Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Definition of Differential Equations Elimination of Arbitrary Constants
Uploaded by
dimarananxyz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views5 pagesThis document outlines the course content and objectives for Academic Week 2 of MATHA43 Differential Equations. It includes defining differential equations, eliminating arbitrary constants, families of curves, and solving first-order ordinary differential equations using separable, homogeneous, linear, and exact differential equations. Examples are provided of determining if equations are ordinary or partial, linear or nonlinear, and identifying their order and degree. Key topics covered are the construction of mathematical models, definitions of order and degree of a differential equation, and classifying examples of different types of differential equations.
Original Description:
Original Title
Definition of Differential Equations; Elimination of Arbitrary Constants
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines the course content and objectives for Academic Week 2 of MATHA43 Differential Equations. It includes defining differential equations, eliminating arbitrary constants, families of curves, and solving first-order ordinary differential equations using separable, homogeneous, linear, and exact differential equations. Examples are provided of determining if equations are ordinary or partial, linear or nonlinear, and identifying their order and degree. Key topics covered are the construction of mathematical models, definitions of order and degree of a differential equation, and classifying examples of different types of differential equations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views5 pagesDefinition of Differential Equations Elimination of Arbitrary Constants
Uploaded by
dimarananxyzThis document outlines the course content and objectives for Academic Week 2 of MATHA43 Differential Equations. It includes defining differential equations, eliminating arbitrary constants, families of curves, and solving first-order ordinary differential equations using separable, homogeneous, linear, and exact differential equations. Examples are provided of determining if equations are ordinary or partial, linear or nonlinear, and identifying their order and degree. Key topics covered are the construction of mathematical models, definitions of order and degree of a differential equation, and classifying examples of different types of differential equations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
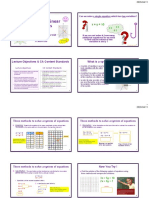
Academic Week 2: (Sept 27 – Oct 1)
MATHA43 Course Outcome 1
• Definition of Differential Equation
• Elimination of Arbitrary Constants
• Families of Curves
• Solutions of First-Order Ordinary Differential Equation:
• Separable Differential Equations
MATHA43 Course Outcome 2
• Homogeneous Differential Equations
• Linear Differential Equations
• Exact Differential Equations
MATHA43 Differential Equations
michelangelo.sucaldito@gsfe.tupcavite.edu.ph
27/09/2021 1
Definition of Differential Equations
The construction of mathematical models to approximate real-world
problems has been one of the most important aspects of the
theoretical development of each of the branches of science. It is often
the case that these mathematical models involve an equation in
which a function and its derivatives play important roles. Such
equations are called differential equations. In a differential equation,
a derivative may be involved implicitly through the presence of
differentials.
Order – the highest-ordered derivative appearing in the equation.
Degree – the power of highest-ordered derivative.
MATHA43 Differential Equations
michelangelo.sucaldito@gsfe.tupcavite.edu.ph
27/09/2021 2
For each of the following, state whether the
equation is ordinary or partial, linear or nonlinear,
its order and degree.
𝑑2𝑥
1. 𝑑𝑡 2 + 𝑘 2 𝑥 = 0
2. 𝑥 2 + 𝑦 2 𝑑𝑥 + 2𝑥𝑦𝑑𝑦 = 0
3. 𝑦 ′′′ − 3𝑦 ′ + 2𝑦 = 0
2 2 2
4. 𝜕 𝑢 + 𝜕 𝑢 + 𝜕 𝑢 = 0
𝜕𝑥 2 𝜕𝑦 2 𝜕𝑧 2
MATHA43 Differential Equations
michelangelo.sucaldito@gsfe.tupcavite.edu.ph
27/09/2021 3
For each of the following, state whether the
equation is ordinary or partial, linear or nonlinear,
its order and degree.
𝑑2𝑦 𝑑2𝑥
5. 𝑥 𝑑𝑡 2 − 𝑦 𝑑𝑡 2 = 𝑐1
6. 𝑥 + 𝑦 𝑑𝑥 + 3𝑥 2 − 1 𝑑𝑦 = 0
2 4
𝑑3𝑤 𝑑𝑤
7. −2 + 𝑦𝑤 = 0
𝑑𝑥 3 𝑑𝑥
8. 𝑦 ′′ + 2𝑦 ′ − 8𝑦 = 𝑥 2 + cos 𝑥
MATHA43 Differential Equations
michelangelo.sucaldito@gsfe.tupcavite.edu.ph
27/09/2021 4
For each of the following, state whether the
equation is ordinary or partial, linear or nonlinear,
its order and degree.
