Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Erythropoiesis - Part 1
Uploaded by
Lucan AnaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Erythropoiesis - Part 1
Uploaded by
Lucan AnaCopyright:
Available Formats
Last edited: 8/11/2021
1. ERYTHROPOIESIS: RED BLOOD CELL FORMATION
Erythropoiesis: Red Blood Cell Formation | Part 1 Medical Editor: Dr. Sofia Suhada M. Uzir
OUTLINE (C) CELLS PRODUCED
I) ERYTHROPOIESIS
II) REVIEW QUESTIONS
III) REFERENCES
I) ERYTHROPOIESIS
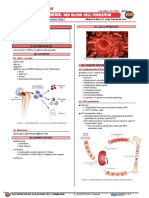
Formation of RBCs is called erythropoiesis
(A) LOCATION
(1) Sites – In order Figure 2. RBCs [European Pharmaceutical Review]
Yolk Sac
Liver
(D) GROWTH FACTORS/ MOLECULES REQUIRED
Spleen
Bone marrow (RED) (Spongy bone trabeculae) (1) Erythropoietin (EPO)
o Skull
Made by PCT cells in kidney due to hypoxia
o Sternum
Hypoxia stimulus:
o Pelvis
o Anemia
o Epiphyses of long bones
o Obstructive Lung disease
o Restrictive Lung Diseases
o Obstructive sleep apnea
o Heart Failure
o Circulatory Shock
o Atherosclerosis
o Thromboembolisms
o Cyanide or Carbon monoxide poisoning
(2) EPO production
Hypoxia
o ↓ Degradation of hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)
o ↑ HIF in kidney cells
HIF transcription factor
o Activates genes that become expressed and lead to
synthesis of a protein called EPO
o EPO then travels to red bone marrow where it acts on
Figure 1. Hematopoiesis - bone marrow [News Medical] myeloid stem cells
This converts myeloid stem cells into RBC
precursor cells
(2) Mnemonic
Young Liver Synthesizes Blood cells
(B) DRIVING FACTOR
Blood loss
o Ulceration
o Stab wound
Hypoxia
o Inadequate oxygen delivery to tissue
o Production of more RBC to supply more oxygen
Anemia
Figure 3. Erythropoiesis induced by hypoxia [Learnhaem]
ERYTHROPOIESIS: RED BLOOD CELL FORMATION HEMATOLOGY: Note #1. 1 of 3
(3) Requirements (iii) In the ileum
B12 o Intrinsic factors bind with the transport protein
Folate Receptor mediated endocytosis
Iron Vitamin B12 is released into the circulation
Carbohydrates through the basolateral membrane
Fats • Binds with transcobalamin I & II
Amino acids
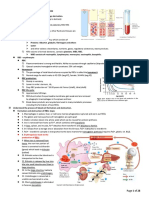
(4) Iron metabolism
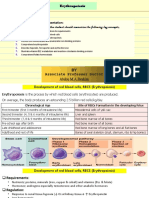
(E) SEQUENCE OF DEVELOPMENT
Iron ingested from food/supplements in Fe3+ state
(1) RBC pathway
(i) In duodenum – enterocytes Hemocytoblast → myeloid stem cell → proerythroblast →
o A ferro-reductase enzyme known as duodenal basophilic erythroblast → polychromatic erythroblast →
cytochrome B converts Fe 3+ into Fe 2+ orthochromatic erythroblast → reticulocyte → erythrocyte
o Then Fe 2+ is brought into duodenal cell with H+ by (RBC) Figure 5
DMT-1
o Once in duodenal cell: (i) Basophilic erythroblasts
Fe 2+ binds with apoferritin converting into ferritin o Stain blue
Ferritin can bind with multiple ferritins forming RNA stains blue
hemosiderin
Ferritin can release Fe 2+ on basal surface of cell (ii) Polychromatic Erythroblasts
where a feroportin channel transports Fe2+ from o Stain blue & red
duodenal cell into blood RNA is being translated into proteins which stain
Before the Fe 2+ binds to transferrin red
• It is oxidized to Fe 3+ by hephaestin
• Transferrin carries the Fe 3+ in the blood to (iii) Orthochromatic Erythroblasts
various organs o Stain red
o Must bound to transferrin because it can RNA has been translated to proteins which stains
undergo Fenton reaction producing free red
radicals
(iv) Reticulocytes
(ii) In the liver
o Have no nucleus or organelles after the
o There are hepatocytes that can detect the changes in orthochromatic erythroblast spit them out
iron levels o The reticulocytes mature into erythrocytes in 2-3 days
It produces hepcidin
B12 and folate are needed for DNA synthesis and
• Hepcidin controls the activity of feroportin by
maturation in developing RBC’s
blocking it
