Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Motivation Edutap
Uploaded by
vavachipapachu017Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Motivation Edutap
Uploaded by
vavachipapachu017Copyright:
Available Formats
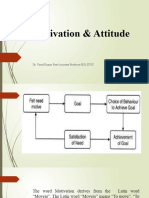
What is meant by morale? How is it related to productivity?
Explain the factors
contributing to morale.
Q.What is Behavioral Reinforcement ? Explain the Positive & Negative reinforcement.
Ans: Behavioral reinforcement is the process of increasing, decreasing or
eliminating the likelihood of happening of a particular behavior in future with the
help of reinforcers which are external and environmentally based.
It is based on law of effect i.e. individual behavior is a function of its
consequences which means that behaviors followed by positive consequences
tend to be repeated and vice-versa.
Behavioural reinforcement theory was given by B.F. Skinner in 19xx and it
ignores that inner state of mind of the individual and concentrates solely on
what happens when he or she takes some action.
Positive Reinforcement: It refers to the process of increasing the incidence of a
particular desired behavior by providing positive response (reinforcer or
stimulus) when an individual shows the required behavior.
Positive response may be in the form of reward, pay hike, recognition etc.
Negative Reinforcement: It refers to the process of increasing the incidence of a
particular desired behavior by removing an unpleasant stimulus.
it is the action of removing the undesirable outcome or stimulus that serves as
the reward for performing the behavior.
For example, a teacher can eliminate that night's homework if kids study hard
and accomplish a lot in class. If this happens multiple times, the kids will
consistently work harder and be more productive while in the classroom.
For instance, at a manufacturing company, employees must attend work five
days a week, eight hours a day. However, to encourage greater productivity, a
supervisor might reduce work hours for the final week of the month. If
employees meet a production goal, they won't have to spend as much time at
work
Q2. Explain How Maslow classified the needs of an individual, also state its merits and
limitations? -15 marks
Ans.
Abhrahm Maslow is considered to be the father of “Humanistic Psychology.” He proposed
“Hierarchy of needs theory” in the early 1940s. As per this theory, human needs are classified in
below mentioned 5 levels, which are further subdivided into lower and higher order needs:
1. Physiological needs: These are the most basic needs which are needed for human
survival such as hunger, thirst, etc. These must be satisfied
2. Safety needs: Once physiological needs are satisfied, then human beings want to be safe
and free from any kind of physical harms such as attack, fight, etc.
Both Physiological and Safety needs are considered to be “Lower order needs” and are satisfied
externally.
3. Social needs: After satisfying lower order needs, human beings want be socially
acceptable by the society being a social animal. Here human beings look for respect and
acceptance by the society.
4. Esteem needs: Human beings want self-esteem not only from society but also from
themselves. We want to be looked into a positive way both by society and ourselves.
5. Self-actualization needs: Once, above mentioned needs are satisfied, then human beings
want to maximize their own potential. At this stage, human beings want to become
what he or she is capable of becoming.
As per this theory, Social, Esteem and Self-actualization needs are considered to be “Higher
order needs” and are satisfied internally by an individual.
Human beings tend to satisfy needs in order of hierarchy or by progressing upwards starting
from physiological needs to satisfy self-actualization needs. Similarly, once higher order needs
are unsatisfied, then human beings tend to resort to a lower level of hierarchy and try to satisfy
them first.
Merits:
1. This theory is very simple, practical and easy to understand.
2. With the help of clearly defined hierarchy of needs, Managers may try to understand
what level of needs is operating in a particular employee. Therefore, by satisfying that
particular need, Managers may motivate that employee.
Limitations:
1. This theory assumed that at any point of time, only one level of needs is deficient in an
individual. However, that is not the case always; any individual may try to satisfy more
than one level of needs at the same time. For example, by satisfying social and esteem
needs at the same time.
2. Rigid Hierarchy- As per this theory, an individual cannot skip any level of needs.
However, we may try to satisfy higher needs first even lower order needs are
unsatisfied.
