Professional Documents
Culture Documents
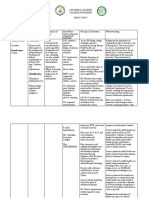
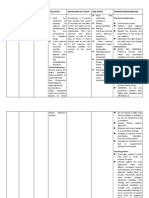
Classification Therapeutic Action Indication Adverse Effect Route Nursing Responsibility Vital Sign Monitoring
Uploaded by
Dawn EncarnacionOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
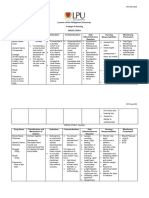
Classification Therapeutic Action Indication Adverse Effect Route Nursing Responsibility Vital Sign Monitoring
Uploaded by
Dawn EncarnacionCopyright:
Available Formats
OPIOD ANALGESIC
Classification Therapeutic Action Indication Adverse Effect Route Nursing responsibility Vital sign monitoring
Treatment for moderate To alleviate moderate Hypotension, sedation, Orally Encourage client to avoid activities Assess BP, PR, RR before
to severe pain to severe pain euphoria, urinary Intravenously that require alertness. administering the drug.
retention Intramuscularly
Suppression of cough or Pulmonary edema Subcutaneous Discuss ways to minimize dry mouth Assess for allergies and
respiratory distress and constipation use of opioid and other
drug
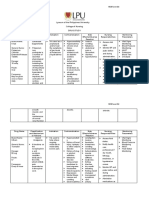
ANTI-HYPERTENSIVE
Ace Inhibitor-pril Decrease heart High blood Dizziness Oral Encourage client to implement Assess sudden drop in
ARBs Angiotensin -sartan workload Fatigue IV healthy lifestyle. blood fluid volume
Alpha blocker- osin Decrease blood pressure Chest pain in people
Beta blocker-lol Decrease heart rate with poor blood flow Administer on empty stomach, 1hr Assess: Baseline status
Calcium channel blocker- before meals or 2hrs after meals
dipine
Diuretics-ide
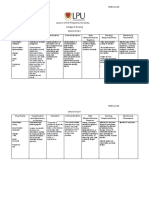
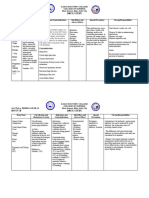
DIURETICS
Thiazide and thiazide like Decrease blood pressure Hypertension Dehydration ORAL Assess for mentioned Assess patient’s drug
Loop diuretics Decrease symptoms of Hypokalemia IV contraindication and cautions. response through vital
Carbonic Anhydrase fluid overload Edema signs, weight, serum
Potassium-sparring Administer oral form early in the electrolyte and hydration
Osmotic day
ORAL ANTIDIABETIC
Biguanide (metformin) Decrease production Management of 2 Hypoglycemia ORAL Assess for contraindication and Monitor blood glucose
and increases the uptake Diabetes Nausea cautions. level
of glucose. GI upset
Heart burm Perform physical assessment. Monitor nutritional status
Alpha glucosidase inhibitor Delay absorption of
glucose Provide patient comfort measure to
help cope with drug effect
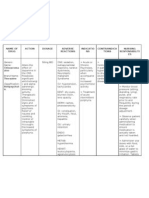
INSULIN
Regulate movement of Type 1 diabetes Hypoglycemia Subcutaneous Assess for contraindication and Obtain blood glucose
blood glucose from Type 2 diabetes when Ketoacidosis cautions. levels as ordered to
blood cells agents failed monitor response to
Perform physical assessment to insulin
Management of establish baseline data before Monitor response
hyperkalemia beginning therapy carefully to avoid adverse
effect
Monitor nutritional status
You might also like
- Drug Study - Med WardDocument13 pagesDrug Study - Med WardFretzgine Lou ManuelNo ratings yet
- NCP DS NCM114 RleDocument12 pagesNCP DS NCM114 RleAllysa Kyle AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- 13 Med MNGTDocument19 pages13 Med MNGTKate ChavezNo ratings yet
- Reg InsulinDocument2 pagesReg InsulinBIRIN, JEHAN KAYLE T.No ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument10 pagesEmergency DrugsnieacatleyaNo ratings yet
- Print MeDocument4 pagesPrint MeDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Insulin LisproDocument2 pagesDrug Study Insulin LisproEzron Kendrick Duran100% (1)
- DruggstudyDocument2 pagesDruggstudySherravedamae Pantollano FerrerNo ratings yet
- Medication Management of Thiazide DiureticsDocument1 pageMedication Management of Thiazide DiureticsMike EveretteNo ratings yet
- Cva Drug StudyDocument5 pagesCva Drug Studykristine86badgirlNo ratings yet
- Paracetamol Tramadol KCLDocument5 pagesParacetamol Tramadol KCLDani DaniNo ratings yet
- ApidraDocument4 pagesApidraRobert Ivan AgujarNo ratings yet
- Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: - SectionDocument2 pagesMindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: - SectionJohn Pearl FernandezNo ratings yet
- Drug study-SECOND TWO MEDICAL WARDSDocument2 pagesDrug study-SECOND TWO MEDICAL WARDSErryl Justine AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Atorvastatin Nursing ConsiderationsDocument5 pagesAtorvastatin Nursing ConsiderationsBani Ann Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyKeanu PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument15 pagesDrug StudyDavid RefuncionNo ratings yet
- MEDICATIONSDocument3 pagesMEDICATIONSchristyNo ratings yet
- Drugs Indications Actions Side Effects / Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration Patient TeachingDocument10 pagesDrugs Indications Actions Side Effects / Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration Patient TeachingTyrone IglesiasNo ratings yet
