Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gr. 10 Bio Semester 2 Revision Sheet Answer Key (2023-2024)
Uploaded by
8fr4xqpcb8Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gr. 10 Bio Semester 2 Revision Sheet Answer Key (2023-2024)
Uploaded by
8fr4xqpcb8Copyright:
Available Formats
Al Corniche International School
Boys’ Section Licence No.S-251/Girls’ Section Licence No. 4321440071
Vision: Our Vision is to offer the highest quality British education to our Mission: The mission of Al Corniche International School is to provide each
students embedded with the Islamic Values, implemented by the Modern student a diverse education in a safe, supportive environment that promotes
Technology to enhance the thinking skills and creativity in our students. self-discipline, motivation and excellence in learning.
Gr. 10 Bio Revision Sheet Answer Key Semester 2 (2023-2024)
MCQs
1. The diagram shows a part of a simplified DNA molecule.
What does X represent?
A. Organic base B. Carbon C. sugar-phosphate chain D. Protein
2. Water is a good solvent. What does this mean?
A. It dissolves well in many other substances. B. It flows easily through vessels.
C. It is permeable to gases. D. Many substances dissolve well in it.
3. One strand of a DNA molecule contains the base sequence TCG.
What is the base sequence on the other strand of the DNA molecule?
A. AGC B. GAT C. TAC D. AGT
4. The diagram represents enzyme action.
What are parts W, X and Y in this chemical reaction?
5. The diagram represents a chemical reaction.
ACIS, Jeddah KSA Page 1 of 13
Which diagram represents the enzyme for this reaction?
6. Lactase is a human enzyme that catalyses the breakdown of lactose in milk. At which
temperature does lactase work fastest?
A. 0°C B. 18°C C. 37°C D. 100°C
7. An enzyme from the stomach that digests protein, and cooked egg white that contains
protein, are placed in four test-tubes. When the egg white is digested the mixture becomes
clear. Which tube becomes clear first?
8. The photograph shows two blood cells, X and Y.
What are the functions of cells X and Y?
9. The diagram shows the heart as seen from the front.
Which section shows the heart cut through line P-Q?
ACIS, Jeddah KSA Page 2 of 13
10. The diagram shows an external view of the human heart.
What is the name of the blood vessel labelled X?
A. coronary artery B. hepatic artery C. pulmonary artery D. renal artery
11. The plan shows the blood system of a mammal.
What does the part labelled X represent? A. heart B. kidneys C. liver D. lungs
12. The list shows four metabolic processes.
Which of these processes occur in muscles?
A. 1 and 2 B. 2 and 3 C. 3 and 4 D. 4 and 1
13. The diagram shows an experiment to investigate the respiration of yeast.
ACIS, Jeddah KSA Page 3 of 13
Which gas is evolved and which new compound is present after 24 hours?
14. The graph shows the energy released by two animals through respiration as the
external temperature changes.
Which conclusion can be drawn from the graph?
A. Animals 1 and 2 release the least energy at 23°C.
B. Animal 2 always respires faster than animal 1.
C. As the temperature rises, respiration always increases.
D. The rate of respiration is the same for both animals at 23°C.
15. An athlete takes part in a race. The graph shows her breathing rate before, during and
after the race. At which point does her body contain the greatest amount of lactic acid?
ACIS, Jeddah KSA Page 4 of 13
16. How are aerobic and anaerobic respiration similar?
A. Both involve breaking down glucose.
B. Both need a low concentration of oxygen.
C. In muscles, both produce carbon dioxide.
D. In yeast, both produce alcohol.
17. The diagram shows the human urinary system.
Which row shows substances that are present in each of these structures in a healthy person?
18. The diagram shows a kidney and its blood vessels.
In a healthy person, which structures transport glucose?
A. artery only B. artery and ureter C. artery and vein D. ureter and vein
19. The diagram shows a neurone.
Which structures could be found at X and Y?
ACIS, Jeddah KSA Page 5 of 13
20. The diagram shows the muscles which control the size of the pupil in an eye.
How do the muscles make the pupil larger?
