Professional Documents
Culture Documents
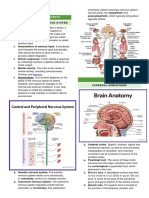
CEREBRUM
Uploaded by
NEIL NETTE S. REYNALDO0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesCEREBRUM
Uploaded by
NEIL NETTE S. REYNALDOCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
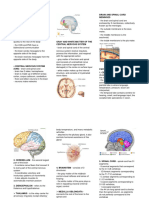
4.
Occipital – assist in coordinating language
generation and visual interpretation, such
as depth perception
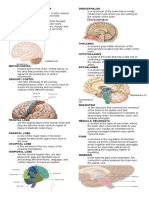
CEREBELLUM
- Located below the cerebrum and is the center
for coordination of movements and postural
adjustments.
- It receives and integrates information from all
areas of the body, such as the muscles, joints,
organs, and other components of the CNS.
- Research has shown that inhibited transmission
of dopamine, a neurotransmitter, in this area is
associated with the lack of smooth coordinated
CEREBRUM
movements in diseases such as Parkinson
- the cerebrum is divided into two hemispheres
disease and dementia.
o Pineal body – is an endocrine gland that influences BRAIN STEM
the activities of the pituitary gland, islets of - Include the midbrain, pons, and medulla
Langerhans, parathyroid, adrenals, and oblongata and the nuclei for cranial nerves III
gonads. through XII
o Corpus callosum - is a pathway connecting the two
hemispheres and coordinating their functions.
o Left hemisphere - controls the right side of the body
and is the center for logical reasoning and
analytic functions such as reading, writing, and
mathematical tasks.
o Right hemisphere - controls the left side of the body
and is the center for creative thinking, intuition,
and artistic abilities.
CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES:
o Medulla – located at the top of the spinal cord,
1. Frontal – control the organization of thought,
body movements, memories, emotions, contains vital centers for respiration and
and moral behavior. cardiovascular functions.
- The integration of all this information o Pons – above the medulla and in front of the
regulates arousal, focuses attention, and cerebrum, the pons, that bridges the gap both
enables problem solving and decision- structurally and functionally. Serving as a primary
making. Abnormalities in the frontal lobes are motor pathway.
associated with schizophrenia, attention- o Midbrain – connects the pons and cerebellum with
deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and the cerebrum. It measures only 0.8 in (2 cm) length
dementia. and includes most of the reticular activating system
and the extrapyramidal system.
2. Parietal - interpret sensations of taste and touch o Reticular activating system – influences motor
and assist in spatial orientation. activity, sleep, consciousness, and awareness.
o Extrapyramidal system relays information about
3. Temporal – are centers for the senses of smell movement and coordination from the brain to the
and hearing and for memory and emotional spinal nerves.
expression. o The locus coeruleus, a small group pf
norepinephrine-producing neurons in the brain
stem, is associated with stress, anxiety, and
impulsive behavior.
