Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Blood Composition & Functions
Uploaded by
Uzma TahseenOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Blood Composition & Functions
Uploaded by
Uzma TahseenCopyright:
Available Formats
Search
BLOOD COMPOSITION & FUNCTIONS
SURESH BABU EMANDI DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOGNOSY Vikas Institute of Pharmaceutical scienes
Apr 7, 2022 • 1 like • 542 views
9 of 13
Education
it is usefull for the D.Pharm,B.Pharm and pharm D students
and also it is give basic knowledge for the blood composition
Recommended
Epithelial tissue
anisha Deshmukh
60K views • 22 slides
Red blood cells or erythrocytes
Amjad Afridi
4.7K views • 10 slides
The cell
Abhay Rajpoot
17.8K views • 19 slides
Blood composition
Biji Saro
25.2K views • 13 slides
Human cell
JAYDIP NINAMA
108.3K views • 31 slides
Blood composition and its functions on
17.09.2016
Biji Saro
123.1K views • 19 slides
Blood formation and composition
Bharati vidyapeeth university
33.9K views • 35 slides
Cell
Ganesh Nair
77.7K views • 91 slides
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Blood Cell organelles
deepainga… • 26.2K views Karl Pointer • 41.2K views
Similar to BLOOD COMPOSITION & FUNCTIONS (20)
BLOOD.pptx Blood part 1
Nerusu sai pri… • 201 views FarhaNaaz14 • 24 views
Slideshows for you (20)
Powerpoint Presentati… Swot analysis
Dr Mohan … • 172.2K views Gunjan Sri… • 412.7K views
More from SURESH BABU EMANDI DEPARTMENT
OF PHARMACOGNOSY Vikas Institute of (20)
Pharmaceutical scienes
NERVOUS SYSTEM DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
SURESH BABU … • 16 views SURESH BAB… • 343 views
Recently uploaded (20)
Disinfo Lectio ICS3211_lecture_week…
Corinne Weis… • 162 views Vanessa Cami… • 224 views
Related Books
Free with a 30 day trial from Everand View All
Ebook Ebook Ebook
Nursing Anatomy & The Liver Cure: Lab Values Pocket
Physiology Natural Solutions… Guide For Nurses
john thuko Russell L. Blaylock
for Liver Health to Rachael Jason
Target Symptoms of
4/5 3Fatty
/ 5 Liver Disease, 4/5
Autoimmune
Related Audiobooks
Free with a 30 day trial from Everand View All
Audiobook Audiobook Audiobook
Nine Pints: A Water Fasting: Lose Relation of the
Journey Through… Weight, Cleanse… Mineral Salts of th…
Rose George
the Money, Timothy Mooreand
Your Body, George
Body toW. Carey
the Signs of
Medicine, and Experience Optimal the Zodiac
3.5 /5
Mysteries of Blood 4.5 /5
Health, Wellness 5/5
and Longevity
BLOOD COMPOSITION & FUNCTIONS
1. COMPOSITION&FUNCTIONS OF BLOOD E.SURESH BABU M.PHARM DEPARTMENT
OF PHARMACOGNOSY VIKAS INSTITUTE OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES , NEAR AIR
PORT,RAJAHMUNDRY-533102.
2. BLOOD • Blood is a connective tissue in fluid form. • It is considered as the ‘fluid of
life’ because it carries oxygen from lungs to all parts of the body and carbon dioxide
from all parts of the body to the lungs. • It is known as ‘fluid of growth’ because it
carries nutritive substances from the digestive system and hormones from endocrine
gland to all the tissues. • The blood is also called the ‘fluid of health’ because it
protects the body against the diseases and gets rid of the waste products and
unwanted substances by transporting them to the excretory organs like kidneys.
