Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gen Phys Summary
Uploaded by
weee 10 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesOriginal Title
GEN PHYS SUMMARY
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesGen Phys Summary
Uploaded by
weee 1Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
GENERAL PHYSICS 2 REVIEWER .
LESSON 1: ELECTRIC CHARGE
Electric charge
● Electric charge - difference in electrons that creates the
ability to attract small pieces of matter when rubbed
○ Positive: lose electrons
○ Negative: gain electrons
● Electrostatics - study of electric charges at rest
Early Greeks
● Amber - a translucent yellowish resin (rubbed)
● Queen Elizabeth I of England - found amber-like things
○ Electrics - substances that form charges
○ Electricity - the ability
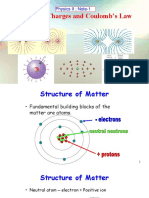
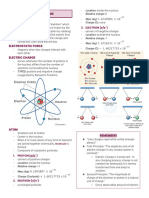
Subatomic Particles
Particle Location Mass Charge Charging by conduction
● Requires physical contact (charging body/neutral body)
Proton Inside 1. 673 × 10
−27 −19
𝑘𝑔 + 1. 602 × 10 𝐶 ○ Charge of CB is charge of NB
(+) nucleus Charging by induction
● Without physical contact
Neutron Inside −27
1. 675 × 10 𝑘𝑔 0 ● Polarization - negative charges of NB is attracted to the
(0) nucleus positive end of CB
○ Opposite charges attract
Electron Outside −31
9. 901 × 10 𝑘𝑔 − 1. 602 × 10 𝐶
−19 ○ Same charges repel
(-) nucleus ● Grounding - touching or wiring (bec charges of
polarization does not stay and goes back to neutral)
Conductors and Insulators
○ Positive: let electrons flow out
● Conductivity - measure of electric charge flow ease
○ Negative: let electrons come in
● Conductors - allow flow of charges (have plenty of free
Coulomb’s Law
electrons allowing movement)
● Coulomb discovered electrical force (magnitude)
○ Superconductors - no resistance below critical
●
temp (close to absolute zero)
GENERAL PHYSICS 2 FORMULAS .
■ Hydrogen sulfide (203K/-70C) - highest
Computation of Electric Charge
● Insulators - resist flow of charges
● Semiconductors - intermediate between C and I 𝑞 = 𝑁𝑒
○ Pure form - Low conductivity
● q - electric charge (C)
○ Doping - adding atoms to improve conductivity
● N - number of electrons
● e - charge of an electron
LESSON 2: INDUCED CHARGES AND COULOMB Computation of Electric Force
Atom charges
|𝑞1 × 𝑞2| 9 2 2
● Neutral: protons = electrons 𝑘 = 9. 0 𝑥10 𝑁 • 𝑚 /𝑐
● Positive: protons > electrons (lose e-) 𝐹𝑒 = 𝑘 2
● Negative: protons < electrons (gain e-) 𝑟
Charging by Friction ● Fe = electric force (N)
● Two different material rubbed together ● q1/q2 = charge of atom 1 and 2 ©
● Electron affinity - measure of attraction to electrons −3
○ 𝑚𝐶 = × 10 𝐶 (milli)
(amount of energy released when e- is added to neutral) −6
○ High affinity = high chance to gain electrons ○ µ𝐶 = × 10 𝐶 (micro)
● Triboelectric series - increasing aff (top to bottom) −9
○ 𝑛𝐶 = × 10 𝐶 (nano)
○ When comparing, one on top is positive and one ● r = radius/distance of atoms (m)
on bottom is negative. ● k = Coulomb’s constant
■ Glass (+) -> silk cloth (-)
■ Fur (+) -> rubber (-)
■ Aluminum (+) -> cotton (-)
GENERAL PHYSICS 2 REVIEWER .
