Professional Documents
Culture Documents
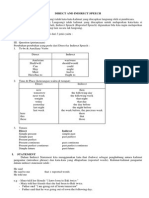
Direct and Indirect Speech
Uploaded by
persibnusaya44Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Direct and Indirect Speech
Uploaded by
persibnusaya44Copyright:
Available Formats
English 3 Direct and Indirect
Speech
Universitas Amikom Yogyakarta
Direct and Indirect Speech
• Direct Speech (quoted speech) >> a report of
the exact words used by a speaker or writer.
• Indirect Speech (Reported Speech) >> a report
on what someone else said or wrote without
using that person's exact words. Or
paraphrasing what someone said or wrote.
Direct & Indirect Speech consist of 3 types:
• 1. Statement (pernyataan)
• 2. Command (perintah)
• 3. Question (pertanyaan)
Universitas Amikom Yogyakarta
Direct Speech
vs
Indirect Speech
Quoted Speech
Ann said, “I am hungry.”
Tom said, “I need my pen.”
Reported Speech
Ann said that she was hungry.
Tom said that he needed his pen.
Universitas Amikom Yogyakarta
Direct to Indirect Speech
1. To be & Auxiliary Verbs
Direct Indirect
am/ is / are Was / were
shall/ will Should/would
Can Could
May
Might
Must
Have/has to
Had to
Ought to
Universitas Amikom Yogyakarta
Direct to Indirect Speech
Quoted Speech Reported Speech
- He said, “I work hard.” - He said (that) he worked hard.
- He said, “I am working hard.” - He said (that) he was working hard.
- He said, “I have worked hard.” - He said (that) he had worked hard.
- He said, “I worked hard.” - He said (that) he had worked hard.
- He said, “I am going to work hard.” - He said (that) he was going to work hard.
- He said, “I will work hard.” - He said (that) he would work hard.
- He said, “I can work hard.” - He said (that) he could work hard.
- He said, “I may work hard.” - He said (that) he might work hard.
- He said, “I have to work hard.” - He said (that) he had to work hard.
- He said, “I must work hard.” - He said (that) he had to work hard.
- He said, “I should work hard.” - He said (that) he should work hard.
Universitas Amikom Yogyakarta
Direct to Indirect Speech
NOTE
Sometimes, epecially in speaking, the verb in the noun/adjective clause is
not changed if the speaker is reporting something immediately or soon
after it was said.
Immediate reporting :
A. What did Ann just say? I didn’t hear her.
B. She said (that) she is hungry.
Later reporting :
A. What did Ann say when she got home last night?
B. She said (that) she was hungry.
Universitas Amikom Yogyakarta
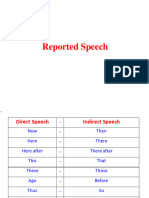
2. Time & Place
Direct Indirect
Now Then
Tomorrow The following day
Next week The following week
Tonight That night
Today That day
Yesterday The day before
Last night The night before
Last week The week before
The precious week
Here There
This That
These those
Universitas Amikom Yogyakarta
3. Tenses
Direct Indirect
Simple Present Simple Past
Simple Past Past Perfect
Present Perfect Past Perfect
Present Continuous Past Continuous
Present Perfect Continuous Past Perfect Continuous
Simple Future Past Future
Universitas Amikom Yogyakarta
STATEMENT
In Indirect Statement , we use “that” as conjuction among
introduce phrase and reported phrases.
He said
He said to me that + reported words
He told me
Universitas Amikom Yogyakarta
STATEMENT
- Mary told her friends “I have been to Bali twice.”
- Mary told her friends that she had been to Bali twice.
- Father said “I am going out of town tomorrow”
- Father said that he was going out of town the following day.
- Mary told John “my father warned me last night”
- Mary told John that her father had warned her the night before.
- My sister said to me “I don’t like tennis”
- My sister said to me that she didn’t like tennis.
- Tom said “I didn’t go to school this morning”
- Tom said that he hadn’t gone to school that morning.
Universitas Amikom Yogyakarta
STATEMENT
When introduction phrase uses Simple Present Tense, then the tense of
reported phrase does not need to be changed.
- John says “I will go to Bandung tomorrow”
- John says that he will go to Bandung tomorrow
- Mary says “I have seen that film”
- Mary says that she has seen that film.