Extended Questions
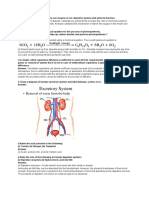
Q. NO: 1. (a) Fig. 1.1 shows some of the structures involved in excretion.
Complete Fig. 1.1 by labelling the structures in the spaces provided.
Choose structures from the list:
bladder bronchus heart liver
lung pancreas trachea ureter urethra
Ans: (Label from top to bottom): bronchus; lung; liver; ureter; bladder
(b) Urea is excreted.
(i) State the name of the substance that urea is made from. Amino acids
ACIS, Jeddah KSA Page 6 of 13
(ii) State where in the body urea is made. Liver
(c) Describe the process that produces the carbon dioxide that is excreted by the lungs.
During aerobic respiration Oxygen break-down of glucose / nutrient molecules to
generate energy and as a by-product CO2 is produced. You can write its chemical
equation as well.
(e) State the name of the component of blood that transports carbon dioxide to the lungs.
Plasma
Q. NO: 2. (a) Fig. 2.1 shows a reflex action that involves the eye. A shows an eye in dim
light. B shows the same eye when a bright blue light is shone into it.
Fig. 2.1
(i) Identify the:
• stimulus to which the eye responds
• receptor cells that detect the stimulus
• effector
• response that the eye makes.
Write your answers in Table 2.1.
Table 2.1
(ii) Describe how the nervous system coordinates the response shown in Fig. 2.1.
(b) Adrenaline is secreted by the adrenal glands to prepare the body for dangerous situations.
Extreme sports, such as bungee jumping shown in Fig. 2.2, are an example of such a
dangerous situation.
ACIS, Jeddah KSA Page 7 of 13
Fig. 2.2
Explain how adrenaline prepares the body for an extreme sport, such as making a bungee
jump.
(c) The response shown in Fig. 2.1 is involuntary. Bungee jumping is a voluntary action.
Describe two ways in which involuntary actions differ from voluntary actions.
Q. NO: 3. Complete the sentences about genetic engineering.
Use words from the list. Each word may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
bacteria crops family insects minerals organism
removing viruses vitamin weeds
In genetic engineering the genetic material of an .............................................. is changed
by .............................................., changing or inserting individual genes. An example of this
is inserting a human gene into .............................................. so that they produce human
ACIS, Jeddah KSA Page 8 of 13
insulin. Crop plants have genes inserted into them to make them resistant to herbicides.
Herbicides kill...............................................
Crop plants can also be genetically engineered by inserting a gene so that they produce
a .............................................. which is a nutrient needed by humans in very small amounts.
Ans: organism; removing; bacteria; weeds; vitamin
Use the given words respectively in the spaces provided.
Q. NO: 4. The glucose concentration of the blood is maintained within the range 80–90mg
per 100cm3 blood. Fig. 4.1 is a flow chart showing how the body responds to changes in the
glucose concentration of the blood after the absorption of a carbohydrate-rich meal and
during strenuous exercise.
Fig. 4.1
(a) Name organ A and hormones B and C.
(b) (i) Name organ D that stores glucose as glycogen.
(b) (i) liver
ACIS, Jeddah KSA Page 9 of 13
(ii) Suggest why glucose is converted to glycogen rather than kept as glucose
inside the cells.
(c) Name the type of control system used in homeostasis that returns the blood glucose
concentration to 80–90mg per 100cm3.
(c)negative feedback
(d) Animal hormones are used in the production of milk and meat. Bovine somatotrophin
(BST) is used to increase milk production by cows. The hormone is produced by
genetically modified bacteria that contain the cattle gene for making BST. It is used in the
United States but is banned for use in the European Union.
(i) Outline how genes, such as the one for BST, are transferred from the cells of cattle
(cows) to bacteria.
Bacteria are used in many biotechnological processes.
(e) Explain why bacteria are useful in biotechnology.
