Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Study On Catalyst
Study On Catalyst
Uploaded by
Vivek BhoirOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Study On Catalyst
Study On Catalyst
Uploaded by
Vivek BhoirCopyright:
Available Formats
STUDY ON
CATALYST
Guided by : C.B.Patil
Submited By:
Deepak Nitin Vishe
Shaikh Mubashira
Vivek Bhoir
ALPINE SKI HOUSE
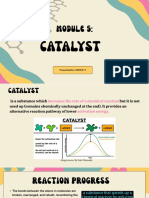
WHAT IS CATALYST?
A Catalyst is a substance that increases
the rate of reaction and recover at the end of
the reaction.
It speeds up a chemical reaction by
providing an alternative reaction pathway with
lower activation energy, which is the minimum
energy required for the reactants to transform
into products.
ALPINE SKI HOUSE
HOMOGENOUS CATALYSTS
TYPES OF CATALYSTS
Homogenous Catalysts
Heterogeneous Catalysts
Enzymatic Catalysts
If in a reaction the reactants , products and the catalysts are I the
same phase are called as Homogeneous Catalyst.
Examples of homogeneous catalysts include various acids, bases,
transition metal complexes, and organometallic compounds.
ALPINE SKI HOUSE
HETEROGENEOUS CATALYSTS
TYPES OF CATALYSTS
Homogenous Catalysts
Heterogeneous Catalysts
Enzymatic Catalysts
If in a reaction the reactants , products and the catalysts are In
the different phase are called as Heterogeneous Catalyst.
Examples of heterogeneous catalysts include Transition Metals,
Zeolites, Metal Oxides, and organometallic compound,etc.
ALPINE SKI HOUSE
ENZYMATIC CATALYSTS
TYPES OF CATALYSTS
Homogenous Catalysts
Heterogeneous Catalysts
Enzymatic Catalysts
Enzyme catalysts or enzymes as a catalyst are biocatalysts that
can be utilised in the transformation of organic compounds.
Examples of enzymatic reactions include the digestion of food in
the human body, the synthesis of DNA and RNA, and the
conversion of glucose into energy through cellular respiration.
ALPINE SKI HOUSE
HOW CATALYST WORKS?
Activation Energy: Activation energy is the minimum
amount of energy required to initiate a chemical
reaction.
Mechanism:Catalysts typically speed up a reaction by reducing
the activation energy or changing the reaction mechanism.
ALPINE SKI HOUSE
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES
ALPINE SKI HOUSE
INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS OF CATALYSTS
• Petroleum Refining:Catalysts, such as zeolites and metal oxides
• Chemical Synthesis: In production of ammonia (Haber-Bosch process), the synthesis of methanol, and the manufacture of various
chemicals, plastics, and polymers.
• Pharmaceuticals:Enzyme catalysts
• Food Industry:Enzymatic catalysts, known as enzymes, are widely used in food production.
• Environmental Protection:Catalytic converters in automobiles contain catalysts like platinum and palladium
ALPINE SKI HOUSE
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, catalysts are like magical helpers in
the world of chemistry and industry. They speed
up important reactions, making them happen
faster and more efficiently. They're used in many
things we use every day, from making fuel for cars
to cooking up medicines and even cleaning the air.
Catalysts are not only making our lives better but
also helping to protect our environment by
reducing pollution.
