Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 8 Soil Profile and Soil Fertility
Uploaded by
MikeCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 8 Soil Profile and Soil Fertility
Uploaded by
MikeCopyright:
Available Formats
Soil Profile and Soil Fertility
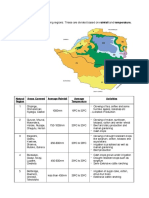
Various layers in soil are called soil horizons.
Right at the top you will see some
vegetation, that is, trees or grass.
Just below the vegetation you will
see a very dark layer of soil, this is
humus. Below the humus you will
see another dark layer, and this is
topsoil. Below the topsoil there is a
layer which is light in colour, and this
is subsoil. Below this you will see
pieces of stones, and this is
gravel/weathered rock fragments.
Below the gravel you will see an
impervious rock, and this is bedrock
or parent rock.
Horizon O (Humus)
- Layer is made up of partially decayed organic matter and surface organisms.
- It is often dark brown to black in colour due to the organic content.
Horizon A (Topsoil)
- The soil is dark in colour.
- It contains humus from rotting vegetation.
- Most roots are found in this horizon.
Horizon B (Subsoil)
- It is light in colour.
- It contains less nutrients than topsoil.
- Roots of long rooted plants are found in this horizon.
Horizon C (Gravel soil)
- This is soil with small stones.
- It is poor in nutrients.
- Tree roots may be found.
Horizon D (Parent/Bed Rock)
- The rock is impervious, that is, it doesn't allow water to pass through, so it forms a water
table.
- If you dig a well and reach this layer, you will have a permanent water supply.
Soil Profile and Soil Fertility
Management of soil fertility
- Fertile soils are soils that can sustain plant growth.
- Soil fertility can be lost hence the need to manage soil fertility.
- The management of soil fertility is important to ensure food security and environmental
sustainability.
- The soil fertility management methods must be able to make the most of crop production
while minimising soil degradation and exhausting soil nutrients.
- Soil degradation is the decline in soil health due to poor management.
Methods of Soil Fertility Management
1. Applying fertilizers both organic and inorganic
- When soil nutrients are missing or in short supply we add fertilizers to replace the lost
nutrients.
- They can be added from a variety of sources like organic matter, for example, compost or
animal manure.
- They can be added from sources like inorganic matter, for example, manufactured fertilisers
that contain nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus.
2. Crop Rotation
- Is the growing of different types of crops on the same piece of land year after year.
- This is done so that the crop does not use up only one set of nutrients as growing the same
crop on the same piece of land year after year (monocropping) gradually exhausts the soil of
certain nutrients.
- Crop rotation helps in reducing soil erosion, increasing soil fertility and crop yield.
3. Adding lime
- Lime is crushed limestone.
- It helps to raise the pH levels of acidic soils.
- When added to soil, it dissolves and neutralises soil acidity.
- It is a source of calcium and magnesium.
- It improves the uptake of major plant nutrients.
- It contains natural nutrients which promote healthy plant growth.
4. Adding ant heap soil
- Farmer’s which cannot afford inorganic fertilizers can use ant soil to boost physical structure
of unfertile soils.
- It improves the water holding capacity of the soil, helps retains soil moisture and texture.
Soil Profile and Soil Fertility
Exercise: Soil Profile and Soil Fertility
Total: 20 Marks
Answer all questions in the spaces provided.
