Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reg Insulin
Uploaded by
BIRIN, JEHAN KAYLE T.0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesOriginal Title
REG INSULIN
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesReg Insulin
Uploaded by
BIRIN, JEHAN KAYLE T.Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
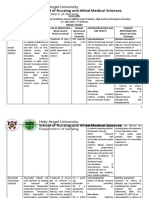
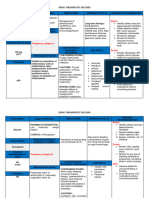
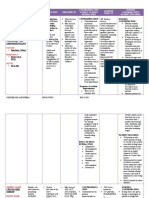
Generic Name Routes of Dosage Mechanism of Side Effects Adverse Nursing Responsibilities
Admini actions & Reaction
-stration Indications
Insulin Subcutaneous 0.5-1 Insulin is a hormone METABOLIC: Hypoglycemia, Before
(Regular) unit/kg/day secreted by beta cells Hyperglycemia, lipoatrophy, Assess glucose level before starting
of pancreas that, by hypoglycemia, lipohypertrophy, therapy. If patient is under stress,
Brand Name: For adults receptor-mediated ketoacidosis obesity, insulin unstable, pregnant, recently diagnosed or
Humulin R with Type 2 effects, promotes the allergy, insulin taking drugs that can interact with insulin,
Novolin R. diabetes storage of the body’s RESPIRATORY antibodies, monitor level more frequently.
Penfill mellitus fuels, facilitating the : insulin induced Assess injection sites for local reactions.
requiring transport of Dyspnea, edema, seizure Check the patient’s skin color, orientation,
Classification: basal insulin metabolites and ions increased cough, and coma reflexes and peripheral sensation.
Antidiabetic control: (potassium) through reduced
Hormone 10 units/day cell membranes and pulmonary During
stimulating the function, Ensure uniform suspension of insulin by
synthesis of glycogen respiratory tract gently rotating the vial containing the
from amino acids. infection agent. Avoid vigorous shaking.
Give maintenance doses subcutaneously,
Insulin is indicated SKIN: rotating injection sites regularly to
for the treatment of Itching, rash, decrease the risk of lipodystrophy.
Type 1 diabetes redness, stinging, Use caution when mixing two types of
mellitus, Type 2 swelling, insulin. Always draw the regular insulin
diabetes that cannot urticaria, warmth into the syringe first.
be controlled by diet at injection site
Double-check or have a colleague check
or oral drugs, severe
the dosage drawn up for patients; even
ketoacidosis, OTHER:
small errors in dosage can cause serious
hyperkalemia, Anaphylaxis,
problems.
gestational diabetes angioedema
and treatment of hypersensitivity
After
patients who require reactions,
Monitor response carefully to avoid
basal insulin control lipoatrophy,
adverse effects.
of hyperglycemia. lipohypertrophy,
rash Provide patient education about drug
effects and warning signs to report to
enhance patient knowledge and to
promote compliance.
Ensure that patient has dietary and
exercise regimen and using good hygiene
practices to improve the effectiveness of
the insulin and decrease adverse effects of
the disease.
Monitor nutritional status to provide
nutritional consultation as needed.
Dispose of used materials properly.
Document that drug has been given.
Reference: Karch, A. (2014). Lippincott’s Nursing Drug Guide.
