Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 8 Lymph and Transport
Chapter 8 Lymph and Transport
Uploaded by
deviOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 8 Lymph and Transport
Chapter 8 Lymph and Transport
Uploaded by
deviCopyright:
Available Formats
Modul I BioMASTERY: Transport System
TOPIC 9 TRANSPORT SYSTEM
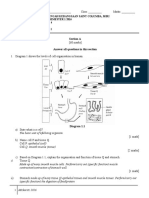
1. Label parts of the lymphatic system shown in FIGURE 2.
FIGURE 2
A : ____________________ B : _____________________
C : ___________________ D : _____________________
2. The structure and functions of human lymphatic system are related to the lipid
transportation. Complete the chart below using words given:
villi glycerol chylomicrons subclavian vein
lacteal lymphatic valves fatty acid
Biology Unit, KMJ (2013/2014)
Modul I BioMASTERY: Transport System
3. FIGURE 3 shows the cross section of a root.
FIGURE 3
a. Using different lines given show the apoplast pathway, symplast pathway and vacuolar
pathway in the FIGURE 3.
i. ====> : apoplast pathway
ii. -------> : symplast pathway
iii. : vacuolar pathway
4. State true / false for each situation given.
Situation True / False
a. Water molecules adhere to one another is called adhesion.
b. Root pressure is the pressure in the xylem that occurs as a result
of the absorption of ions and water into roots from the soil.
c. Translocation is the evaporation of water molecules from plant
parts to the atmosphere.
d. Water molecules adhere to the walls of the tube is called cohesion
e. Casparian strip in the endodermis prevent water from moving by
apoplast pathway
Biology Unit, KMJ (2013/2014)
Modul I BioMASTERY: Transport System
5. Base on FIGURE 4 and the clues given; fill in the blanks with the correct answers.
FIGURE 4
mesophyll starch hydrostatic sieve tube diffusion osmosis
pressure
water sucrose source sink water potential unloaded
(a) __________ is synthesized by photosynthesis in (b) __________ cell and loaded into sieve
tube by active transport. Thus, accumulation of solutes will lower the (c) ______________ inside
the (d) __________. Then, (e) _______ from xylem in leaf move into the sieve tube by (f)
______________. Entry of water will generate higher (g) _________________ than in the root.
Thus, this forces the sucrose to flow along the tube from (h) _________to (i) __________.
Sucrose is (j) __________ into the sink cell by (k) _______, where it is either being consumed or
stored as (l) _________.
Biology Unit, KMJ (2013/2014)
You might also like
- Sea Salt Hidden PowersDocument11 pagesSea Salt Hidden PowersHaSophim100% (2)
- Aromatherapy - 600 Aromatherapy Recipes For Beauty, Health & Home - Plus Advice & Tips On How To Use Essential Oils - Nodrm PDFDocument365 pagesAromatherapy - 600 Aromatherapy Recipes For Beauty, Health & Home - Plus Advice & Tips On How To Use Essential Oils - Nodrm PDFFernanda Rodriguez83% (6)
- 7 Best Natural Remedies For Lymph DetoxDocument17 pages7 Best Natural Remedies For Lymph Detoxrajib100% (1)
- Worksheet Part 2 Plasma MembraneDocument4 pagesWorksheet Part 2 Plasma MembraneAisyahzlee Kimin100% (1)
- Sample Question Paper - Term - Ii: Session 2021-22 SET-1Document5 pagesSample Question Paper - Term - Ii: Session 2021-22 SET-1Yash BhagatNo ratings yet
- Biology Class 9 Final Exam RevisionDocument19 pagesBiology Class 9 Final Exam RevisionPearl SamuelNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 - Transport Across MembraneDocument5 pagesChapter3 - Transport Across MembraneBilly LamNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document15 pagesCH 3Choi MingNo ratings yet
