Professional Documents
Culture Documents
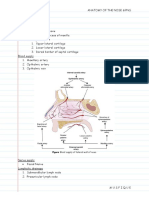
Nose
Uploaded by
aloysius limCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nose
Uploaded by
aloysius limCopyright:
Available Formats
Cartilages (Hyaline)
1. Septal + Lateral + Alar cartilages > allow for movement of nares (nostrils)
Boundaries
Roof Cribriform plate
Anterior portion:
1. Frontal bone
2. Nasal bone
3. Septal and alar cartilages
Posterior portion:
1. Sphenoid bone
2. Sphenoid process of palatine
3. Vomer bone
Floor Hard palate (horizontal plate of palatine + palatine processes of maxillary
bone)
Medial 1. Septal cartilage
(SVEMP) 2. Vomer
Six vultures eat 3. Ethmoid
my palatine 4. Maxillary
5. Palatine
Lateral 1. Sphenoid
(SIMPLE) 2. Inferior concha
3. Maxillary
4. Palatine
5. Lacrimal
6. Ethmoid (Superior + Middle concha)
Nasal concha Function: to create bigger surface area to warm air
Paranasal sinuses Function: Lighten head, produce mucus, increase speech resonance,
crumple zone to project vital structures in trauma
1. Frontal sinuses
2. Sphenoid sinuses
3. Ethmoid sinuses
4. Maxillary sinuses
Nasal meatuses All of them flow into Common Nasal Meatus
1. Sphenoethmoidal recess
2. Superior meatus
3. Middle meatus
4. Inferior meatus
Drainage (Stupid People Must Always Follow My proNouns)
Sphenoid sinus Sphenoethmoidal recess
Posterior ethmoid sinus Superior nasal meatus
Middle ethmoid sinus Opening in ethmoidal bulla
Anterior ethmoid sinus Middle nasal meatus (Ethmoidal infundibulum > SH)
Frontal sinus Middle nasal meatus (Ethmoidal infundibulum > SH)
Maxillary sinus Middle nasal meatus (Semilunar hiatus (SH))
Nasolacrimal sac Nasolacrimal duct > Inferior nasal meatus
Location
Sphenoid sinus Posterior to ethmoid sinus
Ethmoid sinus Between nasal cavity and orbit
Frontal sinus Between ethmoid and orbit
Maxillary sinus Inferior to orbit
Vasculature of nose - Arterial Supply
Lateral wall 1) ECA > Maxillary > Sphenopalatine > Lateral branch
(SAP) 2) ICA > Ophthalmic > Anterior ethmoidal > Lateral branch
3) ICA > Ophthalmic > Posterior ethmoidal > Lateral branch
Medial wall 1) ECA > Maxillary > Sphenopalatine > Medial branch
(SAP + 2) 2) ICA > Ophthalmic > Anterior ethmoidal > Medial branch
3) ICA > Ophthalmic > Posterior ethmoidal > Medial branch
+
4) ECA > Facial > Superior Labial > Septal branch
5) ECA > Maxillary > Greater Palatine
External nose 1) ECA > Facial > Superior Labial > Septal branch
(SAIL) 2) ICA > Ophthalmic > Anterior Ethmoidal > External Nasal branch
3) ECA > Maxillary > Infraorbital > Nasal branch
4) ECA > Facial > Lateral nasal
SAP + 2 anastomose at anterior part (Kiesselbach’s Area) where nosebleeds occur (epistaxis)
Venous drainage of internal nose
1. Facial arteries: Facial vein > IJV
2. Ophthalmic arteries: Ophthalmic vein > cavernous sinus > superior + inferior petrosal
sinus > sigmoid sinus > IJV
3. Maxillary arteries: Sphenopalatine vein > pterygoid plexus > maxillary vein > retro …
Venous drainage of external nose
1. Dorsal and lateral nasal veins > angular vein > facial vein > IJV
Pterygoid plexus: Important point of anastomoses > infection spread into cranial cavity
Innervation
1. Special sensation (Olfactory): CN1
2. General sensation: CNV1 + CNV2
Sphenoid sinus Posterior ethmoidal (V1)
Orbital branches from pterygopalatine ganglion (V2)
Ethmoid sinus Anterior + Posterior ethmoidal (V1)
Orbital branches from pterygopalatine ganglion (V2)
Frontal sinus Supraorbital (V1) + Supratrochlear (V1)
Maxillary sinus Infraorbital + Superior alveolar (V2)