You might also like
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Practical Insulin: A Handbook for Prescribing ProvidersFrom EverandPractical Insulin: A Handbook for Prescribing ProvidersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- InsulinDocument2 pagesInsulinKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Frequency Specific MicrocurrentDocument2 pagesFrequency Specific MicrocurrentAngela Pagliuso50% (2)
- Emergency Eye Care WorkshopDocument21 pagesEmergency Eye Care WorkshopAriani Ratri Dewi100% (1)
- DRUG STUDY Insulin Humulin RDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY Insulin Humulin RFrancesca Icalina Buensuceso100% (12)
- Stanford Hospital & Clinics Antimicrobial Dosing Reference Guide 2013Document3 pagesStanford Hospital & Clinics Antimicrobial Dosing Reference Guide 2013SANCHOSKYNo ratings yet
- CefuroximeDocument6 pagesCefuroximeJoyce Joyx Joycee SalonoiNo ratings yet
- Insulin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesInsulin Drug Studykuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Ketorolac, Metoclopramide, and Cefuroxime Nursing ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesKetorolac, Metoclopramide, and Cefuroxime Nursing ConsiderationsDyanne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Polypectomy CSDocument30 pagesPolypectomy CSMASIINo ratings yet
- Benefits of Spa TreatmentDocument35 pagesBenefits of Spa TreatmentMercy Zonio100% (1)
- Humulin RDocument1 pageHumulin RZyrah Ziska ZafraNo ratings yet
- Humalog Drug StudyDocument3 pagesHumalog Drug StudyKristinelou Marie ReynaNo ratings yet
- CaCO3 Drug StudDocument2 pagesCaCO3 Drug StudAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Insulin LisproDocument2 pagesDrug Study Insulin LisproEzron Kendrick Duran100% (1)
- Ruqyah Instructions and Symptoms: Symptoms of Evil EyeDocument2 pagesRuqyah Instructions and Symptoms: Symptoms of Evil Eyeempty_shake5319100% (1)
- Insulin AspartDocument2 pagesInsulin AspartPatricia MaglasangNo ratings yet
- Insulin GlargineDocument2 pagesInsulin GlarginePatricia MaglasangNo ratings yet
- Gliclazide Diamicron: Generic Name Trade NameDocument8 pagesGliclazide Diamicron: Generic Name Trade NameIsabella SamsonNo ratings yet
- Covid19-Drug StudyDocument7 pagesCovid19-Drug StudynicoleNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (3rd Rot.) (GMC) - JSGSDocument6 pagesDrug Study (3rd Rot.) (GMC) - JSGSJohannes SantosNo ratings yet
- StudyDocument2 pagesStudyit4728No ratings yet
- Before: Drug Therapeutic Record Indications Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument9 pagesBefore: Drug Therapeutic Record Indications Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesIcel Jean QuimboNo ratings yet
- Atorvastatin Nursing ConsiderationsDocument5 pagesAtorvastatin Nursing ConsiderationsBani Ann Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Monsalud - Drug StudyDocument5 pagesMonsalud - Drug StudyJanielle Christine MonsaludNo ratings yet
- InsulinDocument2 pagesInsulinjennierubyjane kimNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: Occasional: DuringDocument2 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: Occasional: Duringhahaha100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument15 pagesDrug StudyDavid RefuncionNo ratings yet
- Classification Therapeutic Action Indication Adverse Effect Route Nursing Responsibility Vital Sign MonitoringDocument1 pageClassification Therapeutic Action Indication Adverse Effect Route Nursing Responsibility Vital Sign MonitoringDawn EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DRDocument3 pagesDrug Study DRGershom Perez AcaboNo ratings yet
