Professional Documents
Culture Documents
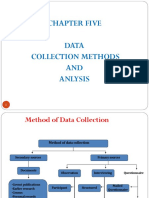
Methods of Data Collection
Uploaded by
Rajju RajjuOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Methods of Data Collection
Uploaded by
Rajju RajjuCopyright:
Available Formats
2/29/2024
METHODS OF DATA COLLECTION RESEARCH INSTRUMENTS
• What is data collection? • The selection of data collection method should • Instrument or a Tool is described as a device used
• The process by which the researcher collects the be based on the following: to collect the data.
information needed to answer the research – The identified hypothesis or research problem • To facilitate variable observation and
problem. – The research design measurement.
• In collecting the data, the researcher must – The information gathered about the variables • The type of instrument used by the researcher
decide: • The methods of data collection vary according to: depends on the data collection method selected.
– Which data to collect ? – Degree of structure • “Massey states that the “Instrument
– How to collect the data? – Degree of quantifiability development requires a high degree of research
– Who will collect the data? – Degree of obtrusiveness expertise, as the instrument must be reliable and
– When to collect the data? – Degree of objectivity valid.”
Guidelines for Developing an Guidelines for Developing an
Types of Research Instruments
Instrument Instrument
• The instrument must be suitable for its • The instrument should be valid. • 1. Questionnaire
• The content of the instrument must be appropriate to
function. test the hypothesis or answer the question being • 2. Checklist
• The research tool will only be effective only as studied. • 3. Distribution
• The instrument should be reliable.
it relates to its particular purpose. • The devised research tool should provide comparable
• 4. Interview
• The instrument must be based on the data every time the subject uses the instrument. • 5. Observation
theoretical framework. • An instrument should include an item that directly • 6. Records
asks the hypothesis.
• The instrument must be based on the • The research tool should be designed and constructed • 7. Experimental Approach
theoretical framework selected for the study. in such a way that cheating is minimized • 8. Survey Approach
Techniques for Developing
1. Questionnaire
Questionnaire
– A series of questions designed to elicit • Advantages of a Questionnaire • Researcher may read literatures about the topic look
through available questionnaires or obtain help from
information, which is filled in by all participants in – 1. Relatively simple method of obtaining data. experts.
the sample. • Open - ended questions are preferable than closed
– 2. Less time is consumed. questions since they reflect respondent’s attitudes,
– This can be gathered either by oral interview or by feelings, which are expressed in his own words.
– 3. Researcher is able to gather data from a widely
written questionnaire. • If yes - no questions are used; additional information may
scattered sample. be gained by leaving space for respondent’s own idea.
– This is the most common type of research
• The possibility of a middle ground statement is also
instrument. important.
• Every item in a questionnaire should relate to the topic
under study.
2/29/2024
Criteria of a Good Questionnaire Characteristic of a Good Questionnaire 3. Interview
• This involves either structure or unstructured verbal
communication between the researcher and subject, during which
– 1. Clarity of Language • 1. Well-stated title information is obtained for a study.
• It must meet the level of understanding of the respondents • 2.Has statement of purpose • Types of Interview
in order to generate needed responses. • 1. Unstructured Interviews
• 3.It assures the respondents about the confidentiality
– 2. Singleness of Objective – more conversational
of responses – long sometimes (hours) and
• An item must have one and only one answer
– 3. One-to-One Correspondence
• 4.It is designed to achieve the objectives of the study – conducted in a usual situation.
– This allows the researcher flexibility in questioning the subject.
• The questionnaire as a whole must correspond with the • 5.It has a clear direction • 2. Structured Interviews
objectives of the study • 6. There are no double-negative questions – always operates within formal written instrument referred as
interview schedule.
– 4. Correct Grammar, Spelling, and Construction • 7. It avoids double barreled questions – researcher designed the questions to be asked prior to interview
• The questionnaire must be constructed observing including the order of the questions.
grammatically correct sentences, correctly spelled words,
• 8. The design corresponds to an easy tabulation of data – The questions are asked orally in either face to face or telephone
coherence in construction of sentences, etc. format.
4.Observation 5. Records
• Advantages of Interview • Observation most commonly used in qualitative • A record refers to all the numbers and
– 1. Data from interview are usable research.
– 2. Depth of response can be assured statistics that institutions, organizations and
• Types of Observation
– 3. In an exploratory study, the interview technique provides
basis for the formulation of questionnaire • 1. Unstructured observation
people keep as a record of their activities.
