Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Moving Charges and Magnetism
Uploaded by
dhanish942006Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Moving Charges and Magnetism
Uploaded by
dhanish942006Copyright:
Available Formats
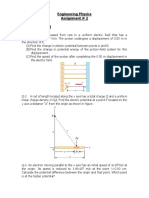
MOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISM
1. A particle of charge q is moving with a velocity 𝑣⃗ through a region, where an electric
field E and a magnetic field B are present. Write an equation for total force on charge.
2. Write the expression for Lorentz force acting on a moving charge.
3. A charged particle enters a uniform magnetic field at an angle of 40o .It’s path becomes ……..
4. (a) An electric charge ‘q’ is moving at right angles to a uniform magnetic field ’B’ with velocity ‘v’ .Write the expression for
the force acting on the charged particle
5. A particle of charge 𝑞 is moving through a uniform magnetic field of intensity B with a velocity v. Write an 0065pression
for the force acting on the particle in vector form.
6. Unit of magnetic field intensity is _________.
(i) joule (ii) tesla (iii) coulomb (iv) none of these
7. The cyclotron is a machine to accelerate particles to high energies.
(i) Draw schematic sketch of the cyclotron.
(ii) Derive an equation for cyclotron frequency.
(iii) Can neutrons be accelerated in a cyclotron ?
8. Cyclotron is a device used to accelerate charged particles.
(a) With a suitable diagram briefly explain the working of a cyclotron and obtain an expression for cyclotron frequency.
(b)A cyclotron oscillator frequency is 10 𝑀𝐻𝑧. What should be the operating magnetic field for accelerating protons?
9. Two charged particles q1 and q2 are moving through a uniform magnetic field (B) as shown in figure :
(a) what is the shape of path of q1 and q2
(b) derive an expression for cyclotron frequency with the help of a neat diagram.
10. What is the radius of the circular path of an electron moving at a speed of 3 x 10 7 m/s in a magnetic field of 6 x 10 -4 T
perpendicular to it?
11. An 𝛼 particle and a proton are moving in a region normal to a uniform magnetic field B. If two particles have equal linear
momenta. What will be the ratio of the radii of their trajectories in the field?
12. State Biot-Savart’s law and express it in the vector form.
13. (a) Using Biot-Savarts law, obtain the expression for the magnetic field due to a
circular loop of radius r carrying a current I at a point on its axis distant 𝑥 from the
centre of the coil.
(b) What is the value of B at the centre ?
14. State Biot - Savart law and express it mathematically.
15. Biot-Savart's law relates current with the magnetic field produced by it.
(a) Write the mathematical expression of the above law in vector form.
(b) Using the law derive an expression for intensity of magnetic field at a point at distance 𝑥 from the centre and on the
axis of a circular current loop.
16. (a) An electric q is moving with a velocity v in the direction of a magnetic field B. The magnetic force acting on the charge
is
𝑞 𝑣
(i) 𝑞𝑣𝐵 (ii) zero (iii) 𝑣𝐵 (iv) 𝑞𝐵
(b) Starting from Biot-Savart law, obtain an expression for the magnetic field at an axial point of a circular coil carrying
current.
17. Using Biot-Savarrt’s law, derive expression for the magnetic field at the centre of a circular coil carrying current.
18. A circular coil of radius R and N turns carries a current I. Show that the intensity of magnetic field at an axial point
𝝁𝟎 𝑵𝑰𝑹𝟐
distant 𝑥 from the centre is 𝑩 = 𝟑/𝟐
𝟐(𝑹𝟐 + 𝑿𝟐 )
19. State Ampere’s circuital law. Use this law to obtain the expression for the magnetic
field inside a current carrying solenoid at an axial point near the centre.
20. Ampere's theorem helps to find the magnetic field in a region around a current carrying c onductor.
a. Write the expression of Ampere's theorem.
b. Draw a graph showing the variation of intensity of magnetic field with the distance from the axis of a current carrying
conductor.
21. (a) State and explain Ampere's Circuital Theorem.
(b) Derive and expression for the magnetic field intensity produced at a point lying
along the axis of a circular coil carrying current
22. Using Ampere's circuital law show that the intensity of magnetic field at an axial point near the centre of a current
carrying solenoid is 𝐵 = 𝜇0 𝑛𝐼.
23. (a)”parallel currents attract, and antiparallel currents repel “. Sate whether this statement is true or false
(b) Define the SI unit of current in terms of force between two current carrying conductors
24. A rectangular loop of area A and carrying a steady current I is placed in a uniform magnetic field.
(a)Derive the expression of torque, 𝜏 = 𝑚 ⃗⃗ , acting on the loop.
