Professional Documents
Culture Documents
VILLASIS - J - Lesson Plan - CC11
VILLASIS - J - Lesson Plan - CC11
Uploaded by
Jecka villasisOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
VILLASIS - J - Lesson Plan - CC11
VILLASIS - J - Lesson Plan - CC11
Uploaded by
Jecka villasisCopyright:
Available Formats
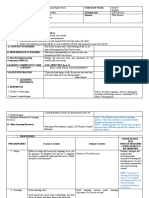
School Northwest samar state University Grade: 5
Daily Teacher Jecka Villasis Learning Area:
Lesson Date / Time: Week 3-5 Quarter: 1 st
Plan
I.OBJECTIVES ANNOTATIONS
A. Content Standard Recognize the types of basic conceptts of simple meter
B. Performance Standard Learn to read the rhythms syllabus
C. Learning Competencies/ Stidents will be able to recognize the types of simple meter in musical pieces. Also, they will
Objectives develop the ability of rhythm dictation.
MU5RH-Ic-e-3
II. CONTENT Simple Meter
III. LEARNING RESOURCES
A. References
1. Teacher’s Guide Pages
2. Learner’s Materials pages Quality Assessed HLAS from the Division Office
3. Curriculum Guide: K to 12 Most Essential Learning competencies with corresponding CG codes
4. Additional Materials from
Learning Resources
B. Other Learning Resources Classroom structures and implementations of rules inside theclassroom Indicator 4: Establish safe
The Melcs music curriculum and secure learning
Instructionals materials environments to enhance
learning through the
consistent implementation of
policies, guidelines, and
procedures
The classroom is structured of
the classrom based and the
rules inside the classroom
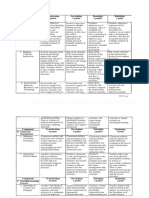
IV. PROCEDURES Teachers activity Students activity
A. Reviewing previous lesson or Review on the previous lesson “time signature ” Indicator 3: Use effective
presenting the new lesson verbal and non-verbal
Hours Minutes Second classroom communication
Directions: please answer the following activities as best 35 45 strategies to support learner
as you can.” 25 49 understanding,
15 24 participation, engagement,
Activity Hours Minutes Seconds and achievement
1. How long does
it take for you or This activity helps the learners
a bath in the to indicate their time
morning before allotment during their rotines
going to in the morning
schools ?
2. How long does Answering by completing the
it take before you the table given from hours to
arrive in school minutes and seconds about
from your house their behavior in the activity
3. How long does
it takee for you to
eat your breakfast
before you go to
school ?
B. Establishing a purpose for the At the end of the lesson, the students will be able to:
lesson Identify the different meters
Student will demonstrate their skills through
listening, exercises,worksheets and
performing meters
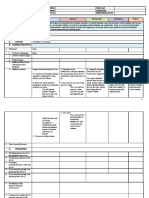
C. Presenting Listening to Simple Meters ndicator 1: Apply
Examples/instances of new lesson Directions: listen to ‘ the star and strips forever” played knowledge of content
by the dallas winds. within and across
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a- curriculum teaching
7XWhyvIpE areas
Applying the songs using
the simple meter using the
video presented to the
Then feeling how the beats group into set of two. teacher s activit and to be
answer by the student by
applying through listening.
Indicator 2: Display
proficient use of Mother
Tongue, Filipino, and
English to facilitate
teaching and learning
The teacher uses English as a
medium of instruction.
The learners encourge to
adopt the lesson plan due to
the performancein theactivity
given.
D. Discussing new concepts and Indicator 3: Use effective
practicing new skills Simple meter verbal and non-verbal
classroom communication
A piece with a time signature of 3/4 has 3 crotchet Students will listen to discussion strategies to support learner
(quarter note) beats in every bar. Each crotchet understanding,
of simple meter that presetn by
participation, engagement,
beat can be divided into 2 quavers (eighth notes) the teacher. and achievement
and so it is in simple meter or simple time. There
are a total of 6 quavers in a bar arranged in twos and
across 3 beats.
Indicator 8: Design, adapt
and implement teaching
strategies that are
responsive to learners with
disabilities, giftedness, and
talents
As the discussion of the lesson
from the different types of
simple meter and follwed by
I’d therefore like to offer a simplified, more the activity that connected to
practical definition: Simple meter is any time the topic or discussion
signature with 4 or less as the top number.