– 4. Clarification is possible – a method of collecting research data that has both • Sources
– 5. No items are overlooked opponents and proponents.
– 6. Higher proportion of responses is obtained – 1. Census data
– 7. Greater amount of flexibility is allowed • 2. Structured observation
– preparation of record-keeping forms such as category – 2. Educational records
Disadvantages of Interview
1. Time element systems, checklists and rating scales. – 3. Hospital/clinic records
2. Biases may result – researcher typically has some prior knowledge about
3. Costly the behaviour or event of interest
6. Experimental Approach 7. Survey Approach
• A powerful design for testing hypothesis of • Non-experimental type in which the
causal relationships among variables. researcher investigates a community or a
• Researcher controls the independent variable group of people.
& watches the effect on the dependent • Another name is FORMULATIVE OR
variable. EXPLORATORY research
• Two Groups of Experimental Approach
– 1. Treatment / Experimental group
– 2. Control group
You might also like
- 11 - Practical ResearchDocument10 pages11 - Practical Researchcabstephanie31No ratings yet
- Nursing Research Data CollectionDocument220 pagesNursing Research Data Collectiondr.anu Rk100% (2)
- DHD RM 22Document39 pagesDHD RM 22Solomon BisetNo ratings yet
- Collecting Primary DataDocument41 pagesCollecting Primary DataDimple May Gianne DumaguitNo ratings yet
- Constructing A Research InstrumentDocument18 pagesConstructing A Research InstrumentJessa Mae GastarNo ratings yet
- Methods of Data Collection MSC N I YrDocument256 pagesMethods of Data Collection MSC N I Yrdr.anu RkNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis DefDocument16 pagesData Analysis DefLhenie Jane SalamatNo ratings yet
- Topic 3: Research DesignDocument59 pagesTopic 3: Research DesignSamirRastogiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: The Characteristics, Strengths, Weaknesses and Kinds of Quantitative ResearchDocument19 pagesLesson 1: The Characteristics, Strengths, Weaknesses and Kinds of Quantitative ResearchAngelica JustoNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Method Research ReviewerDocument6 pagesQuantitative Method Research ReviewerAuvioreNo ratings yet
- Topic 3Document60 pagesTopic 3sid suchakNo ratings yet
- Data Collection 2024 Admin and Psych StudentDocument91 pagesData Collection 2024 Admin and Psych StudentNicoleNo ratings yet
- Types and Designs of ResearchDocument49 pagesTypes and Designs of Researchgon MacknoNo ratings yet
- Business Research Methods-1Document22 pagesBusiness Research Methods-1GEEKNo ratings yet
- Research Design 1Document44 pagesResearch Design 1varunNo ratings yet
- Midterm Prac Research Session 6 PDFDocument18 pagesMidterm Prac Research Session 6 PDFCaine de LeonNo ratings yet
- Research - Design IpuDocument137 pagesResearch - Design Iputrendy FashionNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Research - DesignDocument63 pagesChapter 4 Research - Designteddy demissieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Nature of Inquiry and Research: Arvin C. Diamante Master Teacher II NiDocument30 pagesChapter 1: Nature of Inquiry and Research: Arvin C. Diamante Master Teacher II Nibernadette domoloanNo ratings yet
- Assignment of SPSSDocument12 pagesAssignment of SPSSAkshay poplyNo ratings yet
- Construction of QuestionnaireDocument54 pagesConstruction of QuestionnaireuthiraNo ratings yet
- Methods of Data Collection MalarDocument48 pagesMethods of Data Collection MalarsrimalathiNo ratings yet
- Lecture Four Data CollectionDocument92 pagesLecture Four Data CollectionHamunNo ratings yet
- Research Methods PowerpointDocument95 pagesResearch Methods PowerpointTenywaw IlliamuNo ratings yet
- The Investigatory ProcessDocument4 pagesThe Investigatory ProcessAngelika TibayanNo ratings yet
- Practical Research - Quarter 2Document10 pagesPractical Research - Quarter 2rcesperidarm4No ratings yet
- Research Techniques PDFDocument5 pagesResearch Techniques PDFEzekiel Eljay MacatangayNo ratings yet
