Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Recognising A Circle
Uploaded by
Gan Kok HanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Recognising A Circle
Uploaded by
Gan Kok HanCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 1 Circular Measure
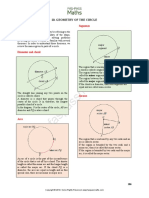
Recognising a Circle
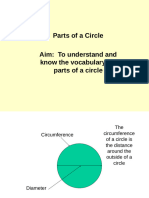
Circle
In geometry, a circle is a closed curve obtained from a set of
points on a plane which are equal distance from a fixed point
called the centre O. This distance is called the radius of the
circle.
Diameter
A diameter of a circle is a line segment that passes through the
centre of a circle and its ends touch the circumference of the
circle. All diameters of a circle have the same length.
Chord
A chord is a line segment with its end points touching the
circumference of the circle. A diameter is also a special chord
which passes through the centre of the circle and it is the
longest chord of that circle.
Radius
The radius of a circle is a line segment drawn from the centre
of the circle to any points on the circumference. In the
diagram, O is the centre of the circle. OB and OC are both
radii with the same length. The radius is half the length of the
1
diameter of that circle, that is, OB = AB .
2
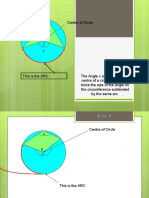
Arc
An arc is a part of a circle. In the diagram, the red line from the
point B to C forms an arc of the circle. An arc can be measured
in degrees. Arc BC = BOC = 45 .
Tangent
A tangent is a line that touches a circle at only one point. A
tangent is always perpendicular to the radius at that point of
contact. In the diagram, the line BC is the tangent to the circle
at the point B.
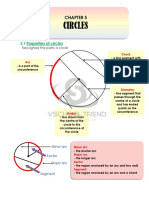
Chapter 1 Circular Measure
Tangent
Chord
Tangent, chord, diameter and radius O
Diameter
Radius
Minor arc
Minor segment
Minor arc, major arc, minor segment and O
major segment
Major segment
Major arc
Minor arc
Minor sector
O
Minor sector and major sector
Major sector
Major arc
You might also like
- CircleDocument11 pagesCircleKathleen Bermejo CatainNo ratings yet
- Circle 10Document27 pagesCircle 10gamingmsop5No ratings yet
- Topik-2 Bulatan CircleDocument36 pagesTopik-2 Bulatan Circle许如楠No ratings yet
- Geometry of The Circle PDFDocument7 pagesGeometry of The Circle PDFGregory LewisNo ratings yet
- Geometry of The CircleDocument7 pagesGeometry of The CircleDane SinclairNo ratings yet
- CirclesDocument20 pagesCirclesMary Grace CacalNo ratings yet
- Math70 F2013 Lecture Sections6 1thru6 2Document4 pagesMath70 F2013 Lecture Sections6 1thru6 2Raiel RoaNo ratings yet
- Central AnglesDocument17 pagesCentral Anglesmichelle azañaNo ratings yet
- Definitions and Theorems For Circle GeometryDocument8 pagesDefinitions and Theorems For Circle GeometryPaula FanaNo ratings yet
- Circle Definitions and TheoremsDocument8 pagesCircle Definitions and TheoremsGani Almeron100% (1)
- CO1 CircleDocument50 pagesCO1 CircleReinabelle Marfil Marquez100% (1)
- Parts of A CircleDocument33 pagesParts of A CircleMr. Rhumer LanojanNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Session 4 CircleDocument57 pagesGrade 10 Session 4 CirclemarlonNo ratings yet
- Circle TheoremDocument5 pagesCircle TheoremJadesola AwosikaNo ratings yet
- Circle - Theorems PPT NotesDocument46 pagesCircle - Theorems PPT Notessakchham agrawalNo ratings yet
- Circle TheoremsDocument19 pagesCircle TheoremsJayson DaguroNo ratings yet
- 4.properties of Shapes PDFDocument17 pages4.properties of Shapes PDFDanish AimanNo ratings yet
- CO1 CircleDocument57 pagesCO1 CircleReinabelle Marfil MarquezNo ratings yet
- CircleDocument6 pagesCircleVishnu PrasadNo ratings yet
- Circles IntroductionDocument1 pageCircles IntroductionNelda OabelNo ratings yet
- Polygons, Congruent, Circle and Its PartsDocument9 pagesPolygons, Congruent, Circle and Its PartsVine AlparitoNo ratings yet
- Circles TheoryDocument4 pagesCircles TheoryJamal AliyevNo ratings yet
- 24c60 Chapter 5 DoneDocument13 pages24c60 Chapter 5 DoneannabellNo ratings yet