• This is to control the amount of iron
• Too much iron is toxic
o HFE protein
Controls hepcidin
In hemochromatosis, there is no production of
functional HFE protein
Hence, iron overload occurs
(iii) In red bone marrow
o The red bone marrow is the organ we need it in for
erythropoiesis
Once Fe 3+ is taken to red bone marrow
• It is taken up into developing RBCs
• Binds with heme pigment called protoporphyrin
with the help of ferro-chelatase
• Eventually the heme will bind with the globin
chains and make hemoglobin
(5) Vitamin B12 and folic acid metabolism
Vitamin B12 and folic acid are ingested from food such as
leafy vegetables and red meat
(i) In duodenum
o Folic acid is absorbed across the gut, into the blood
stream
(ii) In stomach
o Parietal cells make proteins called intrinsic factors
Intrinsic factors bind to vitamin B12
Figure 4. Causes of ineffective erythropoiesis
[Keep Maturation on Track]
2 of 3 HEMATOLOGY: Note #1. ERYTHROPOIESIS: RED BLOOD CELL FORMATION
The precursor of all lines of blood cells is the
a. Myeloblast
b. Hemocytoblast
c. Proerythroblast
d. Progranulocyte
Megakaryocyte give rise to
a. Erythrocyte
b. Agranulocyte
c. Granulocytes
d. Thrombocytes
The production of red blood cells in the bone
marrow is regulated by
a. Renin
b. Angiotensin
c. Erythropoietin
d. Calcium
Which of the following is true regarding
thrombopoiesis?
a. In the red bone marrow
b. Produce RBCs
c. Uses EPO
d. Doesn’t give rise to platelet
Process of formation of blood corpuscles is called
a. Hemolysis
b. Hemozoin
c. Hemopoiesis
d. Haemoter
The blood corpuscles are of _________ kinds.
a. 5
b. 4
c. 2
d. 3
CHECK YOUR ANSWERS
III) REFERENCES
● Alila Medical Media. Shutterstock Hematopoiesis Bone Marrow
[digital image] https://www.news-medical.net/life-
Figure 5. Stages of erythropoiesis [Keep Maturation on Track] sciences/Hematopoiesis-Process.aspx
● European Pharmaceutical Review. Red blood cells with ability to
deliver drugs. 2020. [digital image]
https://www.europeanpharmaceuticalreview.com/news/121018/rese
II) REVIEW QUESTIONS
archers-synthesise-red-blood-cells-with-ability-to-deliver-drugs/
The hormone erythropoietin stimulates red blood ● Erythropoietin and the control of erythropoiesis. Learn Haem.
2019. [digital image]
cell production in the red bone marrow. Where in https://www.learnhaem.com/courses/anaemia/lessons/normal-
the body is erythropoietin produced? haematopoiesis/topic/normal-erythropoiesis/
a. Spleen ● Keep Maturation on Track. [digital image]
https://keepmaturationtrack.eu/ineffective-erythropoiesis/
b. Kidney ● Oxford University Press. Gaskell & Rostron: Therapeutics and
c. Liver Human Physiology. [Quiz]
d. Thyroid https://global.oup.com/uk/orc/pharmacy/ifp_therapeutics/student/mc
qs/ch09/
● Blood circulation. MCQ Biology. [Quiz]
Which of the following statements about https://www.mcqbiology.com/2014/02/mcq-on-haematopoietic-
erythrocytes is correct? system.html
a. They fight infection ● Le T, Bhushan V, Sochat M, Chavda Y, Zureick A. First Aid for
the USMLE Step 1 2018. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Medical; 2017
b. They clot blood ● Marieb EN, Hoehn K. Anatomy & Physiology. Hoboken, NJ:
c. They lack a nucleus Pearson; 2020.
d. They are produced in the spleen ● Boron WF, Boulpaep EL. Medical Physiology.; 2017.
● Urry LA, Cain ML, Wasserman SA, Minorsky PV, Orr RB,
Campbell NA. Campbell Biology. New York, NY: Pearson; 2020.
Where does hematopoiesis take place? ● Jameson JL, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Longo DL,
a. Lungs Loscalzo J. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine. New York
etc.: McGraw-Hill Education; 2018.
b. Pancreas ● Sabatine MS. Pocket Medicine: the Massachusetts General
c. Liver Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine. Philadelphia: Wolters
d. Bone marrow Kluwer; 2020.