1. Topsoil is ________________ in colour, while subsoil is ___________________ in colour. [2]
2. Topsoil is _______________ in nutrients, while subsoil is _______________ in nutrients. [2]
3. Describe Horizon C.
___________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________[3]
4. Which horizon contains most plant roots? ______________________________________ [1]
5. Describe the characteristics of topsoil.
___________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________[2]
6. What is soil degradation?
___________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________[2]
7. Why is it important to manage soil fertility?
___________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________[2]
8. Name and describe 2 methods of soil fertility management.
___________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________[4]
9. Name 2 of the 3 major nutrients needed by plants.
_________________________________________________________________________[2]
You might also like
- Different Types of SoilDocument7 pagesDifferent Types of SoilSeth KnightsNo ratings yet
- Weathering and Soil FormationDocument26 pagesWeathering and Soil FormationrudyNo ratings yet
- Exp SC 7 - Chapter 09Document12 pagesExp SC 7 - Chapter 09megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Appendix Basic Soil Science and Soil Fertility: Npdes Permit Writers' Manual For CafosDocument22 pagesAppendix Basic Soil Science and Soil Fertility: Npdes Permit Writers' Manual For CafosMohamed EL BAGHDADINo ratings yet
- Layers of The EarthDocument6 pagesLayers of The EarthMeredith100% (3)
- Science Q4 Week 1Document31 pagesScience Q4 Week 1ruby loraNo ratings yet
- Abdullah Tariq Roll No: 19744 Section: Q Soil and Environmental Sciences Submitted To: Dr. Nabeel Khan Niazi University of Agriculture FaislabadDocument3 pagesAbdullah Tariq Roll No: 19744 Section: Q Soil and Environmental Sciences Submitted To: Dr. Nabeel Khan Niazi University of Agriculture FaislabadMaria YaseenNo ratings yet
- SCI EN CE 4: Quar Ter 4 - Modu LE 2: Comp Aring THE Diffe Rent Types OF SoilDocument7 pagesSCI EN CE 4: Quar Ter 4 - Modu LE 2: Comp Aring THE Diffe Rent Types OF SoilCristita Macaranas VigoNo ratings yet
- Compositon of The Planet EarthDocument43 pagesCompositon of The Planet EarthLore June CampolloNo ratings yet
- Soil ProfileDocument4 pagesSoil ProfileHidayah DungunNo ratings yet
- Soil and Soil ProfileDocument23 pagesSoil and Soil ProfileBheya Samantha MontieroNo ratings yet
- Biogeography - I - Study NotesDocument17 pagesBiogeography - I - Study Notessvtiwari58No ratings yet
- Weathering and Organic Processes Form Soil.: What Makes Soils Different?Document8 pagesWeathering and Organic Processes Form Soil.: What Makes Soils Different?Precious BalgunaNo ratings yet
- Land, Soil & Water Resources PDFDocument31 pagesLand, Soil & Water Resources PDFPrakrutiShahNo ratings yet
- Quarter 4 - Module 1: "Types and Characteristics of Soil": Science 4Document3 pagesQuarter 4 - Module 1: "Types and Characteristics of Soil": Science 4Marivicsabenorio Subito100% (1)
- Soil - Components, Properties and Processes (1Document12 pagesSoil - Components, Properties and Processes (1Tiffany RishiNo ratings yet
- Week 10 SoilsDocument9 pagesWeek 10 SoilsLyra :]No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Lesson 2 (Soil)Document12 pagesChapter 6 Lesson 2 (Soil)Logina Ibrahim MostafaNo ratings yet
- P5 Science Lesson NotesDocument72 pagesP5 Science Lesson NotesMwaze AssonNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 Soil Physical PropertiesDocument13 pagesCHAPTER 5 Soil Physical PropertiesMica SaweNo ratings yet
- SOILDocument3 pagesSOILCourtney Dela FierraNo ratings yet
- Soil - PPT Level OneDocument24 pagesSoil - PPT Level OneAbdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- Karakteristik TanahDocument44 pagesKarakteristik TanahFaradita RahmaNo ratings yet
- Layers and Properties of SoilDocument30 pagesLayers and Properties of SoilratriziltiNo ratings yet
- SCI EN CE 4: Quar Ter 4 - Modu LE 1: Types OF Soil AND Their Char Acter IsticsDocument4 pagesSCI EN CE 4: Quar Ter 4 - Modu LE 1: Types OF Soil AND Their Char Acter IsticsCristita Macaranas VigoNo ratings yet
- Soil ResourcesDocument7 pagesSoil Resourcessakhi malpaniNo ratings yet
- SoilDocument21 pagesSoilAngelica GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - SoilDocument14 pagesLesson 1 - Soilnadia.changlapenNo ratings yet
- Natsci ReviewerDocument26 pagesNatsci Reviewerhera chanelsNo ratings yet
- Soil Formation WorksheetDocument4 pagesSoil Formation WorksheetMike UesiNo ratings yet
- SOILDocument30 pagesSOILmay bondocNo ratings yet