⃗⃗⃗ × 𝐵
(b)Increasing the current sensitivity may not necessarily increase the voltage. sensitivity of the a galvanometer. Justify.
25. A magnetised needle in uniform magnetic field experiences a torque but no net force. An iron nail near a bar magnet,
however, experiences a force of attraction in addition to a torque. Why ?
26. An air cored solenoid has 1000 turns per metre and carries a current of 2A. Calculate the magnetic intensity (H).
27. The path of a charged particle entering parallel to uniform magnetic field will be
(a) circular (b) helical (c) straight line (d) None of these
28. (a) An ammeter is a current measuring device which is always connected in……. in an electric circuit
(b) Describe a cyclotron and obtain an expression for cyclotron frequency.
29. With a circuit diagram explain how a moving coil galvanometer can be converted to an ammeter.
Explain the theory and working of a moving coil galvanometer.
You might also like
- TEST 9 CH 4Document3 pagesTEST 9 CH 4kumarvishwaa1No ratings yet
- Test-4 (Complete Electromagnetism)Document3 pagesTest-4 (Complete Electromagnetism)L.ABHISHEK KUMARNo ratings yet
- CBSE Board Problems Magnetic FieldsDocument8 pagesCBSE Board Problems Magnetic FieldsAdhish MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Practice SheetDocument3 pagesPractice Sheetabhinavsingh22012006No ratings yet
- Test-4 (Complete Electromagnetism)Document3 pagesTest-4 (Complete Electromagnetism)L.ABHISHEK KUMARNo ratings yet
- Questions Chap 4 Moving Charges & Magnetism - 77547 - 2023 - 02 - 06 - 22 - 57Document4 pagesQuestions Chap 4 Moving Charges & Magnetism - 77547 - 2023 - 02 - 06 - 22 - 57Ranjith MuralidharanNo ratings yet
- W 1Document3 pagesW 1ypurushothamreddy006No ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Current & Magnetism: Previous Year Board Exam Questions (2007-2016)Document36 pagesMagnetic Effect of Current & Magnetism: Previous Year Board Exam Questions (2007-2016)Rishabh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- MovingChargesMagnetismDocument4 pagesMovingChargesMagnetismSheena RizviNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect Full ChapterDocument17 pagesMagnetic Effect Full ChaptervasanthiNo ratings yet
- SodapdfDocument8 pagesSodapdfsdfbvshbdfNo ratings yet
- XII Q Group 2Document3 pagesXII Q Group 2Sanskriti VermaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Current PROBLEMSDocument8 pagesMagnetic Effect of Current PROBLEMSroyal ghostNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument5 pagesDocumentkartik.dedha27No ratings yet
- Class 12 - HY2 - RevisionDocument6 pagesClass 12 - HY2 - RevisionSam SolomonNo ratings yet
- Problems For Electromagnetic Theory TEE3201Document5 pagesProblems For Electromagnetic Theory TEE3201Taboka SialumbaNo ratings yet
- Test Physics CBSE Class XIIDocument1 pageTest Physics CBSE Class XIIAnanthakrishnan Tinneveli VNo ratings yet
- Imp. Derivation 2023Document10 pagesImp. Derivation 2023Tuhin SamantrayNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of CurrentDocument2 pagesMagnetic Effect of CurrentHarsh JuyalNo ratings yet
- Magnetism (2016-2010) : Shivalik ClassesDocument3 pagesMagnetism (2016-2010) : Shivalik Classesrchandra2473No ratings yet
- Class 12 - HY2 - RevisionDocument6 pagesClass 12 - HY2 - RevisionSam SolomonNo ratings yet
- Aissce Asgnmt CH - 04Document5 pagesAissce Asgnmt CH - 04Arunima SinghNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Module 3Document2 pagesAssignment - Module 3Dr. Pradeep Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ninety - Nine Percent of All Failures Come From The People Who Have The Habit of Making ExcusesDocument7 pagesNinety - Nine Percent of All Failures Come From The People Who Have The Habit of Making ExcusesAryan MurghaiNo ratings yet
- CBSE PHYSICS Exam Derivations and long answer questionsDocument23 pagesCBSE PHYSICS Exam Derivations and long answer questionsAham GtyNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Magnetics Effect of CurrentsDocument31 pagesUnit 3 Magnetics Effect of CurrentsTuition MasterNo ratings yet
- Worksheet For Volume - 1Document3 pagesWorksheet For Volume - 1pranavtsababayagaNo ratings yet
- Important Questions EmtDocument9 pagesImportant Questions EmtDinesh PeterNo ratings yet
- Physics Test - Half Test - I: Topic: - NCERT BOOK-1Document4 pagesPhysics Test - Half Test - I: Topic: - NCERT BOOK-1ChetanNo ratings yet