You might also like
- Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesNervous SystemEllanny GloriaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesNervous SystemGee PascalNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System: The BrainDocument76 pagesCentral Nervous System: The BrainMoy UdaundoNo ratings yet
- Bio PsychologyDocument30 pagesBio PsychologyNEHA JUNEJANo ratings yet
- Inner Visions - Iridology - Discovering The Whole You (PDFDrive)Document137 pagesInner Visions - Iridology - Discovering The Whole You (PDFDrive)Gursewak Singh100% (1)
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY marLONDocument4 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY marLONArabelle GONo ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviorDocument8 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviorLaine DerainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Biological Foundations of BehaviorDocument50 pagesChapter 3 - Biological Foundations of BehaviorShermel Joy SolisNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Disorders - AgungDocument40 pagesAutoimmune Disorders - AgungalgutNo ratings yet
- Biological and Neuropsychology 2017 PDFDocument15 pagesBiological and Neuropsychology 2017 PDFSphakanyiswa MabasoNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Neuroscience. Anatomy of The BrainDocument11 pagesCognitive Neuroscience. Anatomy of The BrainKryzhel CuachonNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lec Midterm ReviewerDocument39 pagesAnaphy Lec Midterm ReviewerphoebeNo ratings yet
- LEARNING ACTIVITY 11 - Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesLEARNING ACTIVITY 11 - Nervous SystemCraigyyNo ratings yet
- Neurological AssessmentDocument13 pagesNeurological AssessmentLorenz Jude CańeteNo ratings yet
- AP PSYCH Major Structures of The Brain Review Chart MyersDocument2 pagesAP PSYCH Major Structures of The Brain Review Chart MyersTiffany GallinaNo ratings yet
- Copy CNSDocument2 pagesCopy CNSJesica MarieNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology (Nervous System)Document3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology (Nervous System)Fei Jai100% (1)
- Atlas of Abdominal Ultrasound Images PDFDocument98 pagesAtlas of Abdominal Ultrasound Images PDFBogdan Marius100% (2)
- Central Nervous SystemDocument24 pagesCentral Nervous SystemanushkaNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System DiencephalonDocument18 pagesCentral Nervous System DiencephalonBaisigried SechongNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System: Some of Its Main Functions IncludeDocument3 pagesCentral Nervous System: Some of Its Main Functions IncludeNoemi ReyesNo ratings yet
- April 2022Document141 pagesApril 2022SEIYADU IBRAHIM K100% (1)
- Step 2 CK - Nbme Form 4Document87 pagesStep 2 CK - Nbme Form 4geraldchi100% (8)
- Pentagon NLE Review NotesDocument33 pagesPentagon NLE Review NotesChieChay Dub93% (123)
- Abnormal Menstrual Bleeding - Kiiko Matsumoto Japanese StyleDocument3 pagesAbnormal Menstrual Bleeding - Kiiko Matsumoto Japanese StyleAWEDIOHEADNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 3 - Module 3 The Nervous SystemDocument15 pagesScience: Quarter 3 - Module 3 The Nervous SystemVincqNo ratings yet
- Neurologic DisordersDocument51 pagesNeurologic DisordersYamSomandar100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Cognitive Psychology NotesDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Cognitive Psychology NotesShekinah Pearl Niog100% (1)
- Pathophysiology - CholedocholithiasisDocument1 pagePathophysiology - CholedocholithiasisMark OrculloNo ratings yet
- P and C - OVERVIEW OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEMDocument4 pagesP and C - OVERVIEW OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEMRjayvie BadajosNo ratings yet
- Physiological Psychology - Midterm - ReviewerDocument4 pagesPhysiological Psychology - Midterm - ReviewerAudije, John Michael M.No ratings yet
