Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Turbine+Engine+Theory+Oral+Exam
Uploaded by
Luis Alonso0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views7 pagesPowerplant
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPowerplant
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views7 pagesTurbine+Engine+Theory+Oral+Exam
Uploaded by
Luis AlonsoPowerplant
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
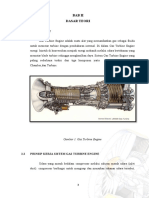
Turbine Engine Theory & Overhaul
Oral Test Questions
Student #1 (five questions)
A. What are the two principal types of compressors currently used in turbine engines?
Centrifugal and axial flow.
B. What prevents burning of the combustion chambers?
Cooling air along the inside wall of the liner.
C. What are carbon seals used for in turbine engines?
As oil seals for the rotor shaft bearings.
D. Where is the highest gas pressure in a turbojet engine?
At the outlet of the compressor or the entrance of the burner section (Diffuser).
E. An exhaust cone placed aft of the turbine in a jet engine will cause the pressure in the first part of the exhaust duct to
Increase and the velocity to decrease.
Student #2 (five questions)
A. What is the profile of a turbine engine compressor blade?
A reduced blade tip thickness.
B. In the dual axial-flow or twin spool compressor system, the first stage turbine drives the
High pressure compressor (N2).
C. What is the effect of relative humidity on turbojet or turbofan power?
Negligible effect.
D. What is the purpose of the interconnect tubes attached between can-type combustion chambers?
For flame propagation during starting.
E. Name the two basic sections of a gas turbine engine.
Cold section and hot section.
Student #3 (five questions)
A. The fan rotational speed of a dual axial compressor forward fan engine is the same as the
Low-pressure compressor (N1).
B. What turbine engine section provides for proper mixing of the fuel and air?
Combustion section.
C. What may be the indications if a turbojet or turbofan engine is out of trim?
The engine has high exhaust gas temperature (EGT) at target engine pressure ratio (EPR) for takeoff.
D. List four types of gas turbine engines:
1-Turbojet, 2-Turboprop, 3-Turboshaft, and 4-Turbofan.
E. What are labyrinth seals used for in turbine engines?
As oil seals for the rotor shaft bearings.
Student #4 (five questions)
A. The abbreviation Pt2 used in turbine engine terminology means
The total pressure at station No. 2.
B. In a gas turbine engine, combustion occurs at a constant
Pressure.
C. What is one method of relieving thermal stress on a turbine disk?
One means is to bleed cooling air back onto the face of the disk.
D. How are turbine engine rotor blades attached to rotor disks? (Name at least two methods.)
By a: (1) bulb-type root, (2) fir tree-type root, or (3) dovetail-type root.
E. What are the two types of thrust and torque producing engines?
(Thrust) Turbojet & Turbofan and (Torque) Turboprop & Turboshaft.
Student #5 (five questions)
A. What are the major components of a typical gas turbine engine?
An air inlet, compressor section, combustion section, turbine section, exhaust section, and accessory section.
B. Name two commonly used types of oil seals in turbine engines?
Labyrinth seal and carbon seal.
C. What prevents ice from building up on turbine engine inlets?
Pneumatic air (bleed air).
D. What is the discharge pressure of the exhaust nozzle compared to ambient?
Slightly higher.
E. How does the turbojet engine generate thrust?
The exhaust section nozzle accelerates the airflow of the gases and creates thrust.
Student #6 (five questions)
A. What happens to the air velocity & pressure when it flows thru a divergent duct?
The air velocity decreases and the pressure increases.
B. Where is the accessory gearbox located on most turbojet and turbofan engines?
At the bottom or six o’clock position of the engine compressor section.
C. How are gas turbine engine tachometers calibrated?
They are calibrated in percent of R.P.M.
D. What powers the variable inlet guide vanes used on some APUs to regulate compressor intake airflow?
Fuel pressure.
E. The secondary purpose of the turbine stators is to:
To direct the gases at the optimum angle into the turbine blades so that the wheel turns with maximum efficiency.
Student #7 (five questions)
A. What is use for deicing the inlet guide vanes?
Pneumatic air (bleed air).