- My brother says “I met Tom at the party last night”
- My brother says that he met Tom at the party last night.
- Tom says “I don’t like English”
- Tom says that he don’t like English.
Universitas Amikom Yogyakarta
STATEMENT
Common VERB used for Indirect Speech
• Advise • Allow • Persuade
• Encourage • Beg • Urge
• Invite • Challenge • Suggest
• Order • Convience • Recommend
• Permit • Direct
• Remind • Expect
• Warn • Instruct
Universitas Amikom Yogyakarta
STATEMENT
- Joe said, “Please come to my party.”
- My teacher invited me to come to his party.
- My mentor said, “I think you should taje another English course.”
- My mentor advised me to take another English course.
- Hannah said, “Make an appointment with the dentist.”
- Hannah reminded me to make an appointment with the dentist.”
- My friend said, “I think you should take a long vacation.”
- My friend encouraged me to take a long vacation.
Universitas Amikom Yogyakarta
COMMAND
1. Positive Command
Add “to” before the command sentence, to connect introduction phrase
and reported command.
He asked me
to + infinitive
He told me
Universitas Amikom Yogyakarta
COMMAND
1. Positive Command
- He asked me “Open your book”
- He asked me to open my book.
- Mary told me “Stop talking to Jane”
- Mary told me to stop talking to Jane.
- Mother asked John “Pay attention to what I say”
- Mother asked John to pay attention to what she says.
- John told Mary “Wait until I come”
- John told Mary to wait until he comes.
- The teacher said to the students “Be quiet while I am talking”
- The teacher told the students to be quiet while she is talking.
Universitas Amikom Yogyakarta
COMMAND
2. Negative Command
Add “not to” before the - Mary told John “Don’t wait for me”
command sentence, to - Mary told John not to wait for her.
connect introduction
phrase and reported - I told him “Don’t mention it to anyone”
command. - I told him not to mention it to anyone.
- Father asked her “Don’t go there alone”
- Father asked her not to go there alone.
- Ira asked Tom “Don’t come to my house again”
- Ira asked tom not to come to her house again.
- Mothers asked John “Don’t smoke too much”
- Mother asked John not to smoke too much.
Universitas Amikom Yogyakarta
QUESTION
If direct question uses question words, where, when, why, what, who, how, etc.,
then those words used to connect introduction phrase and reported question
Positive Form
He asked me where/when/how etc.
Universitas Amikom Yogyakarta
QUESTION
- The man asked me : “Where do you live ?”
- The man asked me where I lived.
- John asked Mary : “Why do you get angry with me ?”
- John asked Mary why she got angry with him.
- I asked him : “When did you get back from your trip ?”
- I asked him when he had got back from his trip.
- He asked me : “How will you go there ?”
- He asked me how I would go there.
- John asked the girl : “What is your name ?”
- John asked the girl what her name was.
Universitas Amikom Yogyakarta
QUESTION
For “yes & no question” in direct speech, use “if” or “whether” to connect
introduction phrase and reported question.
- The boy asked John : “Does Mary live near here?”
- The boy asked John if Mary lived near there.
- The teacher asked her : “Have you finish your homework ?”
- The teacher asked her if she had finished her homework.
- Mary asked me : “Did you she John at the party the night before.
- Mary asked me whether I had seen John at the party the night before.
Universitas Amikom Yogyakarta
QUESTION
- We asked them : “Will you go to the movie with us tonight ?”
- We asked them whether they would go to the movie with us that night.
- Mother asked John : “Are you going to marry her ?”
- Mother asked John if he was going to marry her.
Note : if or whether can be used alternately
Universitas Amikom Yogyakarta
REPORTED SPEECH / MIXED TYPE
If statement and question phrases are mixed in a reported speech, use question
word connect introduction phrase and reported question, then add “AS” before
the reported statement
- She asked me, ”What is the time ?, my watch has stopped.”
- She asked me what the time was as her watch had stopped.
- Ira asked John, ”what is the matter with you ?, You don’t look well.”
- Mary asked John what the matter was with him as he didn’t look well.
- I asked her, ”How long have you been studying English ?, Your accent is very
good.”
- I asked her how long she had been studying English as he her accent was very
good.
