Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How Do Oxygen Formed
How Do Oxygen Formed
Uploaded by
Ey KaguriOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
How Do Oxygen Formed
How Do Oxygen Formed
Uploaded by
Ey KaguriCopyright:
Available Formats
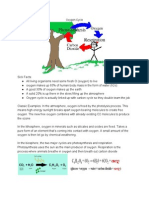
Oxygen is formed through several natural processes, primarily by photosynthesis in plants, algae, and
some bacteria. During photosynthesis, these organisms use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide (CO2) to
produce oxygen (O2) and glucose. The chemical equation for photosynthesis is:
6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2
This process is responsible for a large portion of the Earth's oxygen production. Additionally, oxygen is
released through the photodissociation of water vapor (H2O) in the upper atmosphere by ultraviolet
radiation from the sun:
2H2O + energy (UV) → 4H + O2
Oxygen forms through several natural processes, primarily by photosynthesis in plants, algae, and some
bacteria. During photosynthesis, these organisms use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide (CO2) to
produce oxygen (O2) and glucose. The chemical equation for photosynthesis is:
6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2
This process is responsible for a large portion of the Earth's oxygen production. Additionally, oxygen is
released through the photodissociation of water vapor (H2O) in the upper atmosphere by ultraviolet
radiation from the sun:
2H2O + energy (UV) → 4H + O2
Oxygen is also produced as a byproduct of the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and ozone
(O3) in the atmosphere.
Overall, the primary natural source of oxygen on Earth is photosynthesis, which maintains the balance of
oxygen in the atmosphere and is essential for supporting life on our planet.
You might also like
- Process of PhotosynthesisDocument1 pageProcess of PhotosynthesisGray Lee QueezerNo ratings yet
- Biology EssayDocument1 pageBiology EssayBooster HidroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document18 pagesChapter 8Ananya Sharma - Lincoln Alexander SS (2132)No ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument1 pageCarbon CycleLuke LancasterNo ratings yet
- STANDARD: 1d Students Know That Chloroplasts Capture Sunlight Energy For PhotosynthesisDocument10 pagesSTANDARD: 1d Students Know That Chloroplasts Capture Sunlight Energy For PhotosynthesisJulius Memeg PanayoNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 2Document2 pagesPhotosynthesis 2api-3731257No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis - WikipediaDocument28 pagesPhotosynthesis - WikipediakamaalNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis - Vishal ThoutamDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis - Vishal ThoutamUnbound RacerNo ratings yet
- ORDONEZ ERALAINE G. Photosynthesis SeatworkDocument3 pagesORDONEZ ERALAINE G. Photosynthesis SeatworkRaine OrdonezNo ratings yet
- Composition of Inhaled Air and Exhaled AirDocument2 pagesComposition of Inhaled Air and Exhaled AiredwinmasaiNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument1 pagePhotosynthesisGeorgia BuenavidesNo ratings yet
- EVOLUTION NewDocument16 pagesEVOLUTION Newhancyhero79No ratings yet
- Fertile Soil As A Medium For Effective PhotosynthesisDocument58 pagesFertile Soil As A Medium For Effective PhotosynthesisYahaya Ado WasaiNo ratings yet
- Photosyntheis Worksheet 7th GradeDocument1 pagePhotosyntheis Worksheet 7th GradeJanrod RosiniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Environmental Chemistry (Ib Option E) Summary: Air PollutionDocument7 pagesChapter 16 Environmental Chemistry (Ib Option E) Summary: Air Pollutionalstjq1003No ratings yet
- OxygenDocument9 pagesOxygenapi-310034018No ratings yet
- ENVIROMENTAL CHEMISTRY Unit 5 G12Document10 pagesENVIROMENTAL CHEMISTRY Unit 5 G12Miki melNo ratings yet
- Za NST 1639929128 Photosynthesis and Respiration Ver 1Document7 pagesZa NST 1639929128 Photosynthesis and Respiration Ver 1Alien09No ratings yet
- ON Sci 9 Unit1 Sec12Document7 pagesON Sci 9 Unit1 Sec12Girlie Kaye PagtamaNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle: - Book E PG 50 51Document10 pagesCarbon Cycle: - Book E PG 50 51api-26334461No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis - Dark Reaction and Calvin Cycle Class 9 NotesDocument130 pagesPhotosynthesis - Dark Reaction and Calvin Cycle Class 9 Notesbrajeshitc.raiNo ratings yet
- ORDONEZ ERALAINE G. Photosynthesis Reading and Questions PDFDocument3 pagesORDONEZ ERALAINE G. Photosynthesis Reading and Questions PDFRaine OrdonezNo ratings yet
- Photosynthetic Processes Lecture GuideDocument16 pagesPhotosynthetic Processes Lecture GuideRogianna IsidroNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument7 pagesPhotosynthesisjeankayzelrodelasNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: (Gas) (Gas)Document2 pagesPhotosynthesis: (Gas) (Gas)Joshua WilsonNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument6 pagesPhotosynthesisSeema Rahul100% (1)