- Nursing Responsibilities: Cyrill Alexandria G. Tolentino BSN 2BDocument1 pageNursing Responsibilities: Cyrill Alexandria G. Tolentino BSN 2BCyrill Alexandria TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Drud Study For DutyDocument9 pagesDrud Study For DutyAnonymous AlphaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Action Indication Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Patient's TeachingDocument3 pagesDrugs Action Indication Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Patient's TeachingHazel Palomares100% (1)
- I. Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationDocument4 pagesI. Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationCherubim Lei DC FloresNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Reponsibilities Generic NameDocument4 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Reponsibilities Generic NamehahahaNo ratings yet
- Drug study nursing considerationsDocument4 pagesDrug study nursing considerationsMilky Lescano LargozaNo ratings yet
- Medical ManagementDocument3 pagesMedical ManagementMark Jefferson LunaNo ratings yet
- Escaran - Drug Study - Set ADocument4 pagesEscaran - Drug Study - Set AFrancis Alfred EscaranNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Hydrocortisone)Document1 pageDrug Study (Hydrocortisone)Pauline AñesNo ratings yet
- 4A Drug SheetDocument14 pages4A Drug SheetTherese PagayNo ratings yet
- Insulin Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument9 pagesInsulin Nursing Responsibilitieskuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Fluimicil, Atorvastatin, Piperacillin + Tazobactam..etc.)Document3 pagesDrug Study (Fluimicil, Atorvastatin, Piperacillin + Tazobactam..etc.)Kate PedzNo ratings yet
- DS - Format - MedDocument3 pagesDS - Format - MedChristian MarquezNo ratings yet
- DS (Ibuprofen)Document6 pagesDS (Ibuprofen)Mary April MendezNo ratings yet
- DiabetesDocument9 pagesDiabetesMsPocketbook HoarderNo ratings yet
- Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseDocument1 pageMedication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseCameron JanzenNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Med WardDocument13 pagesDrug Study - Med WardFretzgine Lou ManuelNo ratings yet
- 5 Drug Study SampleDocument5 pages5 Drug Study SampleMarianne Angela CortezNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy JRODDocument4 pagesDrugstudy JRODPeyjeyNo ratings yet
- University of the Philippines Manila College of Nursing Drug StudyDocument3 pagesUniversity of the Philippines Manila College of Nursing Drug StudyAna Luisa Conejos ConeseNo ratings yet
- ApidraDocument4 pagesApidraRobert Ivan AgujarNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyRoland YusteNo ratings yet
- Generic Brand Class Therapeutic Pharmacologic Dosage: PPD's Better Pharmacy Drug Hand Book 9 Edition 2009Document4 pagesGeneric Brand Class Therapeutic Pharmacologic Dosage: PPD's Better Pharmacy Drug Hand Book 9 Edition 2009Crystal Queen MarquezNo ratings yet
- M&N MGMTDocument3 pagesM&N MGMTMark Jefferson LunaNo ratings yet
- Bridget BadiangDocument15 pagesBridget BadiangKrystelle RoslindaNo ratings yet
- Chew, swallow or crush mebendazole tabletsDocument6 pagesChew, swallow or crush mebendazole tabletsDenvicNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (CHF)Document9 pagesDrug Study (CHF)Ericka VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyPark JeongyeonNo ratings yet
- NCP DS Patient 2020Document13 pagesNCP DS Patient 2020Silvestre SanchezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study.Document9 pagesDrug Study.Chelsea Therese GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document4 pagesDrug Study 2EARL GERALD RICAFRANCANo ratings yet
- 13 Med MNGTDocument19 pages13 Med MNGTKate ChavezNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Dosage / Frequency Action Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilityDocument9 pagesGeneric Name Dosage / Frequency Action Side Effects Nursing Responsibilityorhocelo6908No ratings yet
- Insulin Glulisine (rDNA Origin) : (In-Su-Lin Gloo-Lye-Seen)Document3 pagesInsulin Glulisine (rDNA Origin) : (In-Su-Lin Gloo-Lye-Seen)FeliciaDorghamNo ratings yet