Universitas Amikom Yogyakarta
REPORTED SPEECH / MIXED TYPE
- He told me, ”I am off to the movie, Where are you going ?”
- He told me that he was off to the movie and asked me where I was going.
- She said, ”It is cold inside, Is the window open ?”
- She said that it was cold inside and asked if the window was open.
Universitas Amikom Yogyakarta
REPORTED SPEECH / MIXED TYPE
For “yes & no” direct question, use “BUT” to connect “NO” answer; “AND” to
connect “YES” answer
- He asked me, ”Will you go out with me ?” No, I won’t.
- He asked me if I would go out with him, but I said I wouldn’t.
- Mother asked John, ”Have you had lunch ?” No, I haven’t.
- Mother asked John if he had had lunch but he said he hadn’t.
- She asked me, ”Can you meet me tomorrow ?” No.
- She asked me if I could meet her the following day, but I said I couldn’t.
- I asked her, ”Do you like vegetables ?” Yes, I do.
- Is asked her if she liked veggetables and she said she did.
Universitas Amikom Yogyakarta
REPORTED SPEECH / MIXED TYPE
- Mary asked John, ”Did you phone me last night ?” Yes, I did.
- Mary asked John if he had phoned her the night before and he said he had.
- Father asked me, ”Are you going to the movie tonight ?” Yes.
- Father asked me if I was going to the movie that night and I said I was.
Universitas Amikom Yogyakarta
You might also like
- (Materi Kelas X SMA SMSTR 1) : Statement (Pernyataan) Command (Perintah) Question (Pertanyaan)Document8 pages(Materi Kelas X SMA SMSTR 1) : Statement (Pernyataan) Command (Perintah) Question (Pertanyaan)Wardatul MukhlishohNo ratings yet
- B Elaj Ar G R Ammar B Ahasa Inggris: Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument10 pagesB Elaj Ar G R Ammar B Ahasa Inggris: Direct and Indirect SpeechMirza AkmalNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument6 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechAdi Dwi HermawanNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument8 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechAska Latifah HasibuanNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument6 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechDhaifullah fadlilNo ratings yet
- Statement (Pernyataan) Command (Perintah) Question (Pertanyaan)Document6 pagesStatement (Pernyataan) Command (Perintah) Question (Pertanyaan)haris hidayatNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument10 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechseraNo ratings yet
- Direct and IndirectDocument23 pagesDirect and IndirectKamaluddin KhanNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument6 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechAgusta AlgaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument16 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechPuji LestariNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument16 pagesDirect and Indirect Speech-Ita Puspitasari-100% (1)
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument6 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechGoena-One Wibisana100% (1)
- DirectDocument13 pagesDirectidkNo ratings yet
- Direct and IndirectDocument11 pagesDirect and IndirectNabil AbdurrahmanNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument8 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechAldy Kurnia Azhary100% (1)
- DIRECT and INDIRECT SPEECHDocument4 pagesDIRECT and INDIRECT SPEECHAnggoro BonongNo ratings yet
- DirectDocument8 pagesDirectCandra WaskitoNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument4 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechDwi BachtiarNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Speech: Statement (Pernyataan) Command (Perintah) Question (Pertanyaan)Document4 pagesDirect and Indirect Speech: Statement (Pernyataan) Command (Perintah) Question (Pertanyaan)Julie YaneyNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument10 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechVirly AliciaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument23 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechSarah Nazril67% (3)
- .Reported Speech: Statement (Pernyataan) Command (Perintah) Question (Pertanyaan)Document8 pages.Reported Speech: Statement (Pernyataan) Command (Perintah) Question (Pertanyaan)FridaNo ratings yet