- REVISION SHEETS GR 12Document13 pagesREVISION SHEETS GR 12itachirao5No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Moving Charges and FieldDocument19 pagesChapter 4 Moving Charges and FieldSANDRONo ratings yet
- 12TH PHYSICS ftDocument10 pages12TH PHYSICS ftABHISHEK PANDANo ratings yet
- Chapter - 04 (Magnetic Effects of Currents)Document3 pagesChapter - 04 (Magnetic Effects of Currents)ghuNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism - Class 12 QuestionsDocument5 pagesMagnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism - Class 12 QuestionsBug LordNo ratings yet
- LAQs - Current Electricity & Magnetic Effect of Electric CurrentDocument6 pagesLAQs - Current Electricity & Magnetic Effect of Electric CurrentLanaNo ratings yet
- RevisionDocument3 pagesRevisionKaifkhanNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-08-16 at 10.04.10 PMDocument5 pagesScreenshot 2022-08-16 at 10.04.10 PMKanak TaldaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 Ncert Practice QuestionsDocument9 pagesChapter-4 Ncert Practice QuestionsRAHIM MDNo ratings yet
- Moving Charges and MagnetismDocument6 pagesMoving Charges and MagnetismKoyal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Assignment#2, Potential, Capacitors, Magnetic Force and FieldDocument5 pagesAssignment#2, Potential, Capacitors, Magnetic Force and FieldBilal KhalidNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Flux and Induction ExplainedDocument22 pagesMagnetic Flux and Induction ExplainedFranko Urcia100% (1)
- Magnetic Effects of Current & MagnetismDocument2 pagesMagnetic Effects of Current & MagnetismHarsh YadavNo ratings yet
- Book 1 Complete Test 2024Document5 pagesBook 1 Complete Test 2024lukkuyadav050No ratings yet
- Magnetic Eff of CurrentDocument18 pagesMagnetic Eff of CurrentR K SharmaNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics U3 Assignmnt1Document3 pages12 Physics U3 Assignmnt1Nikita BansalNo ratings yet
- Physics 3Document6 pagesPhysics 3Aadit “ThePROkiller”No ratings yet
- 21 Magnetic Forces and Magnetics FieldsDocument48 pages21 Magnetic Forces and Magnetics Fieldspxyooj_1100% (2)
- Moving Charges and MagnDocument7 pagesMoving Charges and Magnatharvbaghel4444No ratings yet
- Physic 12 Sample PaperDocument5 pagesPhysic 12 Sample PaperDeep ChovatiyaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Current - 2Document2 pagesMagnetic Effect of Current - 2rajs8229No ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics Chapter 3Document7 pagesClass 12 Physics Chapter 3Abhishek PandeyNo ratings yet
- Imp. Derivations For XII PhysicsDocument3 pagesImp. Derivations For XII PhysicsJethiya SyckoNo ratings yet
- Physics 12Document6 pagesPhysics 12satishNo ratings yet
- 12th Test PaperDocument5 pages12th Test PaperMd Rizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Assignment On EMIDocument6 pagesAssignment On EMIewrNo ratings yet
- CH 4-MCM-WSDocument8 pagesCH 4-MCM-WSmmkishore067No ratings yet
- Moving Charges and MagnetismDocument2 pagesMoving Charges and MagnetismAslam FaruqiNo ratings yet
- Physics CHDocument3 pagesPhysics CHdhriti1996singhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 (Moving Charges and Magnetism) UnsolvedDocument8 pagesChapter 4 (Moving Charges and Magnetism) UnsolvedDhankhar ShabNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 PDFDocument22 pagesChapter 9 PDFramprasadNo ratings yet
- 14-5633 7100-10a6-GDocument23 pages14-5633 7100-10a6-GHabib AliNo ratings yet
- Joseph Déjacque - Le HumanisphereDocument187 pagesJoseph Déjacque - Le HumanisphereCharles TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- foster care reportDocument64 pagesfoster care reportLindsey BasyeNo ratings yet
- CO Traffic Crash Report on I25 at Milepoint 242Document6 pagesCO Traffic Crash Report on I25 at Milepoint 242Debra DreilingNo ratings yet
- Unethical Issues in Marketing ManagementDocument14 pagesUnethical Issues in Marketing ManagementSreejith VrNo ratings yet
- Antonio Gramci's Concept of IdeologyDocument22 pagesAntonio Gramci's Concept of IdeologyS1LNo ratings yet
- Family Tree of Dacquel-MacabeoDocument31 pagesFamily Tree of Dacquel-MacabeoJimmy C. AndangNo ratings yet
- Your Vi Bill: Mr. Saketkumar BorgaonkarDocument3 pagesYour Vi Bill: Mr. Saketkumar BorgaonkarSaket BorgaonkarNo ratings yet
- Drehkreuz Installation Manual 1 3 en ManDocument58 pagesDrehkreuz Installation Manual 1 3 en ManDouglas Cabral100% (1)
