Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fundamentals in Nursing Practice Reviewer
Uploaded by
Xharen Joy BinondoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fundamentals in Nursing Practice Reviewer
Uploaded by
Xharen Joy BinondoCopyright:
Available Formats
Anaphy
Endocrine system — a major control system of the body; composed of a series
of ductless glands that secrete their products directly into the blood
• Works through the action of hormones to control growth and development,
metabolism, reproduction, and body defense.
Chemistry of Hormones
Hormones are chemical substances secreted by endocrine cells into the
extracellular fluids that regulate the metabolic activity of other cells in the
body.
Although the body produces many different hor-mones, nearly all of them can
be classified chemically as either amino acid-based molecules (including
proteins, peptides, and amines) or steroids. Steroid hormones (made from
choles-terol) include the sex hormones made by the gonads (ovaries and
testes) and the hormones produced by the adrenal cortex.
• Prostaglandins are locally acting lipids. Prostaglandins are made from
highly active lipids released from nearly all cell membranes.
Hormone Action
• Hormones alter the metabolic activities of their target cells or target organs
by turning something on or off, opening or closing ion chan-nels, or activating
or inactivating enzymes.
• Amino acid-based hormones (except thyroid hormone) act through second
messengers.
• Steroid hormones can work by direct gene activation or via
second messenger.
• The ability of a target organ to respond to a hormone requires the presence
of receptors to the hormone in or on its cells to which the hormone binds.
Stimuli for control of hormone release
• Hormonal stimulus—a hormone stimulates another organ to release
its hormones.
• Humoral stimulus—a blood level of something stimulates a hormone to
be released.
• Neural stimulus—direct stimulation by sympathetic neurons signal
hormone release.
• Negative feedback is important in regulating blood hormone levels.
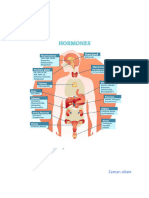
The Major Endocrine Organs
Pituitary Gland
• The pituitary gland hangs from the hypothalamus of the brain by a stalk
and is enclosed by bone.
• Releasing hormones and inhibiting hormones made by the hypothalamus
regulate release of hormones made by the anterior pituitary.
• The hypothalamus also makes two hormones that are transported along the
axons of the hypothalamic neurosecretory cells to the posterior pituitary for
storage and later release.
• The posterior pituitary is neural tissue that stores and releases
hypothalamic hormones on command.
• Oxytocin: Stimulates powerful uterine contractions and causes milk
ejection in nursing women.
• Antidiuretic hormone (ADH): Causes kidney tubule cells to reabsorb and
conserve body water and increases blood pressure by constricting blood
vessels (also called vasopressin).
• Hyposecretion of ADH leads to diabetes insipidus.
You might also like
- Endocrine System: A Tutorial Study GuideFrom EverandEndocrine System: A Tutorial Study GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- ENDOCRINE SYSTEM DISORDERS PROPER BestDocument370 pagesENDOCRINE SYSTEM DISORDERS PROPER BestronaronixstheboyNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Endocrinology: H. KibichoDocument370 pagesEndocrinology Endocrinology: H. KibichoMursal RashidNo ratings yet
- How Endocrine WorksDocument19 pagesHow Endocrine WorksSwad Abdul khalikNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY LEC 12-13 EndocrineDocument29 pagesANAPHY LEC 12-13 EndocrineDior CodmNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument75 pagesEndocrine SystemReneilwe MoshidiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument12 pagesUntitledDerrick kinyaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument27 pagesEndocrine SystemJustinn DukessaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine PhysiologyDocument76 pagesEndocrine Physiologykidusabeje7No ratings yet
- Endocine System Physiology 20-4-2020Document61 pagesEndocine System Physiology 20-4-2020Farah AljayyousiNo ratings yet
- PD22 Hap1 L03Document33 pagesPD22 Hap1 L03Ka Yan LAUNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine System: Presenté ParDocument64 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine System: Presenté ParYackson FrankNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System in FinfishesDocument43 pagesEndocrine System in FinfishesMisbah SayyedNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System The Endocrine System: © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. 1Document12 pagesThe Endocrine System The Endocrine System: © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. 1lourd nabNo ratings yet