- Puluhan Contoh Kalimat Direct Dan Indirect Speech Beserta ArtinyaDocument106 pagesPuluhan Contoh Kalimat Direct Dan Indirect Speech Beserta ArtinyaDewi Purwanti20% (5)
- Direct & Indirect Speech Consists of 3 Types: 1. Statement 2. Command Changes Needed From Direct Speech To Indirect SpeechDocument5 pagesDirect & Indirect Speech Consists of 3 Types: 1. Statement 2. Command Changes Needed From Direct Speech To Indirect SpeechElsy Gustika BuanaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect PPT FinalDocument16 pagesDirect and Indirect PPT FinalTshewang Pelmo50% (2)
- Loi Noi Gian TiepDocument5 pagesLoi Noi Gian TiepNguyễn Bảo Gia HânNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument5 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechGunjan GargNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech: I. - Read The Following Conversation. Then Answer The Questions About ItDocument7 pagesReported Speech: I. - Read The Following Conversation. Then Answer The Questions About Itanalia aviazziNo ratings yet
- Direct and Inderect SpeechDocument7 pagesDirect and Inderect SpeechTo The Point CSSNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument5 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechNadia Eka FebriantiNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument27 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechSELMA ANDANANo ratings yet
- Reported Speech - Docx 2Document3 pagesReported Speech - Docx 2LUCAS SALAZARNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Speech AnswerDocument7 pagesDirect and Indirect Speech AnswerYoges Wary100% (1)
- TERM-2 Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesTERM-2 Reported SpeechMujtaba Ahmed SyedNo ratings yet
- Direct Indirect Speechppt2Document16 pagesDirect Indirect Speechppt2marcelodomingos250No ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Speech: 1. Change of PronounsDocument22 pagesDirect and Indirect Speech: 1. Change of Pronounsmahboobeh hamzelooNo ratings yet
- Class X-Study Material (2020-21)Document17 pagesClass X-Study Material (2020-21)Sangam SinghNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech 1Document24 pagesReported Speech 1avghvg123No ratings yet
- Curso de Ingles - English Lesson - Direct and Reported Speech (Lección de Inglés - El Estilo Directo y Indirecto)Document4 pagesCurso de Ingles - English Lesson - Direct and Reported Speech (Lección de Inglés - El Estilo Directo y Indirecto)David OrtizNo ratings yet
- 1706862325855.mc-Reported Speech 2Document3 pages1706862325855.mc-Reported Speech 2MTNo ratings yet
- Chart Direct IndirectDocument3 pagesChart Direct IndirectBeow Yang ChanNo ratings yet
- Angl - Ta - Direct and Indirect SpeechesDocument4 pagesAngl - Ta - Direct and Indirect SpeechesCroire KenzoNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech-1Document34 pagesReported Speech-1sanchisanchita9No ratings yet
- Penjelasan Tentang Direct and Indirect Speech TerlengkapDocument11 pagesPenjelasan Tentang Direct and Indirect Speech TerlengkapHasby HasbyNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech 2Document11 pagesReported Speech 2Илона ПашенцеваNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument8 pagesReported SpeechHienNo ratings yet
- Direct & Indirect SpeechDocument5 pagesDirect & Indirect SpeechSilviNo ratings yet
- What Is Direct & Indirect Speech?Document2 pagesWhat Is Direct & Indirect Speech?Marielle Villagonzalo100% (2)
- Direct and IndirectDocument37 pagesDirect and IndirectKanoshikita ShimoarikuNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesReported Speechdeliailona cristeaNo ratings yet
- Direct Indirect EditDocument5 pagesDirect Indirect EditJuliaexenNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument36 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechChique LabuguenNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument35 pagesReported SpeechnaniNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesReported Speechvarunun1310% (1)
- Direct and Reported SpeechDocument18 pagesDirect and Reported SpeechAndres Onfire100% (1)
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument3 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechCarlos Alfonzo CalderónNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument10 pagesEnglishAvior Bagas ErtansyahNo ratings yet