For example, a starving artist may try to satisfy self-actualization needs directly.
3. This theory is based on assumptions and lacks research evidence in its support.
You might also like
- Bcca 6 Ed 02 S5Document15 pagesBcca 6 Ed 02 S5Sheetal NafdeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Project: The Concept of MotivationDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Project: The Concept of MotivationSmiti WaliaNo ratings yet
- Employee MotivationDocument13 pagesEmployee MotivationHetvi SurtiNo ratings yet
- MotivationDocument14 pagesMotivationMudassir HanifNo ratings yet
- MC&OB Unit 4Document17 pagesMC&OB Unit 4Tanya MalviyaNo ratings yet
- Educational Motivation TheoriesDocument297 pagesEducational Motivation TheoriesKristine Joy HallaresNo ratings yet
- Motivating Employees: LO2: Evaluate How To Motivate Individuals and Teams To Achieve A GoalDocument46 pagesMotivating Employees: LO2: Evaluate How To Motivate Individuals and Teams To Achieve A GoalHadeel Abdul Salam50% (2)
- 3.1 MotivationDocument44 pages3.1 Motivation22bce068No ratings yet
- Theories of Motivation - Classical Theories: Study NotesDocument10 pagesTheories of Motivation - Classical Theories: Study NotesSatbeer SinghNo ratings yet
- Different Motivation Model & How They Work (In Organization)Document35 pagesDifferent Motivation Model & How They Work (In Organization)Mohibur Rahman MoonNo ratings yet
- OBE Unit 5 (Motivation)Document7 pagesOBE Unit 5 (Motivation)Prateek DaveNo ratings yet
- Motivation, Emotion, and Stress and CopingDocument109 pagesMotivation, Emotion, and Stress and CopingeyobNo ratings yet
- OB BBE5 Unit2b MotivationDocument68 pagesOB BBE5 Unit2b MotivationKeshav AroraNo ratings yet
- Motivation Motivation: Motivation Can Be Defined in A Number of Ways. Generally, It Is Defined As A DrivingDocument5 pagesMotivation Motivation: Motivation Can Be Defined in A Number of Ways. Generally, It Is Defined As A DrivingHarpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Motivation and LeadershipDocument16 pagesModule 4 - Motivation and LeadershipFaraz SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - MotivationDocument34 pagesModule 4 - MotivationfaraztalhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Eight Motivation Chapter Eight MotivationDocument29 pagesChapter Eight Motivation Chapter Eight MotivationgereNo ratings yet
- Module 4 CCI PrintedDocument18 pagesModule 4 CCI PrintedLabour lawNo ratings yet
- Work MotivationDocument76 pagesWork MotivationSayonee BoseNo ratings yet
- MotivationDocument13 pagesMotivationOloka George OkwirNo ratings yet
- Motivation.: Goals Motives BehaviourDocument11 pagesMotivation.: Goals Motives BehaviourOloka George OkwirNo ratings yet
- Unit - II: Individual in Workplace Motivation & Job SatisfactionDocument38 pagesUnit - II: Individual in Workplace Motivation & Job SatisfactionPrachiNo ratings yet
- Psych Research ProjectDocument14 pagesPsych Research ProjectMunira KaidNo ratings yet
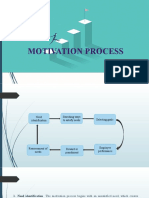
- Motivation Process: Fousiya T PDocument13 pagesMotivation Process: Fousiya T PFouzia imzNo ratings yet
- ProstitutionDocument34 pagesProstitutionGautamNo ratings yet
- Finals - THCC 329Document17 pagesFinals - THCC 329MARITONI MEDALLANo ratings yet