ALPINE SKI HOUSE
ALPINE SKI HOUSE
You might also like
- Unit 6 Progress Test 1 AnswersDocument2 pagesUnit 6 Progress Test 1 Answersjoboga2375% (4)
- Ion Exchange Resins and Adsorbents in Chemical Processing: Second EditionFrom EverandIon Exchange Resins and Adsorbents in Chemical Processing: Second EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- S.D. Burke and R.L. Danheiser - Handbook of Reagents For Organic Synthesis: Oxidizing and Reducing AgentsDocument6 pagesS.D. Burke and R.L. Danheiser - Handbook of Reagents For Organic Synthesis: Oxidizing and Reducing AgentsRoundSTICNo ratings yet
- CATALYSIS by Tejas SahooDocument15 pagesCATALYSIS by Tejas Sahootejassahoo123No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 CatalysisDocument28 pagesLecture 1 CatalysisMo MobarkNo ratings yet
- 1FFF11B1BD16627EE05400144FEB5F70.pptDocument63 pages1FFF11B1BD16627EE05400144FEB5F70.pptNur AishaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Heterogeneous Catalysis: Letcture-1Document14 pagesIntroduction To Heterogeneous Catalysis: Letcture-1hamoodahNo ratings yet
- Pre-Lab 3: 1. What Is A Catalyst and A Catalysis Reaction?Document3 pagesPre-Lab 3: 1. What Is A Catalyst and A Catalysis Reaction?Trần NguyênNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Engineering 2Document99 pagesBiochemical Engineering 2Enaye MajiriNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - The Kinetics of Enzyme Catalyzed ReactionsDocument18 pagesLecture 1 - The Kinetics of Enzyme Catalyzed ReactionsGenevive S. de VeraNo ratings yet
- Prelab 4Document6 pagesPrelab 4Trần Xuân QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Catalysts and CatalysisDocument10 pagesCatalysts and CatalysisKMNo ratings yet
- Pre-Lab 4: 1. What Is A Catalyst and A Catalysis Reaction?Document4 pagesPre-Lab 4: 1. What Is A Catalyst and A Catalysis Reaction?Giao TranNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Kinetics and Applications (Part 1a: Kinetics of Enzyme Catalyzed Reactions)Document26 pagesEnzyme Kinetics and Applications (Part 1a: Kinetics of Enzyme Catalyzed Reactions)Nur AishaNo ratings yet
- Teknologi KatalisDocument18 pagesTeknologi KatalisAttNo ratings yet
- Catalyst Catalysis: Industrial ChemistryDocument23 pagesCatalyst Catalysis: Industrial ChemistryjantskieNo ratings yet
- SCE3204 Lecture 2Document31 pagesSCE3204 Lecture 2ainomugisha arnoldNo ratings yet
- Catalysis & Catalysts: Facts and Figures About CatalystsDocument88 pagesCatalysis & Catalysts: Facts and Figures About CatalystskeatyNo ratings yet
- CatalysisDocument28 pagesCatalysisunknownNo ratings yet
- CatalysisDocument2 pagesCatalysisSuter EvansNo ratings yet
- CH4003 - Lecture Notes 11-21Document88 pagesCH4003 - Lecture Notes 11-21Khalid M MohammedNo ratings yet
- Human Body Is A Product of Different Chemical Reactions and Processes, But What Controls These Reactions?Document8 pagesHuman Body Is A Product of Different Chemical Reactions and Processes, But What Controls These Reactions?ZiarineNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes EnzymeDocument8 pagesBio Notes EnzymeMena Velante MarabeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 NewDocument102 pagesChapter 1 NewFakhrulShahrilEzanieNo ratings yet
- CatalystsDocument2 pagesCatalystsusulasia777No ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Activation Energy and How Catalyst Affects Rate of ReactionDocument5 pagesLesson 4 - Activation Energy and How Catalyst Affects Rate of ReactionJeff ValdezNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY LECTURE NotesDocument31 pagesBIOCHEMISTRY LECTURE NotesFREDRICK OUNDONo ratings yet