𝜕2𝑤 𝜕 2𝑤
9. 𝜕𝑡 2 = 𝑎2 𝜕 2 𝑥
10. 𝑦 ′ + 𝑃 𝑥 𝑦 = 𝑄(𝑥)
11. 𝑦𝑦 = 𝑥
′′
𝑑𝑖
12. 𝐿 + 𝑅𝑖 = 𝐸
𝑑𝑡
MATHA43 Differential Equations
michelangelo.sucaldito@gsfe.tupcavite.edu.ph
27/09/2021 5
You might also like
- Elimination of Arbitrary ConstantsDocument5 pagesElimination of Arbitrary ConstantsdimarananxyzNo ratings yet
- CO1 (3) Families of CurvesDocument6 pagesCO1 (3) Families of CurvesdimarananxyzNo ratings yet
- Math 8 LN 2 Linear Inequalities in Two VariablesDocument10 pagesMath 8 LN 2 Linear Inequalities in Two VariablesDwight Gabriel GasesNo ratings yet
- Guide 10 - Systems of Equations PR23 MCDocument28 pagesGuide 10 - Systems of Equations PR23 MCLucyNo ratings yet
- DLP-8 (Week 1 DAY 2)Document5 pagesDLP-8 (Week 1 DAY 2)JESSA CANOPINNo ratings yet
- 10th Grade Math Lesso File 5 (With Exercizes)Document4 pages10th Grade Math Lesso File 5 (With Exercizes)Andrés CuadraNo ratings yet
- MEEN 630: Advanced Engineering Mathematics: 24 AUGUST 2021Document70 pagesMEEN 630: Advanced Engineering Mathematics: 24 AUGUST 2021Mohd kaleemullahNo ratings yet
- Updated Course Material 5 in Math 2 For 2nd Semester 2021 2022 For DistributionDocument14 pagesUpdated Course Material 5 in Math 2 For 2nd Semester 2021 2022 For DistributionJhenny MTNo ratings yet
- De Module 1 2022 2023 Differential Equation 1Document14 pagesDe Module 1 2022 2023 Differential Equation 1Roxanne PagaduanNo ratings yet
- Week 1genmath Mrs. CiprianoDocument11 pagesWeek 1genmath Mrs. CiprianoSamNo ratings yet
- 62f896029b19ea001261ce5f-1660465185-Math 8 - Q2W1Document15 pages62f896029b19ea001261ce5f-1660465185-Math 8 - Q2W1Elmer HabloNo ratings yet
- MODULE 3 - Data ManagementDocument24 pagesMODULE 3 - Data ManagementROMEL RIMANDO0% (1)
- Basic Calculus: Implicit DifferentiationDocument13 pagesBasic Calculus: Implicit Differentiationgarry100% (1)
- Q2 Remquirements Letter FinalDocument6 pagesQ2 Remquirements Letter FinalNaomi EllaNo ratings yet
- Module 3.6 - TranslationDocument3 pagesModule 3.6 - TranslationsacerezoNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Measures of VariabilityDocument9 pagesModule 4 Measures of VariabilityNiema Tejano FloroNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations Module 2023 2024Document16 pagesDifferential Equations Module 2023 2024Kelly FajardoNo ratings yet
- Grade8-Graphing System of Linear Equations in Two VariablesDocument4 pagesGrade8-Graphing System of Linear Equations in Two VariablesKim Lambert CaubalejoNo ratings yet
- Study Guide - 2 - Math 102-DC-dianne OliverDocument5 pagesStudy Guide - 2 - Math 102-DC-dianne OliverDianne C. OliverNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 11Document40 pagesLecture No 11Wra ArirmiwniNo ratings yet
- v2 SLG-M2-4.1.1 Definition and Types of Systems of Linear Equations in Two VDocument6 pagesv2 SLG-M2-4.1.1 Definition and Types of Systems of Linear Equations in Two VZoey DutcheeNo ratings yet
- BCSLHT Release4Document12 pagesBCSLHT Release4Elixa FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Third Quarter Las in Intermediate AlgebraDocument62 pagesThird Quarter Las in Intermediate AlgebraKean CardenasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.6Document15 pagesLesson 1.6Aliph HamzahNo ratings yet
- Systems of Linear Equations: A System of Equations Unit 8 Grade Math Ji Seon LeeDocument5 pagesSystems of Linear Equations: A System of Equations Unit 8 Grade Math Ji Seon Leeapi-501006705No ratings yet
- Differential Equation (De 221) : Davao Del Sur State College Mati, Digos City Final ExamDocument12 pagesDifferential Equation (De 221) : Davao Del Sur State College Mati, Digos City Final ExamRuthie Ann Namoc MagdadaroNo ratings yet
