Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Example - Section 6 - and Polymerization Steps
Uploaded by
MahlatseOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Example - Section 6 - and Polymerization Steps
Uploaded by
MahlatseCopyright:
Available Formats
Example
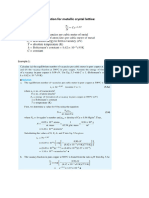
If a particular type of polyethylene has a molecular mass of 150,000 g/mol, what is its
degree of polymerization?
Solution
The repeating unit or mer for polyethylene is [ CH 2 — CH 2 ] . This mer has a mass of
4 atoms × 1 g = 4 g for the hydrogen atoms plus a mass of 2 atoms × 12 g = 24 g for the
carbon atoms, making a total of 28 g for each polyethylene mer.
𝑔
𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑐𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑟 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑝𝑜𝑙𝑦𝑚𝑒𝑟 ( )
𝐷𝑃 = 𝑚𝑜𝑙
𝑔
𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑎 𝑚𝑒𝑟 ( )
𝑚𝑒𝑟
150000 𝑔/𝑚𝑜𝑙
𝐷𝑃 =
28 𝑔/𝑚𝑒𝑟
= 5357 𝑚𝑒𝑟𝑠/𝑚𝑜𝑙
Polymerization Steps:
1. Initiation
Catalyst is used to initiate polymerization. Catalyst act as free radical formers.
Eg. Peroxide (H2O2) is used in polymerization of ethylene.
R-O+CH2=CH2 → R-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH.2
2. Propagation
This process extends the polymer chain by successive addition of monomer units.
Double bonds of monomers opens up by the extended free radical and covalently bonds to it.
R-CH2-CH2+CH2=CH2 → R-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH.2
3. Termination
Is the ending of the chain by addition of a terminator free radical or when 2 polymer chains
combine.
Termination by joining of 2 chains can be represented by:
R(CH2-CH2).m + R’(CH2-CH2).n → R(CH2-CH2)m – (CH2-CH2)nR’
You might also like
- Liquid Liquid ExtractionDocument10 pagesLiquid Liquid ExtractionDeepak Agarwal100% (1)
- Practical ReactionDocument8 pagesPractical ReactionToMemNo ratings yet
- Lembar Perhitungan ReagaenDocument8 pagesLembar Perhitungan ReagaenZahra AlifiaNo ratings yet
- 3 Steady State DiffusionDocument25 pages3 Steady State DiffusionShahadat AwanNo ratings yet
- Lec3 - Final - Revised Stat MechDocument16 pagesLec3 - Final - Revised Stat MechnokosamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - 0Document18 pagesChapter 4 - 0Tsiye TekleyohanisNo ratings yet
- Gas MixDocument20 pagesGas Mixİkigül Aşçıevladı KirlitaşNo ratings yet
- First LawDocument10 pagesFirst LawAhmed Al-ayatNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Chemical Equilibrium.9.08.22 - 1074551406Document26 pagesModule 5 - Chemical Equilibrium.9.08.22 - 1074551406Lei LopezNo ratings yet
- Equations & ConstantsDocument5 pagesEquations & ConstantsJoserineNo ratings yet
- Chbe 6300 Graduate Kinetics and Reactor Design: Carsten Sievers 8/18/2020Document18 pagesChbe 6300 Graduate Kinetics and Reactor Design: Carsten Sievers 8/18/2020AnnNo ratings yet
- Methanol From GlycerolDocument2 pagesMethanol From GlycerolAhmed YounisNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument8 pagesChemical Engineering ThermodynamicsP P DNo ratings yet
- Optimal Evaluation of Coag-Flocculation Factors For Refined PetroleumDocument10 pagesOptimal Evaluation of Coag-Flocculation Factors For Refined Petroleumchinenye igwegbeNo ratings yet
- 2015년봄 열전기Exam1Document11 pages2015년봄 열전기Exam1윤성욱No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document29 pagesChapter 2Bilal shahzadNo ratings yet
- Physic Calculation SheetDocument2 pagesPhysic Calculation Sheetsharon100% (2)
- Dimensions and Units Measures of Amount or SizeDocument5 pagesDimensions and Units Measures of Amount or SizennbNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Activity CoefficientDocument54 pagesThermodynamic Activity Coefficientneerajtrip123No ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetic 2Document5 pagesChemical Kinetic 2azadqayoommalikNo ratings yet
- Module 2.4 Enthalpy and 2ND Corollary of 1ST LawDocument6 pagesModule 2.4 Enthalpy and 2ND Corollary of 1ST LawsubyNo ratings yet
- ThermoDynamics ProcessDocument2 pagesThermoDynamics ProcessSTUDY BEASTNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Fluid Flow and MeasurementsDocument13 pagesFundamentals of Fluid Flow and MeasurementsdbircsNo ratings yet
- CHEM 1252 Exam Information Sheet Fall 2021Document2 pagesCHEM 1252 Exam Information Sheet Fall 2021Joe joeNo ratings yet
- FM IntroductionDocument14 pagesFM IntroductionJayden PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Tugas Termo DameDocument13 pagesTugas Termo DamedesisitompulNo ratings yet