You might also like
- Solid-State Circuits: Electrical Engineering DivisonFrom EverandSolid-State Circuits: Electrical Engineering DivisonRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Lecture 01 - Electric ChargesDocument24 pagesLecture 01 - Electric ChargesRei RamirezNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism Part1Document42 pagesElectromagnetism Part1MJ LopezNo ratings yet
- Electrical Charges and Coulomb's Law: Physics II Note-1Document24 pagesElectrical Charges and Coulomb's Law: Physics II Note-1Helping purpose onlyNo ratings yet
- ELECTROSTATICSDocument31 pagesELECTROSTATICSSweet Krisyl LopezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Voltage and CurrentDocument29 pagesChapter 1 - Voltage and CurrentKucing GemukNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and ElectricityDocument26 pagesMagnetism and ElectricityDean SeepaneNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.5 Electricity 1Document25 pagesLecture 3.5 Electricity 1SYACHBANI AMIN HIDAYATNo ratings yet
- Using Only The PVC, Move The Soda Can, But You Cannot Touch The Can With The PVC or Blow On The Can. Explain How You Did ItDocument37 pagesUsing Only The PVC, Move The Soda Can, But You Cannot Touch The Can With The PVC or Blow On The Can. Explain How You Did Itnazia zulfiqarNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics PowerPointDocument37 pagesElectrostatics PowerPointJose GulitiwNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics PowerPointDocument37 pagesElectrostatics PowerPointpunithaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 - Elecric Field-UpdateDocument53 pagesChapter 23 - Elecric Field-Updatewaelabood51No ratings yet
- Phy-153 Course OutlineDocument26 pagesPhy-153 Course OutlinealdricNo ratings yet
- DSP-PSD - Lecture 2 - Chapter 3-4-X - 16.10.2023Document35 pagesDSP-PSD - Lecture 2 - Chapter 3-4-X - 16.10.2023TheDarkHunters-EldritchNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 GP2 PDFDocument34 pagesLesson 2 GP2 PDFShjajaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Physics 108Document24 pagesModule 1 - Physics 108Redwanul RashikNo ratings yet
- Week 3 24102023 105359pmDocument13 pagesWeek 3 24102023 105359pmentertainmenttv160No ratings yet
- Electric Charge NOTESDocument2 pagesElectric Charge NOTESlwitsfadontNo ratings yet
- Physics AssignmentDocument41 pagesPhysics AssignmentMustapha KaojeNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge CoulombsDocument52 pagesElectric Charge Coulombsbry uyNo ratings yet
- Electrcity Magnetism and Optics: Samra SyedDocument11 pagesElectrcity Magnetism and Optics: Samra SyedFA20-BCS-063 (SUBHAN SHAHZAD) UnknownNo ratings yet
- Unit 15 Electrostatics and Gauss's Law: ExampleDocument21 pagesUnit 15 Electrostatics and Gauss's Law: ExampleBestah Joewellster TeoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism: Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Materials ScienceDocument26 pagesElectromagnetism: Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Materials ScienceJai SheokandNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ElectrostaticsDocument43 pagesChapter 1 ElectrostaticsAeyryll BuanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Electric Charge and Coulomb Law: EP 106 General Physics IIDocument5 pagesChapter 1: Electric Charge and Coulomb Law: EP 106 General Physics IIMouayed ZeadanNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics GSC 113: Week 2Document13 pagesApplied Physics GSC 113: Week 2Peace of HeartNo ratings yet
- CH 17 ElectricityDocument16 pagesCH 17 ElectricityErna GampalNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge, Force & Field: PHYS2212/1114 Dr. Dragos Amarie, GSU/Math-Phys 2050Document19 pagesElectric Charge, Force & Field: PHYS2212/1114 Dr. Dragos Amarie, GSU/Math-Phys 2050Justin MithersNo ratings yet
- MTPDF3 Electric Charge and ForceDocument27 pagesMTPDF3 Electric Charge and ForceMichael Angelo Reyes FernandezNo ratings yet
- Mtpdf3 Electric Charge and ForceDocument27 pagesMtpdf3 Electric Charge and ForceMary KimberlyNo ratings yet
- MTPDF3 Electric Charge and ForceDocument27 pagesMTPDF3 Electric Charge and ForceMary KimberlyNo ratings yet
- Physics PDFDocument276 pagesPhysics PDFBenjamín Medina CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Laboratory College: Monthly Test. 1 University of Agriculture, FaisalabadDocument1 pageLaboratory College: Monthly Test. 1 University of Agriculture, Faisalabadpaggal janNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrostatics (2019)Document21 pagesBasic Electrostatics (2019)Andile MinenhleNo ratings yet