- AGRICDocument3 pagesAGRIClayla landNo ratings yet
- QualitativeDocument32 pagesQualitativeMemoona SheesNo ratings yet
- BRM - Introduction - To - Business - ResearchDocument23 pagesBRM - Introduction - To - Business - Researchmukesh jangidNo ratings yet
- Business Research Methods: Lec # 2 Types of Research Manager-Research RelationshipDocument28 pagesBusiness Research Methods: Lec # 2 Types of Research Manager-Research Relationshiparbaz khanNo ratings yet
- Unit I Reserch MethodsDocument17 pagesUnit I Reserch MethodsIswarya PachamuthuNo ratings yet
- Practical Research I - Midterm ReviewerDocument3 pagesPractical Research I - Midterm ReviewerGerald BajadoNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 1 ReviewDocument9 pagesPractical Research 1 ReviewMary Rose Y. OborNo ratings yet
- Case Study Reasearch2Document10 pagesCase Study Reasearch2Linh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Class CH 5Document22 pagesClass CH 5wabdushukurNo ratings yet
- Value of Qualitative Research: - Used in Exploratory Research Designs - May Be SufficientDocument9 pagesValue of Qualitative Research: - Used in Exploratory Research Designs - May Be SufficientLee Cixin MettaNo ratings yet
- SLK Research 8 q2 1.ADocument18 pagesSLK Research 8 q2 1.Abeth labradorNo ratings yet
- Business Research MethoddssDocument90 pagesBusiness Research Methoddsskomal soniNo ratings yet
- Understanding Data and Ways To Systematically CollectdataDocument33 pagesUnderstanding Data and Ways To Systematically CollectdataGe Ne VieveNo ratings yet
- Understanding Data and Ways To Systematically CollectdataDocument33 pagesUnderstanding Data and Ways To Systematically CollectdataGe Ne VieveNo ratings yet
- The Research Design NeedsDocument4 pagesThe Research Design NeedsJoy AkikiNo ratings yet
- Module Quarter 4Document9 pagesModule Quarter 4Ruffamae CandoNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Data CollectionDocument58 pagesUnit 3 Data Collectionkomalkataria2003No ratings yet
- Practical Research I: Qualitative Research Reviewer: Free Online Database SamplesDocument3 pagesPractical Research I: Qualitative Research Reviewer: Free Online Database SamplesElenear De OcampoNo ratings yet
- Method and Technique of Data Collection: Primary and Secondary DataDocument44 pagesMethod and Technique of Data Collection: Primary and Secondary DataSuruchi Kaprwan100% (2)
- Semifinal ResearchDocument8 pagesSemifinal Researchvaldez.adler.lNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Research ProposalDocument20 pagesHow To Write A Research ProposalFeyzar Al Fariq DjakajaNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Research ProposalDocument20 pagesHow To Write A Research ProposalFeyzar Al Fariq DjakajaNo ratings yet
- Research DefinitionsDocument51 pagesResearch DefinitionsHari PrasadNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Research DesignDocument44 pagesUnit 4 Research DesignAyush DNo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument41 pagesResearchawais khanNo ratings yet
- English 10 ReviewerDocument2 pagesEnglish 10 ReviewerMaYTiNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in RDL: ResearchDocument8 pagesReviewer in RDL: ResearchNathalie Nichole I. Inductivo Pesta�oNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument65 pagesUntitledKarthika.A 20COHE017No ratings yet
- Tomato ProductionDocument29 pagesTomato ProductionjoneforshoNo ratings yet
- Chapter FiveDocument20 pagesChapter FiveYared BitewNo ratings yet
- The Research Process As 8-Step Model - Research Methods Psychology)Document13 pagesThe Research Process As 8-Step Model - Research Methods Psychology)Puneet SoodNo ratings yet
- EN - 6 - Research Methods - 2022-2023 - Empirical StudyDocument18 pagesEN - 6 - Research Methods - 2022-2023 - Empirical Studypierre-benoit.alaisNo ratings yet
- E Passbook 2024 02 19 17 04 55 PMDocument25 pagesE Passbook 2024 02 19 17 04 55 PMRajju RajjuNo ratings yet
- Kolimi Abdul Rajak ResumeDocument3 pagesKolimi Abdul Rajak ResumeRajju RajjuNo ratings yet