- Student's Copy Chapter3 BioDocument10 pagesStudent's Copy Chapter3 BioSaidatul Atyah Mohd ApendaiNo ratings yet
- Exercise G11Document5 pagesExercise G11zyhfqz25zwNo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions in This Section.: SMK Bau Trial Term 1 2018 Section ADocument10 pagesAnswer All Questions in This Section.: SMK Bau Trial Term 1 2018 Section AViola Voon Li WeiNo ratings yet
- Review ArticleDocument12 pagesReview ArticleIkHa RakhmayaniNo ratings yet
- SMK Batu Muda, 51100 KL Ujian 1 Tahun 2011 Biologi Tingkatan 4 Nama: . Tingkatan: . Answer All Questions in Section A, B and C. Section ADocument9 pagesSMK Batu Muda, 51100 KL Ujian 1 Tahun 2011 Biologi Tingkatan 4 Nama: . Tingkatan: . Answer All Questions in Section A, B and C. Section Anurliyana_samsudinNo ratings yet
- Junior Lyceum Annual Examinations 2000: Do Not Write in This MarginDocument4 pagesJunior Lyceum Annual Examinations 2000: Do Not Write in This MarginPui Pui LamNo ratings yet
- Biology Lecture Membrane ProteinsDocument7 pagesBiology Lecture Membrane ProteinslimesoxroxNo ratings yet
- 3 QPDocument5 pages3 QPOMKAR CHAUDHARINo ratings yet
- 1st Exam Science-9Document5 pages1st Exam Science-9Margie AbogadoNo ratings yet
- Movement of Substance Across The Plasma Membrane (Part 2)Document7 pagesMovement of Substance Across The Plasma Membrane (Part 2)LAKIESHANo ratings yet
- HSB Unit Test 2Document11 pagesHSB Unit Test 2Jessica Kinney0% (1)
- G9 Absorption of FoodDocument4 pagesG9 Absorption of FoodkenzaNo ratings yet
- MCQs & QUs On Fsirst Year First ComDocument74 pagesMCQs & QUs On Fsirst Year First Commaisara10No ratings yet
- G Transport (Plants I)Document18 pagesG Transport (Plants I)luciferNo ratings yet
- 9700 BiologyDocument10 pages9700 Biology2190ibrahimazeemNo ratings yet
- ReseachDocument4 pagesReseachitangishaka alphonse100% (1)
- AP Biology Cells Test 09: Identify The Letter of The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument12 pagesAP Biology Cells Test 09: Identify The Letter of The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The Questionchrwelch3No ratings yet
- Report in Bio Transport MechanismDocument7 pagesReport in Bio Transport MechanismElaiza Nicole AccatanNo ratings yet
- Markscheme HL Paper2Document56 pagesMarkscheme HL Paper2George KoukouvesNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 Sem 1 p2 2016 JWPNDocument15 pagesBiology Form 4 Sem 1 p2 2016 JWPNMiz KarstzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Unit 2.1 and 2.3 WorksheetDocument6 pagesChapter 2 Unit 2.1 and 2.3 Worksheetmaariamshamsi2No ratings yet
- Ib1 Formative-2 Key - SonDocument7 pagesIb1 Formative-2 Key - Son88x64z6m6dNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Exam CellsDocument8 pagesUnit 3 Exam Cellsapi-110789702No ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Movement Across The Plasma Membrane: Intervention-Biology Chapter 3 (Answer)Document4 pagesChapter 3: Movement Across The Plasma Membrane: Intervention-Biology Chapter 3 (Answer)Anonymous 6qork2No ratings yet
- HKALE Cytology (Cell Structure and Function) Question Paper and MSDocument18 pagesHKALE Cytology (Cell Structure and Function) Question Paper and MSNeetenin NeeteninNo ratings yet
- 2017sample LifeDocument9 pages2017sample Lifenatukundajoshua42No ratings yet