- Lec 13 - ElectrostaticsDocument22 pagesLec 13 - ElectrostaticsAna ZarateNo ratings yet
- Creative Technology 10: Pre - TestDocument4 pagesCreative Technology 10: Pre - TestAliyah RuizNo ratings yet
- Electric Forces and Fields: Charge Coulomb's Law Electric Fields Conductors & Insulators Parallel Plates DipolesDocument28 pagesElectric Forces and Fields: Charge Coulomb's Law Electric Fields Conductors & Insulators Parallel Plates DipolesSaifodine CarlosNo ratings yet
- CH 20 (Coulomb)Document31 pagesCH 20 (Coulomb)Baktynur AzhybaevNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 1Document42 pagesLecture - 1salemalbulushi123No ratings yet
- General Chemistry NotesDocument13 pagesGeneral Chemistry NotesAli BadreldeenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Fis 2a - Muatan - Gaya Dan Medan Listrik Pada Muatan Titik - FixDocument23 pagesLecture 1 - Fis 2a - Muatan - Gaya Dan Medan Listrik Pada Muatan Titik - FixReza Gustyan sukmaraNo ratings yet
- 001 Physics2b Lecture PDFDocument48 pages001 Physics2b Lecture PDFJC DoloritoNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and FieldsDocument6 pagesElectric Charges and FieldsNiranjan RajaNo ratings yet
- Physics - 1 - LESSON 1 (Final Term - Fall 2023-24)Document18 pagesPhysics - 1 - LESSON 1 (Final Term - Fall 2023-24)famidrabbifrNo ratings yet
- Electric DipoleDocument29 pagesElectric DipoleDr-Amr HesseinNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Fields Bs-1Document19 pagesElectric Charges and Fields Bs-1midhunesh41No ratings yet
- Dielectric MaterialsDocument45 pagesDielectric MaterialsBhavya TanneruNo ratings yet
- Genius Physics ..Pradeep Kshetrapal ElectrostaticsDocument24 pagesGenius Physics ..Pradeep Kshetrapal ElectrostaticsAditya Athwasiya100% (1)
- 640a3e44767ae727c8db02c3 - AP - Physics - C - E - M - Cram - ChartDocument1 page640a3e44767ae727c8db02c3 - AP - Physics - C - E - M - Cram - ChartDizart YtNo ratings yet
- PHY167 1 Electrostatics PDFDocument11 pagesPHY167 1 Electrostatics PDFAljhon MarajuniNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and BondingDocument33 pagesAtomic Structure and BondingstdphdNo ratings yet
- As 11a Matter&RadiationDocument56 pagesAs 11a Matter&RadiationJeffreyNo ratings yet
- Gerneral Physics ReviewerDocument4 pagesGerneral Physics ReviewerQueenie LucasNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Electrostatics Study NotesDocument158 pagesCBSE Class 12 Electrostatics Study NotesKarthick0% (1)
- 1 Physics 2 IntroDocument25 pages1 Physics 2 IntroMariah PagcaliuanganNo ratings yet
- General Physics II q3Document7 pagesGeneral Physics II q3Glaiza Mae GalizaNo ratings yet
- General Physics IIDocument26 pagesGeneral Physics IIJohn Rudolf CatalanNo ratings yet
- PHYS 221 General Physics: Electricity, Light and Modern Physics Lecture 1 Electric Charges & Coulomb's LawDocument7 pagesPHYS 221 General Physics: Electricity, Light and Modern Physics Lecture 1 Electric Charges & Coulomb's LawabdooufNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Basics of ElectromagnetismDocument74 pagesChapter 3 - Basics of ElectromagnetismDr. ASHOK CHILUKOTINo ratings yet
- Electric Charges & Fields. Full Notes21Document15 pagesElectric Charges & Fields. Full Notes21DHANUSH PATEL .MNo ratings yet
- Accounting at Biovail ReportDocument7 pagesAccounting at Biovail ReportimeldafebrinatNo ratings yet
- Ipa RasaDocument3 pagesIpa RasaText Texts50% (2)
- F.miklosich - Chronica NestorisDocument258 pagesF.miklosich - Chronica NestorisДжу ХоNo ratings yet
- PACTO de RETRO Deed of Sale With Right of RepurchaseDocument2 pagesPACTO de RETRO Deed of Sale With Right of RepurchaseRalph Gene Trabasas Flora90% (10)
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To AccountingDocument17 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To AccountingPatrick John AvilaNo ratings yet
- Hotel Reservation FormDocument2 pagesHotel Reservation FormAhmad Faisal NasutionNo ratings yet
- ASTM D2628 (1998) - Preformed Polychloroprene Elastastomeric Joint Seals For Concrete PavingDocument3 pagesASTM D2628 (1998) - Preformed Polychloroprene Elastastomeric Joint Seals For Concrete Pavingnoto SugiartoNo ratings yet
- Ground RulesDocument2 pagesGround RulespulithepogiNo ratings yet
- Abhishek SrivastavaDocument1 pageAbhishek SrivastavaAmit SinghNo ratings yet
- Kuda - External Analysis Delta FinalDocument10 pagesKuda - External Analysis Delta Finalkays chapanda100% (2)
- Tax Invoice: Warranty Expired:NDocument3 pagesTax Invoice: Warranty Expired:NSanjay PatelNo ratings yet