3. Parasympathetic to serous glands: CN7 (greater petrosal nerve)
4. Sympathetic to serous glands: T1 of spinal cord
You might also like
- Scalp - Face - BrainDocument7 pagesScalp - Face - Brainaloysius limNo ratings yet
- 3 Nose - Paranasal Sinus (More Modified)Document28 pages3 Nose - Paranasal Sinus (More Modified)adham bani younesNo ratings yet
- The Skull & Vertebral ColumnDocument41 pagesThe Skull & Vertebral ColumnBadria Al-najiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1structure & Function of Respiratory System Nose & Paranasal SinusesDocument7 pagesLecture 1structure & Function of Respiratory System Nose & Paranasal Sinusesadham bani younesNo ratings yet
- 2 04 Upper Airways Larynx English 2014-2Document22 pages2 04 Upper Airways Larynx English 2014-2Mariam AlavidzeNo ratings yet
- Nose & Paranasal Sinuses 2018Document63 pagesNose & Paranasal Sinuses 2018yasrul izadNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Nose & Paranasal Air SinusesDocument4 pagesAnatomy of The Nose & Paranasal Air SinusesMusfique RashidNo ratings yet
- 1 Anatomy of Nose PnsDocument70 pages1 Anatomy of Nose PnsDubow DigaleNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Hidung Dan Sinus Paranasal 2Document54 pagesAnatomi Hidung Dan Sinus Paranasal 2anditri weningtyas0% (1)
- Mouth - Pharynx - LarynxDocument15 pagesMouth - Pharynx - Larynxaloysius limNo ratings yet
- The Head and Neck Lectures: Anas Ibrahim YahayaDocument242 pagesThe Head and Neck Lectures: Anas Ibrahim YahayaBilkisu badamasiNo ratings yet
- Summary of Anatomy-1Document23 pagesSummary of Anatomy-1Omer AlsameiNo ratings yet
- Skull Osteology & Cranial Cavity - TUSKDocument66 pagesSkull Osteology & Cranial Cavity - TUSKterima kasihNo ratings yet
- 0900 - L Kiss Anna - Eng - Skull IIDocument29 pages0900 - L Kiss Anna - Eng - Skull IIOrNo ratings yet
- Blood SupplyDocument10 pagesBlood Supplysyed ahmedNo ratings yet
- Prof. Hamiadji - Ear, Nose, Throat PDFDocument28 pagesProf. Hamiadji - Ear, Nose, Throat PDFSANDA NABILAH FATINNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Fisiologi HidungDocument29 pagesAnatomi Fisiologi HidungRomanna100% (1)
- 01 Head and Neck JMDocument16 pages01 Head and Neck JMJowi SalNo ratings yet
- Prof. DR - Mohamed Talaat ElghonemyDocument49 pagesProf. DR - Mohamed Talaat Elghonemyadel madanyNo ratings yet
- Bones of The H&NDocument12 pagesBones of The H&Naminshafihassan902No ratings yet
- Anatomy Orbit Nasalcavity Sinuses Cranial NervesDocument137 pagesAnatomy Orbit Nasalcavity Sinuses Cranial Nervesalhader libraryNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Nose and Sinus Paranasal, Case RhinosinusitisDocument51 pagesAnatomy of The Nose and Sinus Paranasal, Case RhinosinusitisDera Seta SaputriNo ratings yet
- Semilunare Gasseri) - What Is Located Here? 2.2.5. Internal Acoustic Opening (Porus Acusticus Internus)Document10 pagesSemilunare Gasseri) - What Is Located Here? 2.2.5. Internal Acoustic Opening (Porus Acusticus Internus)michelle leeNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi HidungDocument51 pagesAnatomi Dan Fisiologi HidungVania GirsangNo ratings yet
- 1 Advanced Anatomy of The ENTDocument63 pages1 Advanced Anatomy of The ENTMariam QaisNo ratings yet
- Cranial FossaDocument9 pagesCranial FossaDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Norma FrontalisDocument79 pagesNorma Frontalisrenzvalorant28No ratings yet
- Good Morning EverybodyDocument52 pagesGood Morning EverybodyJabedNo ratings yet