The top number of a time signature in simple time
is almost always 2, 3 or 4. It doesn’t matter what After the discussion there is an
the bottom number is, but I’ll give some examples activity that they will going to
anyway: answer at the end of the
discussion given by teachers.
2/4 means that there are two beats per measure,
and each beat is a quarter note:
3/4 means that there are three beats per measure,
and each beat is a quarter note:
4/4 means that there are four beats per measure,
and each beat is a quarter note. 4/4 is often
abbreviated as C in sheet music. C stands for
common time, since 4/4 is the most common time
signature
Remember that 4/4 and common time are
identical. Here are a few more examples of simple
meter: 2/8 means that there are two beats per
measure, and each beat is an eighth note:
3/8 means that there are three beats per measure,
and each beat is an eighth note:
4/8 is extremely uncommon, since in most cases it
can be reduced to 2/4. Four eighth notes have the
same duration as two quarter notes. It’s essential to
remember that this is the case only for simple time.
For example, 6/8 is not the same as 3/4, even
though six eighth notes indeed have the same
duration as three quarter notes. The reason is that
6/8 is a compound meter and it has only two beats
(each adding up to three eighth notes) per measure,
not six. 2/2 is also an example of simple meter
It is called cut time:
Cut time is abbreviated by a C with a vertical slash
through it. Here, there are two beats per measure,
and each beat is a half note. After this brief lesson
you should now understand everything you need to
know about simple meter!
Directions: answers all questions your test
1. What notes gets that beat in 4/4 time ?
a. Quarter note
b. Half note
c. Eight note
d. Dotted quarteer note
2. What notes get the beat in 3/4?
a. Quarter note
b. Half note
c. Dotted quarter note
d. Eight note
3. How many eight notes fit in a dotted
a. 3
b. 4
c. 2
d. 5
4. 9/8 is what type of meter ?
a. Simple complex
b. Simple meter
c. Compound triple
d. Simple duple
5. In 2/4 time …..
a. There are two beats in a measure
b. There are 4 beats in a measrure
c. Ther are 3 beats in a measure
d. Ther are 6 beats in a quarter
E. Developing mastery Drills: Students will perform the pieces shown on the Indicator 7: Apply a range
(Leads to Formative Assessment) screen to the beat of the provided backing track of successful strategies that
maintain learning
1. Time signatures classified in simple meter have environments that motivate
notes that can be divided into groups of learners to work
a. 3 productively by assuming
responsibility for their own
b. 2
learning
c. 1
d. 4 The teacher provided multiple
choice about the different
2. Simple meter time signatures must have a _, _ , types of metter to clasify of.
or __ as the top #.
a. 4,3,5
b. 1,2,3
c. 2,4,3
d. 6,9,12
3. Time signatures with a "2" as the top # are
qualified as
a. Duple
b. Triple
c. Quarter
d. None of the above
4. Time signatures with a "3" as the top # are
qualified as...
a. Duple
b. Triple
c. Quarter
d. None of the above
5. Time signatures with a "4" as the top # are
qualified as…
a. Duple
b. Triple
c. Quarter
d. None of the above
F. Finding Practical applications Drumline Indicator 5: Maintain
of concepts and skills Direction: give the questions needed learning environments that
promote fairness, respect,
and care to encourage
learning
and
Indicator 6: Maintain
learning environments that
nurture and inspire learners
to participate, cooperate
and collaborate in
continued learning
The indicate were givin an
need the lerners to answer
with their own
understnding
G. Making generalizations and Reflection Questions:
abstractions about the lesson
Does the activity aquire you from the previous activity?
What important points in the lesson have you learned
today?
H. Evaluating Learning Application activity serves as assessment
I. Additional activities for
application or remediation
V. REMARKS
VI. REFLECTION
A. No. of learners who earned 80% on
the formative assessment
B. No. of Learners who require
additional activities for remediation
C. Did the remedial lessons work? No.
of learners who have caught up with
the lesson.
D. No. of learners who continue to
require remediation
E. Which of my teaching strategies
worked well? Why did these work?
F. What difficulties did I encounter
which my principal or supervisor can
help me solve?
G. What innovation or localized
materials did I use/discover which I
wish to share with other teachers?