- TVM Problems SolvedDocument4 pagesTVM Problems SolvedCharlie Ercole Mercado0% (1)
- Loan, Pledge & Mortgage - Mcqs Sy 2013-14 2nd SemDocument7 pagesLoan, Pledge & Mortgage - Mcqs Sy 2013-14 2nd Semincubus_yeahNo ratings yet
- Provide Accommodation Reception ServicesDocument61 pagesProvide Accommodation Reception ServicesMike MojicaNo ratings yet
- 21 - Amended Complaint Adding Bucyrus Bratwurst Festival As PlaintiffDocument46 pages21 - Amended Complaint Adding Bucyrus Bratwurst Festival As PlaintiffFinney Law Firm, LLCNo ratings yet
- Understanding Public Administration SyllabusDocument77 pagesUnderstanding Public Administration Syllabusalex compas94% (16)
- Ligot Vs RepublicDocument5 pagesLigot Vs RepublicPaolo MendioroNo ratings yet
- Salatul Jama'AhDocument26 pagesSalatul Jama'AhAatif ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Bsba - Curriculum MapDocument2 pagesBsba - Curriculum Mapxxxx100% (2)
- Cambridge IGCSE: Accounting 0452/13Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Accounting 0452/13grengtaNo ratings yet
- Social Issues Brainstorming and SpeakingDocument7 pagesSocial Issues Brainstorming and SpeakingNatasa BudisinNo ratings yet
- Düvell, F. (2011) - Irregular Migration. en Global Migration Governance (Pp. 78-108) .-50-63Document14 pagesDüvell, F. (2011) - Irregular Migration. en Global Migration Governance (Pp. 78-108) .-50-63Juan Jose Garzon CamposNo ratings yet
- Walkathon Brochure - 2021 Trifold 2Document2 pagesWalkathon Brochure - 2021 Trifold 2api-208159640No ratings yet
- Certificate of Non-Coverage: (CNC-OL-CAR-2020-09-00520)Document1 pageCertificate of Non-Coverage: (CNC-OL-CAR-2020-09-00520)Jennie AmandoNo ratings yet
- EXIM Bank (100 Marks BlackBook)Document57 pagesEXIM Bank (100 Marks BlackBook)Tejas Makwana83% (6)
- Rental Income and Expenses 2021Document2 pagesRental Income and Expenses 2021Finn KevinNo ratings yet
- Joint Venture in Biotech & PharmaDocument9 pagesJoint Venture in Biotech & PharmaAjayktr100% (1)
- First Merit List - Private Sector HITEC/HBS Medical/Dental CollegesDocument2 pagesFirst Merit List - Private Sector HITEC/HBS Medical/Dental CollegesIftikhar hussain shahNo ratings yet
- Fin254.7 Group ReportDocument46 pagesFin254.7 Group ReportJannatul Ferdousi PrïtyNo ratings yet
- Colloquium Script - 1Document4 pagesColloquium Script - 1MinSU Bongabong Guidance OfficeNo ratings yet
- Power and Functions of UNDocument7 pagesPower and Functions of UNSaklain SakibNo ratings yet
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldFrom EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (64)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1395)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceFrom EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Paradox: The Nine Greatest Enigmas in PhysicsFrom EverandParadox: The Nine Greatest Enigmas in PhysicsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (57)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismFrom EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (500)
- The Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceFrom EverandThe Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (23)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayFrom EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (125)
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsFrom EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (94)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseFrom EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)From EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (155)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeFrom EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeNo ratings yet
- In Search of Schrödinger’s Cat: Quantum Physics and RealityFrom EverandIn Search of Schrödinger’s Cat: Quantum Physics and RealityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (380)
- The Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectFrom EverandThe Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (48)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishFrom EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Professor Maxwell's Duplicitous Demon: The Life and Science of James Clerk MaxwellFrom EverandProfessor Maxwell's Duplicitous Demon: The Life and Science of James Clerk MaxwellRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)