- Potassium ChlorideDocument2 pagesPotassium ChlorideBIRIN, JEHAN KAYLE T.No ratings yet
- DiazepamDocument2 pagesDiazepamBIRIN, JEHAN KAYLE T.No ratings yet
- HF & Arf - CCNDocument11 pagesHF & Arf - CCNBIRIN, JEHAN KAYLE T.No ratings yet
- 24 Hour Urine CollectionDocument2 pages24 Hour Urine CollectionBIRIN, JEHAN KAYLE T.No ratings yet
- Guaiac TestDocument2 pagesGuaiac TestBIRIN, JEHAN KAYLE T.No ratings yet
- Thoracentesis Reflective EssayDocument2 pagesThoracentesis Reflective EssayAnjae GariandoNo ratings yet
- MMSEDocument2 pagesMMSEVarsha KNo ratings yet
- Contoh SoapDocument11 pagesContoh SoapIlham riandaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 013Document36 pagesChapter 013Aria LeNo ratings yet
- FFR vs. iFR vs. RFR vs. QFR: T. SantosoDocument30 pagesFFR vs. iFR vs. RFR vs. QFR: T. SantosoJosé Raúl Cascante AlpízarNo ratings yet
- Cucms Rheumatology Questions PDFDocument3 pagesCucms Rheumatology Questions PDFMaisara JhsNo ratings yet
- AlopeciaDocument2 pagesAlopeciaAldrich ArquizaNo ratings yet
- Morning Report: Pembimbing: Dr. Djunifer Hasudungan Sagala, Sp. OT (K) Dr. Andreas Wahyu W, Sp. OTDocument55 pagesMorning Report: Pembimbing: Dr. Djunifer Hasudungan Sagala, Sp. OT (K) Dr. Andreas Wahyu W, Sp. OTSinda AgathaNo ratings yet
- SFP-Vol403 Unit2Document10 pagesSFP-Vol403 Unit2TnchNo ratings yet
- Ors, Hyd Mix& Road To H CardDocument10 pagesOrs, Hyd Mix& Road To H CardAnonymous hYMWbANo ratings yet
- Syllabus Cancer of ColonDocument7 pagesSyllabus Cancer of ColonMoonyeen NatanawanNo ratings yet
- A Cochrane Review of Superficial Heat or ColdDocument9 pagesA Cochrane Review of Superficial Heat or ColdIvanFierroNo ratings yet
- Prevalence of Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Two Brazilian Quilombola Communities in Southwest Bahia StateDocument7 pagesPrevalence of Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Two Brazilian Quilombola Communities in Southwest Bahia StateIJAERS JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Clinical Implications of Left Atrial Enlargement - A ReviewDocument6 pagesClinical Implications of Left Atrial Enlargement - A ReviewRMO RSJDNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Oral Cavity, Salivary Glands and Jaws (K00-K14) : Search (Advanced Search)Document13 pagesDiseases of Oral Cavity, Salivary Glands and Jaws (K00-K14) : Search (Advanced Search)Ria MarthantiNo ratings yet
- Early Intensive Care Unit Mobility Therapy in The Treatment of Acute Respiratory FailureDocument6 pagesEarly Intensive Care Unit Mobility Therapy in The Treatment of Acute Respiratory FailureTakashi NakamuraNo ratings yet
- Dialog Diabetes B.inggris Kel 5-1Document4 pagesDialog Diabetes B.inggris Kel 5-1Desma LindaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Pharmacology For Nurses A Pathophysiologic Approach 5th EditionDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Pharmacology For Nurses A Pathophysiologic Approach 5th Editiontipsterchegoe.t8rlzv100% (41)
- ppl10 - WebsiteDocument14 pagesppl10 - Websiteapi-270774299No ratings yet
- Philippine College of Physicians Daily Census Ward Hospital de Los Santos-Sti Medical CenterDocument22 pagesPhilippine College of Physicians Daily Census Ward Hospital de Los Santos-Sti Medical Centercruz_johnraymondNo ratings yet
- Vegetable Kingdom Continued: SciaticDocument14 pagesVegetable Kingdom Continued: SciaticSatyendra RawatNo ratings yet
- Medicine CNS-ENDODocument11 pagesMedicine CNS-ENDOmrcopy xeroxNo ratings yet
- New global hospital and critical care centre in AkolaDocument2 pagesNew global hospital and critical care centre in AkolaPrashant WankhadeNo ratings yet
- Assessing Body TemperatureDocument6 pagesAssessing Body TemperatureemailNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Head Trauma GuideDocument5 pagesPediatric Head Trauma Guideherman76No ratings yet