- Topic 4: Sediment & Sedimentary Rock: Eg208 Physical Geology (SOIL)Document28 pagesTopic 4: Sediment & Sedimentary Rock: Eg208 Physical Geology (SOIL)Lionel MessiNo ratings yet
- Exp SC 4 - Chapter 06Document7 pagesExp SC 4 - Chapter 06megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Composition of SoilDocument18 pagesComposition of SoilsampadaNo ratings yet
- SoilDocument9 pagesSoilRajeevSangamNo ratings yet
- Soil Chemistry: CHM 001 Chemistry For EngineersDocument40 pagesSoil Chemistry: CHM 001 Chemistry For EngineersEjay CabangcalaNo ratings yet
- Texture, Structure, & Horizons: Integrated ScienceDocument10 pagesTexture, Structure, & Horizons: Integrated ScienceJonel GallazaNo ratings yet
- Soil Survey Lab Exerecise-02Document6 pagesSoil Survey Lab Exerecise-02Sachin ShrivastavNo ratings yet
- Types of Soil and Rocks and Physical Properties of Each Soils and RocksDocument17 pagesTypes of Soil and Rocks and Physical Properties of Each Soils and RocksJelou LumakinNo ratings yet
- Geography Y9Document34 pagesGeography Y9Sylvia LawNo ratings yet
- Soil Class7Document14 pagesSoil Class7Nova 777No ratings yet
- Lecture GeologyDocument4 pagesLecture GeologyAnne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Physics of Ground: Solid Phase: ObjectivesDocument11 pagesPhysics of Ground: Solid Phase: ObjectivesKuys JENo ratings yet
- Lecture On Soil and IrrigationDocument18 pagesLecture On Soil and IrrigationMuniru QudusNo ratings yet
- Soil Properties: Unit Four: Soil Science Agriscience IDocument32 pagesSoil Properties: Unit Four: Soil Science Agriscience Idynamesimsy11No ratings yet
- 1 Soil ResourcesDocument24 pages1 Soil ResourcesBelle ÂmeNo ratings yet
- G7 SoilDocument43 pagesG7 SoilJamika ReyesNo ratings yet
- Soil Resources: Earth Science'SDocument59 pagesSoil Resources: Earth Science'SJoshua Glenn EbronNo ratings yet
- Soil Profile DescriptionDocument7 pagesSoil Profile DescriptionAmar DhereNo ratings yet
- Soils and How They Affect Plant Growth (Diagram)Document7 pagesSoils and How They Affect Plant Growth (Diagram)Aravind KetchumNo ratings yet
- SOILDocument5 pagesSOILJessa Mae B. DacuyaNo ratings yet
- Science 8vo Terrestrial EnvironmentDocument127 pagesScience 8vo Terrestrial EnvironmentYaney Yulei BrownNo ratings yet
- Lesson: Science 4 Comparing The Different Types of SoilDocument5 pagesLesson: Science 4 Comparing The Different Types of SoilLena Beth Tapawan YapNo ratings yet
- Science q4 w1Document48 pagesScience q4 w1lowell simbulanNo ratings yet
- MIDTERM EXAMINATION COVERAGE Part 2Document8 pagesMIDTERM EXAMINATION COVERAGE Part 2jeanbonono1818No ratings yet
- SoilDocument26 pagesSoilkentlary.tedios-21No ratings yet
- Soils and Plant Nutrients - NC State Extension PublicationsDocument57 pagesSoils and Plant Nutrients - NC State Extension PublicationsNEWS WORLDNo ratings yet
- SoilDocument5 pagesSoilJerico Nelvin ArbisNo ratings yet
- Soil Resource S: Bhenito Tuyao Clark Tumlad Cholo Gargarita Christ Ian PalganDocument35 pagesSoil Resource S: Bhenito Tuyao Clark Tumlad Cholo Gargarita Christ Ian PalganCHRIST IAN JAN PALGANNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Soil ComponentsDocument3 pagesLesson 5 Soil ComponentsMikeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Soil PollutionDocument1 pageLesson 1 Soil PollutionMikeNo ratings yet
- SoilDocument2 pagesSoilMikeNo ratings yet
- Soil FormationDocument3 pagesSoil FormationMikeNo ratings yet
- Soil TypesDocument2 pagesSoil TypesMikeNo ratings yet
- Weather and ClimateDocument3 pagesWeather and ClimateMikeNo ratings yet
- Soil Erosion Lesson 3Document1 pageSoil Erosion Lesson 3MikeNo ratings yet
- Natural Farming RegionsDocument2 pagesNatural Farming RegionsMikeNo ratings yet
- Safety in AgricultureDocument2 pagesSafety in AgricultureMikeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Agriculture Week 1Document2 pagesIntroduction To Agriculture Week 1MikeNo ratings yet
- Basic Farm Tools Week 2Document2 pagesBasic Farm Tools Week 2MikeNo ratings yet
- Assignment F225summer 20-21Document6 pagesAssignment F225summer 20-21Ali BasheerNo ratings yet
- Numerical Problems Ni AccountingDocument7 pagesNumerical Problems Ni AccountingKenil ShahNo ratings yet
- Cultural Materialism and Behavior Analysis: An Introduction To HarrisDocument11 pagesCultural Materialism and Behavior Analysis: An Introduction To HarrisgabiripeNo ratings yet
- TS4F01-1 Unit 3 - Master DataDocument59 pagesTS4F01-1 Unit 3 - Master DataLuki1233332100% (1)
- SCRIPT IRFANsDocument2 pagesSCRIPT IRFANsMUHAMMAD IRFAN BIN AZMAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Reflective EssayDocument5 pagesReflective EssayBrandy MorganNo ratings yet
- Mt-Requirement-01 - Feu CalendarDocument18 pagesMt-Requirement-01 - Feu CalendarGreen ArcNo ratings yet