You might also like
- Asprova ScriptDocument109 pagesAsprova ScriptAnh VuNo ratings yet
- Minassian Full Reasons For JudgementDocument69 pagesMinassian Full Reasons For JudgementCityNewsTorontoNo ratings yet
- Sabah Traditions and CultureDocument33 pagesSabah Traditions and Culturevladioastapq100% (11)
- Design of Yagi Uda Antenna Using HFSS SoftwareDocument10 pagesDesign of Yagi Uda Antenna Using HFSS SoftwareNafi Wibowo0% (1)
- Cot English 2021 2022 Blancaflor JemmalynDocument12 pagesCot English 2021 2022 Blancaflor JemmalynJëm A. LörïcäNo ratings yet
- BONGOLAN, STEPHANIE N. - TI-Activity-2-BSE - SST-IV-1Document8 pagesBONGOLAN, STEPHANIE N. - TI-Activity-2-BSE - SST-IV-1smileydaintyNo ratings yet
- Quarter 4 Module 1 UAM With Obj 14Document5 pagesQuarter 4 Module 1 UAM With Obj 14PHEE MAY DIELNo ratings yet
- Cot 1 PR2docxDocument5 pagesCot 1 PR2docxJudel Aquino LumberaNo ratings yet
- FS1-Activity-4 - Mosada, Jersey O.Document9 pagesFS1-Activity-4 - Mosada, Jersey O.John Paul Sarmiento LatojaNo ratings yet
- Fs 1 and 4 SyllabusDocument8 pagesFs 1 and 4 SyllabusLyn JuvyNo ratings yet
- Individual Work PlanDocument1 pageIndividual Work PlanArthur ShimotweNo ratings yet
- Salarda, Abegail T, Chapter 2-4Document10 pagesSalarda, Abegail T, Chapter 2-4Zach Yghaill AdralasNo ratings yet
- Charles LawDocument10 pagesCharles LawChary Joy BiñasNo ratings yet
- Rhea Mae Dubal - Elc102 - Episode 7Document10 pagesRhea Mae Dubal - Elc102 - Episode 7Rhea Mae DubalNo ratings yet
- Cot Math 6 1st QTR Week 5 Multiplies Decimals and Mixed DecimalsDocument11 pagesCot Math 6 1st QTR Week 5 Multiplies Decimals and Mixed DecimalsSofiaNo ratings yet
- LESSON-PLAN-FORMAT-4As-QUARTER-4-WEEK-1 TELLING TIME EDITEDDocument11 pagesLESSON-PLAN-FORMAT-4As-QUARTER-4-WEEK-1 TELLING TIME EDITEDJenny G. MuscaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For CoDocument5 pagesLesson Plan For CoMary Grace M Arabilla100% (1)
- DLL For Demo TeachingDocument6 pagesDLL For Demo Teachingglaiza.riveraNo ratings yet
- Sas#4 - Edu 023Document12 pagesSas#4 - Edu 023Arnold Mark Ian CacanindinNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan Science 3Document11 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan Science 3breadpaan921No ratings yet
- Emtech Le Q1 W2Document7 pagesEmtech Le Q1 W2Diego Jay VasquezNo ratings yet
- DLL Edmar NewDocument5 pagesDLL Edmar NewJane EdmarNo ratings yet
- Field Study 2 - Modules 2Document22 pagesField Study 2 - Modules 2janine jalecoNo ratings yet
- 2-SCIENCE-OBSERVATION Dipa TaposDocument10 pages2-SCIENCE-OBSERVATION Dipa TaposzachharveyneilNo ratings yet
- Demo Teaching Guide Video Presentation of LPDocument5 pagesDemo Teaching Guide Video Presentation of LPLuci fireNo ratings yet
- DLL - Classpoint Integration-Jhon G. Furio-SRNHS-CPD Training Output (Gamification)Document3 pagesDLL - Classpoint Integration-Jhon G. Furio-SRNHS-CPD Training Output (Gamification)academic.jfurioNo ratings yet
- Activity 3Document7 pagesActivity 3Jane Marriane Leocadio CantorNo ratings yet
- COT3Document6 pagesCOT3NORHANA DIRAMPATENNo ratings yet
- GRADE 10 - English DLPDocument4 pagesGRADE 10 - English DLPchubzroswellNo ratings yet
- Cot-Dlp-Grade Scie-Week7Document15 pagesCot-Dlp-Grade Scie-Week7joylenmalunes484No ratings yet
- FS 2 Activity 3Document7 pagesFS 2 Activity 3Julianne MerinNo ratings yet