(e) any three from:
(small so do) not need much space
Rapid reproduction rate, can not make complex molecules, no ethiclal concerns over
use
Idea that genetic code is universal, they have plasmids
Idea that plasmids are used as vectors / in genetic engineering
Simple requirements so easy / cheap tp grow
Q. NO: 5. Heart surgeons may stop the heart beating during operations. While this happens
blood is pumped through a heart-lung machine that oxygenates the blood. Fig. 5.1 is a
diagram showing a heart-lung machine in use.
ACIS, Jeddah KSA Page 10 of 13
Fig. 5.1
(a) Name the structures labelled A to D.
(b) Name the blood vessels E and F.
(c) The heart-lung machine is used so that surgeons can operate on the arteries supplying
heart muscle. These arteries may be diseased.
Name these arteries and explain how they may become diseased.
name of arteries: coronary arteries
explanation:
Humans have a double circulation system. There is a low pressure circulation and a high
pressure circulation.
(d) Explain the advantages of a double circulation.
Any three from: 1. Oxygenated and deoxygenated blood are kept separate / do not mix /
separated by septum, 2. Ensures efficient supply of oxygen to the body 3. Ensure
efficient supply of (named) nutrient to the body 4. Lower pressure in pulmonary
artery / circuit 4. To prevent damage to (capillary in the) lungs 5. Allows more time for
gas exchange, allow high pressure in the body 6. To ensure efficient blood supply to rest
ACIS, Jeddah KSA Page 11 of 13
of the body 7. To allow filtration in kidneys (for excretion) 8. To allow / maintain a high
metabolic rate / rate of respiration
(e) Some people have Type 1 diabetes. Outline the treatment of Type 1 diabetes.
Any two from: Taking up insulin (ref; to injection / pump
(regular) monitoring of blood glucose concentration
Controlling carbohydrate intake
Regular exercise / maintain a healthy body mass
Q. NO: 6. Define the terms excretion, hormone and genetic engineering mean?
Excretion: removal from the body / organism / cell poisons / toxins / harmful substances
named example OR waste products / of metabolism / respiration / deamination / chemical
reactions in cells or in the body substances in excess (of requirements)
Hormone: A hormone is defined as a chemical substance, produced by a gland and carried
by the blood, which alters the activity of one or more specific target organs.
Genetic modification (engineering): Changing the genetic material of an organism by
removing, changing or inserting individual genes
Q. NO: 7. Fig. 7.1 shows a kidney tubule and the blood vessels associated with it.
Fig. 7.1
(a) Table 7.1 shows some processes that occur in a kidney.
In Table 7.1, write the letter of the part shown in Fig. 7.1 where each process occurs.
You must put one letter in each box. You may use the same letter more than once.
Table 7.1
process Letter
Filtration of blood H
Reabsorption of most of the solutes from C, F
the filtrate
Water is absorbed by osmosis to determine G
the concentration of urine
Unfiltered blood returns to the renal vein D
(b) Table 7.2 lists the components of blood, filtrate and urine.
ACIS, Jeddah KSA Page 12 of 13
Table 7.2
Complete the table by using ticks ) to show whether or not each
component is present in filtrate and in urine of a healthy person. The first component
has been done for you.