Platelets are formed from what type of cell?
a. Melanocytes
b. Macrophages
c. Astrocytes
d. Megakaryocytes
ERYTHROPOIESIS: RED BLOOD CELL FORMATION HEMATOLOGY: Note #1. 3 of 3
You might also like
- HematologyDocument15 pagesHematologyGilberto GonzalezNo ratings yet
- 345 - Hematology Physiology) PolycythemiasDocument3 pages345 - Hematology Physiology) PolycythemiasAro DanaNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell AnemiaDocument37 pagesSickle Cell Anemiahazelposis75% (4)
- BOC Study Guide Sixth EditionDocument377 pagesBOC Study Guide Sixth EditionBjörn Daamo88% (24)
- Sel HewanDocument489 pagesSel HewanRahmat Reza100% (1)
- The Role of Gut and Genital Microbiota and The Estrobolome in Endometriosis, Infertility and Chronic Pelvic PainDocument40 pagesThe Role of Gut and Genital Microbiota and The Estrobolome in Endometriosis, Infertility and Chronic Pelvic PainsefzanimeriaNo ratings yet
- Ninja Nerd AnemiaDocument13 pagesNinja Nerd AnemiaAndra Bauer100% (3)
- RBC Production and DestructionDocument44 pagesRBC Production and DestructionNehemiah FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Blood Pharmacology PDFDocument13 pagesBlood Pharmacology PDFManikanta GupthaNo ratings yet
- Red Blood Cells, Anemia, and PolycythemiaDocument7 pagesRed Blood Cells, Anemia, and PolycythemiaShi no Me100% (1)
- Iron OverloadDocument37 pagesIron OverloadMohamed MidoNo ratings yet
- ANEMIAS (Sickle Cell Anemia With Pathophysiology)Document31 pagesANEMIAS (Sickle Cell Anemia With Pathophysiology)mabec pagaduan70% (10)
- Lab Output For Blood (Human Anatomy and Physiology)Document8 pagesLab Output For Blood (Human Anatomy and Physiology)Dayledaniel Sorveto0% (1)
- 5.1.6. Alternative Methods For Control of Microbiological QualityDocument10 pages5.1.6. Alternative Methods For Control of Microbiological QualityLEPESANTNo ratings yet
- 342 - Hematology Physiology) Erythropoiesis Red Blood Cell FormationDocument6 pages342 - Hematology Physiology) Erythropoiesis Red Blood Cell Formationhasanatiya41No ratings yet
- 342 Hematology Physiology Erythropoiesis Red Blood Cell FormationDocument3 pages342 Hematology Physiology Erythropoiesis Red Blood Cell FormationAndra BauerNo ratings yet
- P.07 ANEMIA Dr. Buliyat 09 03 18Document5 pagesP.07 ANEMIA Dr. Buliyat 09 03 18Raymund Dan AldabaNo ratings yet
- Hematology 1 L3 Erythrocytes LectureDocument3 pagesHematology 1 L3 Erythrocytes LectureChelze Faith DizonNo ratings yet
- APP2 E1 NoteDocument28 pagesAPP2 E1 NotelifecostNo ratings yet
- Unit Viii: The Hematologic SystemDocument1 pageUnit Viii: The Hematologic SystemAqi RamenaiNo ratings yet
- Hematology: FANER, Ned Denebe LACANILAO, Sunshine NUCUM, Billie Kim PAGADUAN, Maribec PUA, MonalisaDocument31 pagesHematology: FANER, Ned Denebe LACANILAO, Sunshine NUCUM, Billie Kim PAGADUAN, Maribec PUA, MonalisatzuquinoNo ratings yet
- Physiology I Blood & ImmunityDocument13 pagesPhysiology I Blood & Immunitynadine azmyNo ratings yet
- ErythropoiesisDocument11 pagesErythropoiesisْNo ratings yet
- Physiology Lecture 2: RBC S Characteristics, Function and FormationDocument20 pagesPhysiology Lecture 2: RBC S Characteristics, Function and FormationdarkboiNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Blood Student Notes 1Document12 pagesWeek 1 Blood Student Notes 1pham vanNo ratings yet
- Blood and Lymph (Autosaved)Document46 pagesBlood and Lymph (Autosaved)Shaikh SaqibNo ratings yet
- Alteration in OxygenationDocument8 pagesAlteration in Oxygenationraquel maniegoNo ratings yet
- 5 2 Microcytic Anemias PDFDocument3 pages5 2 Microcytic Anemias PDFPrabhat GuptaNo ratings yet
