Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Research Scope in Nuclear Energy
Uploaded by
mininghod240 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views22 pagesOriginal Title
Research scope in Nuclear Energy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views22 pagesResearch Scope in Nuclear Energy
Uploaded by
mininghod24Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 22
RESEARCH SCOPE IN NUCLEAR ENERGY
Dr. Lalit Singh
Senior Scientist
Head, Artificial Intelligence Applications
NPCIL-BARC
Department of Atomic Energy
Government of India
Nuclear Reactor
➢ Device designed to maintain a chain
reaction producing a steady flow of
neutrons generated by the fission of
heavy nuclei.
➢ It is an apparatus in which heat is
produced due to nuclear fission chain
reaction for the generation of the
electricity.
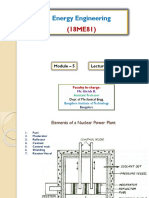
Components of Nuclear Reactor
Pressure Vessel / Tubes
➢ Usually a robust steel vessel
containing the reactor core and
moderator/coolant.
➢ Or it may be a series of tubes
holding the fuel and conveying the
coolant through the surrounding
moderator.
Reactor Core
➢ It consists of fuel elements,
control rods, coolant,
moderator.
➢ Cores generally have shapes of
right circular cylinders with
diameters ranging from 0.5 to
15 metres.
Reflector
➢ It is placed round the
core, to reflect back
some of the neutrons
that leak out from core
surface.
Fuel
➢ Uranium-235 is the basic
fuel.
➢ Usually pellets of uranium
oxide (UO2) are arranged in
tubes to form fuel rods.
Control Rods
➢ Usually made up of cadmium or boron.
➢ Function:
✓ Slow down the rate of reaction to a
controllable limit . Other wise chain
reaction blows up like a nuclear bomb.
✓ Raising and lowering the control rods
allow operators to control the rate of the
nuclear reaction.
Moderator
➢ Function: -
To slow down neutrons
from high velocities and hence high energy
level which they have on being released
from fission process so that probability of
neutron to hit the fuel rods increases.
➢ Main moderator used: -
Water H2O
Heavy water D2O
Graphite
Beryllium
Coolant
➢Function: -
Coolant is used to remove intense heat produced
in the reactor and that heat can be transferred to water in a separate
vessel which is converted into steam and runs the turbine.
➢ Main coolant used: -
Water H2O , CO2, Hg, He
Containment
➢ The structure around the reactor and associated steam
generators which is designed to protect it from outside
intrusion and to protect those outside from the effects of
radiation in case of any serious malfunction inside.
➢ It is typically a meter-thick concrete and steel structure.
Nuclear
Power
Plants in
India
Classification of Nuclear Reactor: -
1. On the basis of Neutron Energy 4. On the basis of Coolant used
a) Fast Reactors a) Water cooled reactor (Ordinary
b) Thermal Reactors or Heavy)
2. On the basis of Fuel used b) Gas cooled reactor
a) Natural fuel c) Liquid metal cooled reactor
b) Enriched Uranium d) Organic liquid cooled reactor
3. On the basis of Moderator used
a) Water Moderator
b) Heavy water Moderator
c) Graphite Moderator
d) Beryllium Moderator
Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR)
Boiling Water Reactor (BWR)
Disadvantages
Possibility of radioactive contamination in the turbine
mechanism.
Safety precautions are needed which can turn out to be costly.
Wasting of steam and resulting of lower thermal efficiency.
Only 3% - 5% by mass can be converted to steam per pass.
Control Room
Control Room
Artificial Intelligence Applications
Questions?