- Use Quotation Marks in Direct Speech. Someone Said But Not The Exact Words. We Do Not Use Quotation Marks in Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesUse Quotation Marks in Direct Speech. Someone Said But Not The Exact Words. We Do Not Use Quotation Marks in Reported SpeechIeva VaičikauskaitėNo ratings yet
- Writing With Ease Level 1Document4 pagesWriting With Ease Level 1hweta173No ratings yet
- A2 - End of Course Test - With KeyDocument14 pagesA2 - End of Course Test - With KeynevenkaNo ratings yet
- Digvijaya Singh - Cooking Delights of The Maharajas - Exotic Dishes From The Princely House of Sailana-Vakils, Feffer Simons, Riddler (1982)Document374 pagesDigvijaya Singh - Cooking Delights of The Maharajas - Exotic Dishes From The Princely House of Sailana-Vakils, Feffer Simons, Riddler (1982)Abhishek Roy100% (2)
- Style Context Register - FINALDocument3 pagesStyle Context Register - FINALakshayaNo ratings yet
- Overview of NLPTEA-2020 Shared Task For Chinese Grammatical Error DiagnosisDocument11 pagesOverview of NLPTEA-2020 Shared Task For Chinese Grammatical Error DiagnosisrhkktcouNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Activity PDFDocument15 pagesPresent Perfect Activity PDFLaura I. Hernandez C.No ratings yet
- Adverbial ClauseDocument23 pagesAdverbial ClauseJulius RichardNo ratings yet
- 16 Speakout - Vocabulary - Extra - Starter - Unit - 2 PDFDocument2 pages16 Speakout - Vocabulary - Extra - Starter - Unit - 2 PDFFreddy Flores ÁvilaNo ratings yet
- Zikpuiipa Leh Literary CriticismDocument4 pagesZikpuiipa Leh Literary CriticismThlanthlá PeuleuNo ratings yet
- Sbi Clerk FormDocument5 pagesSbi Clerk FormDinesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Reading Test 7°Document2 pagesReading Test 7°Liliana fernandezNo ratings yet
- Aime 12 (2000-2023 Problems)Document159 pagesAime 12 (2000-2023 Problems)Dheeraj AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document19 pagesLesson 1NORHAFIZAH BT. ABD. RASHID MoeNo ratings yet
- LIT17 ANC G7U2 DarEye CS RPDocument2 pagesLIT17 ANC G7U2 DarEye CS RPHeba SahsahNo ratings yet
- Consti Law Final EssayDocument7 pagesConsti Law Final EssayKeishia TabingNo ratings yet
- (ACV-S04) Week 04 - Task - Assignment - Have You Ever - (PA)Document5 pages(ACV-S04) Week 04 - Task - Assignment - Have You Ever - (PA)Santy Nataly Peve RomanNo ratings yet
- Practtice No. 28 - Past Perfect Tense.Document4 pagesPracttice No. 28 - Past Perfect Tense.MiguelNo ratings yet
- Nama: Ninda Usnita No: 26 Kelas: Xi-Mipa 8: One of The Famaous Tourist Spots in Indonesia Is Bali IslandDocument2 pagesNama: Ninda Usnita No: 26 Kelas: Xi-Mipa 8: One of The Famaous Tourist Spots in Indonesia Is Bali IslandNindaNo ratings yet
- Applying Vygotskian Developmental Theory To Langua PDFDocument15 pagesApplying Vygotskian Developmental Theory To Langua PDFGo MavNo ratings yet
- English Grammar Workbook For IELTSDocument216 pagesEnglish Grammar Workbook For IELTSJJ PersonalityNo ratings yet
- Pamatay Na Banat Tagalog Love Quotes Pickup Lines Pinoy JokesDocument5 pagesPamatay Na Banat Tagalog Love Quotes Pickup Lines Pinoy JokesJustin DesolatorNo ratings yet
- Ix Grammar Test 13Document1 pageIx Grammar Test 13Kaizzar Ibn IhsaanNo ratings yet
- Intso Education: General Knowledge Talent Search Olympiad (Gtso) 2016 - 2017Document3 pagesIntso Education: General Knowledge Talent Search Olympiad (Gtso) 2016 - 2017Ranjith Kumar100% (1)
- Macro Plan - Class 2Document10 pagesMacro Plan - Class 2Gayathri SenthilmuruganNo ratings yet
- КТП 4 класс Smiles-4Document16 pagesКТП 4 класс Smiles-4Данил ГагаринNo ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad (Department of English Language & Applied Linguistics) WarningDocument3 pagesAllama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad (Department of English Language & Applied Linguistics) WarningMoazama BatoolNo ratings yet
- RedundancyDocument13 pagesRedundancyArvin Antonio OrtizNo ratings yet
- Modulo 2 BasicDocument24 pagesModulo 2 BasicJose Miguel Ramirez LuisNo ratings yet
- Class 8 All Subjects PortionsDocument5 pagesClass 8 All Subjects PortionsEswara PrasadNo ratings yet
- Effective Communication & Barriers To It! - SomolekhaDocument17 pagesEffective Communication & Barriers To It! - SomolekhaZinneerah HibaNo ratings yet