3. PROPERTIESOFBLOOD • 1. Color: Blood is red in color. Arterial blood is scarlet red
because it contains more oxygen and venous blood is purple red because of more
carbon dioxide. Blood • 2. Volume: Average volume of blood in a normal adult is 5 L. •
In a newborn baby, the volume is 450 ml. It increases during growth and reaches 5 L at
the time of puberty. • In females, it is slightly less and is about 4.5 L. It is about 8% of
the body weight in a normal young healthy adult, weighing about 70 kg. • 3. Reaction
and pH: Blood is slightly alkaline and its pH in normal conditions is 7.4. • 4. Specific
gravity: • Specific gravity of total blood : 1.052 to 1.061 • Specific gravity blood cells :
1.092 to 1.101 • Specific gravity of plasma : 1.022 to 1.026 • 5. Viscosity: Blood is five
times more viscous than water. It is mainly due to red blood cells and plasma proteins
4. COMPOSITIONOF BLOOD
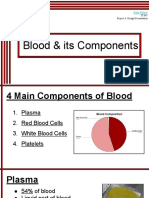
5. COMPONENTSOFBLOOD • There are many cellular structures in the composition of
blood. • When a sample of blood is spun in a centrifuge machine, • They separate into
the following constituents: Plasma, bu!y coat and erythrocytes.
6. COMPOSITIONOFPLASMA
7. Plasma • Plasma is a straw-colored clear liquid part of blood. • It contains 91% to
92% of water and 8% to 9% of solids. • The solids are the organic and the inorganic
substances • Serum is the clear straw-colored fluid that oozes from blood clot. • When
the blood is shed or collected in a container, it clots. In this process, the fibrinogen is
converted into fibrin and the blood cells are trapped in this fibrin forming the blood
clot. • A"er about 45 minutes, serum oozes out of the blood clot. Serum Serum =
Plasma – Fibrinogen
8. FUNCTIONS OF BLOOD REGULATION FUNCTIONS TRANSPORT FUNCTIONS
SYNTHETIC FUNCTIONS MAINTENANCE FUNCTIONS STORAGE FUNCTIONS
DEFENSIVE FUNCTIONS FUNCTIONS OF BLOOD
9. FUNCTIONSOFBLOOD 1. NUTRITIVE FUNCTION • Nutritive substances like glucose,
amino acids, lipids and vitamins derived from digested food are absorbed from
gastrointestinal tract and carried by blood to di!erent parts of the body for growth
and production of energy. 2. RESPIRATORY FUNCTION • Transport of respiratory gases
is done by the blood. • It carries oxygen from alveoli of lungs to di!erent tissues and
carbon dioxide from tissues to alveoli.
10. 3. EXCRETORY FUNCTION Waste products formed in the tissues during various
metabolic activities are removed by blood and carried to the excretory organs like
kidney, skin, liver, etc. for excretion. „ 4. TRANSPORT OF HORMONES AND ENZYMES
Hormones which are secreted by ductless (endocrine) glands are released directly into
the blood. The blood transports these hormones to their target organs/tissues. Blood
also transports enzymes. „
11. 5. REGULATION OF WATER BALANCE Water content of the blood is freely
interchangeable with interstitial fluid. This helps in the regulation of water content of
the body. 6. REGULATION OF ACID-BASE BALANCE Plasma proteins and hemoglobin
act as bu!ers and help in the regulation of acid-base balance. 7. REGULATION OF BODY
TEMPERATURE Because of the high specific heat of blood, it is responsible for
maintaining the thermoregulatory mechanism in the body, i.e. the balance between
heat loss and heat gain in the body.
12. 8. STORAGE FUNCTION Water and some important substances like proteins,
glucose, sodium and potassium are constantly required by the tissues. Blood serves
as a readymade source for these substances. And, these substances are taken from
blood during the conditions like starvation, fluid loss, electrolyte loss, etc. „ 9.