- 003 Potenciana Evangelista v. People, G.R. Nos. 108135-36, 14 August 2000Document12 pages003 Potenciana Evangelista v. People, G.R. Nos. 108135-36, 14 August 2000John WickNo ratings yet
- Re Assignment MarriageDocument2 pagesRe Assignment MarriageSamNo ratings yet
- CCB-MDM Installation GuideDocument40 pagesCCB-MDM Installation GuidevikasNo ratings yet
- Resource Ordering Management API REST SpecificationDocument34 pagesResource Ordering Management API REST SpecificationalexfarcasNo ratings yet
- Mind Map of Accounting ElementsDocument4 pagesMind Map of Accounting ElementsSapphire Au MartinNo ratings yet
- 859 - By71h6kcls - Fire - Wordings For Add On Covers ClausesDocument9 pages859 - By71h6kcls - Fire - Wordings For Add On Covers ClausesShivNo ratings yet
- The OpsRamp Platform Security and ComplianceDocument9 pagesThe OpsRamp Platform Security and ComplianceJesus Huerta VilchisNo ratings yet
- The Taiping Rebellion 1851-66Document50 pagesThe Taiping Rebellion 1851-66tomalakis100% (6)
- Equitable Mortgage DeedDocument3 pagesEquitable Mortgage DeedchandrashekharNo ratings yet
- PD 1144Document7 pagesPD 1144Dinnah Mae AlconeraNo ratings yet
- James Rafferty.2024.Q1.L6.How Long Will You Judge UnjustlyDocument7 pagesJames Rafferty.2024.Q1.L6.How Long Will You Judge UnjustlyLaurent DecouvrirDieuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document19 pagesChapter 5Harsh SharmaNo ratings yet
- 15439rr04 12Document16 pages15439rr04 12Sy HimNo ratings yet
- Saima Wazed WikiDocument3 pagesSaima Wazed WikiMichaelStevansNo ratings yet
- Decide Which Answer (A, B, C or D) Best Fits Each Space.: Inspector Crumbs InvestigatesDocument2 pagesDecide Which Answer (A, B, C or D) Best Fits Each Space.: Inspector Crumbs InvestigatesХристина КоникNo ratings yet
- Checklist For Audit HSEMSDocument12 pagesChecklist For Audit HSEMSBalla BammouneNo ratings yet
- MBF14e Chap05 FX MarketsDocument20 pagesMBF14e Chap05 FX MarketsHaniyah Nadhira100% (1)
- Greenwood P. 66 Goveia P. 77Document4 pagesGreenwood P. 66 Goveia P. 77Subordinating ConjunctionNo ratings yet
- What Holds Japan BackDocument6 pagesWhat Holds Japan BackMaryamNo ratings yet
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldFrom EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (64)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (409)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyFrom EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyNo ratings yet
- The Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectFrom EverandThe Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismFrom EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (500)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1395)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldFrom EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayFrom EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (125)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceFrom EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseFrom EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (48)
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsFrom EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (94)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldFrom EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (60)
- Genius: The Life and Science of Richard FeynmanFrom EverandGenius: The Life and Science of Richard FeynmanRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (480)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners: Simple Illustrated Guide to Discover with Practical Explanations the Paradoxes of the Life and Universe Reconsidering RealityFrom EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners: Simple Illustrated Guide to Discover with Practical Explanations the Paradoxes of the Life and Universe Reconsidering RealityRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityFrom EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (76)
- Chernobyl 01:23:40: The Incredible True Story of the World's Worst Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandChernobyl 01:23:40: The Incredible True Story of the World's Worst Nuclear DisasterRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (264)
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 4A: Math for PhysicistsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 4A: Math for PhysicistsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Universe: The book of the BBC TV series presented by Professor Brian CoxFrom EverandThe Universe: The book of the BBC TV series presented by Professor Brian CoxRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (27)