- A Powerpoin Presentation On CircleDocument26 pagesA Powerpoin Presentation On CircleNitesh BhuraNo ratings yet
- Non Linear Optimization BookDocument34 pagesNon Linear Optimization Bookbimal agrawalNo ratings yet
- CirclesDocument8 pagesCircles246macvillaNo ratings yet
- CircleDocument31 pagesCirclesunilkalekar200550% (2)
- Q2 WK No.2 LAS Math10 Finalcopy1Document8 pagesQ2 WK No.2 LAS Math10 Finalcopy1Ramil J. MerculioNo ratings yet
- Circles and Related Terms: G7 MathematicsDocument21 pagesCircles and Related Terms: G7 MathematicsAnya ThereseNo ratings yet
- Q4 Las CirclesDocument4 pagesQ4 Las Circlesaljohn.nerzaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.6 Parts of A CircleDocument13 pagesLesson 2.6 Parts of A CircleFrankie Alcelle PadronesNo ratings yet
- CircletheoremsDocument19 pagesCircletheoremsRaiel RoaNo ratings yet
- Bombay Cambridge Gurukul Bombay Cambridge Gurukul: CircleDocument34 pagesBombay Cambridge Gurukul Bombay Cambridge Gurukul: Circleankithns102No ratings yet
- CirclesDocument27 pagesCirclesSkrt brrt brtNo ratings yet
- Las Mathematics 10 Week 2 Quarter 2 Jonathan D NunagDocument9 pagesLas Mathematics 10 Week 2 Quarter 2 Jonathan D NunagJONATHAN NUNAGNo ratings yet
- Deped - Region Iva CalabarzonDocument25 pagesDeped - Region Iva CalabarzonJesselle BalderamaNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Math 7Document7 pagesWeek 7 Math 7Girlie Mae FloresNo ratings yet
- Relationships Among Chords, Arcs, Central Angles, and Inscribed AnglesDocument12 pagesRelationships Among Chords, Arcs, Central Angles, and Inscribed AnglesMobile legends gamer100% (2)
- Geometry CirclesDocument12 pagesGeometry Circlespearl ann pacioNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument46 pagesUntitledCory Ann PujanesNo ratings yet
- Parts of The CircleDocument8 pagesParts of The CircleMari CelNo ratings yet
- Circle: MathematicsDocument34 pagesCircle: MathematicsKM Laysa GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Circle and Its PartsDocument16 pagesCircle and Its PartsArmestides Bargayo VINo ratings yet
- CIRCLE 8.ppsxDocument12 pagesCIRCLE 8.ppsxiwan60No ratings yet
- Parts of The CircleDocument7 pagesParts of The Circlenica monNo ratings yet
- Circleanditsparts 130904032217Document34 pagesCircleanditsparts 130904032217mark joseph pamplonaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 10 2nd QuarterDocument3 pagesMathematics 10 2nd QuarterTrizia Venisce BitonioNo ratings yet
- CIRCLES - Angles, ChordsDocument158 pagesCIRCLES - Angles, ChordsMika Pelagio100% (2)
- UntitledDocument9 pagesUntitledJames MangulabnanNo ratings yet
- Math 10 Q2W2Document69 pagesMath 10 Q2W2Leander Kelly Transporte MarianoNo ratings yet
- Good Afternoon Class!: HELLO, I Am Teacher AnnDocument36 pagesGood Afternoon Class!: HELLO, I Am Teacher AnnAnn Claudeth MaboloNo ratings yet
- Grade 7/8 Math Circles Circle Geometry: SolutionsDocument13 pagesGrade 7/8 Math Circles Circle Geometry: SolutionsEvia Diane YapNo ratings yet
- Circular MeasureDocument23 pagesCircular MeasureWOON RAY MINGNo ratings yet
- Circle TheoremsDocument16 pagesCircle TheoremsErwin Joaquin CabigaoNo ratings yet
- G7 - Week 6 - 3rd QDocument28 pagesG7 - Week 6 - 3rd Q246macvillaNo ratings yet
- We Will Identify Parts of A CircleDocument37 pagesWe Will Identify Parts of A CircleLutong Bahay AdventuresNo ratings yet
- Math ScrapbookDocument13 pagesMath ScrapbookMark Danielle GeolagioNo ratings yet
- Circle TheoremsDocument7 pagesCircle TheoremsAnmol DurehaNo ratings yet
- S1-2 Key Points: Part II: Measures, Shape and Space StrandDocument44 pagesS1-2 Key Points: Part II: Measures, Shape and Space StrandCharlotteNo ratings yet
- Cylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsFrom EverandCylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsNo ratings yet
- Pusas Gasing 2024Document3 pagesPusas Gasing 2024Gan Kok HanNo ratings yet
- Alternative Method To Derive The Formula of Area of A Sector of A CircleDocument1 pageAlternative Method To Derive The Formula of Area of A Sector of A CircleGan Kok HanNo ratings yet
