Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GenChem Vocabulary
Uploaded by
angela mendoza0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views2 pagesThis document defines key chemistry terms including:
- Absorption - the process by which atoms, ions, or molecules enter a bulk phase.
- Acid - a chemical species that accepts electrons or donate protons or hydrogen ions.
- Adsorption - the adhesion of a chemical species onto a surface.
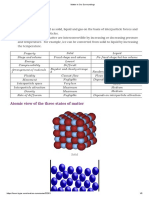
- Atom - the smallest particle.
- Boiling - phase transition from the liquid to gas state.
- Chemical - any matter or substance that has mass.
- Chemical change - a process by which one or more substances are altered to form new substances.
- Chemistry - the study of matter and energy and the interactions between them.
Original Description:
General Chemistry-Vocabulary Words
Original Title
GenChem_Vocabulary
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document defines key chemistry terms including:
- Absorption - the process by which atoms, ions, or molecules enter a bulk phase.
- Acid - a chemical species that accepts electrons or donate protons or hydrogen ions.
- Adsorption - the adhesion of a chemical species onto a surface.
- Atom - the smallest particle.
- Boiling - phase transition from the liquid to gas state.
- Chemical - any matter or substance that has mass.
- Chemical change - a process by which one or more substances are altered to form new substances.
- Chemistry - the study of matter and energy and the interactions between them.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views2 pagesGenChem Vocabulary
Uploaded by
angela mendozaThis document defines key chemistry terms including:
- Absorption - the process by which atoms, ions, or molecules enter a bulk phase.
- Acid - a chemical species that accepts electrons or donate protons or hydrogen ions.
- Adsorption - the adhesion of a chemical species onto a surface.
- Atom - the smallest particle.
- Boiling - phase transition from the liquid to gas state.
- Chemical - any matter or substance that has mass.
- Chemical change - a process by which one or more substances are altered to form new substances.
- Chemistry - the study of matter and energy and the interactions between them.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Word Definition
Absorption process by which atoms, ions, or molecules enter a bulk phase.
Acid a chemical species that accepts electrons or donate protons or
hydrogen ions.
Adhesion the tendency of dissimilar particles or surfaces to cling to one
another.
Adsorption the adhesion of a chemical species onto a surface.
Air the mixture of gases that make up the Earth's atmosphere
Atom The smallest particle.
Boiling phase transition from the liquid to gas state.
Boiling point temperature at which a liquid's vapor pressure is equal to the
external gas pressure.
Chemical any matter or substance that has mass.
Chemical change process by which one or more substances are altered to form new
substances.
Chemical property characteristic that may be observed when matter undergoes a
chemical change.
Chemical reaction a chemical change in which reactants form one or more new
products.
Chemistry study of matter and energy and the interactions between them
Combustibility The ability of the material to combust or burn.
Combustion chemical reaction between a fuel and oxygen that yields energy
(usually heat and light).
Condensation state of matter changes from vapor phase to liquid phase.
Conductivity The ability of a material to allow heat to pass through easily.
Density mass per unit volume.
Deposition settling of sediment or particles onto a surface or the phase change
from the vapor to solid phase.
Dissolve a solute passing into solution, usually a solid going to the liquid
phase.
Ductility The ability of a material to be easily drawn into wires.
Electron stable negatively charged subatomic particle.
Extensive property Property that depends on the amount of matter.
Flammability The ability to combustible material to catch flame easily.
Fluorine Most reactive element.
Freezing Process in which a liquid turns into a solid.
Freezing point The temperature at which a liquid turns into a solid matter.
Gas state of matter characterized by having neither a defined shape nor
defined volume.
Heat the energy that flows between matter samples because of a
temperature difference.
Insoluble unable to dissolve in a solvent.
Intensive property property of matter that is independent of the quantity of matter in a
sample.
Liquid state of matter characterized by having a definite volume but not a
definite shape.
Mass amount of matter a substance contains or property of matter that
resists acceleration.
Matter anything that has mass and occupies volume.