- Neurological System Assessment Part 1 - NCM 101 H.ADocument5 pagesNeurological System Assessment Part 1 - NCM 101 H.ALexie KepnerNo ratings yet
- Cognitive PsychologyDocument5 pagesCognitive Psychologymain.22001454No ratings yet
- Lobes of The BRAIN: Right Hemisphere Left HemisphereDocument9 pagesLobes of The BRAIN: Right Hemisphere Left HemisphereAsniah Hadjiadatu AbdullahNo ratings yet
- NERVOUS SYSTEM-WPS OfficeDocument15 pagesNERVOUS SYSTEM-WPS OfficeJoshua DauzNo ratings yet
- Neuro Ppt. Lec. 1Document49 pagesNeuro Ppt. Lec. 1Jay successNo ratings yet
- Neuro Ana and PhysioDocument2 pagesNeuro Ana and PhysioJacqueline de AsisNo ratings yet
- Biological Psychology (BRAIN AND ITS DISEASES)Document16 pagesBiological Psychology (BRAIN AND ITS DISEASES)Shenne Ann MaghuyopNo ratings yet
- Biological PsychologyDocument9 pagesBiological PsychologyShenne Ann MaghuyopNo ratings yet
- Compiled SCTL 1 m18Document60 pagesCompiled SCTL 1 m18Muhammad Ammar Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System: Spinal Cord BrainDocument4 pagesCentral Nervous System: Spinal Cord BrainRaizah GozosNo ratings yet
- In Nervous System: Divided Into 4 LobesDocument5 pagesIn Nervous System: Divided Into 4 LobesXandra BasnilloNo ratings yet
- Psych IiDocument8 pagesPsych IiNadia AbdurasidNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Nueroscience - NotesDocument8 pagesCognitive Nueroscience - NotesEirrah AcenasNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesNervous SystemBSLMS1D - Depasupil, Laurice Ann A.No ratings yet
- Nervous System SGDocument4 pagesNervous System SGNammywhammyNo ratings yet
- Neuro Notes #1Document15 pagesNeuro Notes #1Monica JubaneNo ratings yet
- The Brain and The Nervous SystemDocument17 pagesThe Brain and The Nervous SystemElena-Andreea MutNo ratings yet
- Biological Bases, AssignmentDocument6 pagesBiological Bases, AssignmentBenjii CarlosNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY LAB W7 ReviewerDocument5 pagesANAPHY LAB W7 Reviewerangelmalang41No ratings yet
- 8B Coordination in Animals and Plants 8B Checkpoint: 8B.1 The Central Nervous SystemDocument8 pages8B Coordination in Animals and Plants 8B Checkpoint: 8B.1 The Central Nervous SystemsalmaNo ratings yet
- Personal Development Reviewer: © Angelica GarciaDocument14 pagesPersonal Development Reviewer: © Angelica GarciaFat AjummaNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter - ScienceDocument12 pages3rd Quarter - ScienceJohn David AbatayoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer CognitiveDocument12 pagesReviewer CognitiveAmbrad, Merlyn H.No ratings yet
- Coordination and ResponseDocument9 pagesCoordination and Responsevictory IsaacNo ratings yet
- Body SystemsDocument9 pagesBody Systems12 Dy NicoleNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 Pharmacology MidtermsDocument25 pagesNCM 106 Pharmacology MidtermsCrecia Bullecer2No ratings yet
- Personality Development Weeks 7-8 Lecture NoteDocument8 pagesPersonality Development Weeks 7-8 Lecture NoteCzarina Ciara AndresNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesNervous SystemJanica Pauline DaydayNo ratings yet
- Perdev The BrainDocument4 pagesPerdev The BrainJL BautistaNo ratings yet
- Unit3 NeurologicalProcessesDocument3 pagesUnit3 NeurologicalProcessesMay Anne BañagaNo ratings yet
- Ceballos, Mary Kate L. (BSN 1-Ya-18) - Week 7 - Laboratory Exercise - The Nervous System Cns and PnsDocument9 pagesCeballos, Mary Kate L. (BSN 1-Ya-18) - Week 7 - Laboratory Exercise - The Nervous System Cns and PnsKay ChoiNo ratings yet
- Cogpsy ReviewerDocument21 pagesCogpsy ReviewerTrisha SabaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1,2,3Document8 pagesChapter 1,2,3세핌No ratings yet
- Iia. Neurobiological BasisDocument54 pagesIia. Neurobiological BasisLing CapeloNo ratings yet
- Module 2: Biology and PsychologyDocument23 pagesModule 2: Biology and Psychologyshain aldovinoNo ratings yet