ACIS, Jeddah KSA Page 13 of 13
You might also like
- Term Test 2Document12 pagesTerm Test 2languagetuitionlabzNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY AND HEALTH SCIENCES EXERCISESDocument10 pagesBIOLOGY AND HEALTH SCIENCES EXERCISESAKAYEZU Body santiveNo ratings yet
- BOARD EXAM QUESTION PAPER 2023 Biology (Chapter 1, 2)Document8 pagesBOARD EXAM QUESTION PAPER 2023 Biology (Chapter 1, 2)Anisha ThomasNo ratings yet
- Mansukhbhai Kothari National School ACADEMIC YEAR 2021-2022 Topical Worksheet - 1Document7 pagesMansukhbhai Kothari National School ACADEMIC YEAR 2021-2022 Topical Worksheet - 1Aarnav SinghNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 Biology 1996 Paper 2+ansDocument19 pagesPaper 2 Biology 1996 Paper 2+ansapi-3812894100% (1)
- UntitledDocument12 pagesUntitledLyshanya HymanNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument18 pagesMultiple Choice QuestionsGranpaXNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 Biology 1995 Paper 2+ansDocument30 pagesPaper 2 Biology 1995 Paper 2+ansapi-3812894No ratings yet
- 2023 Xe Biology WorksheetDocument5 pages2023 Xe Biology Worksheetsomeonehalp12No ratings yet
- Analysis of Past Question PapersDocument72 pagesAnalysis of Past Question PapersShamaNo ratings yet
- Class X Science Worksheet No 4 CH 6 Answer KeyDocument6 pagesClass X Science Worksheet No 4 CH 6 Answer KeyYASHVI MODINo ratings yet
- Biology (E) 2024Document48 pagesBiology (E) 2024Gowtham ReddyNo ratings yet
- s4 Biology Paper 1 Set 9Document10 pagess4 Biology Paper 1 Set 9David NalodaNo ratings yet
- Year 10 BiologyDocument15 pagesYear 10 BiologylkipsangNo ratings yet
- 9. BIOLOGICAL SCIENCE REVIEWDocument10 pages9. BIOLOGICAL SCIENCE REVIEWgiathanhha2007No ratings yet
- Exercise PDFDocument12 pagesExercise PDFAmsyidi Asmida100% (1)
- AQA GCSE Organisation Questions: A. Principles of OrganisationDocument6 pagesAQA GCSE Organisation Questions: A. Principles of OrganisationJoeNo ratings yet
- Ulangkaji Berfokus SPM 2015 p1 Theme 2Document99 pagesUlangkaji Berfokus SPM 2015 p1 Theme 2Norizan DarawiNo ratings yet
- Cbse LP RevisionDocument18 pagesCbse LP RevisionKanak ChhajerNo ratings yet
- Bio SPM Intervensi m1Document10 pagesBio SPM Intervensi m1teahockNo ratings yet
- Biology End-Of-Course Practice ExamDocument23 pagesBiology End-Of-Course Practice ExamMacner JobeNo ratings yet
- Name: - Class: - Date Submitted: - Exercise Biology Enzyme and Excretion I. Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument7 pagesName: - Class: - Date Submitted: - Exercise Biology Enzyme and Excretion I. Multiple Choice QuestionsMaharsiwi Diah Chandra DewiNo ratings yet
- Summer Vacation Assignment - QuestionsDocument7 pagesSummer Vacation Assignment - QuestionsSidra QueenNo ratings yet
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN BIOLOGY EXAMDocument9 pagesKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN BIOLOGY EXAMShradha SharmaNo ratings yet
- HKCEE - Biology - 1995 - Paper II - Q&ADocument30 pagesHKCEE - Biology - 1995 - Paper II - Q&ACharlie Ng1216No ratings yet
- Worksheet Final Exam III TermDocument10 pagesWorksheet Final Exam III Termluizzzu.03No ratings yet
- 2020 Form 5 Biology Mock Exam: A Saliva Secretion Is An Involuntary Action Controlled by U (Medulla)Document22 pages2020 Form 5 Biology Mock Exam: A Saliva Secretion Is An Involuntary Action Controlled by U (Medulla)UniversityJCNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY II FBI1224 2022 Question Paper 1Document10 pagesBIOLOGY II FBI1224 2022 Question Paper 1zoulzz0903No ratings yet
