Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Carbohydrates
Uploaded by
Wen CenaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Carbohydrates
Uploaded by
Wen CenaCopyright:
Available Formats
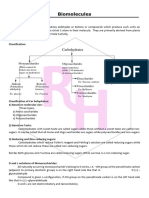
BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES
SYNTHESIS AND HYDROLYSIS OF POLYMERS
- most important biological compounds are polymers
Poly means “many”
Polymers
- A many piece chain of subunits
- Subunits are; sugars, amino-acids, nucleotides, or fatty acids.
- These are made (synthesized) or broken down (Hydrolysis) over and
over in living cells
Small molecules
(monamers, or building
blocks)
-sugars, amino
acids, etc.
H2O
H2O (a water
(one molecule of molecule
water is added results from
for each linkage each
broken) linkage)
Polymers
- protein, carbohydrates,
etc
TYPES OF POLYMERS
Proteins: Polymers of amino acids
Nucleic acids (DNA, RNA): Polymers of nucleotides
Carbohydrates: Polymers of sugars
Lipids: Polymers of fatty acids and glycerol
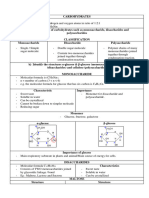
CARBOHYDRATES
- Empirical formula CnH2nOn AKA (CH20)n
- A repeating chain of sugars (saccharides)
- polysaccharides - many saccharides linked together
Glucose - a basic sugar (C6 H12 O6)
Has a ring structure
OH
H-C-H
C O
H H
C C
OH
OH
C C
OH H H OH
This is a mono (one) saccharide
- others include fructose, ribose, deoxyribose, etc.
Disaccharide - two sugars joined together
Dehydrolysis (H2O is lost)
a C-O-C bond forms
Examples of disaccharides:
- maltose (two glucoses)
- sucrose (a glucose and fructose)
- lactose (a glucose and galactose)
To break the bond between two sugars, a H2O is needed (Hydrolysis)
The Main Functions of Carbohydrates are:
Energy: Bonds between Carbon atoms can be broken, the Hydrogen
atoms stripped off and the energy released can be used by cells
Structural: Cellulose is the major structural compound in plants
- used in the cell wall
Three Important Polysaccharides:
I) Starch: - The main storage form of sugar in plants
- few side chains
- many glucose molecules linked together
II) Glycogen - Main sugar storage in animals
- Many side chains
- linked as for starch
III) Cellulose - structural (cell walls)
- long chains (wound together)
- linkage between C atoms of adjacent chains sugars is different
than I and II above
- no mammal can break this bond
You might also like
- CarbohydrateDocument26 pagesCarbohydratemuhammad furqanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Molecules of LifeDocument67 pagesChapter 2 Molecules of LifeNatalie GraceNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules: Module - 7Document18 pagesBiomolecules: Module - 7Alvin Pabores100% (1)
- L31 PDFDocument33 pagesL31 PDFadane aynalemNo ratings yet
- Sbi4u1 - BiochemistryDocument60 pagesSbi4u1 - BiochemistryRory Collins-GreenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Molecules of LifeDocument68 pagesChapter 2 Molecules of LifeMohd Abdul azizNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates, Lipids & Nucleic Acids:: Forms Chain Like Molecules-PolymersDocument8 pagesCarbohydrates, Lipids & Nucleic Acids:: Forms Chain Like Molecules-PolymersJojo LouNo ratings yet
- Cape Biology Unit 1 SpeedrunDocument178 pagesCape Biology Unit 1 SpeedrunBrado BradoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: The Chemical Building Blocks of Life: Enantiomers . These Are Mirror Images of Each Other. MirroredDocument17 pagesChapter 3: The Chemical Building Blocks of Life: Enantiomers . These Are Mirror Images of Each Other. Mirroredapi-524244445No ratings yet
- Biological MoleculesDocument8 pagesBiological MoleculesQaran PrintingNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument4 pagesCarbohydratesJovan SernaNo ratings yet
- Biological MoleculesDocument43 pagesBiological MoleculesRS JNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates and GlycobiologyDocument21 pagesCarbohydrates and GlycobiologyjaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules NotesDocument4 pagesBiomolecules Notesalex caitlinNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument14 pagesBio MoleculessvjbxgjNo ratings yet
- Carbon-Based Molecules: Carbon Atoms Have Unique Bonding PropertiesDocument5 pagesCarbon-Based Molecules: Carbon Atoms Have Unique Bonding PropertiesajisafeNo ratings yet
- 3-Bch202 Carbohydrates ModifiedDocument67 pages3-Bch202 Carbohydrates Modifiedccc67 ghNo ratings yet
- Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry: Fourth EditionDocument137 pagesLehninger Principles of Biochemistry: Fourth Editionruaa mhmad100% (1)