- Module2-Measures of LocationDocument11 pagesModule2-Measures of LocationRACHEL NAVARRONo ratings yet
- II Sem-Module 5-Numerical Methods-II-NotesDocument26 pagesII Sem-Module 5-Numerical Methods-II-NotesHarsha MayankNo ratings yet
- TG-Basic Cal Q3 W25Document6 pagesTG-Basic Cal Q3 W25JohnNo ratings yet
- MATH 208 Differential EquationsDocument11 pagesMATH 208 Differential EquationscharlesNo ratings yet
- Mte 482 Final Project - First StepsDocument13 pagesMte 482 Final Project - First Stepsapi-532488404No ratings yet
- IM4 CALCULUS-ModuleDocument18 pagesIM4 CALCULUS-ModuleDarryl Kane CulambotNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document17 pagesModule 3leyn sanburgNo ratings yet
- Signed Learning Material No. 4C Data ManagementDocument12 pagesSigned Learning Material No. 4C Data ManagementAira Mae Quinones OrendainNo ratings yet
- BSEd MATH 3A COLAO EVELYN DLPDocument7 pagesBSEd MATH 3A COLAO EVELYN DLPCOLAO, EVELYNNo ratings yet
- 01 - DE - Definition and ClassificationDocument3 pages01 - DE - Definition and ClassificationCome on think PacleNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1.1Document4 pagesLecture 1.1Karen DarilaNo ratings yet
- A Stat and Probab 11 q3w2.3 Teacher Copy Final LayoutDocument16 pagesA Stat and Probab 11 q3w2.3 Teacher Copy Final LayoutlumenvirzkieNo ratings yet
- PreCalcQ1W2 - 02 ASDocument11 pagesPreCalcQ1W2 - 02 ASJake AblaoNo ratings yet
- Holy Trinity High School: Self-Paced Learning Module in Mathematics 10Document6 pagesHoly Trinity High School: Self-Paced Learning Module in Mathematics 10Art Vincent Abenes AntiquinaNo ratings yet
- LAS 5 Statistics and ProbabilityDocument7 pagesLAS 5 Statistics and Probabilitychad lowe villarroyaNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 1 - Definition and Classifications of Differential EquationsDocument3 pagesLECTURE 1 - Definition and Classifications of Differential EquationsCamille SalmasanNo ratings yet
- Module in Mathematics 8Document7 pagesModule in Mathematics 8HaxProductions 6996No ratings yet
- Grade 11 Functions Unit 2 - Equivalent Algebraic Expressions Student NotesDocument15 pagesGrade 11 Functions Unit 2 - Equivalent Algebraic Expressions Student NotesȺȺNo ratings yet
- MATH-8 Q2 Mod3Document17 pagesMATH-8 Q2 Mod3Joshua BaluyotNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 - COE - 108 Post TestDocument8 pagesMODULE 2 - COE - 108 Post TestAslyn MagallanesNo ratings yet
- 2 ND QModule#1Document1 page2 ND QModule#1JohnNo ratings yet
- ODE1Document108 pagesODE1Yonas D. EbrenNo ratings yet
- GM Week 2 MELC 6Document18 pagesGM Week 2 MELC 6kierashleerafalloNo ratings yet
- Math Plus Ulo-2Document30 pagesMath Plus Ulo-2Azialee YingNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Quadratic Equations and InequalitiesDocument49 pagesModule 1 Quadratic Equations and InequalitiesKatherine Joy CruzNo ratings yet
- (Q) MCV4U Chapter 1-3 SummativeDocument4 pages(Q) MCV4U Chapter 1-3 SummativelaureniscapuletNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Problems Involving Systems of Linear Inequalities in Two VariablesDocument10 pagesMathematics: Problems Involving Systems of Linear Inequalities in Two VariablesisipMath Tutorial FilesNo ratings yet
- Matrix Operations: Presented BY Mrs Djankou PriscilleDocument13 pagesMatrix Operations: Presented BY Mrs Djankou PriscilleEnabewhkom OhpmNo ratings yet