- Hormones 080623Document83 pagesHormones 080623Rao Asad MubeenNo ratings yet
- General Concept of Endocrine Glands and HormonesDocument51 pagesGeneral Concept of Endocrine Glands and HormonesTutde SedanaNo ratings yet
- Hormonal Regulation of ExerciseDocument11 pagesHormonal Regulation of ExerciseMozil Fadzil KamarudinNo ratings yet
- 439 en Intro 1Document74 pages439 en Intro 1Omotosho DavidNo ratings yet
- Endocrine PharmacologyDocument87 pagesEndocrine PharmacologyHarrison Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- EndocrinologyDocument4 pagesEndocrinologyRekesh SaeedNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument133 pagesEndocrine SystemAudrey KenfacNo ratings yet
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument3 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationNANDAKUMAR BABUNo ratings yet
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument3 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationNANDAKUMAR BABUNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 6 Sistem EndokrinDocument61 pagesPertemuan 6 Sistem EndokrinKezia RachelNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Endocrine System: "The Body Regulator"Document31 pagesEndocrine System Endocrine System: "The Body Regulator"angelus008No ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument69 pagesEndocrine SystemDivya JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Hormones:: Signaling MoleculesDocument20 pagesHormones:: Signaling MoleculesSangeeta DwivediNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System PDFDocument86 pagesEndocrine System PDFsheryl dungogNo ratings yet
- CH 18 Endocrine3Document65 pagesCH 18 Endocrine3adamaditya666No ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument12 pagesEndocrinejamille consingNo ratings yet
- Regulasi Endokrin 22 IntensifDocument25 pagesRegulasi Endokrin 22 IntensifWignes WarenNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument95 pagesEndocrine SystemUmar Ilyasu JibrilNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System-1Document90 pagesEndocrine System-1markmuiruri581No ratings yet
- Principles of Hormonal Control SystemDocument25 pagesPrinciples of Hormonal Control SystemFAHEEM UD DINNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physiology For Pharmacy Students-2023Document118 pagesEndocrine Physiology For Pharmacy Students-2023Alemnew YohannesNo ratings yet
- Endocrine ReportingDocument39 pagesEndocrine ReportingJed mariñasNo ratings yet
- BBT221 Lecture 6Document41 pagesBBT221 Lecture 6Al Sabri Bhuiyan 1812098042No ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Endocrine SystemDocument53 pagesStructure and Function of The Endocrine Systemwalt65No ratings yet
- Activity 16 HormonesDocument16 pagesActivity 16 HormonesKendrix Aguiluz FlorendoNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument93 pagesThe Endocrine SystemMaryela Maceda GalozoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument22 pagesEndocrine Systempranutan739No ratings yet
- HORMONSDocument7 pagesHORMONShasan0000No ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesThe Endocrine SystemMary Christelle100% (1)
- EndocrinologyDocument74 pagesEndocrinologysyedahaleemajunaidsNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Dr. Annette M. Parrott GPC BIOL1612Document34 pagesEndocrine System: Dr. Annette M. Parrott GPC BIOL1612Nathan TaylorNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology - The Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology - The Endocrine SystemKraig Andre RellegueNo ratings yet
- Introduction Endocrine Physiology 2Document52 pagesIntroduction Endocrine Physiology 2IshaqNo ratings yet
- Care of Clients With Problem On EndocrineDocument48 pagesCare of Clients With Problem On EndocrineAngel CauilanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1, Introduction To EndocrinologyDocument86 pagesLecture 1, Introduction To EndocrinologyAlexandru Ionut Popistaș100% (1)
- EndocrinologyDocument23 pagesEndocrinologysaikat55No ratings yet
- Chemical Control and CoordinationDocument19 pagesChemical Control and CoordinationShubhamNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Pertama (Pendahuluan)Document18 pagesKuliah Pertama (Pendahuluan)kiki rawitriNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System OutlineDocument17 pagesEndocrine System OutlineEsthermae PanadenNo ratings yet