- Metformin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMetformin Drug StudyArone SebastianNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Reponsibilities Generic NameDocument4 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Reponsibilities Generic NamehahahaNo ratings yet
- ChlorpromazineDocument3 pagesChlorpromazineMarinel Agulto100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument15 pagesDrug StudymonmonNo ratings yet
- CaCO3 Drug StudDocument2 pagesCaCO3 Drug StudAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- Nursing responsibilities for common drugsDocument3 pagesNursing responsibilities for common drugsVinssy RevicNo ratings yet
- Ketorolac, Metoclopramide, and Cefuroxime Nursing ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesKetorolac, Metoclopramide, and Cefuroxime Nursing ConsiderationsDyanne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Fall 2023 Classification of MedicationsDocument6 pagesFall 2023 Classification of Medicationsramyharoon2004No ratings yet
- CITICOLINE, Drugs in MedicalDocument10 pagesCITICOLINE, Drugs in MedicalInosanto May AnnNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Care For Mca LabDocument1 pageDrug Study Care For Mca LabAlessandro MadrigalNo ratings yet
- HF and CAD Case ScenarioDocument17 pagesHF and CAD Case ScenarioElla Neiza AngelesNo ratings yet
- Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseDocument1 pageMedication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseMike EveretteNo ratings yet
- Ate Mitch HN DRUG STUDYDocument23 pagesAte Mitch HN DRUG STUDYMarice VenNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyKaye Aligato ParaderoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyRosemarie CarpioNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug Studyjasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- 014 Drug StudyDocument3 pages014 Drug StudyGrey KnighttNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological Sheet Patient Name: BALDESTOY, Benedict Age: 19 Years Old Sex: Male Diagnosis: Hepatoma CAP-MRDocument5 pagesPharmacological Sheet Patient Name: BALDESTOY, Benedict Age: 19 Years Old Sex: Male Diagnosis: Hepatoma CAP-MRIngrid NicolasNo ratings yet
- Medication Generic/Brand Classification Nursing Implications (3) Dosage Route Schedule /time Desired Effect Side Effects (3) TeachingDocument5 pagesMedication Generic/Brand Classification Nursing Implications (3) Dosage Route Schedule /time Desired Effect Side Effects (3) TeachingrunnermnNo ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument1 pageAcetazolamideKyuSheenNo ratings yet
- St. Paul College of Ilocos SurDocument5 pagesSt. Paul College of Ilocos SurCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- DRUGS. Hypertensive Pantoloc, Diamicron Vit B, Furosemide CozaarDocument9 pagesDRUGS. Hypertensive Pantoloc, Diamicron Vit B, Furosemide CozaarEzron Kendrick DuranNo ratings yet
- ParaDocument2 pagesParaMary Kate ClarosNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Gantala Drug Stusy-TabhsoDocument8 pagesGantala Drug Stusy-TabhsoHey it's FerdyNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (V.luna)Document4 pagesDrug Study (V.luna)carizzajoyNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy JRODDocument4 pagesDrugstudy JRODPeyjeyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyMaxine RicafortNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Drug StudyDocument16 pagesChapter 5 Drug StudyRegee Rose LacsonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Patient with DiarrheaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for Patient with DiarrheaThan Ramile Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Drug GlucotrolDocument1 pageDrug GlucotrolSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Drug Study...Document6 pagesDrug Study...Johanz PacrisNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologic Class: Therapeutic Class: Atypical: Dibenzothiazepine Derivative AntipsychoticDocument2 pagesPharmacologic Class: Therapeutic Class: Atypical: Dibenzothiazepine Derivative AntipsychoticBianca Nicole Gacad Fernandez100% (1)
- Drug Study LosartanDocument3 pagesDrug Study LosartanQueenie Mae ReyesNo ratings yet
- NCP DS Patient 2020Document13 pagesNCP DS Patient 2020Silvestre SanchezNo ratings yet
- Clinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsDocument1 pageClinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsENo ratings yet
- Drug Study FinalDocument6 pagesDrug Study FinalJade HemmingsNo ratings yet
- RandomDocument2 pagesRandomAllen YnionNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NCMHDocument5 pagesDrug Study NCMHnhyceNo ratings yet