- An Introduction To The Methods Available For Ion Channel ReconstitutionDocument21 pagesAn Introduction To The Methods Available For Ion Channel ReconstitutionMadhu MidhaNo ratings yet
- Exam Paper U1Document16 pagesExam Paper U1samantha_ong_22No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Plant Transport Revision Questions 15 November 2023Document3 pagesUnit 2 Plant Transport Revision Questions 15 November 2023icedragonslayer429No ratings yet
- Guia MPDocument2 pagesGuia MPJaviera Catrón MuñozNo ratings yet
- Ans Chapter 3 Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneDocument16 pagesAns Chapter 3 Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneGWENDOLYN OLIVER TEOH MoeNo ratings yet
- Kertas 1 SPM (Percubaan) 1-10Document76 pagesKertas 1 SPM (Percubaan) 1-10Hazizi HanapiNo ratings yet
- Cell PhysiologyDocument2 pagesCell Physiologyernesto_ayocNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Transport in Plants - WorksheetDocument3 pagesChapter 9 Transport in Plants - Worksheetapi-372850890% (10)
- 2.2 Cell Organisation SDocument10 pages2.2 Cell Organisation Ssylent gohNo ratings yet
- Essential Biology 02: CellsDocument13 pagesEssential Biology 02: CellsRichard ZhouNo ratings yet
- Biology WorksheetDocument3 pagesBiology WorksheetBushraNo ratings yet
- SMK Dpha Gapor Trial Term 1 2018 QPDocument6 pagesSMK Dpha Gapor Trial Term 1 2018 QPViola Voon Li WeiNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport Review WorksheetDocument5 pagesCell Transport Review WorksheetЯн ЛомNo ratings yet
- bioF4-Bab 3Document16 pagesbioF4-Bab 3Harvin RajNo ratings yet
- Unlock SGCh07Document7 pagesUnlock SGCh07SilaxNo ratings yet
- CH 7 KeyDocument4 pagesCH 7 KeyJa'mia100% (1)
- (Edu - Joshuatly.com) Trial Malacca STPM 2012 Biology Paper 1 (A6DCE16B) PDFDocument23 pages(Edu - Joshuatly.com) Trial Malacca STPM 2012 Biology Paper 1 (A6DCE16B) PDFChai Kah ChunNo ratings yet
- Cell Processes Study Guide KeyDocument4 pagesCell Processes Study Guide Keyapi-260817414No ratings yet
- Sarawak Sibu QNADocument11 pagesSarawak Sibu QNAPAVITRA A/P THEVINDRAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument4 pagesChapter 2 Cell Structures and FunctionsNur SakiahNo ratings yet
- Figure 1 Shows A Process Carried Out by An Amoeba SP.: Rajah 1 Menunjukkan Proses Yang Dijalankan Oleh Ameoba SPDocument16 pagesFigure 1 Shows A Process Carried Out by An Amoeba SP.: Rajah 1 Menunjukkan Proses Yang Dijalankan Oleh Ameoba SPBrandi WebbNo ratings yet
- Topic: Movement Across The Plasma Membrane SUB TOPIC 3.1: Analysing The Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneDocument13 pagesTopic: Movement Across The Plasma Membrane SUB TOPIC 3.1: Analysing The Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneQieppNo ratings yet
- NSEB Solved Paper 2013Document15 pagesNSEB Solved Paper 2013kasNo ratings yet
- Pepepriksaan Pra-STPM Penggal 1 2018 (SOALAN)Document7 pagesPepepriksaan Pra-STPM Penggal 1 2018 (SOALAN)Viola Voon Li WeiNo ratings yet
- Biology SL 2025 Uniform & Function - Membranes & Membrane TransportDocument22 pagesBiology SL 2025 Uniform & Function - Membranes & Membrane TransportAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Year 10 BiologyDocument15 pagesYear 10 BiologylkipsangNo ratings yet
- Video Recap of Cell Transport by Amoeba SistersDocument2 pagesVideo Recap of Cell Transport by Amoeba Sisters5zhrbrtbwdNo ratings yet
- MLB 111 - Lecture Unit 1 TutorialDocument3 pagesMLB 111 - Lecture Unit 1 TutorialnonosimapsNo ratings yet