- Laughing Is Also Good For Your Respiratory System!Document5 pagesLaughing Is Also Good For Your Respiratory System!A-Naeem To'mah Al-sawaieNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report: (Scalp and Face, Ear and TIPS)Document23 pagesLaboratory Report: (Scalp and Face, Ear and TIPS)VarenLagartoNo ratings yet
- Axial SkeletonDocument34 pagesAxial SkeletonFachriza EffendiNo ratings yet
- FaceDocument31 pagesFaceikawaraztutyNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi TelingaDocument67 pagesAnatomi Dan Fisiologi TelingaDANDYNo ratings yet
- Cranial Fossa Notes - HelpfulDocument4 pagesCranial Fossa Notes - HelpfulKo HakuNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System: A Fixed Learning ModuleDocument38 pagesThe Respiratory System: A Fixed Learning ModulerezaNo ratings yet
- Essay Solution On Space in The SkullDocument21 pagesEssay Solution On Space in The SkullEmmanuel IshiomaNo ratings yet
- Skull ScalpDocument19 pagesSkull ScalpmaggieNo ratings yet
- Specific Osteology: Skeleton Axiale - Cranium (Skull) - Truncus (Trunk)Document46 pagesSpecific Osteology: Skeleton Axiale - Cranium (Skull) - Truncus (Trunk)Defi Sofianti AnnoNo ratings yet
- 6theear 100505202518 Phpapp01Document30 pages6theear 100505202518 Phpapp01Marjan MarolovNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Fisiologi Hidung Baru BGTDocument48 pagesAnatomi Fisiologi Hidung Baru BGTDzulfiqarNo ratings yet
- Cranial BaseDocument47 pagesCranial BaseYuvashreeNo ratings yet
- The Nose & Paranasal SinusesDocument17 pagesThe Nose & Paranasal SinusesMarera DomnicNo ratings yet
- Head and Neck Cheat Sheets PDFDocument8 pagesHead and Neck Cheat Sheets PDFJM LiensNo ratings yet
- Anatomi WajahDocument30 pagesAnatomi WajahamandarestykbNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Human Anatomy Dr. Mohammed WasnanDocument12 pagesLecture 4 Human Anatomy Dr. Mohammed Wasnanspo9equtabaNo ratings yet
- R R A T L: Two Types: 1-Alveodental Ligament 2-Transseptal FibersDocument8 pagesR R A T L: Two Types: 1-Alveodental Ligament 2-Transseptal FibersPrince AhmedNo ratings yet
- Head and NeckDocument11 pagesHead and NeckdrsamnNo ratings yet
- The Trigeminal NerveDocument83 pagesThe Trigeminal NerveRicha BhosaleNo ratings yet
- ScalpDocument17 pagesScalpKaruna PrabhuNo ratings yet
- ENT - Anatomy and Physiology of The Nose 2014Document3 pagesENT - Anatomy and Physiology of The Nose 2014pbmaristelaNo ratings yet
- Respitatory System I. 2018Document43 pagesRespitatory System I. 2018TodesengelNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Nose 2Document23 pagesAnatomy Nose 2Max Fax100% (1)
- Anatomi HidungDocument27 pagesAnatomi HidungFivi KurniawatiNo ratings yet
- 14 темаDocument8 pages14 темаSungdeok MinNo ratings yet
- 14 темаDocument8 pages14 темаSungdeok MinNo ratings yet
- Labelled Anatomy ModelsDocument12 pagesLabelled Anatomy ModelsSulaman AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The NoseDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The NoseManveer DhaliwalNo ratings yet
- PlantsDocument4 pagesPlantsaloysius limNo ratings yet
- Molecular BiologyDocument3 pagesMolecular Biologyaloysius limNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Concepts in Covalent BondingDocument12 pagesLesson 1 Concepts in Covalent Bondingextreme fattypunchNo ratings yet
- Colorimetric AssaysDocument2 pagesColorimetric Assaysaloysius limNo ratings yet
- AnswersDocument2 pagesAnswersaloysius limNo ratings yet
- Practice 2Document16 pagesPractice 2aloysius limNo ratings yet