- Time Table April 2017 Phy. EduDocument3 pagesTime Table April 2017 Phy. EduRajju RajjuNo ratings yet
- Pine Outlets Locations 23022021Document157 pagesPine Outlets Locations 23022021Rajju RajjuNo ratings yet
- FINAL EXAM Exam in Oral CommunicationDocument3 pagesFINAL EXAM Exam in Oral CommunicationSofia Tulabing75% (4)
- Write Up - Data Analysis & InterpretationDocument10 pagesWrite Up - Data Analysis & InterpretationReem NurNo ratings yet
- Thesis - Angela Josette Magon - Gender, The Brain and Education Do Boys and Girls Learn Differently PDFDocument108 pagesThesis - Angela Josette Magon - Gender, The Brain and Education Do Boys and Girls Learn Differently PDFmeristafauziahNo ratings yet
- Cause and Effect EssayDocument25 pagesCause and Effect Essayersoy100% (1)
- What Is Science?: Include Thinking Skills Science Process SkillsDocument7 pagesWhat Is Science?: Include Thinking Skills Science Process Skillsollie tikaNo ratings yet
- Morphed Animal Rubric 2015Document1 pageMorphed Animal Rubric 2015api-325718341No ratings yet
- Kingfisher School of Business and Finance: Keitsen'S Shared VisionDocument4 pagesKingfisher School of Business and Finance: Keitsen'S Shared VisionRomel BucaloyNo ratings yet
- Writing Negative Messages: Chapter 9 - 1Document29 pagesWriting Negative Messages: Chapter 9 - 1Arijit DasNo ratings yet
- Action Research Using Strategic Inquiry To Improve Teaching and Learning 1st Edition Rock Test BankDocument35 pagesAction Research Using Strategic Inquiry To Improve Teaching and Learning 1st Edition Rock Test Banksophic.shikaree.y8rt100% (26)
- Research Paper (20 PTS) - GuidelinesDocument1 pageResearch Paper (20 PTS) - GuidelinesjasonmscofieldNo ratings yet
- Kelsey Sherman ResumeDocument2 pagesKelsey Sherman Resumeapi-547816688No ratings yet
- Reflective Journal RubricDocument1 pageReflective Journal Rubricapi-202765737No ratings yet
- Week 2 NuhanDocument5 pagesWeek 2 NuhanCikgu Nuhan BalliaNo ratings yet
- Speech According To Manner of DeliveryDocument19 pagesSpeech According To Manner of DeliveryPerfect BeanNo ratings yet
- TV Can Be A Good ParentDocument6 pagesTV Can Be A Good ParentPuna Ram GhimireNo ratings yet
- Essential Research Skills For Teens Unit - Sheet1 2Document9 pagesEssential Research Skills For Teens Unit - Sheet1 2api-642237718No ratings yet
- Operant ConditioningDocument14 pagesOperant Conditioningniks2409No ratings yet
- Principles of LearningDocument8 pagesPrinciples of LearningRoxan DosdosNo ratings yet
- Mini RPT Tahun 4 W1-W5Document2 pagesMini RPT Tahun 4 W1-W5ROSNAKIAH BINTI HOSNIN KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organizational Systems: UNIT-2Document50 pagesIntroduction To Organizational Systems: UNIT-2nandini swamiNo ratings yet
- Steup - An Introduction To Contemporary EpistmeologyDocument127 pagesSteup - An Introduction To Contemporary Epistmeologytruchulo23No ratings yet
- CU Cullture of Divinity Ture of Divinity: Madhusüdana Month, 529th Gaura-Era (May 2015) Sixth IssueDocument14 pagesCU Cullture of Divinity Ture of Divinity: Madhusüdana Month, 529th Gaura-Era (May 2015) Sixth IssueMehul AahirNo ratings yet
- 09 - Chapter 2 PDFDocument43 pages09 - Chapter 2 PDFIrizh DanielleNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Philosophy - HeideggerDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Philosophy - HeideggerRonaldo Carvalho100% (1)
- An Exploratory Examination of The EffectDocument8 pagesAn Exploratory Examination of The EffectPaula CelsieNo ratings yet
- PHD Thesis On Development EconomicsDocument6 pagesPHD Thesis On Development Economicsleslylockwoodpasadena100% (2)
- Instant Download Ebook PDF Exploring Child Adolescent Development by Laura e Berk PDF ScribdDocument42 pagesInstant Download Ebook PDF Exploring Child Adolescent Development by Laura e Berk PDF Scribdida.clemmons523100% (47)
- Intermediate ReadingDocument2 pagesIntermediate Readingapi-33610044No ratings yet
- PDP PrashantDocument4 pagesPDP PrashantprashantNo ratings yet
- Research Methods in Cognitive PsychologyDocument3 pagesResearch Methods in Cognitive Psychologyi am PerfectNo ratings yet