- Christ in The Bible - Jude - A. B. SimpsonDocument9 pagesChrist in The Bible - Jude - A. B. Simpsonhttp://MoreOfJesus.RR.NUNo ratings yet
- Managing A Person With ADHD - Team Skills FromDocument7 pagesManaging A Person With ADHD - Team Skills FromHieu PhanNo ratings yet
- Corporate Social Responsibility in Bangladesh:: A Comparative Study of Commercial Banks of BangladeshDocument12 pagesCorporate Social Responsibility in Bangladesh:: A Comparative Study of Commercial Banks of BangladeshSaima Binte IkramNo ratings yet
- Information Security NotesDocument15 pagesInformation Security NotesSulaimanNo ratings yet
- Final Test 1 Grade 10Document4 pagesFinal Test 1 Grade 10Hường NgôNo ratings yet
- Women's Heart HealthDocument3 pagesWomen's Heart HealthMatt ThielkeNo ratings yet
- Suggested Answer: Business Strategy May-June 2018Document10 pagesSuggested Answer: Business Strategy May-June 2018Towhidul IslamNo ratings yet
- EDUC - 115 D - Fall2018 - Kathryn GauthierDocument7 pagesEDUC - 115 D - Fall2018 - Kathryn Gauthierdocs4me_nowNo ratings yet
- Balkan Nationalism (Shodhangana Chapter) PDFDocument40 pagesBalkan Nationalism (Shodhangana Chapter) PDFsmrithiNo ratings yet
- PS2082 VleDocument82 pagesPS2082 Vlebillymambo0% (1)
- MOP Annual Report Eng 2021-22Document240 pagesMOP Annual Report Eng 2021-22Vishal RastogiNo ratings yet
- Coding Decoding 1 - 5311366Document20 pagesCoding Decoding 1 - 5311366Sudarshan bhadaneNo ratings yet
- Development of Modern International Law and India R.P.anandDocument77 pagesDevelopment of Modern International Law and India R.P.anandVeeramani ManiNo ratings yet
- SLP Application For Withdrawal of Case From Supreme Court On SettlementDocument2 pagesSLP Application For Withdrawal of Case From Supreme Court On SettlementharryNo ratings yet
- Quiz On Cash and Cash EquivalentDocument5 pagesQuiz On Cash and Cash EquivalentJomel BaptistaNo ratings yet
- 8299 PDF EngDocument45 pages8299 PDF Engandrea carolina suarez munevarNo ratings yet
- 2b22799f-f7c1-4280-9274-8c59176f78b6Document190 pages2b22799f-f7c1-4280-9274-8c59176f78b6Andrew Martinez100% (1)
- Bung Tomo InggrisDocument4 pagesBung Tomo Inggrissyahruladiansyah43No ratings yet
- Pip Assessment GuideDocument155 pagesPip Assessment Guideb0bsp4mNo ratings yet
- Biopolitics and The Spectacle in Classic Hollywood CinemaDocument19 pagesBiopolitics and The Spectacle in Classic Hollywood CinemaAnastasiia SoloveiNo ratings yet
- Presidential Form of GovernmentDocument4 pagesPresidential Form of GovernmentDivy YadavNo ratings yet
- E3 - Mock Exam Pack PDFDocument154 pagesE3 - Mock Exam Pack PDFMuhammadUmarNazirChishtiNo ratings yet
- Travel Insurance CertificateDocument9 pagesTravel Insurance CertificateMillat PhotoNo ratings yet
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldFrom EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (597)
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessFrom EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessNo ratings yet
- The Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsFrom EverandThe Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (65)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (812)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- Fire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutFrom EverandFire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (142)
- The Hawk's Way: Encounters with Fierce BeautyFrom EverandThe Hawk's Way: Encounters with Fierce BeautyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (19)
- The Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorFrom EverandThe Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (137)
- When You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsFrom EverandWhen You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (13)
- Spoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeFrom EverandSpoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (19)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (35)
- Come Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogFrom EverandCome Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (10)
- Darwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignFrom EverandDarwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (19)
- The Hidden Life of Trees: What They Feel, How They CommunicateFrom EverandThe Hidden Life of Trees: What They Feel, How They CommunicateRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1003)
- World of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsFrom EverandWorld of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (223)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)