- InheritanceDocument78 pagesInheritancealoysius limNo ratings yet
- 2022 Ks Bull Issue 1Document81 pages2022 Ks Bull Issue 1aloysius limNo ratings yet
- Hematology SOPsDocument99 pagesHematology SOPssalamon2t100% (1)
- Eaton BECOPAD P Range TechnicalDataSheet enDocument4 pagesEaton BECOPAD P Range TechnicalDataSheet enEsteban Fernando Meza IbacetaNo ratings yet
- Beta CaroteneDocument2 pagesBeta CaroteneValeria MarcuțăNo ratings yet
- Lord You Know All Things, You Can Do All Things and You Love Me Very MuchDocument4 pagesLord You Know All Things, You Can Do All Things and You Love Me Very Muchal bentulanNo ratings yet
- AAA V Edgardo SalazarDocument2 pagesAAA V Edgardo SalazarNiajhan PalattaoNo ratings yet
- Calamity and Disaster Preparedness Chapter IXDocument34 pagesCalamity and Disaster Preparedness Chapter IXANGEL ALBERTNo ratings yet
- 3926 An Premium DxiDocument400 pages3926 An Premium DxiMartin Bugár100% (2)
- Raymond Lo - The Feng Shui of Swine FluDocument1 pageRaymond Lo - The Feng Shui of Swine Fluay2004jan100% (1)
- Park Ch. 1 - A1000 - Spring13Document21 pagesPark Ch. 1 - A1000 - Spring13lingyeeNo ratings yet
- FF Recipe BookDocument17 pagesFF Recipe BookElectrox3dNo ratings yet
- Allnex Powder BrochureDocument28 pagesAllnex Powder BrochureandreathomeNo ratings yet
- Urie BronfenbrennerDocument27 pagesUrie Bronfenbrennerapi-300862520100% (1)
- Radiation Hazards & Radiation ProtectionDocument62 pagesRadiation Hazards & Radiation ProtectionGurupada JanaNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) Processes On Different Welding Parameters - DoneDocument5 pagesThe Effect of Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) Processes On Different Welding Parameters - DoneAsim AliNo ratings yet
- Clobazam For The Treatment ofDocument3 pagesClobazam For The Treatment ofpronto4meNo ratings yet
- The D - Block ElementsDocument30 pagesThe D - Block ElementsNandya AristaNo ratings yet
- q5 Nursery SchoolDocument4 pagesq5 Nursery SchoolPK CheahNo ratings yet
- 1635 The Papal Stakes - Eric FlintDocument1,813 pages1635 The Papal Stakes - Eric Flintwon100% (2)
- Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR), Synthetic Latex: ApplicationDocument2 pagesNitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR), Synthetic Latex: ApplicationbobNo ratings yet
- X FEDEX EIDocument13 pagesX FEDEX EINISREEN WAYANo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 - TLC - Updated Summer 2021Document4 pagesWorksheet 2 - TLC - Updated Summer 2021Bria PopeNo ratings yet
- Notes About BurnsDocument11 pagesNotes About BurnsMichelle Ann GacudNo ratings yet
- Pulverizers: By: G. RamachandranDocument140 pagesPulverizers: By: G. Ramachandranshivshankar prajapatiNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Soup ProjectDocument98 pagesComprehensive Soup ProjectSachin Soni63% (8)
- DiffusionDocument25 pagesDiffusionbonginkosi mathunjwa0% (1)
- Pre-Feasibility Report: at Plot No. 15/B-3, Jigani Industrial Area Anekal Taluk, Bangalore South District Karnataka byDocument41 pagesPre-Feasibility Report: at Plot No. 15/B-3, Jigani Industrial Area Anekal Taluk, Bangalore South District Karnataka by12mchc07No ratings yet
- 6L45, 6L50, 6L80, 6L90: Time Tested - Industry TrustedDocument1 page6L45, 6L50, 6L80, 6L90: Time Tested - Industry TrustedCelso BidinotiNo ratings yet
- What Is Aerobic Exercise?Document27 pagesWhat Is Aerobic Exercise?Zedy GullesNo ratings yet
- Pipe TobaccoDocument6 pagesPipe TobaccoVictorIoncuNo ratings yet
- B 700 FDocument25 pagesB 700 FMohammed HdyliNo ratings yet