- Erytropoiesis Part 1&2 Ninja Nerd ScienceDocument2 pagesErytropoiesis Part 1&2 Ninja Nerd Sciencewati100% (4)
- Bloodbld 2020007025 CDocument2 pagesBloodbld 2020007025 CFrancieudo SampaioNo ratings yet
- C19 2 Hemopoiesis Eythropoiesis LeukopoiesisDocument11 pagesC19 2 Hemopoiesis Eythropoiesis Leukopoiesisnurul azisyah auraNo ratings yet
- 3A Blood PhysiologyDocument7 pages3A Blood PhysiologyRen AlvNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology With PhatophysiologyDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology With PhatophysiologyJustine Mae OyongNo ratings yet
- Blood Physiology: Biconcave Discs 120 DaysDocument6 pagesBlood Physiology: Biconcave Discs 120 DaysHanamiNo ratings yet
- Blood: Erythropoeisis by U.SivakumarDocument41 pagesBlood: Erythropoeisis by U.SivakumarAkash JaatNo ratings yet
- Iron Defisience AnemiaDocument61 pagesIron Defisience AnemiaYeni Jesika SilitongaNo ratings yet
- Erythropoiesis Amna MalikDocument19 pagesErythropoiesis Amna MalikZardari SaddamNo ratings yet
- Copper Metabolism: Distribution of Copper in The BodyDocument4 pagesCopper Metabolism: Distribution of Copper in The BodyMichael HiiNo ratings yet
- Cardio WhatsoeverDocument12 pagesCardio WhatsoeverFernando DisuNo ratings yet
- New Insights Into Erythropoiesis: The Roles of Folate, Vitamin B12, and IronDocument32 pagesNew Insights Into Erythropoiesis: The Roles of Folate, Vitamin B12, and Ironyaumil fauziahNo ratings yet
- Anemia & Sickle Cell AnemiaDocument5 pagesAnemia & Sickle Cell AnemiaDIANA CAMILLE CARITATIVONo ratings yet
- Hematology L8 - ٠٩٢٥١٩Document32 pagesHematology L8 - ٠٩٢٥١٩shakib33001No ratings yet
- In2Med HaematologyDocument30 pagesIn2Med Haematologye148659No ratings yet
- Topic 29: Pathophysiology of Red Cell Series: 1. HematopoiesisDocument10 pagesTopic 29: Pathophysiology of Red Cell Series: 1. HematopoiesisAelita RuseelNo ratings yet
- Feline Nonregenerative Anemia Pathophysiology and ErilologiesDocument7 pagesFeline Nonregenerative Anemia Pathophysiology and ErilologiesTORRES GUTIERREZ JOYNY RAQUEL catedraticoNo ratings yet
- ErythropoisesDocument30 pagesErythropoisesPriyanka RameshNo ratings yet
- M6 BloodDocument7 pagesM6 BloodNel joy PaurilloNo ratings yet
- Hematology L7 - ٠٨٢١١٩Document22 pagesHematology L7 - ٠٨٢١١٩shakib33001No ratings yet
- Ap2 Chapter18 Powerpoint Blood SU21Document37 pagesAp2 Chapter18 Powerpoint Blood SU21btheresakNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Blood: Ratna Kusumawati Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Sebelas Maret SurakartaDocument65 pagesPhysiology of Blood: Ratna Kusumawati Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Sebelas Maret SurakartaRizal AbdurrahmanNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Blood Continuation - 105835Document6 pagesCardiovascular System Blood Continuation - 105835KIM KALIBAYNo ratings yet
- LEC 5 RBC METABOLISM AND Membrane StructureDocument30 pagesLEC 5 RBC METABOLISM AND Membrane StructureFrancis ValdezNo ratings yet
- Erythrocytes Red Blood CellsDocument54 pagesErythrocytes Red Blood Cellsclarence fernandezNo ratings yet
- EyrthrokineticsDocument4 pagesEyrthrokineticsKenneth Jake BatiduanNo ratings yet
- CARDIOVASCULARDocument20 pagesCARDIOVASCULARpriya garciaNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Blood: Ratna Kusumawati Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Sebelas Maret SurakartaDocument60 pagesPhysiology of Blood: Ratna Kusumawati Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Sebelas Maret SurakartaZidaneNo ratings yet
- PHY LE 2 Finals ReviewerDocument22 pagesPHY LE 2 Finals Reviewerroxanne.viriNo ratings yet
