Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Homework
Homework
Uploaded by
Afnan AbdulazizOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Homework
Homework
Uploaded by
Afnan AbdulazizCopyright:
Available Formats
Homework
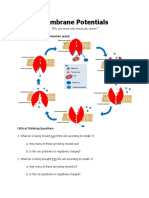
15.3 b) The inside of the axon has a charge of –70mV compared with the outside.
c) By active transport using ATP to provide energy for sodium–potassium pumps in the
membrane of the axon. Both sodium and potassium ions are positively charged. Three
sodium ions are pumped out for every two potassium ions pumped in, so this builds up a
positive charge outside compared with inside. There are also many negatively charged
organic compounds inside the axon that contribute to the resting potential.
d) i) It is called depolarisation because the axon was polarised so that it had a negative
charge inside and a positive charge outside. Now this is altered and there is a negative
charge outside and a positive charge inside.
ii) Annotations for the rising phase of the action potential could be: Voltage-gated sodium ion
channels in the membrane open and allow sodium ions to diffuse in down their
electrochemical gradient. As they enter the axon, their positive charge causes the negative
charge inside the axon to be brought to zero and become more positive until it reaches
+30mV. There is a positive feedback at this time as depolarisation stimulates more and more
voltage-gated sodium ion channels to open.
e) Annotations could be: Between 1ms and 2ms, the axon is repolarised. The voltage-gated
sodium ion channels close (and cannot open). Voltagegated potassium ion channels open
and potassium ions diffuse out to restore the resting potential.
f) about 4ms
You might also like
- Ionization Potential of MercuryDocument7 pagesIonization Potential of Mercurylucy lucy100% (8)
- Excitable Tissue PhysiologyDocument13 pagesExcitable Tissue PhysiologyAlbert Che33% (3)
- Action Potential: DR Raghuveer Choudhary Associate ProfessorDocument63 pagesAction Potential: DR Raghuveer Choudhary Associate ProfessorPhysiology by Dr Raghuveer100% (2)
- 2.membrane Physiology, Nerve and MuscleDocument6 pages2.membrane Physiology, Nerve and MuscleCLEMENT100% (1)
- Sodium Potassium Pump and Action PotentialDocument4 pagesSodium Potassium Pump and Action PotentialPiyush BhallaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project On Electrochemical CellDocument12 pagesChemistry Project On Electrochemical CellSatyam Giri84% (142)
- Topic 3-Active Transport - EditedDocument7 pagesTopic 3-Active Transport - Editedsalve joy villanuevaNo ratings yet
- Physiology Lec 14Document34 pagesPhysiology Lec 14omer.naeem.366No ratings yet
- Mineral Ion TransportDocument1 pageMineral Ion TransportmrztweetbeakNo ratings yet
- Na+ - K+ Pump PresentationDocument12 pagesNa+ - K+ Pump Presentationakshatvats346No ratings yet
- Membrane PotentialDocument66 pagesMembrane PotentialGksNo ratings yet
- Neurons Notes 1 PDFDocument16 pagesNeurons Notes 1 PDFabcdeNo ratings yet
- Notes - Communication Within The NeuronDocument2 pagesNotes - Communication Within The NeuronDaian MorganNo ratings yet
- Active TransportDocument51 pagesActive Transportericka khimNo ratings yet
- Negative Negative: Chapter Two: Electrical Signals in Nerve CellsDocument6 pagesNegative Negative: Chapter Two: Electrical Signals in Nerve CellsStacy BrenesNo ratings yet
- A2 Level Biology: Coordination-Lecture 3 by Muhammad Ishaq KhanDocument10 pagesA2 Level Biology: Coordination-Lecture 3 by Muhammad Ishaq KhanAwais BodlaNo ratings yet
- Types of Neuron Transmission and Communication SystemDocument5 pagesTypes of Neuron Transmission and Communication SystemRbbani AwanNo ratings yet
- Questions For Chapter 5: Membrane Potential and Action PotentialDocument3 pagesQuestions For Chapter 5: Membrane Potential and Action PotentialElectrifying SaurabhNo ratings yet
- Membrane Potentials: "Why Are Some Cells Electrically Active?"Document5 pagesMembrane Potentials: "Why Are Some Cells Electrically Active?"yasmine laarajNo ratings yet
- Primary Active TransportDocument2 pagesPrimary Active TransportMaya SariNo ratings yet
- Solid Semiconductors Are Used To Make A TransistorDocument6 pagesSolid Semiconductors Are Used To Make A TransistorGodwinNo ratings yet
- CHEMISRTYDocument16 pagesCHEMISRTYAmal AmalNo ratings yet
- Semiconductors Module 2Document10 pagesSemiconductors Module 2zaidkadiri9No ratings yet
- ECCDocument4 pagesECCSanat ChopraNo ratings yet