Malleability The ability of a material to be flattened into thin sheets.
Melting the phase change of matter from solid to liquid.
Melting point temperature at which the solid and liquid phases of matter coexist
in equilibrium.
You might also like
- Children Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeFrom EverandChildren Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Chemistry 10 - 12Document333 pagesChemistry 10 - 12Théé Néw SåmûNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Matter and The Atomic Structure Chemistry Form 4 KSSMDocument84 pagesCH 2 Matter and The Atomic Structure Chemistry Form 4 KSSMteresa0% (1)
- PhasechangesseDocument5 pagesPhasechangesseapi-30969951177% (57)
- Y9 CH 1 & CH 2 NotesDocument10 pagesY9 CH 1 & CH 2 NotesTeck TieNo ratings yet
- CH1 - States of Matter (IGCSE Study Notes)Document13 pagesCH1 - States of Matter (IGCSE Study Notes)Amal HassanNo ratings yet
- CBE 9 SCDocument104 pagesCBE 9 SCd_narnolia0% (1)
- Chapter 1 Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument12 pagesChapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundingsshashi kumar sinhaNo ratings yet
- Chem 1 L1 W1Document51 pagesChem 1 L1 W1Desire JoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter No 1-Matter STD 8Document17 pagesChapter No 1-Matter STD 8Harshita MunotNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Particulate Nature of MatterDocument3 pagesChapter 2 - The Particulate Nature of MatterMahad AsimNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surroundings NotesDocument5 pagesMatter in Our Surroundings NotesRajesh Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Freezing Calculations Q.T. PhamDocument163 pagesFreezing Calculations Q.T. Phamrodrigo nunezNo ratings yet
- (Cambridge University Press) Evolution of Phase Transitions - A Continuum Theory 1st Edition by Rohan Abeyaratne (2006)Document259 pages(Cambridge University Press) Evolution of Phase Transitions - A Continuum Theory 1st Edition by Rohan Abeyaratne (2006)cjp6124100% (2)
- PNG 520 - Course On Phase RelationsDocument172 pagesPNG 520 - Course On Phase RelationsDenstar Ricardo SilalahiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Principles of ChemistryDocument14 pagesUnit 1 Principles of ChemistryKhin Yadanar KyawNo ratings yet
- Third Form Packet WorkDocument19 pagesThird Form Packet WorkLizbeth Chi100% (1)
- M Sc-Physics PDFDocument55 pagesM Sc-Physics PDFRobin Kerenzz AbiezzNo ratings yet
- SHS-General Chemistry 1Document32 pagesSHS-General Chemistry 1JC PerezNo ratings yet
- 09 Science Notes Ch01 Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument9 pages09 Science Notes Ch01 Matter in Our SurroundingsAmbika RamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- (PChemI - Atkins) Chapter 4Document36 pages(PChemI - Atkins) Chapter 4Raja Akmal100% (1)
- States of MatterDocument17 pagesStates of MatterhelperforeuNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Relations - Applications - v44 - P4Document40 pagesThermodynamic Relations - Applications - v44 - P4Santiago Cardona ArroyaveNo ratings yet
- Class 9th PDFDocument9 pagesClass 9th PDFHitesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Properties of Matter and Changes in MatterDocument55 pagesProperties of Matter and Changes in MatterPrinces April ArrezaNo ratings yet
- G9-Chem-Matter 1-NotesDocument11 pagesG9-Chem-Matter 1-NotesvijahatNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Picture Vocabulary - MatterDocument50 pagesChemistry Picture Vocabulary - Matterapi-254514513No ratings yet
- Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument15 pagesMatter in Our SurroundingsLogical airNo ratings yet
- States of Matter NotesDocument8 pagesStates of Matter NotesRaya Ibarra LumogdangNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its ClassificationDocument13 pagesMatter and Its ClassificationChandraSekharNo ratings yet