- 3 PDFDocument11 pages3 PDFFranchezca ChavezNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Biology Sec.2.4Document33 pagesGrade 10 Biology Sec.2.4zakaria AlshurmanNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: by Nura Malahayati THP-FP UnsriDocument71 pagesEnzymes: by Nura Malahayati THP-FP UnsriIkhsan muttaqinNo ratings yet
- Physci Catalyst 101Document34 pagesPhysci Catalyst 101Kyuptonite KimNo ratings yet
- Chem. Termpaper 1 .RK6004B41Document13 pagesChem. Termpaper 1 .RK6004B41supriyakumari7No ratings yet
- Catalysis & Catalysts: Facts and Figures About CatalystsDocument88 pagesCatalysis & Catalysts: Facts and Figures About CatalystsAonigioaiei Carmen NicoletaNo ratings yet
- Types of Catalysts: Homogeneous CatalystsDocument1 pageTypes of Catalysts: Homogeneous CatalystsAwaisNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of EnzymesDocument44 pagesBiochemistry of EnzymesShaira Elyze GabrielNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On CatalystDocument48 pagesLecture Notes On CatalystJITENDRA CARPENTER100% (1)
- Heterogeneous Catalysis: Ph.D. Course Work Report Submitted by Poonam Reddu Research ScholarDocument21 pagesHeterogeneous Catalysis: Ph.D. Course Work Report Submitted by Poonam Reddu Research ScholarSurender MalikNo ratings yet
- Kinetika Kimia: Studi/kajian Tentang Laju ReaksiDocument38 pagesKinetika Kimia: Studi/kajian Tentang Laju Reaksiakbar yudha angkasaNo ratings yet
- Catalyst Science & Technology Lab. By: Year Dr. Farhad & Mr. MohammedDocument12 pagesCatalyst Science & Technology Lab. By: Year Dr. Farhad & Mr. MohammedMUHAMMAD AKRAMNo ratings yet
- Catalysis: by Prof. Abhinav Shukla 9096905695Document12 pagesCatalysis: by Prof. Abhinav Shukla 9096905695Noor AL HudaNo ratings yet
- Pure Biology CHP 5 Enzymes 1Document35 pagesPure Biology CHP 5 Enzymes 1rabiayub21No ratings yet
- KatalisDocument37 pagesKatalismeri hardina zdNo ratings yet
- Catalysis: Srujal RanaDocument45 pagesCatalysis: Srujal RanavandanNo ratings yet
- Surface Chemistry - 3Document15 pagesSurface Chemistry - 3PREJAN RAJANo ratings yet
- Practical 4: ENZYMES: Student Name: Lê Hà Phương Ly ID: BTBTIU21220Document3 pagesPractical 4: ENZYMES: Student Name: Lê Hà Phương Ly ID: BTBTIU21220Le Phuong LyNo ratings yet
- Homogeneous Catalysis-243762230Document35 pagesHomogeneous Catalysis-243762230Rahim KalathilNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document18 pagesLecture 2warden tambiNo ratings yet
- Fine Chemicals - CatalystsDocument46 pagesFine Chemicals - CatalystsSiddharth chandan dasNo ratings yet
- Enzyme RegulationDocument36 pagesEnzyme RegulationVincentNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Lect-6Document26 pagesEnzymes Lect-6Yonas Isa'acNo ratings yet
- CREII-Module-I - Lecture 2Document28 pagesCREII-Module-I - Lecture 2Aditya parasNo ratings yet
- Mekelle University Ethiopian Institute of Technology-Mekelle Department of Chemical Engineering Process EngineeringDocument77 pagesMekelle University Ethiopian Institute of Technology-Mekelle Department of Chemical Engineering Process EngineeringetayhailuNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Dr. Walid Said Zaki Lecturer of Biochemistry & Molecular BiologyDocument52 pagesEnzymes: Dr. Walid Said Zaki Lecturer of Biochemistry & Molecular Biologyeman el saeedNo ratings yet
- Catalysis PDFDocument23 pagesCatalysis PDFFlorence FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Catalyst DefinitionDocument17 pagesCatalyst DefinitionTRIBRATA BASKORONo ratings yet
- Catalytic Chemistry in Industry: PremiseDocument36 pagesCatalytic Chemistry in Industry: Premisejai d gr8No ratings yet
- Enzyme: Ns. Shila Wisnasari, S.Kep., M.BiomedDocument55 pagesEnzyme: Ns. Shila Wisnasari, S.Kep., M.BiomedSyahdaJuvenilProfitamelaNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument46 pagesEnzymesHighlifeNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument18 pagesEnzymesMarie Veatrice Jacomille100% (1)