Thank You
https://www.youtube.com/@easyml1615
You might also like
- Types of Nuclear ReactorDocument32 pagesTypes of Nuclear Reactorsapna100% (1)
- NIHARDocument18 pagesNIHARsubudhihareshNo ratings yet
- Chapter-Iii Nuclear Power StationDocument24 pagesChapter-Iii Nuclear Power StationPrathap VuyyuruNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Reactors: Presented To: Sir Aiman ShabbirDocument33 pagesNuclear Reactors: Presented To: Sir Aiman Shabbirabubakar chohaanNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power PlantDocument50 pagesNuclear Power PlantBLACK GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Neuclear Power Plants PresentationDocument24 pagesNeuclear Power Plants PresentationShreeNo ratings yet
- ME5129 - Lecture XXIDocument13 pagesME5129 - Lecture XXIAnandNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Nuclear Reactor: Bhabani Sankar Hota ROLL NO - 107EE007Document28 pagesSeminar On Nuclear Reactor: Bhabani Sankar Hota ROLL NO - 107EE007Saptarshi Pal ChaudhuriNo ratings yet
- B Nuclear Power PlantsDocument21 pagesB Nuclear Power PlantsArun PatilNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Plant: Swami Keshvanand Institute of Technology Management & Gramothan, JaipurDocument27 pagesNuclear Power Plant: Swami Keshvanand Institute of Technology Management & Gramothan, JaipurNikhil ChopraNo ratings yet
- Boiling Water Reactor (BWR)Document7 pagesBoiling Water Reactor (BWR)SudharshanNo ratings yet
- Lecture #4 Fission Reactor 1Document11 pagesLecture #4 Fission Reactor 1Kennedy Oswald AikaruwaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear PowerplantDocument39 pagesNuclear Powerplantwiljhon sunioNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Plant: LoungeDocument38 pagesNuclear Power Plant: LoungeRaveendran KNo ratings yet
- ME 5129 - Principles of Thermal Energy Conversion: Introduction To Nuclear Power ReactorsDocument12 pagesME 5129 - Principles of Thermal Energy Conversion: Introduction To Nuclear Power ReactorsAnandNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Plant: Nishkam Dhiman Asst Prof: Electrical and Electronics Engineering Chitkara University, PunjabDocument38 pagesNuclear Power Plant: Nishkam Dhiman Asst Prof: Electrical and Electronics Engineering Chitkara University, PunjabCarlos WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- Nikhil Gaurav MSESP75010Document23 pagesNikhil Gaurav MSESP75010RabinNo ratings yet
- Nuclearpowerplant 170804051105Document31 pagesNuclearpowerplant 170804051105Carlos WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Reactor and Power Plant:: Research Reactors Are Operated at Universities and Research CentresDocument19 pagesNuclear Reactor and Power Plant:: Research Reactors Are Operated at Universities and Research CentresNiteshBhuwaniaNo ratings yet
- Solution Winter-17 Subject: Energy Conversion - IIIDocument8 pagesSolution Winter-17 Subject: Energy Conversion - IIIsuhasvkaleNo ratings yet
- Nuclear ReactorDocument2 pagesNuclear Reactorrajath_vubaNo ratings yet
- Types of Reactors Used in Nuclear Power Plants: Generation of Electrical ENERGY (13EE63)Document20 pagesTypes of Reactors Used in Nuclear Power Plants: Generation of Electrical ENERGY (13EE63)PreethiNo ratings yet
- Nuclear PP1Document23 pagesNuclear PP1Aiyub MiahNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power PlantDocument12 pagesNuclear Power PlantAnil BhattaNo ratings yet
- Elements of Nuclear Power StationDocument50 pagesElements of Nuclear Power StationHassan MalghaniNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document43 pagesUnit 2A ABHISHEK MARSHALLNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Plant-1Document10 pagesNuclear Plant-1tiweb53031No ratings yet