- Motivation: Motivation Is A Psychological Feature That Induces An Organism To Act Towards ADocument63 pagesMotivation: Motivation Is A Psychological Feature That Induces An Organism To Act Towards ANagireddy KalluriNo ratings yet
- Module 2 and 3 - Motivational Theories (Autosaved)Document48 pagesModule 2 and 3 - Motivational Theories (Autosaved)Nikhil JadhavNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 MC and Ob $Document31 pagesUnit-4 MC and Ob $Sneha prajapatiNo ratings yet
- OB Ch-4Document48 pagesOB Ch-4Asegid gezehagnNo ratings yet
- 08 Back To Basics in Motivation TheoryDocument8 pages08 Back To Basics in Motivation Theoryaneetamadhok9690No ratings yet
- A Study On Employees MotivationDocument89 pagesA Study On Employees MotivationT S Kumar KumarNo ratings yet
- Motivation 1980007641Document12 pagesMotivation 1980007641kshitizNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Motivation: 1. ConceptsDocument12 pagesUnit 4 Motivation: 1. ConceptsFatima AliNo ratings yet
- Null 1Document18 pagesNull 1marshadNo ratings yet
- Unit 6: Motivation, Emotion and StressDocument89 pagesUnit 6: Motivation, Emotion and StressPuna Ram GhimireNo ratings yet
- PPTDocument8 pagesPPTRiya ChawlaNo ratings yet
- What Is MotivationDocument11 pagesWhat Is MotivationAbhishek GargNo ratings yet
- UCC - Intro To Psy - Ppoint Unit 9Document19 pagesUCC - Intro To Psy - Ppoint Unit 9Demeico DavisNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour - 2: MotivationDocument4 pagesConsumer Behaviour - 2: MotivationHimansu S M100% (5)
- Motivation and EmotionDocument12 pagesMotivation and EmotionSristi RayNo ratings yet
- Mot Vat IonDocument17 pagesMot Vat IonmmrashmiNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour - 2: Motivation Induvidual Determinats of BehaviuorDocument10 pagesConsumer Behaviour - 2: Motivation Induvidual Determinats of BehaviuorddurgeshNo ratings yet
- Motivation: How to Develop an Inner Fire That Helps You Achieve Your GoalsFrom EverandMotivation: How to Develop an Inner Fire That Helps You Achieve Your GoalsNo ratings yet
- Motivation and Entrepreneurship DevelopmentDocument20 pagesMotivation and Entrepreneurship DevelopmentPriyanshu ParidaNo ratings yet
- Module 5 HBODocument11 pagesModule 5 HBONovell PepigaNo ratings yet
- Motivation Term PaperDocument34 pagesMotivation Term Paperadnan_rosa0% (1)
- Motivation WorkshopDocument38 pagesMotivation WorkshopMax EldridgeNo ratings yet
- Intrinsic MotivationDocument3 pagesIntrinsic MotivationdeenaismeehNo ratings yet
- Motivation TheoriesDocument4 pagesMotivation Theorieseliver ladrilloNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Motivation NotesDocument20 pagesModule 2 Motivation Notesrahul rameshNo ratings yet
- Kuldeep Singh HRMDocument13 pagesKuldeep Singh HRMKaran BishtNo ratings yet
- Learning TheoriesDocument20 pagesLearning TheoriesDaniel DubeNo ratings yet
- SS Motivation P1Document19 pagesSS Motivation P1ROMEL CHAKMANo ratings yet
- Maslow' S Hierarchy Abraham MaslowDocument38 pagesMaslow' S Hierarchy Abraham MaslowCriza Mae Castor PadernalNo ratings yet
- Business AdministrationDocument12 pagesBusiness AdministrationBharat NandaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 MotivationDocument16 pagesChapter 6 MotivationYosef TsegayeNo ratings yet
- Borland C++Document3 pagesBorland C++Sanjay SethNo ratings yet
- Engineering Council of South Africa: Training and Mentoring Guide For Professional CategoriesDocument26 pagesEngineering Council of South Africa: Training and Mentoring Guide For Professional CategoriesMECHANICAL ENGINEERINGNo ratings yet