- Example 8-11 Multiple Reaction in A PFRDocument4 pagesExample 8-11 Multiple Reaction in A PFRAenErzaAisyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 27 Thermal Engineering II (08.09.2020)Document81 pagesLecture 27 Thermal Engineering II (08.09.2020)Dr. BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Session 3Document6 pagesSession 3THE SEZARNo ratings yet
- Week 01-v.2Document5 pagesWeek 01-v.2Togi Jevenson SimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- Kunci JawabanDocument6 pagesKunci Jawabanriza fahlevineNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument10 pagesChemical Engineering ThermodynamicsP P DNo ratings yet
- MT112 - Week 6 - Lecture#01Document11 pagesMT112 - Week 6 - Lecture#01Muhammad AzeemNo ratings yet
- Midterm 1 - SolutionDocument2 pagesMidterm 1 - Solutioninci nisa çakırNo ratings yet
- Pak Hanif Reactions Approaching EquilibriumDocument17 pagesPak Hanif Reactions Approaching Equilibriumidew23No ratings yet
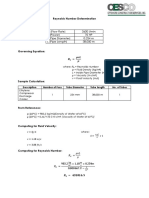
- Calculation of Fluid VelocityDocument3 pagesCalculation of Fluid VelocityArmand FloresNo ratings yet
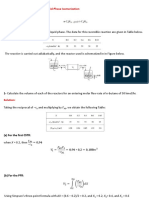
- University of The Philippines Chemical Engineering Society, Inc. (UP KEM)Document8 pagesUniversity of The Philippines Chemical Engineering Society, Inc. (UP KEM)AcademicBMNo ratings yet
- ThermoDocument2 pagesThermoSalvador Monroy GalvánNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer-DESKTOP-TMOCD0EDocument20 pagesMass Transfer-DESKTOP-TMOCD0EAshna WaseemNo ratings yet
- Diesel CycleDocument1 pageDiesel CycleGladys Ruth PaypaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document31 pagesLecture 1Nimit RiniNo ratings yet
- Week 10 Tutorial Chem R Eng 08-02-2023Document13 pagesWeek 10 Tutorial Chem R Eng 08-02-2023Zain Ul AbedinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 09 Thermal Ii (08.07.2020)Document40 pagesLecture 09 Thermal Ii (08.07.2020)Dr. BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- 2016년봄 열전기Exam1Document7 pages2016년봄 열전기Exam1윤성욱No ratings yet
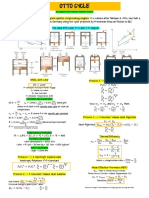
- The Ideal Otto CycleDocument1 pageThe Ideal Otto CycleNurlaila DalidigNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 2: Supplementary Notes Example: Comparison of Van Der Waals Forces For Pure SpeciesDocument14 pagesLECTURE 2: Supplementary Notes Example: Comparison of Van Der Waals Forces For Pure SpeciesAnıl KahvecioğluNo ratings yet
- Tugas Kelompok 6 Teknik Reaksi Kimia 2 Kelas 02: Additional InformationDocument12 pagesTugas Kelompok 6 Teknik Reaksi Kimia 2 Kelas 02: Additional InformationZakiaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 2 ThermodynamicsDocument5 pagesLecture Notes 2 ThermodynamicsAndrewNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Handout - Introduction To Reaction KineticsDocument14 pagesLecture 1 Handout - Introduction To Reaction Kineticsaliggulam16No ratings yet
- MCEE5210 2023F L6 Rate-Based MethodDocument74 pagesMCEE5210 2023F L6 Rate-Based Methodtc1992423No ratings yet
- محاضرة الكيمياء الفيزياوية 4Document3 pagesمحاضرة الكيمياء الفيزياوية 4Fuji 57No ratings yet
- Lecture 12 Thermal Ii (15 .07.2020)Document22 pagesLecture 12 Thermal Ii (15 .07.2020)Dr. BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 3 - Tugas 6 - TRK2-03-dikonversiDocument30 pagesKelompok 3 - Tugas 6 - TRK2-03-dikonversiMuhammad AzharNo ratings yet
- Q3 Pointers To ReviewDocument10 pagesQ3 Pointers To ReviewRonel CahayagNo ratings yet
- at What Temperature The Root Mean Square Velocity Will Be Half of That Standard Pressure and Temperature, The Pressure Being Kept ConstantDocument6 pagesat What Temperature The Root Mean Square Velocity Will Be Half of That Standard Pressure and Temperature, The Pressure Being Kept ConstantMohitNo ratings yet
- Cheat - Sheet - Exam 1Document2 pagesCheat - Sheet - Exam 1LoganNo ratings yet
- Introductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)From EverandIntroductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)No ratings yet
- Section 3 - Examples 1-5Document3 pagesSection 3 - Examples 1-5MahlatseNo ratings yet
- Solution To An Exercise - Section 3Document1 pageSolution To An Exercise - Section 3MahlatseNo ratings yet
- Examples - Section 3Document7 pagesExamples - Section 3MahlatseNo ratings yet
- OE - 2023 - Study GuideDocument40 pagesOE - 2023 - Study GuideMahlatseNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Chapter 1 - Productivity and Quality of Life ....Document38 pagesLecture 1 - Chapter 1 - Productivity and Quality of Life ....Mahlatse100% (1)