- Biological ElementsDocument16 pagesBiological Elementsmarwaaishah01No ratings yet
- Sbi4u1 - BiochemistryDocument61 pagesSbi4u1 - Biochemistryalathena alathenaNo ratings yet
- Module 9Document29 pagesModule 9Andrew Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules (Bio-Molecules)Document28 pagesBiological Molecules (Bio-Molecules)Bibek YadavNo ratings yet
- Life Substances: The BiomoleculesDocument97 pagesLife Substances: The BiomoleculesMark Eleazar DuclayanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 BiomoleculesDocument65 pagesChapter 6 BiomoleculesT MokshithaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules: Module - 7Document26 pagesBiomolecules: Module - 7TeachingTrainingCoaching KnowledgeSharingSessionNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument53 pagesCarbohydratesFrance Jan First SaplacoNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules - 054325Document18 pagesBiomolecules - 054325Baninla NerusNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - CarbohydratesDocument91 pagesLecture 3 - CarbohydratesAsyraf Arshat0% (1)
- 12 - Chemistry - Notes - ch14 - Biomolecules (2) Word FormDocument12 pages12 - Chemistry - Notes - ch14 - Biomolecules (2) Word FormSurekha raoNo ratings yet
- 1.2 CarbohydrateDocument3 pages1.2 Carbohydrate2023820042No ratings yet
- Unit 2 - 1Document35 pagesUnit 2 - 1Sunita SharmaNo ratings yet
- SugarsDocument4 pagesSugarschristina leonNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates and Amino Acids Polymers-01-TheoryDocument36 pagesCarbohydrates and Amino Acids Polymers-01-TheoryRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- AS Unit 1: Basic Biology and Cell Organisation 1.1 Syllabus Objectives AssessedDocument26 pagesAS Unit 1: Basic Biology and Cell Organisation 1.1 Syllabus Objectives AssessedZoé LennonNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument29 pagesCarbohydratesMilena De CresentNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Biological MacromoleculesDocument32 pagesChapter 3 Biological MacromoleculeslolaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lesson-1Document18 pagesBiochemistry Lesson-1Priyadarshini LenkaNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULES Plustwo Chemistry HssliveDocument5 pagesBIOMOLECULES Plustwo Chemistry HssliveKunal Goel100% (3)
- BiomoleculesDocument27 pagesBiomoleculesStarsNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Chemistry 2020-1Document99 pagesCarbohydrate Chemistry 2020-1WixHal MalikNo ratings yet
- Saccharide Chemistry FunctionDocument38 pagesSaccharide Chemistry FunctionZarin MesbahNo ratings yet
- Biomolecule, Polymer - POC SHEET PDFDocument52 pagesBiomolecule, Polymer - POC SHEET PDFrajni bhardwajNo ratings yet
- 4.1.1. - Macromolecules and Composition of CellsDocument2 pages4.1.1. - Macromolecules and Composition of CellscarlNo ratings yet
- (CN 112) 1st Exam ReviewerDocument6 pages(CN 112) 1st Exam Reviewermariyvonne01No ratings yet
- 2023 Biological Molecules PPT SF PDFDocument90 pages2023 Biological Molecules PPT SF PDFKaran SingNo ratings yet
- Biological Moleculer: Chemical CompenentDocument53 pagesBiological Moleculer: Chemical CompenentHafidz Jazuli LuthfiNo ratings yet
- BMM LEC 4 SN Structure Function of Carbohydrates & LipidsDocument3 pagesBMM LEC 4 SN Structure Function of Carbohydrates & LipidsSARAH SAFIAH TAJUL ARIFFINNo ratings yet
- 12 Biomolecules 1Document18 pages12 Biomolecules 1keerthigasriitNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Anomeric Carbon. Such Isomers, I.e.Document4 pagesCarbohydrates: Anomeric Carbon. Such Isomers, I.e.Sanju PatelNo ratings yet
- Chap07 PDFDocument35 pagesChap07 PDF錢子傑No ratings yet
- CH 2 Biological MoleculesDocument48 pagesCH 2 Biological Molecules9G11 Aulia KayanaNo ratings yet
- 2 - Molecular BiologyDocument183 pages2 - Molecular BiologyGoran VasićNo ratings yet
- L4 CarbohydratesDocument21 pagesL4 Carbohydrateshaiqalfariq07No ratings yet
- Biochemistry: CarbohydratesDocument40 pagesBiochemistry: CarbohydratesShubham KumarNo ratings yet
- 2 BiomoleculesDocument5 pages2 Biomoleculessofia zhouNo ratings yet
- 2 BiomoleculesDocument5 pages2 BiomoleculesTala AlkhawajaNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY FinalDocument21 pagesBIOCHEMISTRY FinalJoliem Phya E. IdongNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Chemistry: DR Amina Tariq BiochemistryDocument49 pagesCarbohydrate Chemistry: DR Amina Tariq BiochemistrykalloliNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Chemistry of CarbohydratesDocument40 pagesUnit 3 - Chemistry of CarbohydratesClaire GUMAPACNo ratings yet