- 5th Series by DR - KaleemDocument41 pages5th Series by DR - KaleemBobNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power PlantDocument27 pagesNuclear Power PlantYash MenonNo ratings yet
- Nuclearpowerplant 3 PDFDocument48 pagesNuclearpowerplant 3 PDFmharitmsNo ratings yet
- UNIT-IV-Nuclear Power Plant-IDocument13 pagesUNIT-IV-Nuclear Power Plant-IMehdiNo ratings yet
- UGC - 9 - Ali HosinDocument7 pagesUGC - 9 - Ali HosinVIKRAM KUMARNo ratings yet
- Reactor, Its Components, TypesDocument32 pagesReactor, Its Components, TypesAzhar AliNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Reactor: How It WorksDocument17 pagesNuclear Reactor: How It WorkscbeprabhugmailNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power StationDocument42 pagesNuclear Power StationTonmoy SinghaNo ratings yet
- 5 Chapter-5Document24 pages5 Chapter-5hamzah dayyatNo ratings yet
- Nuclear ReactorsDocument45 pagesNuclear ReactorsAtul100% (3)
- PPE LAYOUTpower Plant)Document29 pagesPPE LAYOUTpower Plant)Akash smartNo ratings yet
- What Is A Nuclear ReactorDocument12 pagesWhat Is A Nuclear ReactorShams ShamsNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power PlantDocument16 pagesNuclear Power PlantSUMANTA KUMAR NAIKNo ratings yet
- M5 - L3 - Different Nuclear ReactorsDocument27 pagesM5 - L3 - Different Nuclear ReactorsGirish DNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power ReactorsDocument10 pagesNuclear Power ReactorsJos TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- Components of Nuclear ReactorDocument17 pagesComponents of Nuclear ReactormrinalNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Advanced NPP-2Document11 pagesLecture - Advanced NPP-2Shams ShawonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Nuclear Power PlantDocument28 pagesChapter 4-Nuclear Power PlantbaseakelNo ratings yet
- Amantarakesh 170306122801Document16 pagesAmantarakesh 170306122801Sam RajibNo ratings yet
- Nuclear ReactorDocument21 pagesNuclear ReactorPrajithNo ratings yet
- Nuclear TechnologyDocument18 pagesNuclear Technologysipun acharyaNo ratings yet
- NuclearDocument49 pagesNuclearA ABHISHEK MARSHALLNo ratings yet
- Best On ReactorsDocument13 pagesBest On Reactorshafeez khanNo ratings yet
- Various Types of Reactors With Special Reference To India & Brief Design FeaturesDocument19 pagesVarious Types of Reactors With Special Reference To India & Brief Design Featurespetros jereNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Plant PDFDocument4 pagesNuclear Plant PDFSamsung TabletNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power PlantDocument125 pagesNuclear Power PlantJomari BautistaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear ReactorsDocument11 pagesNuclear ReactorsadhamelthnNo ratings yet
- Amantarakesh 170306122801Document16 pagesAmantarakesh 170306122801Sam RajibNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy: Saswata Bag 14/CE/92 Haldia Institute of TechnologyDocument18 pagesNuclear Energy: Saswata Bag 14/CE/92 Haldia Institute of TechnologySaswata PradhanNo ratings yet
- M5 - L2 - Elements of NUCLEAR POWER PLANTDocument19 pagesM5 - L2 - Elements of NUCLEAR POWER PLANTGirish DNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy: Saswata Bag 14/CE/92 Haldia Institute of TechnologyDocument16 pagesNuclear Energy: Saswata Bag 14/CE/92 Haldia Institute of TechnologySaswata PradhanNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Plant: Er. Shaikh Arshad Vjti Mtech CM Guided By: Dr. Sumedh MhaskeDocument25 pagesNuclear Power Plant: Er. Shaikh Arshad Vjti Mtech CM Guided By: Dr. Sumedh Mhaskeফারহান আহমেদ আবীরNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow in Nuclear SystemsFrom EverandHeat Transfer and Fluid Flow in Nuclear SystemsHenri FenechNo ratings yet