DEFENSIVE FUNCTION Blood plays an important role in the defense of the body. The
white blood cells are responsible for this function. Neutrophils and monocytes
engulf the bacteria by phagocytosis. Lymphocytes are involved in development of
immunity. Eosinophils are responsible for detoxification, disintegration and removal
of foreign proteins
13. THANK Q
About Support Terms Privacy Copyright
Cookie Preferences English
Do not sell or share my personal information
© 2023 SlideShare from Scribd
You might also like
- The Complete Biomonster Vocabulary Reference GuideDocument26 pagesThe Complete Biomonster Vocabulary Reference Guideapi-110789702100% (1)
- Kangen Water Demo 21.3.1Document81 pagesKangen Water Demo 21.3.1Pavan Reddy100% (1)
- The Liver Cure: Natural Solutions for Liver Health to Target Symptoms of Fatty Liver Disease, Autoimmune Diseases, Diabetes, Inflammation, Stress & Fatigue, Skin Conditions, and Many MoreFrom EverandThe Liver Cure: Natural Solutions for Liver Health to Target Symptoms of Fatty Liver Disease, Autoimmune Diseases, Diabetes, Inflammation, Stress & Fatigue, Skin Conditions, and Many MoreRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Pathophysiology - Step by Step G - Albert Nolan PHDDocument171 pagesPathophysiology - Step by Step G - Albert Nolan PHDΑΘΑΝΑΣΙΟΣ ΚΟΥΤΟΥΚΤΣΗΣ71% (7)
- Edexcel Unit 1 Notes Cystic FibrosisDocument2 pagesEdexcel Unit 1 Notes Cystic FibrosisIllharm Sherrif100% (2)
- BIO1 Circulatory and Hematologic System 3Document20 pagesBIO1 Circulatory and Hematologic System 3CAMELA KIM TENORIONo ratings yet
- BIO1 Circulatory and Hematologic System 2Document20 pagesBIO1 Circulatory and Hematologic System 2Camela Kim Domider TenorioNo ratings yet
- E LESSON - 10 BIO 7thmayDocument6 pagesE LESSON - 10 BIO 7thmayArchanaGuptaNo ratings yet
- Blood and Body Fluids-Nurs-EbaaDocument56 pagesBlood and Body Fluids-Nurs-EbaaEbaa Moh'd ZayadnehNo ratings yet
- 1.5 BloodDocument19 pages1.5 BloodAla' ShehadehNo ratings yet
- Cyprus International University Faculty of Pharmacy Instr. Övgü İşbilenDocument31 pagesCyprus International University Faculty of Pharmacy Instr. Övgü İşbilenAmirabbas SaffariNo ratings yet
- Blood Circulatory System - Lecture NoteDocument81 pagesBlood Circulatory System - Lecture NoteVihanga NimsaraNo ratings yet
- KS4 What Is BloodDocument40 pagesKS4 What Is BloodVictoria VirgoNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System PDFDocument40 pagesCirculatory System PDFRabia Imran100% (2)
- Lab. 7Document6 pagesLab. 7tamanranya234No ratings yet
- Thermo CO2 Basics Training 2007Document21 pagesThermo CO2 Basics Training 2007rajeeshNo ratings yet
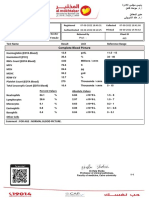
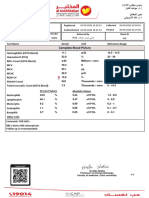
- Complete Blood Picture: 38 Year Female 20424500962Document3 pagesComplete Blood Picture: 38 Year Female 20424500962amerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - CellsDocument23 pagesChapter 1 - CellsDale TelgenhoffNo ratings yet
- Transplantation EthicalDocument36 pagesTransplantation Ethicalhukor.rscmNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To Human BodyDocument33 pages1.introduction To Human BodyBilawal KhanNo ratings yet
- Atlas Urine Formed Elements - FUS - 2017Document170 pagesAtlas Urine Formed Elements - FUS - 2017damaNo ratings yet
- Blood General. Lecture 3Document21 pagesBlood General. Lecture 3Panashe MawaroNo ratings yet
- Hematology 1Document13 pagesHematology 1Genos XavierNo ratings yet
- GR 10 Blood TissueDocument10 pagesGR 10 Blood TissueMelanie TrevelyanNo ratings yet
- L2-SCBM 343-2 Urine-WJDocument42 pagesL2-SCBM 343-2 Urine-WJpond_1993No ratings yet
- Body FluidsDocument46 pagesBody FluidsMohmmadRjab SederNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis and The Excretory SystemDocument21 pagesHomeostasis and The Excretory Systemmark smithNo ratings yet
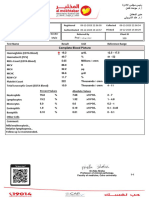
