalities - Symmetrization Isoperimetry and InterpolationMohamedBouguechaNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Applications of First Order ODE-Orthogonal Trajectories-TthDocument16 pagesModule 7 Applications of First Order ODE-Orthogonal Trajectories-Tthgreg hansNo ratings yet
- LG 4.4.1Document6 pagesLG 4.4.1autumn leavsNo ratings yet
- Systems of Linear Equations: A System of Equations Unit 8 Grade Math Ji Seon LeeDocument5 pagesSystems of Linear Equations: A System of Equations Unit 8 Grade Math Ji Seon Leeapi-501006705No ratings yet
- Troc HoidDocument25 pagesTroc HoidksdndknNo ratings yet
- Differential Geometry M Usman HamidDocument125 pagesDifferential Geometry M Usman HamidKalaiNo ratings yet
- Radius of CurvatureDocument11 pagesRadius of CurvatureLakshayNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument19 pagesMathsShubham SharmaNo ratings yet
- TANGENTSDocument26 pagesTANGENTSSrikanth SriNo ratings yet
- Birational Geometry of Generalized Hessenberg Varieties and The Generalized Shareshian-Wachs ConjectureDocument35 pagesBirational Geometry of Generalized Hessenberg Varieties and The Generalized Shareshian-Wachs ConjectureFarhan RasheedNo ratings yet
- Graphing Rational Functions 2Document4 pagesGraphing Rational Functions 2scribd-in-actionNo ratings yet
- Discriminant Math MazeDocument2 pagesDiscriminant Math MazeAron Paul San MiguelNo ratings yet
- MBD J StraukaiteDocument69 pagesMBD J StraukaiteKornelija RutkauskaiteNo ratings yet
- E Books SpringerDocument2,186 pagesE Books SpringerCésarArias0% (1)
- 2.1. Representation of Curves: Geometric ModelingDocument88 pages2.1. Representation of Curves: Geometric ModelingSrinith KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document25 pagesUnit 3cooooool1927No ratings yet
- B Spline C ImplementationDocument24 pagesB Spline C ImplementationSnehalNo ratings yet
- Co OrdinateDocument37 pagesCo OrdinateVincent VetterNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Practice TestDocument2 pagesUnit 4 Practice Testmelannie caballeroNo ratings yet
- Bézier Curves: Step by Step SolutionDocument4 pagesBézier Curves: Step by Step Solutionswathy reghuNo ratings yet
- Hyperbola Example ProblemsDocument3 pagesHyperbola Example ProblemsDevine Grace A. MaghinayNo ratings yet
- NCERT-Books-for-class 11-Maths-Hindi-Medium-Chapter 11Document33 pagesNCERT-Books-for-class 11-Maths-Hindi-Medium-Chapter 11busuuuNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing II (Conic Sections) Updated Feg 214Document52 pagesEngineering Drawing II (Conic Sections) Updated Feg 214harryrobertson8955No ratings yet
- Circle TangentsDocument8 pagesCircle TangentsdolfusNo ratings yet
- Toán NG D NG - Nhóm MATH - Week 1Document2 pagesToán NG D NG - Nhóm MATH - Week 1Uyển Nhi Lê ĐoànNo ratings yet
- Hyperbola (Conic Sections)Document14 pagesHyperbola (Conic Sections)Ann CandidoNo ratings yet
- Co-Ordinate Geometry PDFDocument39 pagesCo-Ordinate Geometry PDFshyamNo ratings yet
- A Scrapbook of Complex Curves H. ClemensDocument196 pagesA Scrapbook of Complex Curves H. ClemensArmando Treibich KohnNo ratings yet
- Marawi National High School: Pre - Calculus First Semester, S.Y. 2022-2023Document3 pagesMarawi National High School: Pre - Calculus First Semester, S.Y. 2022-2023Jessa May MarcosNo ratings yet
- Assignment AdvanceDocument27 pagesAssignment AdvanceUng Hui WengNo ratings yet