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument2 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESISVivien LancinNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Worksheet Name - : ChloroplastsDocument1 pagePhotosynthesis Worksheet Name - : ChloroplastspsdeviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 OutlineDocument13 pagesChapter 10 OutlineJosephinemwNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesisapi-3729258No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: 6H O + 6co +light C H O + 6ODocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis: 6H O + 6co +light C H O + 6Ojohn_42494No ratings yet
- Bio - HydrogenDocument18 pagesBio - HydrogenHarsh Vinay SinghNo ratings yet
- Topic 2: Elemental and Environmental ChemistryDocument43 pagesTopic 2: Elemental and Environmental ChemistryChangWeiTanNo ratings yet
- The Carbon Cycle HandoutDocument2 pagesThe Carbon Cycle HandoutthereseNo ratings yet
- The Process of PhotosynthesisDocument9 pagesThe Process of Photosynthesismenmic749No ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument63 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESISrania samirNo ratings yet
- Learning Evidence - Team 2 PDFDocument8 pagesLearning Evidence - Team 2 PDFAna Marcela LópezNo ratings yet
- 3 Plant Processes: Plants Perform Certain Processes Necessary For SurvivalDocument34 pages3 Plant Processes: Plants Perform Certain Processes Necessary For SurvivalDedy WijayaNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3: Air Pollution, Sources and Effects: Chapter 8: Chemistry of The AtmosphereDocument6 pagesLESSON 3: Air Pollution, Sources and Effects: Chapter 8: Chemistry of The Atmospherecory kurdapyaNo ratings yet
- OcycleskitDocument1 pageOcycleskitapi-284336383No ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument2 pagesCarbon CycleShehzadi KhanNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument1 pagePHOTOSYNTHESISVina Rose AlomeaNo ratings yet
- Oxygen CycleDocument11 pagesOxygen CycleMarc Jonas DiazNo ratings yet
- RQ57CP. Ass6Document6 pagesRQ57CP. Ass6Zlata TumanovaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Is A Process Used by Plants and Other Organisms ToDocument7 pagesPhotosynthesis Is A Process Used by Plants and Other Organisms ToDharmendra SinghNo ratings yet
- 1 2 Global Redox CyclesDocument2 pages1 2 Global Redox CyclesMaria TorresNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Energy Flow in EcosystemsDocument3 pages2.4 Energy Flow in EcosystemsuhNo ratings yet
- Integrating Act. Chemistry S1Document7 pagesIntegrating Act. Chemistry S1Yisus Alberto Molina ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- Natural Resources Biogeochemical CyclesDocument4 pagesNatural Resources Biogeochemical Cyclesboris pocusNo ratings yet
- Fotosintesis 1213Document25 pagesFotosintesis 1213scanny16No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Quiz ReviewerDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Quiz ReviewerhjNo ratings yet
- BioIGCSE 07 PhotosynthesisDocument34 pagesBioIGCSE 07 PhotosynthesisNADIANo ratings yet
- Water Cycles and Carbon Cycles and Oxygen CyclesDocument2 pagesWater Cycles and Carbon Cycles and Oxygen CyclesB-Sadorra, Marls Angel Roe N.No ratings yet
- Biosynthesis and Pharmacognosy Lecture 2 - Biosynthesis of CarbohydratesDocument19 pagesBiosynthesis and Pharmacognosy Lecture 2 - Biosynthesis of CarbohydratesFrogWarriorNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesisMason PeinNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Plants and AnimalsDocument27 pagesNutrition in Plants and AnimalsObudra CeasarNo ratings yet
- Oxygen CycleDocument3 pagesOxygen Cycleزيد صباح الحلوNo ratings yet
- The Carbon CycleDocument12 pagesThe Carbon CycleClariene CaburnayNo ratings yet
- The Carbon CycleDocument10 pagesThe Carbon CycleFoisal SwarupNo ratings yet
- BuoyancyDocument2 pagesBuoyancyEy KaguriNo ratings yet
- No 2Document1 pageNo 2Ey KaguriNo ratings yet
- DensityDocument2 pagesDensityEy KaguriNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Design Is A Fundamental Aspect of Civil Engineering and ConstructionDocument1 pageReinforced Concrete Design Is A Fundamental Aspect of Civil Engineering and ConstructionEy KaguriNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument2 pagesScienceEy KaguriNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Sytem FemaleDocument1 pageReproductive Sytem FemaleEy KaguriNo ratings yet
- How Do Clouds FormDocument1 pageHow Do Clouds FormEy KaguriNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Sytem MaleDocument1 pageReproductive Sytem MaleEy KaguriNo ratings yet
- Science Is A Systematic and Organized Endeavor To Understand The Natural World Through ObservationDocument1 pageScience Is A Systematic and Organized Endeavor To Understand The Natural World Through ObservationEy KaguriNo ratings yet
- Computations UT 1Document2 pagesComputations UT 1Ey KaguriNo ratings yet