- Spatial Agent-Based Simulation Modeling in Public Health: Design, Implementation, and Applications for Malaria EpidemiologyFrom EverandSpatial Agent-Based Simulation Modeling in Public Health: Design, Implementation, and Applications for Malaria EpidemiologyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Immune SytemDocument91 pagesIntroduction To Immune SytemFrankenstein MelancholyNo ratings yet
- A. Fisiologi RespirasiDocument77 pagesA. Fisiologi RespirasiasriNo ratings yet
- How Can We Use Herbs For Lymphatic PDFDocument2 pagesHow Can We Use Herbs For Lymphatic PDFHerbNo ratings yet
- Class 10 TransportationDocument5 pagesClass 10 TransportationKanishk KumarNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Form 5 Chapter 1 TransportDocument42 pagesBIOLOGY Form 5 Chapter 1 TransportShephard Png91% (95)
- Close Book/Open Book/Open Note : Kerjakan Secara Mandiri, Setiap Kecurangan Berarti Nilai EDocument10 pagesClose Book/Open Book/Open Note : Kerjakan Secara Mandiri, Setiap Kecurangan Berarti Nilai EAlvin FahmiNo ratings yet
- Lymph Drainage For DetoxificationDocument8 pagesLymph Drainage For DetoxificationJay JonesNo ratings yet
- Cleaning of Brain Cells by SoundDocument27 pagesCleaning of Brain Cells by SoundRadoslav Shterev100% (1)
- Ch09 - Notes - e 2Document7 pagesCh09 - Notes - e 21A22 LI SIU MAN 李兆旻100% (1)
- The Breasts - Structure - Vasculature - TeachMeAnatomyDocument4 pagesThe Breasts - Structure - Vasculature - TeachMeAnatomywzt2001No ratings yet
- Helen Hodgson - Couple's Massage Handbook Deepen Your Relationship With The Healing Power of TouchDocument268 pagesHelen Hodgson - Couple's Massage Handbook Deepen Your Relationship With The Healing Power of TouchLuca DatoNo ratings yet
- GCSE Biology RevisionDocument2 pagesGCSE Biology RevisionsannnnnNo ratings yet
- Maximizing Your Breast Health: Q&A With DR Melissa Gallagher For Breast Health TipsDocument2 pagesMaximizing Your Breast Health: Q&A With DR Melissa Gallagher For Breast Health TipsAlexis TaylorNo ratings yet
- 14 Days Rapid KetoDocument103 pages14 Days Rapid KetoPradeep Kumar0% (1)
- Medical Terminology 2 Blood, Lymphatic, Immune System Lesson 1Document5 pagesMedical Terminology 2 Blood, Lymphatic, Immune System Lesson 1sotman58No ratings yet
- CaVital WRC - BroshureDocument12 pagesCaVital WRC - Broshuresazaki224No ratings yet
- An End To All DiseasesDocument25 pagesAn End To All Diseaseskukuman1234100% (6)
- Lymphedema 13Document16 pagesLymphedema 13Iqra RazzaqNo ratings yet
- Pamela Minett, Laura Ginesi - Anatomy & Physiology - An Introduction For Nursing and Healthcare-Lantern Publishing LTD (2020)Document417 pagesPamela Minett, Laura Ginesi - Anatomy & Physiology - An Introduction For Nursing and Healthcare-Lantern Publishing LTD (2020)varsityebooksNo ratings yet
- Cell Power ECourseDocument25 pagesCell Power ECoursekeithmac100% (1)
- WaterDocument77 pagesWatereeyanMUSTdieNo ratings yet
- Life Process - TransportationDocument20 pagesLife Process - TransportationAARTI1012100% (1)
- Dse Bio Ch8 & Cross Topic AnsDocument8 pagesDse Bio Ch8 & Cross Topic AnsyungcheukyinryanNo ratings yet
- Physiology MCQs PDFDocument361 pagesPhysiology MCQs PDFDrAmit Verma90% (10)
- Indiba InglésDocument16 pagesIndiba Inglésberenice100% (1)
- CVS HistologyDocument43 pagesCVS Histologyبراءة أحمد السلامات100% (1)
- Acta Universitatis Palackianae Olomucensis GymnicaDocument76 pagesActa Universitatis Palackianae Olomucensis GymnicamiljanceNo ratings yet