- Chapter1..practice 1Document1 pageChapter1..practice 1Gan Kok HanNo ratings yet
- Tude S. 1413 in G Minor La Campanella LisztDocument8 pagesTude S. 1413 in G Minor La Campanella LisztGan Kok HanNo ratings yet
- KM170, KM171, KM172, F3A21, F3A22: 3 SPEED FWD (Lock Up & Non Lock Up)Document4 pagesKM170, KM171, KM172, F3A21, F3A22: 3 SPEED FWD (Lock Up & Non Lock Up)krzysiek1975No ratings yet
- Catalogue - Central Battery SystemDocument12 pagesCatalogue - Central Battery SystemarifzakirNo ratings yet
- Taylorism vs. FordismDocument2 pagesTaylorism vs. FordismLiv Maloney67% (3)
- Oral Communication in ContextDocument19 pagesOral Communication in ContextAzory ZelleNo ratings yet
- ENSC1001 Unit Outline 2014Document12 pagesENSC1001 Unit Outline 2014TheColonel999No ratings yet
- Presentation LI: Prepared by Muhammad Zaim Ihtisham Bin Mohd Jamal A17KA5273 13 September 2022Document9 pagesPresentation LI: Prepared by Muhammad Zaim Ihtisham Bin Mohd Jamal A17KA5273 13 September 2022dakmts07No ratings yet
- PedagogicalDocument94 pagesPedagogicalEdson MorenoNo ratings yet
- Pull Cord Switch JayashreeDocument1 pagePull Cord Switch JayashreeNCNo ratings yet
- Sistemas de Mando CST Cat (Ing)Document12 pagesSistemas de Mando CST Cat (Ing)Carlos Alfredo LauraNo ratings yet
- DADTCO Presentation PDFDocument34 pagesDADTCO Presentation PDFIngeniería Industrias Alimentarias Itsm100% (1)
- Nails Care: Word Search: Name: - DateDocument1 pageNails Care: Word Search: Name: - DateDeverly Hernandez Balba-AmplayoNo ratings yet
- Bullying Report - Ending The Torment: Tackling Bullying From The Schoolyard To CyberspaceDocument174 pagesBullying Report - Ending The Torment: Tackling Bullying From The Schoolyard To CyberspaceAlexandre AndréNo ratings yet
- The Other Twelve Part 1Document5 pagesThe Other Twelve Part 1vv380100% (2)
- Lesson Plan 1Document3 pagesLesson Plan 1api-311983208No ratings yet
- S4 Computer Sciences Exercises PDFDocument2 pagesS4 Computer Sciences Exercises PDFHenriette Desanges UwayoNo ratings yet
- 2396510-14-8EN - r1 - Service Information and Procedures Class MDocument2,072 pages2396510-14-8EN - r1 - Service Information and Procedures Class MJuan Bautista PradoNo ratings yet
- General Return Service Agreement (RSA) GuidelinesDocument2 pagesGeneral Return Service Agreement (RSA) GuidelinesJune Francis AngNo ratings yet
- Shelly Cashman Series Microsoft Office 365 Excel 2016 Comprehensive 1st Edition Freund Solutions ManualDocument5 pagesShelly Cashman Series Microsoft Office 365 Excel 2016 Comprehensive 1st Edition Freund Solutions Manualjuanlucerofdqegwntai100% (10)
- Cella Di Carico Sartorius MP77 eDocument3 pagesCella Di Carico Sartorius MP77 eNCNo ratings yet
- RESEARCHDocument5 pagesRESEARCHroseve cabalunaNo ratings yet
- VERGARA - RPH Reflection PaperDocument2 pagesVERGARA - RPH Reflection PaperNezer Byl P. VergaraNo ratings yet
- Shoshana Bulka PragmaticaDocument17 pagesShoshana Bulka PragmaticaJessica JonesNo ratings yet
- Cummins: ISX15 CM2250Document17 pagesCummins: ISX15 CM2250haroun100% (4)
- DeadlocksDocument41 pagesDeadlocksSanjal DesaiNo ratings yet
- Te-Chemical Sem5 CPNM-CBCGS Dec19Document2 pagesTe-Chemical Sem5 CPNM-CBCGS Dec19Mayank ShelarNo ratings yet
- A Structural Modelo of Limital Experienci Un TourismDocument15 pagesA Structural Modelo of Limital Experienci Un TourismcecorredorNo ratings yet
- Grua Grove 530e 2 Manual de PartesDocument713 pagesGrua Grove 530e 2 Manual de PartesGustavo100% (7)
- Gandhi and The Non-Cooperation MovementDocument6 pagesGandhi and The Non-Cooperation MovementAliya KhanNo ratings yet
- (Schottel) Aspects of The Design Procedure For Propellers Providing Max Bollard PullDocument10 pages(Schottel) Aspects of The Design Procedure For Propellers Providing Max Bollard Pulldevu2chodankarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Microelectronic Fabrication PDFDocument332 pagesIntroduction To Microelectronic Fabrication PDFChristy Moore92% (13)