- Complete Blood Picture: 6 Year Female 24622524341Document5 pagesComplete Blood Picture: 6 Year Female 24622524341Samir YahiaNo ratings yet
- Tests Results 66423514212Document2 pagesTests Results 66423514212ramadan.seydNo ratings yet
- 1-Lecture 01-Blood PDFDocument26 pages1-Lecture 01-Blood PDFMuhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 Dialysis - Anna Philomena B. FerrerDocument5 pagesActivity 4 Dialysis - Anna Philomena B. FerrerSebs BerebsNo ratings yet
- THE Excretory SystemDocument24 pagesTHE Excretory SystemZain HaiderNo ratings yet
- Bio B Physiology Urine Homeostasis Lab 1Document6 pagesBio B Physiology Urine Homeostasis Lab 1api-500743288No ratings yet
- Effect of Exercise On Circulatory SystemDocument13 pagesEffect of Exercise On Circulatory SystemMuskan DabasNo ratings yet
- Complete Blood Picture: 3 Year Male 61623504391Document4 pagesComplete Blood Picture: 3 Year Male 61623504391dr.mohamed nabilNo ratings yet
- Lab Training Sample ReportDocument53 pagesLab Training Sample ReportAnwar Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Student - Module 9 - Renal AlterationsDocument44 pagesStudent - Module 9 - Renal AlterationsHannaNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument24 pagesExcretory Systemjosejazmine4No ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument50 pagesThe Circulatory SystemZara16No ratings yet
- Theory 5 - Analysis of BloodDocument27 pagesTheory 5 - Analysis of BloodNavoda ThathsaraniNo ratings yet
- Tests Results 24423521985Document2 pagesTests Results 24423521985kokoamir1029No ratings yet
- Body Fluid Compartments 0Document15 pagesBody Fluid Compartments 0Abdo MohdyNo ratings yet
- Constituent of Blood PDFDocument49 pagesConstituent of Blood PDFNia Sofea Mat ZaitNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular SystemDocument18 pagesThe Cardiovascular SystemVENUS LIRIA PANTINo ratings yet
- Pathofisiologi Cairan TubuhDocument16 pagesPathofisiologi Cairan Tubuhsuci nurmantiyasNo ratings yet
- Therapy 101207215845 Phpapp01Document43 pagesTherapy 101207215845 Phpapp01paraisoptpt100% (1)
- Project 3 - Google PresentationDocument9 pagesProject 3 - Google Presentationapi-362258156No ratings yet
- Complete Blood Picture: 1 Year Male 49324501929Document1 pageComplete Blood Picture: 1 Year Male 49324501929hager.ramdan77No ratings yet
- Welcome: by DR - Mrs. Grace Helina Prof - and Head Dept - of Exercise Physiology and Nutrition Tnpesu Chennai - 06Document18 pagesWelcome: by DR - Mrs. Grace Helina Prof - and Head Dept - of Exercise Physiology and Nutrition Tnpesu Chennai - 06Ajay Pal NattNo ratings yet
- Intravenous TherapyDocument46 pagesIntravenous TherapyJudah Paulo EsperoNo ratings yet
- Twelve Tissue RemediesDocument34 pagesTwelve Tissue RemediesDhawal Modi100% (8)
- Medsurg Midterm LecturesDocument33 pagesMedsurg Midterm LecturesLongyapon Sheena StephanieNo ratings yet
- Bone Marrow Aspiration and BiopsyDocument7 pagesBone Marrow Aspiration and BiopsyPriyanjali SainiNo ratings yet
- Quiz Bank - Capoten (Mar-22)Document4 pagesQuiz Bank - Capoten (Mar-22)saad awanNo ratings yet
- GiveLife Challenge PresentationDocument35 pagesGiveLife Challenge PresentationARAVIND SivaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Transport in MammalsDocument119 pagesChapter 8 - Transport in Mammalsapi-3728508100% (1)
- Revised Case Study Umbilical HerniaDocument14 pagesRevised Case Study Umbilical HerniaLance Angelo Bernandino100% (1)
- 1.physiology Body Fluid Compartments Lecture 1Document26 pages1.physiology Body Fluid Compartments Lecture 1Humanic GenesNo ratings yet
- Blood Physiology Lec1Document40 pagesBlood Physiology Lec1Sherwan R ShalNo ratings yet