B. What are the three functions of the diffuser?
Reduce air velocity, increase air pressure, and increase air temperature.
C. What are the two functional elements in a centrifugal compressor?
Impeller and diffuser.
D. What is the proper starting sequence for a turbojet engine?
Starter, ignition, fuel.
E. What advantages are gained using the active tip clearance control?
Keeps tip losses at a minimum at all power settings.
Student #8 (five questions)
A. What type of inlet duct is found on commercial aircraft?
Fixed geometry and have a divergent shape.
B. What is the purpose of primary and secondary airflow in the combustor?
Primary air is routed to the fuel nozzle area to support combustion. Secondary air is used for cooling.
C. What must be done after the fuel control unit has been replaced on an aircraft gas turbine engine?
Retrim the engine.
D. Generally, when starting a turbine engine, the starter should be disengaged
After the engine has reached self-accelerating speed.
E. What are three methods used to cool turbine rotor and stator blades?
Internal air flow cooling (convection cooling), surface film cooling, and a combination of both.
Student #9 (five questions)
A. Is the inlet duct, cowlings, and exhaust duct part of the engine?
No, the airframe.
B. What is the first engine instrument indication of a successful start of a turbine engine?
A rise in the exhaust gas temperature.
C. The diffuser section of a jet engine is located between
The compressor section and the burner section.
D. The abbreviation Pt7 used in turbine engine terminology means
The total pressure at station No. 7.
E. Shrouded tip turbine blades are normally used on which compressor?
Low pressure turbine.
Student #10 (five questions)
A. What is the ram recovery point?
This is the point at which pressure inside the inlet returns to ambient value.
B. The velocity of supersonic air as it flows through a divergent nozzle
Increases.
C. Compressor stall is caused by
A high angle of attack airflow through the first stages of compression.
(If the airflow entering the engine is restricted, reducing its velocity, the angle of attack of the compressor blade
will increase to such a point that compressor stall can occur.)
D. Who manufacturers the tail pipe?
The airframe manufactures.
E. Subsonic aircraft have what shape of exhaust?
Convergent shape.
Student #11 (five questions)
A. What type of inlet duct is used on helicopters?
Bellmouth inlet type.
B. What is the function of the inlet guide vane assembly on an axial-flow compressor?
Directs the air into the first stage rotor blades at the proper angle.
C. What is another name for the combustor section?
The burner section.
D. In what section of a turbojet engine is the jet nozzle located?
Exhaust.
E. What are the two basic elements of the turbine section in a turbine engine?
Stator and rotor.
Student #12 (five questions)
A. What type of inlet duct would be used on a supersonic aircraft?
Convergent-divergent inlet type.
B. The purpose of a bleed valve, located in the beginning stages of the compressor, in an gas turbine engine is to
Vent some of the air overboard to prevent a compressor stall.
C. What may be used to accomplish internal inspection of an assembled turbine engine?
A borescope.
D. In a gas turbine engine, combustion occurs at a constant
Pressure.
E. Some engine manufacturers of twin spool gas turbine engines identify turbine discharge pressure in their
maintenance manuals as
Pt7.
Student #13 (five questions)
A. What three elements that make up the centrifugal compressor?
The impeller rotor, the diffuser, and the manifold.
B. Main bearing oil seals used with turbine engines are usually what type(s)?
Labyrinth and/or carbon rubbing.
C. At what stage in a turbine engine are gas pressures the greatest?
Compressor outlet.
D. A turbine engine hot section is particularly susceptible to which kind of damage?
Cracking.
E. The pressure of subsonic air as it flows through a convergent nozzle
Decreases.
Student #14 (five questions)
A. What is the function of the inlet guide vanes?
To direct airflow into the rotor at the most desirable angle.
B. Anti-icing of jet engine air inlets is commonly accomplished by
Engine bleed air ducted through the critical areas.
C. The non-rotating axial-flow compressor airfoils in an aircraft gas turbine engine, are called
Stator vanes.
D. How many ignitor plugs are used in a turbine engine?
Two.
E. Turbine blades are generally more susceptible to operating damage than compressor blades because of
Exposure to high temperatures.
Student #15 (five questions)
A. What are two elements that make up one stage in an axial flow compressor?
Stator and Rotor.