- Perturbation MethodDocument27 pagesPerturbation MethodBillyawanNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors: Bachelor of ScienceDocument18 pagesAn Introduction To Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors: Bachelor of ScienceUjjal Kumar NandaNo ratings yet
- Math Las - q2-w1Document10 pagesMath Las - q2-w1jam ananggoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Differential Equations: Module No. 1Document15 pagesIntroduction To Differential Equations: Module No. 1Dave Mhelvin SalvadorNo ratings yet
- IntroDocument8 pagesIntroZen MarkNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine EngineDocument44 pagesGas Turbine EngineManas BatraNo ratings yet
- Bio FermentationDocument8 pagesBio FermentationCecil ClaveriaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus in Invertebrate ZoologyDocument11 pagesSyllabus in Invertebrate ZoologyAnonymous lKxkZ9MNo ratings yet
- Geostationary & Polar-Orbiting SatellitesDocument83 pagesGeostationary & Polar-Orbiting SatellitesAngelie LapeNo ratings yet
- Marketing I - Price ListDocument3 pagesMarketing I - Price ListthimotiusNo ratings yet
- Codigos Obd RENAULTDocument1 pageCodigos Obd RENAULTedsononoharaNo ratings yet
- Hazards and Risks in AviationDocument40 pagesHazards and Risks in AviationAzeemNo ratings yet
- Lincoln 180HD Users PDFDocument96 pagesLincoln 180HD Users PDFratpacNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Brake - SynopsisDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic Brake - SynopsisShubham Ahire100% (1)
- Allengers 150-R Users ManualDocument14 pagesAllengers 150-R Users ManualMarlon DeteraNo ratings yet
- ABB Power Transformer PDFDocument112 pagesABB Power Transformer PDFsudeep karunNo ratings yet
- Clarinet Yamaha ManualDocument14 pagesClarinet Yamaha ManualMarcoNo ratings yet
- 28 27 - Bell - Gossett - HistoricalDocument7 pages28 27 - Bell - Gossett - HistoricalthepimpoNo ratings yet
- Year 4 5 6 SimilesDocument5 pagesYear 4 5 6 SimilesRachel FaizatulNo ratings yet
- Medical Device Risk Management - IsO 14971Document86 pagesMedical Device Risk Management - IsO 14971novdic71% (7)
- Protocol No: Laboratory ReportDocument1 pageProtocol No: Laboratory ReportДимић УрошNo ratings yet
- HW 4Document5 pagesHW 4dzs6w3No ratings yet
- The Princess and The FrogDocument5 pagesThe Princess and The FrogJariyah NurjanahNo ratings yet
- Transport of Carbon DioxideDocument9 pagesTransport of Carbon DioxideBarkat ShazliNo ratings yet
- Manual PainpenDocument2 pagesManual PainpenElson GomesNo ratings yet
- Promax ReferenceDocument32 pagesPromax ReferenceSiti Nuraisyah100% (1)
- Pediatrics: Rheumatology Will Roll Up To Pediatrics: General Pediatrics: Urology Will Roll Up To UrologyDocument47 pagesPediatrics: Rheumatology Will Roll Up To Pediatrics: General Pediatrics: Urology Will Roll Up To UrologydasbosiNo ratings yet
- The Yearof Zayed 2018Document462 pagesThe Yearof Zayed 2018robin lakisNo ratings yet
- 25 Drug Interactions QuestionsDocument7 pages25 Drug Interactions Questionssazaki22483% (6)
- Overview - Talha Nibras Ali (62646)Document2 pagesOverview - Talha Nibras Ali (62646)Talha Nibras AliNo ratings yet
- 2021 Summer Season Club Turban Thermal Fac Sheet - EngDocument12 pages2021 Summer Season Club Turban Thermal Fac Sheet - EngPENA LAURANo ratings yet
- CBR Correlations With MRDocument1 pageCBR Correlations With MRdavidduranrodasNo ratings yet
- The Role of Intratympanic Dexamethasone in Sudden Sensorineural Hearing LossDocument5 pagesThe Role of Intratympanic Dexamethasone in Sudden Sensorineural Hearing LossAditya HendraNo ratings yet
- DirectionalDocument4 pagesDirectionalHimdad Tahir100% (2)