- C1 W14 EnzymesDocument49 pagesC1 W14 EnzymesJasmine Kaye CuizonNo ratings yet
- Materi 2Document34 pagesMateri 2siti purnamaNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 - Catalysis and Catalytic ReactorsDocument44 pagesUnit-1 - Catalysis and Catalytic ReactorsAP Naidu UNo ratings yet
- Learner AutonomyDocument3 pagesLearner AutonomyvanessitacoolNo ratings yet
- CCNA1 R&S Introducion A Las RedesDocument3 pagesCCNA1 R&S Introducion A Las RedesJorge Antonio MartinezNo ratings yet
- Alexa Griffiths: Special Educator - Allen, TXDocument1 pageAlexa Griffiths: Special Educator - Allen, TXapi-549213511No ratings yet
- MOTIVATIONDocument14 pagesMOTIVATIONJohn PaulNo ratings yet
- Sci8 Q1-M1 Laws of MotionDocument30 pagesSci8 Q1-M1 Laws of MotionPagudpud National HSNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - Technology For Teaching and LearningDocument2 pagesActivity 1 - Technology For Teaching and LearningRivera, Trishia PilonNo ratings yet
- Stage 1: Identify Desired Results or OutcomeDocument6 pagesStage 1: Identify Desired Results or OutcomestefknNo ratings yet
- Employability Skills Front SheetDocument10 pagesEmployability Skills Front SheetWijdan saleemNo ratings yet
- FS 2 Ep 16Document4 pagesFS 2 Ep 16Hanz Christian PadiosNo ratings yet
- Grundtvig Project LeadlabDocument2 pagesGrundtvig Project LeadlabEleonora GuglielmanNo ratings yet
- Exothermic, Endothermic WebquestDocument2 pagesExothermic, Endothermic Webquestshaylabrack1No ratings yet
- Objective Means of Verification Description of Mov Presented AnnotationsDocument2 pagesObjective Means of Verification Description of Mov Presented AnnotationsJonicaJaneJoseNo ratings yet
- How Learners' Needs Affect Syllabus Design: Setting General and Specific ObjectivesDocument3 pagesHow Learners' Needs Affect Syllabus Design: Setting General and Specific ObjectivesRania Abd El-WhabNo ratings yet
- Cl-XI LP03 Value of Determinants, Minors and Co-FactorsDocument2 pagesCl-XI LP03 Value of Determinants, Minors and Co-FactorsTshering TashiNo ratings yet
- Sarah L. Williamson: EducationDocument2 pagesSarah L. Williamson: Educationapi-354618203No ratings yet
- Resume ReflectionDocument2 pagesResume Reflectionapi-457004717No ratings yet
- Instructional Design ModelsDocument29 pagesInstructional Design Modelsapi-580144661No ratings yet
- Stephen KrashenDocument7 pagesStephen KrashenjamesramilNo ratings yet
- Workshop ScheduleDocument2 pagesWorkshop ScheduleatozdhiyanesNo ratings yet
- Patrick Mackenzie ResumeDocument3 pagesPatrick Mackenzie Resumeapi-446551981No ratings yet
- Sigmatropic - Processes SunitaDocument43 pagesSigmatropic - Processes SunitaShivraj BhosikarNo ratings yet
- Is Massive Tree Planting A Good Response To Climate Change?Document2 pagesIs Massive Tree Planting A Good Response To Climate Change?Lutfullah RasikhNo ratings yet
- Transfer: Transfer Goal Performance TaskDocument3 pagesTransfer: Transfer Goal Performance TaskDonna VariasNo ratings yet
- MEM 673 Assignment Individu - 2018!04!01Document3 pagesMEM 673 Assignment Individu - 2018!04!01Azrul ZafrieNo ratings yet
- Developmental Plan 2021 2022 Manlises Joanne PDocument2 pagesDevelopmental Plan 2021 2022 Manlises Joanne PJoanne ManlisesNo ratings yet
- 8.4.3 Institutionalizing The Philippine Greenhouse Gas Inventory Management and Reporting System PDFDocument12 pages8.4.3 Institutionalizing The Philippine Greenhouse Gas Inventory Management and Reporting System PDFChrlene CoNo ratings yet
- Small Group Teaching: Presenter: Dr. Pravin Moderator: Dr. PrasadDocument38 pagesSmall Group Teaching: Presenter: Dr. Pravin Moderator: Dr. PrasadPravin SurendranNo ratings yet
- CoachDocument4 pagesCoachapi-401497100No ratings yet