- Science Test-10TH-SCIENCEDocument5 pagesScience Test-10TH-SCIENCEtensazangestuiit24No ratings yet
- Life Processes Class XDocument4 pagesLife Processes Class Xartikhandelwal1234No ratings yet
- Combined Past Paper Questions On Excretion and HomeostasisDocument76 pagesCombined Past Paper Questions On Excretion and HomeostasisRamesh Iyer81% (26)
- Unit 3 Exam CellsDocument8 pagesUnit 3 Exam Cellsapi-110789702No ratings yet
- UFP Biology for Life Sciences Exam B PRACTICE QUESTIONSDocument109 pagesUFP Biology for Life Sciences Exam B PRACTICE QUESTIONSbayigamellisaNo ratings yet
- SET 6 QNADocument11 pagesSET 6 QNAJolene ChiaNo ratings yet
- General InstructionsDocument5 pagesGeneral InstructionsMehak ShireenNo ratings yet
- set-3 BiologyXIDocument6 pagesset-3 BiologyXIavishank584No ratings yet
- Biology 2Document15 pagesBiology 2AlexanderGramtNo ratings yet
- Science Daily Test 1Document5 pagesScience Daily Test 1yuniNo ratings yet
- 1697623080105_QUESTION_BANK_X_202324_BIOLOGYDocument9 pages1697623080105_QUESTION_BANK_X_202324_BIOLOGYvaibhav4gameNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis & the KidneyDocument6 pagesHomeostasis & the KidneyBF CLNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Life ProcessesDocument4 pagesWorksheet - Life ProcessesPadma pulivarthiNo ratings yet
- Essential Life Processes Biology AssignmentDocument25 pagesEssential Life Processes Biology AssignmentOjasNo ratings yet
- (Edu - Joshuatly.com) Trial Malacca STPM 2012 Biology Paper 1 (A6DCE16B) PDFDocument23 pages(Edu - Joshuatly.com) Trial Malacca STPM 2012 Biology Paper 1 (A6DCE16B) PDFChai Kah ChunNo ratings yet
- Life Processes-Question BankDocument9 pagesLife Processes-Question Bankkfjg47zq26No ratings yet
- This Question Paper Consists of 3 Sections and Answer All QuestionsDocument12 pagesThis Question Paper Consists of 3 Sections and Answer All QuestionsKhusyairy Daeng Sailendra0% (1)
- Regents Cell Membrane and DiffusionDocument5 pagesRegents Cell Membrane and Diffusionapi-303120399No ratings yet
- (VCE Biology) 2017 YVG Unit 1 Exam v2Document10 pages(VCE Biology) 2017 YVG Unit 1 Exam v2Justine LyNo ratings yet
- 2017 P2 MuarDocument8 pages2017 P2 MuarNorbert LimNo ratings yet
- REv2 - movementInAndOutOfCells & BiomoleculesDocument13 pagesREv2 - movementInAndOutOfCells & BiomoleculesvimalNo ratings yet
- KENDRIYAVIDYALAYA SANGATHAN SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER CLASS XI BIOLOGYDocument5 pagesKENDRIYAVIDYALAYA SANGATHAN SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER CLASS XI BIOLOGYYash BhagatNo ratings yet
- Kibuli SS A Level Biology Seminar September 2022 FinalDocument15 pagesKibuli SS A Level Biology Seminar September 2022 Finalmins.succesorNo ratings yet
- 10 Bio - Worksheet 2022-23Document5 pages10 Bio - Worksheet 2022-23skyskyNo ratings yet
- Dharumavantha School Examinations: First Term 2009 Grade 10Document15 pagesDharumavantha School Examinations: First Term 2009 Grade 10afoo1234No ratings yet
- M.C Activity For 01,02 & 03 (Qurrat)Document11 pagesM.C Activity For 01,02 & 03 (Qurrat)sumizulfi786No ratings yet
- Soalan Trial Semester 1 2013Document10 pagesSoalan Trial Semester 1 2013Saiful MaslulNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument19 pagesBIOLOGYAnum ObaidNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers HomeostasisFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers HomeostasisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Understanding Cancer: A Guide to the Disease and TreatmentDocument104 pagesUnderstanding Cancer: A Guide to the Disease and TreatmentERAN MARK ROJASNo ratings yet