- HRM Chapt 4 With AnswersDocument3 pagesHRM Chapt 4 With Answersjoebloggs1888No ratings yet
- Measurement of Hindered Phenolic Antioxidant Content in HL Turbine Oils by Linear Sweep VoltammetryDocument6 pagesMeasurement of Hindered Phenolic Antioxidant Content in HL Turbine Oils by Linear Sweep VoltammetryMohanadNo ratings yet
- Obermeier1985 - Thermal Conductivity, Density, Viscosity, and Prandtl-Numbers of Di - and Tri Ethylene GlycolDocument5 pagesObermeier1985 - Thermal Conductivity, Density, Viscosity, and Prandtl-Numbers of Di - and Tri Ethylene GlycolNgoVietCuongNo ratings yet
- NDBS - Exit Interview Form - UpdatedDocument2 pagesNDBS - Exit Interview Form - UpdatedRaichetty VenuNo ratings yet
- Decoding of Convolution CodeDocument3 pagesDecoding of Convolution Codesonali_raisonigroupNo ratings yet
- Literature & MedicineDocument14 pagesLiterature & MedicineJoyce LeungNo ratings yet
- SAEP-35 Valves Handling, Hauling, Receipt, Storage, and Testing-15 April 2020Document10 pagesSAEP-35 Valves Handling, Hauling, Receipt, Storage, and Testing-15 April 2020Ahdal NoushadNo ratings yet
- The Differences Between OHS Management System StandardsDocument27 pagesThe Differences Between OHS Management System StandardsRommel100% (2)
- IASDocument3 pagesIASankit sharmaNo ratings yet
- Ampd Data Sheet Vacuum Casting Resin 8263Document2 pagesAmpd Data Sheet Vacuum Casting Resin 8263Lorenzo Guida0% (1)
- Question Bank 1st UnitDocument2 pagesQuestion Bank 1st UnitAlapati RajasekharNo ratings yet
- SSP700ADocument4 pagesSSP700AKanwar Bir SinghNo ratings yet
- 33198Document8 pages33198tatacpsNo ratings yet
- Moxa Eds 2005 El Series Datasheet v1.3 PDFDocument3 pagesMoxa Eds 2005 El Series Datasheet v1.3 PDFPatrick RNo ratings yet
- Route TrainingDocument14 pagesRoute Trainingjohn100% (1)
- Green Bill: Easypa Y Scan & PayDocument4 pagesGreen Bill: Easypa Y Scan & Paymohamed elmakhzniNo ratings yet
- 8th Chemical Effects of Electric Current Solved QuestionsDocument3 pages8th Chemical Effects of Electric Current Solved QuestionsGururaj KulkarniNo ratings yet
- The Journal of The Acoustical Society of AmericaDocument12 pagesThe Journal of The Acoustical Society of Americadr01dNo ratings yet
- Curs FinalDocument8 pagesCurs FinalandraNo ratings yet
- Rough Translation of Emil Stejnar's Schutzengel BookDocument119 pagesRough Translation of Emil Stejnar's Schutzengel BookJustA Dummy100% (1)
- Miele G 666Document72 pagesMiele G 666tszabi26No ratings yet
- Honeywell S4565 CVI Ignition ControlDocument66 pagesHoneywell S4565 CVI Ignition ControlcarlosNo ratings yet
- Wood Support-Micro Guard Product DataDocument13 pagesWood Support-Micro Guard Product DataM. Murat ErginNo ratings yet
- Pugh ChartDocument1 pagePugh Chartapi-92134725No ratings yet
- Aras Jung Curriculum IndividualDocument72 pagesAras Jung Curriculum IndividualdianavaleriaalvarezNo ratings yet
- Syncronex Single Copy 3.1 Users GuideDocument208 pagesSyncronex Single Copy 3.1 Users GuideTony BoscoNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris Teknik Individual Assignment 3Document5 pagesBahasa Inggris Teknik Individual Assignment 3Khaiza SyNo ratings yet
- Nielsen Millennial Traveler Study Jan 2017Document11 pagesNielsen Millennial Traveler Study Jan 2017nhocti1610No ratings yet