- Red Blood Cells, Functions, Diseases A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment, And Related ConditionsFrom EverandRed Blood Cells, Functions, Diseases A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment, And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of Body Fluids in Small Animal CytologyFrom EverandDifferential Diagnosis of Body Fluids in Small Animal CytologyNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Hypertension in Small Animals 2010 Veterinary Clinics of North America Small Animal PracticeDocument18 pagesEndocrine Hypertension in Small Animals 2010 Veterinary Clinics of North America Small Animal PracticeEduardo PalaciosNo ratings yet
- 10bio AssignmentDocument4 pages10bio AssignmentKrishna GovilNo ratings yet
- Materi Dr. Fitri Vidyastuti, SPGK - NUTRITION MANAGEMENT ofDocument22 pagesMateri Dr. Fitri Vidyastuti, SPGK - NUTRITION MANAGEMENT ofSyarief NurseNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument152 pagesMale Reproductive SystemRoshan MevadaNo ratings yet
- Fitness Exam OutlineDocument16 pagesFitness Exam OutlineChris NuttallNo ratings yet
- B Y: - Idr. Megha Gaur BDS IDocument89 pagesB Y: - Idr. Megha Gaur BDS IRishab GaurNo ratings yet
- Dmba Kerdelhue 2018Document7 pagesDmba Kerdelhue 2018EN Ka ERNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Nervous System2Document20 pagesDisorders of The Nervous System2Ian Rizavi Villamor AntopinaNo ratings yet
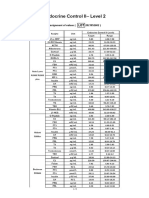
- Assignment of Values-Endocrine Control II-Level 2-2021052602Document2 pagesAssignment of Values-Endocrine Control II-Level 2-2021052602Ân Đình100% (1)
- Pacop Pink Pharmacology ReviewerDocument100 pagesPacop Pink Pharmacology Reviewer;'SiLeNt';100% (1)
- ASSESSMENTDocument1 pageASSESSMENTBryant Riego IIINo ratings yet
- Concepts of FitnessDocument51 pagesConcepts of FitnessNathan VieningsNo ratings yet
- Placebo EffectDocument22 pagesPlacebo EffectZendaya Slim TargaryenNo ratings yet
- Department of Clinical Biochemistry: Lipid ProfileDocument3 pagesDepartment of Clinical Biochemistry: Lipid ProfilegeorgeNo ratings yet
- Annals of Medicine and Surgery: SciencedirectDocument5 pagesAnnals of Medicine and Surgery: Sciencedirectjaime andresNo ratings yet
- Anemia at Older AgeDocument10 pagesAnemia at Older AgeAbdullah ZuhairNo ratings yet
- Complete Endocrinolog-BcqsDocument9 pagesComplete Endocrinolog-BcqsJahanzaib BashirNo ratings yet
- Eggs PDFDocument25 pagesEggs PDFmusfirahNo ratings yet
- Metformina y Estrés Oxidativo en Pacientes DiabéticosDocument14 pagesMetformina y Estrés Oxidativo en Pacientes DiabéticosJesus D. Hernandez GuitianNo ratings yet
- Thyroid PathophysiologyDocument7 pagesThyroid PathophysiologyS RiarNo ratings yet
- Session 05-Types of Cell InjuryDocument24 pagesSession 05-Types of Cell Injurykasper mkNo ratings yet
- Sano Feeding DairycowDocument36 pagesSano Feeding DairycowDaneeNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument4 pagesQuestionsProduktemeuljeNo ratings yet
- Helping Fertility, by The Book: The Essential Fertility Plan For Healthy Pregnancy and Clearing Blocked Fallopian TubesDocument69 pagesHelping Fertility, by The Book: The Essential Fertility Plan For Healthy Pregnancy and Clearing Blocked Fallopian TubesJames Akibon100% (1)
- h1 Reproductive Physiology Course Summary NotesDocument11 pagesh1 Reproductive Physiology Course Summary NotesHoney BaseriNo ratings yet
- GlucoseDocument4 pagesGlucoseGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State in Adults - Treatment - UpToDateDocument36 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis and Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State in Adults - Treatment - UpToDateHiKa SaGoNo ratings yet
- Adult-Onset Type 1 Diabetes - Current Understanding and Challenges Nov 2021Document8 pagesAdult-Onset Type 1 Diabetes - Current Understanding and Challenges Nov 2021Katuya KatuyaNo ratings yet
- Designed To Enhance From The Inside Out: Apd TherapyDocument7 pagesDesigned To Enhance From The Inside Out: Apd TherapyNumael Alfonso Serrato AlvaradoNo ratings yet