- Handout On Matter (2018)Document9 pagesHandout On Matter (2018)scientistgenerosoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Matter in NatureDocument1 pageChapter 5 Matter in NatureYuhannNo ratings yet
- For More Information On Matter Around UsDocument9 pagesFor More Information On Matter Around UsTathagat DhimanNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Notes 123Document4 pagesGeneral Chemistry Notes 123Stephanie VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Stages of AggregationDocument6 pagesStages of AggregationgrandayaizaNo ratings yet
- 1 States of MatterDocument7 pages1 States of MatterAiman SanobarNo ratings yet
- CSO Olympiad Book For Class 9Document10 pagesCSO Olympiad Book For Class 9Malith MadushanNo ratings yet
- Notes - Matter in Our Surroundings - ExpDocument6 pagesNotes - Matter in Our Surroundings - Expdeborah hildaNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument8 pagesKinetic Particle TheoryShaikh IradNo ratings yet
- Science 12-16 Grade 4Document23 pagesScience 12-16 Grade 4Yvonne OrellanaNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary List - 7th GradeDocument10 pagesVocabulary List - 7th GradeEast AfricaNo ratings yet
- Chem 1Document1 pageChem 1wamexi5918No ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2Document5 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2Dwayne Alin alinNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 1 Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument68 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 1 Matter in Our SurroundingsParesh RanjanNo ratings yet
- Matter Solid Liquid Gas: Page - 1Document5 pagesMatter Solid Liquid Gas: Page - 1Anonymous l309xEA6No ratings yet
- MatterDocument40 pagesMatterMarianne B. HingpesNo ratings yet
- The States of Matter CWDocument3 pagesThe States of Matter CWPraveenaNo ratings yet
- States of MattesDocument3 pagesStates of Mattesyashmiganegoda13No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document12 pagesChapter 1anurag777.class9No ratings yet
- States of Matter, Heat Capacity and Latent Heat: PhysicsDocument7 pagesStates of Matter, Heat Capacity and Latent Heat: PhysicsAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Q3L1 GenSci8Document5 pagesQ3L1 GenSci8yurudumpaccNo ratings yet
- Short Notes - Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument3 pagesShort Notes - Matter in Our SurroundingsHardikNo ratings yet
- LN1 Chem NotesDocument4 pagesLN1 Chem Notesridhimarani16207No ratings yet
- Topic 1 The Particulate Nature of Matter NotesDocument7 pagesTopic 1 The Particulate Nature of Matter Notessteve KingNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Term 1 NotesDocument28 pagesChemistry Term 1 Notesepicfortnite063No ratings yet
- Ionic CompoundDocument65 pagesIonic CompoundRonalyn CariñoNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument10 pagesStates of Matterm.umerfaizan1895No ratings yet
- 01 04 JournalDocument3 pages01 04 JournalAkshay KarthikNo ratings yet
- Science MatterDocument38 pagesScience MatterAlezander GalindoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 10 - 12 PDFDocument283 pagesChemistry 10 - 12 PDFRon ShamendeNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry A - Notes Chapter 1 - The Particulate Nature of MaterDocument25 pagesIGCSE Chemistry A - Notes Chapter 1 - The Particulate Nature of MaterDhingra shellyNo ratings yet
- Glossary Terms - Let's Start CookingDocument2 pagesGlossary Terms - Let's Start CookingElias AyubiNo ratings yet
- Chapter: 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Class-Ix ScienceDocument4 pagesChapter: 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Class-Ix Scienceapi-400692183No ratings yet
- Science Reviewer MATTERDocument3 pagesScience Reviewer MATTERRACHELL SATSATINNo ratings yet