- Lab Sheet TemplateDocument1 pageLab Sheet TemplateKayleighGabrielleNo ratings yet
- 6476 Formulation of Alternative Culture Media For Bacterial and Fungal GrowthDocument6 pages6476 Formulation of Alternative Culture Media For Bacterial and Fungal GrowthHanief MitsukhaNo ratings yet
- Host Bromeliads and Their Associated Frog Species Furher Considerations On The Importance of Species Interactions For ConservationDocument11 pagesHost Bromeliads and Their Associated Frog Species Furher Considerations On The Importance of Species Interactions For ConservationAna Maria MoncadaNo ratings yet
- Annotated BibliographyDocument5 pagesAnnotated Bibliographyapi-399404406100% (2)
- Physiology, Lecture 6, Urinary SystemDocument74 pagesPhysiology, Lecture 6, Urinary SystemAli Al-QudsiNo ratings yet
- Toddler Age (1 - 3 Years)Document11 pagesToddler Age (1 - 3 Years)Piao Liang JingNo ratings yet
- The Perceptual Implications of GaiaDocument12 pagesThe Perceptual Implications of Gaiaapi-279625022No ratings yet
- Disease Detectives B-Answer KeyDocument14 pagesDisease Detectives B-Answer KeyskdfkjlNo ratings yet
- Postpartum HemorrhageDocument11 pagesPostpartum HemorrhageColeen Aubrey TanNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Non-Starch Polysaccharides (NSP)Document6 pagesEnzymes: Non-Starch Polysaccharides (NSP)amamùra maamarNo ratings yet
- 18 Dna Structure and Replication-SDocument5 pages18 Dna Structure and Replication-Sapi-2623786400% (2)
- Flowering PhysiologyDocument50 pagesFlowering PhysiologyElen Batlayeri100% (1)
- Energy Efficient Landscape Forests of Nilgiris, Tamil NaduDocument8 pagesEnergy Efficient Landscape Forests of Nilgiris, Tamil NaduHues of SundropNo ratings yet
- Unfamiliar Words Activity 1Document1 pageUnfamiliar Words Activity 1Sharmaine Ann AustriaNo ratings yet
- Hottest Babe Videos M C Lennan S Work, and If TheyDocument4 pagesHottest Babe Videos M C Lennan S Work, and If Theyvernonmendieta0% (1)
- Balaytigue National High SchoolDocument2 pagesBalaytigue National High School3 stacksNo ratings yet
- Shaba Lovs Kaya 2008Document21 pagesShaba Lovs Kaya 2008Kmilo A EcheverriaNo ratings yet
- Care and Conservation of Natural History Collections (Inglés) Autor Hendry, D.Document38 pagesCare and Conservation of Natural History Collections (Inglés) Autor Hendry, D.javier ambrosio hernandezNo ratings yet
- Kohar Hari Santoso, H.R. Eddy Rahardjo, HarjantoDocument8 pagesKohar Hari Santoso, H.R. Eddy Rahardjo, Harjantovela latifahNo ratings yet
- Mass SpectraDocument64 pagesMass SpectraLuis Alberto AnguianoNo ratings yet
- Immunology For Pharmacy StudentsDocument199 pagesImmunology For Pharmacy StudentsPizzaChowNo ratings yet
- GA-02 Encoding TechniquesDocument42 pagesGA-02 Encoding TechniqueskiranNo ratings yet
- Do Emotions Cause Actions, and If So How?: Andrea ScarantinoDocument9 pagesDo Emotions Cause Actions, and If So How?: Andrea ScarantinoyoNo ratings yet
- Healthy Bodies Slide3Document11 pagesHealthy Bodies Slide3Larissa RevillaNo ratings yet
- Basic Human Anatomy: Lesson 5: Muscular SystemDocument10 pagesBasic Human Anatomy: Lesson 5: Muscular SystemIshita SinghNo ratings yet
- Actor Si RizalDocument6 pagesActor Si RizalRezzmah Alicia Tomon KhadrawyNo ratings yet
- Soal PAT English Kelas 10 Edit1Document22 pagesSoal PAT English Kelas 10 Edit1Dony Petrus, S.Pd.No ratings yet
- SOL BIO Anatomical Evidence of Evolution Henry PriceDocument7 pagesSOL BIO Anatomical Evidence of Evolution Henry PriceHenry PriceNo ratings yet
- EpidemiologyDocument10 pagesEpidemiologyMUTHUKUMARANNo ratings yet