- LP in Nail CareDocument14 pagesLP in Nail CareJaylyn AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- FS 2 Activity 2 1Document7 pagesFS 2 Activity 2 1steffiii dawnNo ratings yet
- LP in Food ProcessingDocument13 pagesLP in Food ProcessingJaylyn AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- FS1 - EP8 DoneeDocument9 pagesFS1 - EP8 DoneeDorado Lammy S.No ratings yet
- Grade 1-Dlp-Math-Week8-Ordinal NumbersDocument15 pagesGrade 1-Dlp-Math-Week8-Ordinal NumbersrievandilNo ratings yet
- Demo Teaching RubricsDocument8 pagesDemo Teaching RubricsRonald DaquipilNo ratings yet
- Philippine Demo Teaching RubricDocument6 pagesPhilippine Demo Teaching RubricDom Unson100% (2)
- COT Q4-TypesofconflictsDocument5 pagesCOT Q4-Typesofconflictsjade suaybaguioNo ratings yet
- CurriculumDocument19 pagesCurriculumIlene Rose BuencochilloNo ratings yet
- Grade3 English AdjectivesDocument14 pagesGrade3 English AdjectivesLee Knee JoiNo ratings yet
- LP CONS COT 2 (Telling Time)Document5 pagesLP CONS COT 2 (Telling Time)connie saunar100% (1)
- Daily Lesson LOGDocument4 pagesDaily Lesson LOGVergenia EspielNo ratings yet
- Miss Joanna Molabola Grade 6Document6 pagesMiss Joanna Molabola Grade 6Jinky BracamonteNo ratings yet
- FS 2 Activity 3Document7 pagesFS 2 Activity 3Karen BulataoNo ratings yet
- LessonPlan Electrical CircuitDocument7 pagesLessonPlan Electrical Circuitgrace.ledresNo ratings yet
- Week 1 (Handicraft)Document13 pagesWeek 1 (Handicraft)Jaylyn AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Classroom Management: ExperienceDocument4 pagesClassroom Management: ExperienceFS1 KATHLYN TEJADANo ratings yet
- Lumapas M - Inset - LPDocument10 pagesLumapas M - Inset - LPMichelle Delos Reyes LumapasNo ratings yet
- Cot 2 DLL May 25 2022Document8 pagesCot 2 DLL May 25 2022glaiza.riveraNo ratings yet
- GRADES 9DDLL FINAL Co1Document9 pagesGRADES 9DDLL FINAL Co1danzbazexviNo ratings yet
- Tausa - 1st Progress Report (FS 100)Document10 pagesTausa - 1st Progress Report (FS 100)tbabygieNo ratings yet
- Grades 11 Daily Lesson Log San Jose Del Monte National High School Grade 11 Joseph Bernard C. Dalusong General Chemistry 1 JANUARY 14, 2022 FirstDocument5 pagesGrades 11 Daily Lesson Log San Jose Del Monte National High School Grade 11 Joseph Bernard C. Dalusong General Chemistry 1 JANUARY 14, 2022 FirstJoshua John A. RomeroNo ratings yet
- FS 1 Learning Episode 8Document20 pagesFS 1 Learning Episode 8damacion2020No ratings yet
- FS 1 Episode 8, 9Document11 pagesFS 1 Episode 8, 9Tyndale Faith Hagas CastillonNo ratings yet
- DLL J.-Capulong Cot2 2021-2022Document6 pagesDLL J.-Capulong Cot2 2021-2022Florence Mae CarlosNo ratings yet
- Mendoza, M - DLP (Demo Teaching)Document11 pagesMendoza, M - DLP (Demo Teaching)Myka Kristie MendozaNo ratings yet
- Cabarles Danica Lean FS2 WS3Document7 pagesCabarles Danica Lean FS2 WS3Danica Lean CabarlesNo ratings yet
- Q2.COT - Identify Family MembersDocument10 pagesQ2.COT - Identify Family MembersPearl Obliga100% (1)
- Final Lesson Plan Cot 1 2022 BPPDocument11 pagesFinal Lesson Plan Cot 1 2022 BPPMarichu Linda100% (1)
- FS1 Worksheet-8Document3 pagesFS1 Worksheet-8Lyn AlegadoNo ratings yet
- Rubric For DEMO TEACHING 2022Document4 pagesRubric For DEMO TEACHING 2022Isaiah MendiaNo ratings yet
- Classroom Observation Tool COTDocument4 pagesClassroom Observation Tool COTRudy ClariñoNo ratings yet