B. Standard sea level pressure is
29.92" Hg.
C. Stator blades in the compressor section of an axial-flow turbine engine
Decrease the air velocity and prevent swirling.
D. The air passing through the combustion chamber of a turbine engine is used to
Support combustion and to cool the engine.
E. The velocity of subsonic air as it flows through a convergent nozzle
Increases.
Student #16 (five questions)
A. What is the primary purpose of the compressor?
Is to increase the pressure of the air mass.
B. Which turbine engine compressor offers the greatest advantages for both starting flexibility and improved high-
altitude performance?
Split-spool, axial-flow.
C. The compressor stators in a gas turbine engine act as diffusers to
Decrease the velocity of the gas flow.
D. Hot spots in the combustion section of a turbojet engine are possible indicators of
Malfunctioning fuel nozzles.
E. What type of turbine blade is most commonly used in aircraft jet engines?
Impulse-reaction.
Student #17 (five questions)
A. What is compressor bleed air used for?
To cool hot section parts, pressurize bearing seals, anti-icing the inlet, and fuel system deicing.
B. Using standard atmospheric conditions, the standard sea level temperature is
59°F.
C. What is the primary factor which controls the pressure ratio of an axial-flow compressor?
Number of stages in compressor.
D. Which of the following types of combustion sections are used in aircraft turbine engines?
Multiple-can, annular, and can-annular.
E. The exhaust section of a turbine engine is designed to
Impart a high exit velocity to the exhaust gases.
Student #18 (five questions)
A. What kind of bearings are used to support the rotor shaft of an aircraft turbine engine?
Anti-friction bearings, such as ball bearings and roller bearings.
B. Between each row of rotating blades in a turbine engine compressor, there is a row of stationary blades which act to
diffuse the air. These stationary blades are called
Stators.
C. In an axial-flow compressor, one purpose of the stator vanes at the discharge end of the compressor is to
Straighten the airflow and eliminate turbulence.
D. The highest heat-to-metal contact in a jet engine is the
Turbine inlet guide vanes.
E. The stators in the turbine section of a gas turbine engine
Increase the velocity of the gas flow.
Student #19 (five questions)
A. On a dual spool axial flow engine, what drives the accessory section?
A bevel gear drive shaft system driven by the main rotor shaft of the HPC (N2).
B. What is the mid span shroud?
Supports the blades against the bending forces from the airstream.
C. A gas turbine engine comprises which three main sections?
Compressor, combustion, and turbine
D. A condition known as 'hot streaking' in turbine engines is caused by
A partially clogged fuel nozzle.
E. Why do some turbine engines have more than one turbine wheel attached to a single shaft?
To extract more power from the exhaust gases than a single wheel can absorb.
Student #20 (five questions)
A. What is the secondary function of the main gear box?
To provide a collecting point for scavenged oil before being pumped back to the oil tank.
B. The pressure of supersonic air as it flows through a divergent nozzle
Decreases.
C. What is the major function of the turbine assembly in a turbojet engine?
Supplies the power to turn the compressor.
D. What is the purpose of the dump valve used on aircraft gas turbine engines?
The fuel is quickly cut off to the nozzles and the manifolds are drained preventing fuel boiling off as a result of
residual engine heat.
E. What is meant by a shrouded turbine?
The turbine blades are shaped so that their ends form a band or shroud.
Student #21 (five questions)
A. What name are giving to the compressor blade that have a reduced thickness at the tips?
Profile or squealer tip blades.
B. What is the difference of the compressor exit guide vanes?
The stators are stray to prevent turbulence.
C. What prevents the flame from contacting the combustors liner?
A portion of secondary air.
D. What are the three turbine blade designs?
Impulse, reaction, and impulse-reaction.
E. What is a choked nozzle?
Convergent duct.
Student #22 (five questions)
A. How are the compressor blades attached to the disk?
Dovetail-type root & Bulb-type root.
B. Which combustor design is the most efficient?
Annular combustor.
C. What is the function of the turbine stators?
Act as nozzles that increase velocity, decrease pressure, and direct the mass airflow to drive the turbine rotor at a
specific angle.