- MAX Communication Protocol20210217Document26 pagesMAX Communication Protocol20210217Алексей ЫкнкемнNo ratings yet
- Helium Balloon Windmill: International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)Document6 pagesHelium Balloon Windmill: International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)Akhila AkkiNo ratings yet
- Geoactive 1 Stage 4 Global Geography by Susan BlissDocument408 pagesGeoactive 1 Stage 4 Global Geography by Susan BlissRoshan KonkisaNo ratings yet
- JO LBK-017 Unload CTUDocument1 pageJO LBK-017 Unload CTUbayuNo ratings yet
- Installation, Operation & Maintenance Manual: Sentry ET-100 Insertion ToolDocument12 pagesInstallation, Operation & Maintenance Manual: Sentry ET-100 Insertion Toolhernidasari hasibuanNo ratings yet
- 01 - Topic 1 - ElectricalDocument8 pages01 - Topic 1 - ElectricalAmaranthine FrazierNo ratings yet
- Rock Cycle PowerpointDocument30 pagesRock Cycle PowerpointIdkNo ratings yet
- Executive Summary: 0.1 Name of The WorkDocument12 pagesExecutive Summary: 0.1 Name of The WorkDevdoot SahuNo ratings yet
- Technical Datasheet - Rev01-OldDocument19 pagesTechnical Datasheet - Rev01-Oldkenneth1195No ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Astm A159 Standard Specification For Automotive Gray Iron CastingsDocument2 pagesDokumen - Tips - Astm A159 Standard Specification For Automotive Gray Iron CastingsJeovanne CabralNo ratings yet
- DeltaDocument59 pagesDeltasunil_gopalNo ratings yet
- Pumproom Layout Bldg. 8 & 9: Scale 1:30MDocument7 pagesPumproom Layout Bldg. 8 & 9: Scale 1:30MBrownstreet ArchitectsNo ratings yet
- CHL ArranX Zone2 Spec-1Document3 pagesCHL ArranX Zone2 Spec-1Jalal AlbadriNo ratings yet
- D'amico Questions 2023Document13 pagesD'amico Questions 2023Mohammed MazinNo ratings yet
- Massey Ferguson 2615 TRACTOR Service Parts Catalogue Manual (Part Number 3906193)Document17 pagesMassey Ferguson 2615 TRACTOR Service Parts Catalogue Manual (Part Number 3906193)hujiao66072800% (2)
- Wellbore Cleanup SolutionsDocument2 pagesWellbore Cleanup SolutionsmasgontarNo ratings yet
- Deputy Engineer ElectricalDocument3 pagesDeputy Engineer ElectricalSargi BeepumohanNo ratings yet
- ETHIOPIAN NATIONAL ENERGY POLICY Full 2013Document54 pagesETHIOPIAN NATIONAL ENERGY POLICY Full 2013EsheFikirNo ratings yet
- Installation, Use and Maintenance Manual: Chillers and Heat PumpsDocument68 pagesInstallation, Use and Maintenance Manual: Chillers and Heat PumpsesaNo ratings yet
- NNSD291Document26 pagesNNSD291Patrice PaulNo ratings yet
- 6653035147.1.6653614603 en-US MT431B - MT436B Stage II - Maintenance PDFDocument264 pages6653035147.1.6653614603 en-US MT431B - MT436B Stage II - Maintenance PDFeduamaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Multiple Choice Questions in Engineering MathematicsDocument159 pages3 - Multiple Choice Questions in Engineering MathematicsPJBautistaMaddumaNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification - HvacDocument46 pagesTechnical Specification - Hvacdhanu_lagwankarNo ratings yet
- ChE ReviewerDocument82 pagesChE ReviewerKristineNo ratings yet
- Sustainability 13 00794Document21 pagesSustainability 13 00794shiva19892006No ratings yet
- DIM100D283490 (1) - 7.5MVA - CommentsDocument1 pageDIM100D283490 (1) - 7.5MVA - CommentsnisarbashaNo ratings yet
- Datasheet - Solis 30K 5GDocument2 pagesDatasheet - Solis 30K 5GPablo Federico Hernández MenaNo ratings yet
- A Smart Fault Detection Approach For PV Modules Using Neuro-Fuzzy Inference FrameworkDocument14 pagesA Smart Fault Detection Approach For PV Modules Using Neuro-Fuzzy Inference FrameworkAndre RangelNo ratings yet
- Well Logs and Seismic Data Analysis ForDocument15 pagesWell Logs and Seismic Data Analysis Foridoko alfaNo ratings yet
- Manual WolfClasicDocument231 pagesManual WolfClasicedumoranrubNo ratings yet