- A-level Sciences Revision Boxset: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Sciences Revision Boxset: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- My Fair Neighbour - Rabindranath TagoreDocument4 pagesMy Fair Neighbour - Rabindranath TagoreYêu Văn HọcNo ratings yet
- Medullary Nephrocalcinosis With UnderlyingDocument4 pagesMedullary Nephrocalcinosis With UnderlyingahmadwidyatmaNo ratings yet
- Exam EngDocument14 pagesExam EngVK KhannaNo ratings yet
- International Financial Management Abridged 10 Edition: by Jeff MaduraDocument17 pagesInternational Financial Management Abridged 10 Edition: by Jeff MaduraHiếu Nhi TrịnhNo ratings yet
- Sawit-Sumbermas-Sarana TBK Billingual 31 Des 20 Released1617291310Document158 pagesSawit-Sumbermas-Sarana TBK Billingual 31 Des 20 Released1617291310Ade FajarNo ratings yet
- 2014 Artículo RegionalizaciónDocument19 pages2014 Artículo RegionalizaciónVerónica RangelNo ratings yet
- Draft 2 WCPSS 2022-23 Student Enrollment PlanDocument19 pagesDraft 2 WCPSS 2022-23 Student Enrollment PlanKeung HuiNo ratings yet
- Sample Business Directory 20-21Document38 pagesSample Business Directory 20-21Suresh RNo ratings yet
- Condom Size by John GerofiDocument27 pagesCondom Size by John GerofiCondomSize100% (1)
- Bernard Porter - The Freiheit Prosecutions, 1881-1882Document25 pagesBernard Porter - The Freiheit Prosecutions, 1881-1882Nathan GibbonsNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Listening PracticeDocument1 pageUnit 6 Listening PracticeMarta Sampedro GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Thyr Care: The Trust. The TruthDocument27 pagesThyr Care: The Trust. The TruthShadabNo ratings yet
- Paragon CreddsfsaturesDocument4 pagesParagon CreddsfsaturesAppleNo ratings yet
- Azcueta Vs Republic of The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesAzcueta Vs Republic of The PhilippinesEuneun BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Group 5: Topic: Graphical Representation. Submitted To:-Miss - Faryal Submitted ByDocument28 pagesGroup 5: Topic: Graphical Representation. Submitted To:-Miss - Faryal Submitted Bysheraz hussainNo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plan Grade 3Document3 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan Grade 3Joseph NoblezaNo ratings yet
- 2010 Revised Manual of Regulations For Private Schools in Basic Education I. General ProvisionsDocument21 pages2010 Revised Manual of Regulations For Private Schools in Basic Education I. General ProvisionsAnnalyn EndrinalNo ratings yet
- Application: Visitor VisaDocument16 pagesApplication: Visitor VisaKP ZakateNo ratings yet
- Osaki Syllabus ACCT101 Spring2019 Accessible UaDocument5 pagesOsaki Syllabus ACCT101 Spring2019 Accessible UaNardos AmdeNo ratings yet
- p3 ContentsDocument1 pagep3 ContentslesiaNo ratings yet
- D1.05 - Matthew Ibrahim - Isometrics For Tendon Health Gains PDFDocument1 pageD1.05 - Matthew Ibrahim - Isometrics For Tendon Health Gains PDFok okNo ratings yet
- DLP Grade 11 Back Pattern (1) EditedDocument6 pagesDLP Grade 11 Back Pattern (1) EditedMarie Jess MurdenNo ratings yet
- DM00628 QUALITROL QTMS-BM Commissioning ManualDocument26 pagesDM00628 QUALITROL QTMS-BM Commissioning Manualijan jansNo ratings yet
- Gabriel v. Petron Corp Et Al. GR No 19475 DigestDocument2 pagesGabriel v. Petron Corp Et Al. GR No 19475 DigestGeremae MataNo ratings yet
- Choose The Correct Answer:: Fill in With An Indefinite PronounDocument2 pagesChoose The Correct Answer:: Fill in With An Indefinite Pronounsaul enrique silva moncadaNo ratings yet
- Carter EW, Austin D, Trainor AA. (2012) Predictors of Postschool Employment Outcomes For Young Adults With Severe DisabilitiesDocument15 pagesCarter EW, Austin D, Trainor AA. (2012) Predictors of Postschool Employment Outcomes For Young Adults With Severe DisabilitiesTomislav CvrtnjakNo ratings yet
- CenovnikDocument20 pagesCenovnikAleks StojkovNo ratings yet
- 15 & 16. LSCM - Planning and Managing Inventories in A SC - Aggregating Multiple Products in A Single OrderDocument49 pages15 & 16. LSCM - Planning and Managing Inventories in A SC - Aggregating Multiple Products in A Single OrderAKASH RAJNo ratings yet
- Educ 606 Module 2 Early Childhood DevelopmentDocument5 pagesEduc 606 Module 2 Early Childhood DevelopmentLennex Marie Sario100% (1)
- Heirs of Ramon Durano, Sr. vs. UyDocument34 pagesHeirs of Ramon Durano, Sr. vs. Uypoiuytrewq9115No ratings yet