- Gen ChemmotDocument4 pagesGen Chemmotgrishamcacal19No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings 1Document6 pagesChapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings 1Maahi ChhabraNo ratings yet
- 2002 Barman Layered Long Chain Amine Perovskite Phase TransDocument9 pages2002 Barman Layered Long Chain Amine Perovskite Phase TransNacho Delgado FerreiroNo ratings yet
- 10 1016-j Rser 2014 02 032Document16 pages10 1016-j Rser 2014 02 032yasamanasadianNo ratings yet
- Symmetry and Confinement: Jeff Greensite Quarks and Hadrons in Strong QCD St. Goar, GermanyDocument54 pagesSymmetry and Confinement: Jeff Greensite Quarks and Hadrons in Strong QCD St. Goar, Germanycifarha venantNo ratings yet
- Nano MaterialsDocument252 pagesNano MaterialsSms RajaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics of Phase Transitions: 3.A. 3.B. 3.C. 3.D. 3.E. 3.F. 3.G. 3.HDocument49 pagesThermodynamics of Phase Transitions: 3.A. 3.B. 3.C. 3.D. 3.E. 3.F. 3.G. 3.HAnonymous 4nyKDmNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Q1 Lesson 5 Endothermic and Exotheric Reaction and Heating and Cooling CurveDocument19 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Q1 Lesson 5 Endothermic and Exotheric Reaction and Heating and Cooling CurveJolo Allexice R. PinedaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Properties PDFDocument18 pagesThermodynamic Properties PDFUdayan Panda100% (1)
- Venkitaraj2019 (1) New NewDocument12 pagesVenkitaraj2019 (1) New Newramesh tNo ratings yet
- An Introduction of Topological Orders: 1 States of Matter and Internal Or-DersDocument8 pagesAn Introduction of Topological Orders: 1 States of Matter and Internal Or-DersSamrat RoyNo ratings yet
- Phase TransitionDocument3 pagesPhase TransitionMudassar IqbalNo ratings yet
- Euclidean Field Theory: Kasper Peeters & Marija ZamaklarDocument41 pagesEuclidean Field Theory: Kasper Peeters & Marija ZamaklarSourav Sen ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Characteristics of Thermal Energy Storage System Using PCM Capsules - A Review - 2008Document21 pagesHeat Transfer Characteristics of Thermal Energy Storage System Using PCM Capsules - A Review - 2008navidelecNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9Document17 pagesLecture 9yash1239No ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2 Q2 Module 7Document29 pagesGen Chem 2 Q2 Module 7Sou MeiNo ratings yet
- Experiment: E3 Title: The Study of Phase Change Duration: 2 Hours: 1 0F 5Document5 pagesExperiment: E3 Title: The Study of Phase Change Duration: 2 Hours: 1 0F 5GnabryNo ratings yet
- Indrakanty Surya ShashankDocument10 pagesIndrakanty Surya ShashankINDRAKANTY SURYA SHASHANKNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion and Management: Mohamed Lachheb, Mustapha Karkri, Fethi Albouchi, Foued Mzali, Sassi Ben NasrallahDocument9 pagesEnergy Conversion and Management: Mohamed Lachheb, Mustapha Karkri, Fethi Albouchi, Foued Mzali, Sassi Ben NasrallahsaltyNo ratings yet
- E302 - Heat and CalorimetryDocument9 pagesE302 - Heat and CalorimetryGael Canillas RabeNo ratings yet
- DSC - DTA - TG PrezDocument9 pagesDSC - DTA - TG PrezhydromaniaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Energy Analysis Using TRNSYS in PCM Storage TankDocument5 pagesThermal Energy Analysis Using TRNSYS in PCM Storage TankAnonymous lPvvgiQjRNo ratings yet
- Condensed Matter Physics - Wikipedia The Free EncyclopediaDocument13 pagesCondensed Matter Physics - Wikipedia The Free EncyclopediaŠtŸløžx Prıı'nc AadiNo ratings yet
- Name: - : Class: F4B Lesson: Date: TimeDocument11 pagesName: - : Class: F4B Lesson: Date: TimeChrise RajNo ratings yet
- S. Brazovski and N. Kirova - Topological Coupling of Dislocations and Magnetization Vorticity in Spin Density WavesDocument5 pagesS. Brazovski and N. Kirova - Topological Coupling of Dislocations and Magnetization Vorticity in Spin Density WavesYamcsaNo ratings yet