- Johanna Jane H. Macasero - Endocrine System TranscriptDocument13 pagesJohanna Jane H. Macasero - Endocrine System TranscriptJohanna MacaseroNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Glands & HormonesDocument78 pagesEndocrine System: Glands & HormonesJerilee SoCute WattsNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINE SYSTEM - Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument10 pagesENDOCRINE SYSTEM - Anatomy and PhysiologyJay Crishnan Morales CajandingNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and Integration Handwriten Notes For Neet and JeeDocument5 pagesChemical Coordination and Integration Handwriten Notes For Neet and JeetechnosonicindiaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System - MorphophysiologyDocument88 pagesEndocrine System - MorphophysiologyKarina Bustillo100% (1)
- Introduction To Endocrinology: Dr. Jehad Al-ShuneigatDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Endocrinology: Dr. Jehad Al-Shuneigatyousef sarairehNo ratings yet
- CC Chatterjee's Human Physiology 12th Volume 2Document7 pagesCC Chatterjee's Human Physiology 12th Volume 2food onNo ratings yet
- Diabetes InsipidusDocument8 pagesDiabetes InsipidusNader Smadi100% (5)
- Test Bank Chapter 67: Nursing Management: Shock, Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome, and Multiple Organ Dysfunction SyndromeDocument11 pagesTest Bank Chapter 67: Nursing Management: Shock, Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome, and Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndromebbianca1990100% (1)
- The Endocrine SystemDocument24 pagesThe Endocrine System속강대No ratings yet
- Biology Assignment HBSC3103 - V2Document23 pagesBiology Assignment HBSC3103 - V2Lester Randy RubintinusNo ratings yet
- Nclex Cram SheetDocument24 pagesNclex Cram Sheettoni100% (5)
- (Pediaii) 013 Pediatric Endocrine DisordersDocument29 pages(Pediaii) 013 Pediatric Endocrine DisordersdoktoraronaNo ratings yet
- BP503T Unit 1-3Document432 pagesBP503T Unit 1-3Solomon GyampohNo ratings yet
- Q Bank Physio 30Document30 pagesQ Bank Physio 30haleemeltayebNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Anesthesia MCQsDocument18 pagesEndocrine Anesthesia MCQsMuhammad Aasim Maan100% (2)
- PHA3032 Notes: Theme 2: Pharmacology of Mood and BehaviourDocument45 pagesPHA3032 Notes: Theme 2: Pharmacology of Mood and BehaviourJoshuaWestNo ratings yet
- Garrahy 2020Document13 pagesGarrahy 2020Ana Elizabeth Gangotena CoralNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Diabetes InsipidusDocument11 pagesPediatric Diabetes InsipidusVictor Matias BarriosNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On UterusDocument19 pagesDrugs Acting On Uterus101 102No ratings yet
- Quiz EndocrineDocument84 pagesQuiz EndocrineMedShare92% (12)
- Signal Molecule TrackerDocument4 pagesSignal Molecule Trackerarman_azad_2No ratings yet
- 39 Prep GuideDocument73 pages39 Prep Guidedaljit chahalNo ratings yet
- Diabetes InsipidusDocument7 pagesDiabetes Insipiduspaul_stefenson10No ratings yet
- Adaptasi Fisiologis Selama PuasaDocument9 pagesAdaptasi Fisiologis Selama PuasaCanva IdNo ratings yet
- Yxik8 Clinical Biochemistry and Metabolic Medicine Eighth EditionDocument441 pagesYxik8 Clinical Biochemistry and Metabolic Medicine Eighth EditionShahinuzzamanAda100% (11)
- Treatment of Orthostatic and Postprandial HypotensionDocument13 pagesTreatment of Orthostatic and Postprandial HypotensionRebeca RiveraNo ratings yet
- Endocrine DisordersDocument106 pagesEndocrine DisordersMansur MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Renal Urology HistoryDocument131 pagesRenal Urology Historysharu4291No ratings yet
- Dams Manipal 2.endo MCQ 2021Document44 pagesDams Manipal 2.endo MCQ 2021deepikaNo ratings yet
- Coordination and Control: Animation 12.1: Neuron Source & Credit: Nichd - NihDocument37 pagesCoordination and Control: Animation 12.1: Neuron Source & Credit: Nichd - Nihwardah nooriNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhagic Shock - The "Physiology Approach"Document18 pagesHemorrhagic Shock - The "Physiology Approach"carloshgmedeirosNo ratings yet
- 102 Lec Post-TestDocument7 pages102 Lec Post-TestMarie Fatima Quidet UdalbeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Electrolyte and Acid - Base Disorders in MalignancyDocument7 pagesChapter 5: Electrolyte and Acid - Base Disorders in MalignancyPratita Jati PermatasariNo ratings yet
- The Urinary System & Fluid BalanceDocument8 pagesThe Urinary System & Fluid BalanceMarianne DugosNo ratings yet
- Inotrópicos y Vasopresores PDFDocument22 pagesInotrópicos y Vasopresores PDFJosé Luis Méndez ChagoyaNo ratings yet