- Motivating and Rewarding University Teachers to Improve Student Learning: A Guide for Faculty and AdministratorsFrom EverandMotivating and Rewarding University Teachers to Improve Student Learning: A Guide for Faculty and AdministratorsNo ratings yet
- 24XX ChronicleDocument4 pages24XX ChronicleJosé Ricardo100% (1)
- Tereshchenko Talk 1Document22 pagesTereshchenko Talk 1Aomr MysticRose Aomr MysticRose100% (1)
- 6 - English-How I Taught My Grandmother To Read and Grammar-Notes&VLDocument11 pages6 - English-How I Taught My Grandmother To Read and Grammar-Notes&VLManav100% (3)
- USF Affidavit of SupportDocument1 pageUSF Affidavit of SupportMaan CheemaNo ratings yet
- Pointer and Array Review & Introduction To Data StructureDocument39 pagesPointer and Array Review & Introduction To Data Structurebryan chandraNo ratings yet
- Building Social TiesDocument48 pagesBuilding Social TiesGissele AbolucionNo ratings yet
- PHIL1013 Logic: Student Information Student Number Last Name First Name M.IDocument16 pagesPHIL1013 Logic: Student Information Student Number Last Name First Name M.IPUP OUS CHEMNo ratings yet
- Rules of A British Parliamentary Debate TournamentDocument4 pagesRules of A British Parliamentary Debate TournamentJohnNicoRamosLuceroNo ratings yet
- The Vital Problems of Pistol ShootingDocument15 pagesThe Vital Problems of Pistol Shootingapi-3695814100% (4)
- Horizons, Vol. 60, No. 3, Pp. 395-404.: Singh, Poonam, 6585450Document2 pagesHorizons, Vol. 60, No. 3, Pp. 395-404.: Singh, Poonam, 6585450Poonam SinghNo ratings yet
- Hongkong v. Olalia, Jr. (CASE DIGEST)Document3 pagesHongkong v. Olalia, Jr. (CASE DIGEST)Samantha NicoleNo ratings yet
- Tamil University Act, 1982Document82 pagesTamil University Act, 1982Latest Laws TeamNo ratings yet
- Definition of Qada & QadarDocument4 pagesDefinition of Qada & QadarSadaph fayyazNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug Studykakienz100% (7)
- Jinny Choe Temp Mem CardDocument1 pageJinny Choe Temp Mem CardginauineNo ratings yet
- Obj Day 1 Science DLLDocument5 pagesObj Day 1 Science DLLRoss AnaNo ratings yet
- Recent Aspects On The Implementation of TQM in German EnterprisesDocument12 pagesRecent Aspects On The Implementation of TQM in German EnterprisesPratik KadamNo ratings yet
- Benefits and DetrimentsDocument16 pagesBenefits and DetrimentsAdolfo LasinNo ratings yet
- How To Trade With Supply and Demand Zone - Trading With Smart MoneyDocument8 pagesHow To Trade With Supply and Demand Zone - Trading With Smart MoneyVIGNESH RKNo ratings yet
- What Is A Rhythm Syllable? How Many Beats Are in A Rhythm?Document5 pagesWhat Is A Rhythm Syllable? How Many Beats Are in A Rhythm?marisol corpuzNo ratings yet
- Final Action ResearchDocument11 pagesFinal Action ResearchKARENNo ratings yet
- Ijesit201601 23 PDFDocument10 pagesIjesit201601 23 PDFMouaad BousounaNo ratings yet
- MURLIDocument4 pagesMURLIrabinpadhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Earthquake Resistant Design..Earthquake and Urbanization - History of Major International and Philippine Earthquake. The Ring of FireDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Earthquake Resistant Design..Earthquake and Urbanization - History of Major International and Philippine Earthquake. The Ring of FireJeffry VargasNo ratings yet
- Crimethinc - Fighting For OurlivesDocument13 pagesCrimethinc - Fighting For OurlivesHCaruthersIsDeadNo ratings yet
- ch05 Project Organisation September 2023Document65 pagesch05 Project Organisation September 2023Tota SimatupangNo ratings yet