- הגישה לאנמיהDocument9 pagesהגישה לאנמיהddNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument9 pagesBloodJoselle OrateNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Chapter 11 BloodDocument4 pagesAnaphy Chapter 11 BloodJohnNo ratings yet
- HO Notecards 1Document12 pagesHO Notecards 1MrSomnambululNo ratings yet
- Biology Shift 2 Nest 2023Document17 pagesBiology Shift 2 Nest 2023Hardik JoshiNo ratings yet
- 2019 Haplogroup CDocument424 pages2019 Haplogroup CKlaus MarklNo ratings yet
- Ovarian ReserverDocument35 pagesOvarian Reserverpramod singhNo ratings yet
- SorghumDocument6 pagesSorghumASHUTOSH MOHANTYNo ratings yet
- 2021 Journal Impact Factorand QuartileDocument492 pages2021 Journal Impact Factorand QuartileKondreddy Nageswara ReddyNo ratings yet
- Lung Center of The Philippines: Advantages of 3 and 6 Gene Panel The MDCTL FacilitiesDocument2 pagesLung Center of The Philippines: Advantages of 3 and 6 Gene Panel The MDCTL FacilitiesYannah ReonalNo ratings yet
- iHFG - Part - B - IVF - Unit - Facility GuidelinesDocument18 pagesiHFG - Part - B - IVF - Unit - Facility Guidelineslijo workNo ratings yet
- Second Written Test in Earth and Life ScienceDocument9 pagesSecond Written Test in Earth and Life ScienceLucas GodfreyNo ratings yet
- Enzymes NotesDocument46 pagesEnzymes NotesCuthbert MweembaNo ratings yet
- Proceedings 89 00027Document7 pagesProceedings 89 00027gustirandyNo ratings yet
- A Systemic Review Covid-19 VaccineDocument13 pagesA Systemic Review Covid-19 VaccineIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- ĐÁP ÁN Môn Tiếng Anh Đề 1 FINAL Tách Trắc NghiệmDocument15 pagesĐÁP ÁN Môn Tiếng Anh Đề 1 FINAL Tách Trắc NghiệmFish lolNo ratings yet
- Trabajo de InglesDocument5 pagesTrabajo de Inglesmayraguerrero31No ratings yet
- BACTERIOFERRITINDocument5 pagesBACTERIOFERRITINnurulunismuhNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Test Paper Ch4 1Document4 pages11 Biology Test Paper Ch4 1Akhil AkhilNo ratings yet
- Congenital Deformities and Developmental Abnormalities of The Mandibular Condyle in The Temporomandibular JointDocument8 pagesCongenital Deformities and Developmental Abnormalities of The Mandibular Condyle in The Temporomandibular JointMarcelaGutiérrezCarranzaNo ratings yet
- Groundwater MicrobiologyDocument77 pagesGroundwater MicrobiologyJoaquín Javier GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Etextbook 978 0323319676 Andrews Diseases of The Skin Clinical DermatologyDocument61 pagesEtextbook 978 0323319676 Andrews Diseases of The Skin Clinical Dermatologyeric.chandler298100% (49)
- The 100 Articles by Burhan ReadingDocument213 pagesThe 100 Articles by Burhan ReadingMD Sheikh SadiNo ratings yet
- Identification of Potent Antimicrobial Peptides Via A Machine-Learning Pipeline That Mines The Entire Space of Peptide SequencesDocument17 pagesIdentification of Potent Antimicrobial Peptides Via A Machine-Learning Pipeline That Mines The Entire Space of Peptide Sequencesxinyuwu0528No ratings yet
- Gastrulationin MammalsDocument16 pagesGastrulationin MammalsHarsha MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 11 Invertebrates AnswersDocument68 pagesBiology Chapter 11 Invertebrates Answers44012821No ratings yet
- Breeding Guppy - Guppy Guru DerekDocument5 pagesBreeding Guppy - Guppy Guru DerekAnthony JohanNo ratings yet
- Science G5: Quarter 2Document40 pagesScience G5: Quarter 2John ChristianNo ratings yet
- Genetics - Student SampleDocument13 pagesGenetics - Student SampleMaria Isabel MorandiNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan: 7e's ApproachDocument6 pagesDaily Lesson Plan: 7e's ApproachSonny MagdadaroNo ratings yet