- MEDSURG 1 NotesDocument43 pagesMEDSURG 1 NotesNEIL NETTE S. REYNALDONo ratings yet
- CWorld 3 - Midterm (SDG Goals)Document4 pagesCWorld 3 - Midterm (SDG Goals)NEIL NETTE S. REYNALDONo ratings yet
- CWorld 3 - Midterm (Global Migration)Document1 pageCWorld 3 - Midterm (Global Migration)NEIL NETTE S. REYNALDONo ratings yet
- NCM 107N - MaternalDocument46 pagesNCM 107N - MaternalNEIL NETTE S. REYNALDONo ratings yet
- NCM 113.Document5 pagesNCM 113.NEIL NETTE S. REYNALDONo ratings yet
- Sample TransDocument5 pagesSample TransNEIL NETTE S. REYNALDONo ratings yet
- Registration FormDocument1 pageRegistration FormNEIL NETTE S. REYNALDONo ratings yet
- 2023 - Mood Disorders Lecture NotesDocument13 pages2023 - Mood Disorders Lecture NotesNEIL NETTE S. REYNALDONo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Diet TherapyDocument7 pagesNutrition and Diet TherapyNEIL NETTE S. REYNALDONo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus in Children 1Document89 pagesDiabetes Mellitus in Children 1Vinay PatilNo ratings yet
- 361-Teks Artikel-945-1-10-20220128Document8 pages361-Teks Artikel-945-1-10-20220128Joniyespapa 24No ratings yet
- T06002.006 Viva E System Onsite Training Workbook Eff Date 09-13-21Document66 pagesT06002.006 Viva E System Onsite Training Workbook Eff Date 09-13-21Zitouni LamineNo ratings yet
- General Medicine Lec4 Adrenal GlandsDocument9 pagesGeneral Medicine Lec4 Adrenal GlandsAli MONo ratings yet
- 14.30 Wed - Bone Age Review CGDocument26 pages14.30 Wed - Bone Age Review CGveronica selviaNo ratings yet
- Uptd Puskesmas Koni Uptd Puskesmas Koni: Pemerintah Kota Jambi Dinas Kesehatan Pemerintah Kota Jambi Dinas KesehatanDocument2 pagesUptd Puskesmas Koni Uptd Puskesmas Koni: Pemerintah Kota Jambi Dinas Kesehatan Pemerintah Kota Jambi Dinas KesehatanImilda Utami DewiNo ratings yet
- DKA Concept MapDocument2 pagesDKA Concept MapJanetNo ratings yet
- Physical Education: Questions and AnswersDocument34 pagesPhysical Education: Questions and AnswersQNo ratings yet
- Precociou S Puberty: BY Vishnupriya Ravimohandoss Year-6 Group-1Document31 pagesPrecociou S Puberty: BY Vishnupriya Ravimohandoss Year-6 Group-1Priya RaviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15. Drugs Affecting The Central Nervous System: Multiple ChoiceDocument41 pagesChapter 15. Drugs Affecting The Central Nervous System: Multiple ChoiceAlejandro Daniel Landa MoralesNo ratings yet
- Cellular Responses To Stress and Noxious StimuliDocument78 pagesCellular Responses To Stress and Noxious Stimulisinte beyuNo ratings yet
- The Two-Process Model of Sleep Regulation A ReappraisalDocument13 pagesThe Two-Process Model of Sleep Regulation A ReappraisalwestNo ratings yet
- epidyolex-SmPC Product-Information - enDocument38 pagesepidyolex-SmPC Product-Information - enpharmashri5399No ratings yet
- Anatomy 1.01 Introduction To Gross AnatomyDocument6 pagesAnatomy 1.01 Introduction To Gross AnatomyMark AbrazaldoNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 8 Science, Reaching The Age of AdolescenceDocument5 pagesCBSE Class 8 Science, Reaching The Age of AdolescenceR.Shruti 1040-12No ratings yet
- Microbiology Unit: Urine Analysis and C/SDocument2 pagesMicrobiology Unit: Urine Analysis and C/SaswanwaterNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles in Surgical Oncology - Cady1997 Arch Surg PDFDocument9 pagesBasic Principles in Surgical Oncology - Cady1997 Arch Surg PDFDiego EskinaziNo ratings yet
- Major Intracellular and Extracellular IonsDocument20 pagesMajor Intracellular and Extracellular IonsTricia RestriveraNo ratings yet
- Product Information Proviron: CH OH CHDocument6 pagesProduct Information Proviron: CH OH CHDNo ratings yet
- HTTP WWW - Drlam.com Blood Type Diet Blood o ChartDocument5 pagesHTTP WWW - Drlam.com Blood Type Diet Blood o ChartOrduña FGab100% (2)
- Peptide Specifications 2Document4 pagesPeptide Specifications 2Branden KoepferNo ratings yet
- Catalogue ChungdoDocument2 pagesCatalogue ChungdoHienNo ratings yet