- Action Potential: Nams, Bir Hospital B.SC - MIT 1 Year Suraj Sah Roll No. 9Document42 pagesAction Potential: Nams, Bir Hospital B.SC - MIT 1 Year Suraj Sah Roll No. 9Maxamed Cali AtomNo ratings yet
- Membrane Potential and Action PotentialDocument30 pagesMembrane Potential and Action Potentialironik kimiaNo ratings yet
- Active TransportDocument7 pagesActive Transportidokofavour2015No ratings yet
- DSR Elektronika BartsaDocument6 pagesDSR Elektronika BartsaBarNo ratings yet
- Membrane Potentials and Action PotentialsDocument14 pagesMembrane Potentials and Action Potentialsabd al rahman HindiNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Cell OriginalDocument7 pagesElectrochemical Cell OriginalShajathi MNo ratings yet
- Celeste Physics Final2Document8 pagesCeleste Physics Final2Hwee Hong AngNo ratings yet
- Finding EMF of Electrochemical CellDocument4 pagesFinding EMF of Electrochemical CellVivek Singh Yadav100% (1)
- Uptake of Nutrients by PlantsDocument40 pagesUptake of Nutrients by PlantsmkmikmiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MOSFET Operation: ECE/CS 5720/6720 Analog Integrated Circuit DesignDocument52 pagesIntroduction To MOSFET Operation: ECE/CS 5720/6720 Analog Integrated Circuit DesignitsmyturnNo ratings yet
- The Action Potential: Page 1. IntroductionDocument12 pagesThe Action Potential: Page 1. IntroductionSimón JimenezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 The Sodium Potassium PumpDocument10 pagesLesson 3 The Sodium Potassium Pumpanulorance98No ratings yet
- BE Lecture 2Document23 pagesBE Lecture 2Daniyal MughalNo ratings yet
- Linear Particle AcceleratorsDocument3 pagesLinear Particle AcceleratorsburhanNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2 NeurophysiologyDocument2 pagesProblem Set 2 NeurophysiologyTiffany YehNo ratings yet
- Physiology Course: Dr. Velu M. RachelDocument56 pagesPhysiology Course: Dr. Velu M. RachelKunda JosephNo ratings yet
- Guyton Notes Chapter 05Document4 pagesGuyton Notes Chapter 05aima_uy50% (2)
- Fisdas2 - Faraday Law - 4201419040Document18 pagesFisdas2 - Faraday Law - 420141904040 Dani Firmansyah KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Problems Set912 Solutions 1lc83ckDocument6 pagesDynamics Problems Set912 Solutions 1lc83ckNasir GujjjarNo ratings yet
- Class 8 - Science - Chemical Effects of Electric CurrentDocument7 pagesClass 8 - Science - Chemical Effects of Electric CurrentSougrakpam SNo ratings yet
- Viii Chapter 14Document6 pagesViii Chapter 14Shubh tiwari TiwariNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Inestigatory ProjectDocument16 pagesChemistry: Inestigatory ProjectAnshulNo ratings yet
- Primary CellDocument4 pagesPrimary CellganeshpreetamNo ratings yet
- Sodium and Potassium - Atp Ase PumpDocument18 pagesSodium and Potassium - Atp Ase PumpYaswanthyadavNo ratings yet
- Ch04 Questions Answer KeyDocument16 pagesCh04 Questions Answer KeyMichaelNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 The Nervous ImpulseDocument25 pagesLesson 1 The Nervous Impulsesohailnoreen5062No ratings yet
- TP 2: Studying Rectifiers and Semi-ConductorsDocument5 pagesTP 2: Studying Rectifiers and Semi-ConductorsZiad FAwalNo ratings yet
- Danish ChemistryDocument13 pagesDanish ChemistryNaveen Kumar.RNo ratings yet
- About Lead Acid BatteriesDocument8 pagesAbout Lead Acid BatteriesAurvin SinghNo ratings yet
- Fisdas2 Inductance 4201419040Document16 pagesFisdas2 Inductance 420141904040 Dani Firmansyah KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project On Electrochemical CellDocument12 pagesChemistry Project On Electrochemical CellløzanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project On Electrochemical CellDocument13 pagesChemistry Project On Electrochemical CellArin SinghNo ratings yet
- Dainell CellDocument7 pagesDainell Cellhack babaNo ratings yet
- Psybio Lesson 3Document25 pagesPsybio Lesson 3Lago, Azel Chin L.No ratings yet
- LRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronFrom EverandLRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument1 pageEnglishAfnan AbdulazizNo ratings yet
- EngDocument1 pageEngAfnan AbdulazizNo ratings yet
- Bio StaticsDocument1 pageBio StaticsAfnan AbdulazizNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument2 pagesChemistryAfnan AbdulazizNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry AsDocument56 pagesOrganic Chemistry AsAfnan AbdulazizNo ratings yet
- Bio StaticsDocument1 pageBio StaticsAfnan AbdulazizNo ratings yet