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Classification Therapeutic Action Indication Adverse Effect Route Nursing Responsibility Vital Sign MonitoringDocument1 pageClassification Therapeutic Action Indication Adverse Effect Route Nursing Responsibility Vital Sign MonitoringDawn EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Classification Therapeutic Action Indication Adverse Effect Route Nursing Responsibility Vital Sign MonitoringDocument1 pageClassification Therapeutic Action Indication Adverse Effect Route Nursing Responsibility Vital Sign MonitoringDawn EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Adolf and Nelson DifferencesDocument1 pageAdolf and Nelson DifferencesDawn EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Texture in Art Docent TrainingDocument19 pagesTexture in Art Docent TrainingDawn EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Nelson MandelaDocument6 pagesNelson MandelaDawn EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Covid-19 Vaccines Research WorkDocument1 pageCovid-19 Vaccines Research WorkDawn EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Human Defenses Student'sDocument96 pagesHuman Defenses Student'sDawn EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Mobuzz Dengue AppDocument10 pagesMobuzz Dengue AppMae DacerNo ratings yet
- Localizing the SDGs for a Sustainable Cauayan CityDocument7 pagesLocalizing the SDGs for a Sustainable Cauayan CityAlyssa Marie M. ObenarNo ratings yet
- NCP 5 Ovarian CancerDocument6 pagesNCP 5 Ovarian Cancersaint_ronald886% (29)
- INFANCY Nutrition and Diet TherapyDocument23 pagesINFANCY Nutrition and Diet TherapyRoseKelly TayagNo ratings yet
- MSCDFSM Prog. GuideDocument108 pagesMSCDFSM Prog. Guidesamraju1No ratings yet
- Tricho Till Omani ADocument25 pagesTricho Till Omani AYzel SeniningNo ratings yet
- Why HACCPDocument2 pagesWhy HACCPKemphoNo ratings yet
- The Natural Way To A Healthy HealingDocument111 pagesThe Natural Way To A Healthy HealingAnjanaNo ratings yet
- MSOSH Academy Training Calendar 2020Document23 pagesMSOSH Academy Training Calendar 2020Muhammad FizreeNo ratings yet
- TFN Resource UnitDocument80 pagesTFN Resource UnitAira Alaro50% (2)
- Woodend Nursery Day Care of ChildrenDocument11 pagesWoodend Nursery Day Care of ChildrenSRARNo ratings yet
- Reconsider Licensure Appeal for Top StudentDocument6 pagesReconsider Licensure Appeal for Top StudentFrancis Edrian CellonaNo ratings yet
- AmendmentsDocument1 pageAmendmentsJaime GaviolaNo ratings yet
- Teens Your Brain Needs Real FoodDocument4 pagesTeens Your Brain Needs Real FoodGiovana NavaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Services For Outpatients: Citizen'S CharterDocument1 pageLaboratory Services For Outpatients: Citizen'S CharterAlianna Arnica MambataoNo ratings yet
- Self-Assessment of Nursing Standards of PracticeDocument32 pagesSelf-Assessment of Nursing Standards of Practiceapi-242114301No ratings yet
- Convulsive Disorders: Presenters: Kabwe Chanda EliasDocument30 pagesConvulsive Disorders: Presenters: Kabwe Chanda EliasHomeground entertainmentNo ratings yet
- Community-Based Approach For Dengue Prevention and Control in Sta. Cruz, Laguna, PhilippinesDocument7 pagesCommunity-Based Approach For Dengue Prevention and Control in Sta. Cruz, Laguna, PhilippinesBella LifindraNo ratings yet
- Newest - Hled325 Stress Management Lesson Plan StartDocument6 pagesNewest - Hled325 Stress Management Lesson Plan Startapi-199880580No ratings yet
- 1.6 - Maslow's Hierarchy of NeedsDocument3 pages1.6 - Maslow's Hierarchy of NeedsOkoye CynthiaNo ratings yet
- A. Historical Perspectives: Women's RolesDocument11 pagesA. Historical Perspectives: Women's RolesJoanne SarzonaNo ratings yet
- 17 Types of Working Conditions - SimplicableDocument23 pages17 Types of Working Conditions - SimplicableSharina Canaria ObogNo ratings yet
- Health 7: Topic: Nutrition (Food Group and Elements of Nutrition) Grade 7Document42 pagesHealth 7: Topic: Nutrition (Food Group and Elements of Nutrition) Grade 7Zchecsh Blace AceNo ratings yet
- Notification: of TheDocument4 pagesNotification: of TheSushma DeviNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pharmacy Thesis TopicsDocument6 pagesClinical Pharmacy Thesis Topicsbsk561ek100% (2)
- Prognostic Value of Admission Blood Glucose in Diabetic and Non-Diabetic Patients With Intracerebral HemorrhageDocument7 pagesPrognostic Value of Admission Blood Glucose in Diabetic and Non-Diabetic Patients With Intracerebral HemorrhageNur Irma SafitriNo ratings yet
- 00 06992Document5 pages00 06992enockprivateNo ratings yet
- Lesson 52ND Q ManifestoDocument30 pagesLesson 52ND Q ManifestoLiya Mae SantiagoNo ratings yet
- 10.1007@s11065 020 09443 7Document14 pages10.1007@s11065 020 09443 7José NettoNo ratings yet
- Learn The Basics Behind Basal Body TemperatureDocument6 pagesLearn The Basics Behind Basal Body TemperatureAaloka vermaNo ratings yet