D. What reduces gas leakage over the turbine blade tips?
Blade tip shroud and knife-edge seal.
E. Who manufacturers the tail pipe?
The airframe manufactures.
Student #23 (five questions)
A. What is used to prevent compressor stalls and stabilize airflow?
Variable inlet guide vanes actuated by fuel or pneumatic air pressure to change the AOA.
B. At what point in the axial flow engine is the gas pressure the highest?
At the diffuser section.
C. What is the purpose of the turbine in the jet engine?
To drive the compressor and accessories.
D. What are the four types of combustors?
Multiple-can, annular, can-annular, and annular reverse-flow combustors.
E. At what point in a turbine engine is the temperature the highest?
At the inlet to the high-pressure turbine.
Student #24 (five questions)
A. What does a combination of a rotor and a stator make up in an axial compressor?
A compression stage.
B. What is the purpose of flame propagation tubes?
To interconnect the liners and to assist the flame during start up.
C. What is another name for the turbine stators?
Turbine nozzle, nozzle diaphragm, or the turbine nozzle guide vane assembly.
D. What holds the turbine blades in place?
Rivets, lock tabs, lock wires, and roll pins.
E. What two blade tip designs may be used?
Open at the tip or fitted with interlocking shrouds.
Student #25 (five questions)
A. On a dual spool turbofan engine, the fan is considered to be what?
First stage of the compressor.
B. What two designs may be found on the compressor blade tip?
Flat-machined tip and profile or squealer tip.
C. What would happen if the combustor primary airflow were too high?
Flameout.
D. How many ignitor plugs are used in a turbine engine?
Two.
E. How are the turbine blades attached to the disk?
By the fir-tree design.
You might also like
- ASA A4 Jet Engine BasicsDocument6 pagesASA A4 Jet Engine BasicsimannurNo ratings yet
- Indonesian Licence Basic AviationDocument13 pagesIndonesian Licence Basic AviationMagic of SholawatNo ratings yet
- Assessment 1 Porpulsion 16BDocument5 pagesAssessment 1 Porpulsion 16BMr. SeventeenNo ratings yet
- Turbine Engine Design and ConstructionDocument4 pagesTurbine Engine Design and ConstructionWanda Aulia SukmaNo ratings yet
- 50 Questions and Answers For Marine Engineers: Issue 3Document10 pages50 Questions and Answers For Marine Engineers: Issue 3Tara Gonzales100% (3)
- Study Question! Powerplant Section (Gas Turbine)Document8 pagesStudy Question! Powerplant Section (Gas Turbine)IdrisNo ratings yet
- Propulsion engines - Gas turbine engines (GTEDocument7 pagesPropulsion engines - Gas turbine engines (GTEMc FridonNo ratings yet
- Question Gte 1 20DHDocument8 pagesQuestion Gte 1 20DH2155200046No ratings yet
- Turbine engine inspection and component identificationDocument10 pagesTurbine engine inspection and component identificationcarlos tantacalleNo ratings yet
- Piston Engines 97 QuestDocument19 pagesPiston Engines 97 QuestChatchai PrasertsukNo ratings yet
- Piston Engines: 97 QuestionsDocument19 pagesPiston Engines: 97 QuestionsamilaNo ratings yet
- Basic Aircraft Gas Turbine Engine MaintenanceDocument7 pagesBasic Aircraft Gas Turbine Engine MaintenanceNisrina Rahiyana NabilaNo ratings yet
- MotorDocument84 pagesMotorSarath Raghav100% (1)
- End of Chapter 1 Jet Engine Theory and Design Cáceres Buitrago, Méndez Mesa, Cortés Quintero Review QuestionsDocument18 pagesEnd of Chapter 1 Jet Engine Theory and Design Cáceres Buitrago, Méndez Mesa, Cortés Quintero Review QuestionsGERALDINE MENDEZ MESANo ratings yet
- Part3 Q A Marine EngineerDocument10 pagesPart3 Q A Marine Engineer12345No ratings yet
- Part1 Q A Marine EngineerDocument7 pagesPart1 Q A Marine EngineerSamir Alshaar100% (1)
- Basic GT EngineDocument22 pagesBasic GT EngineabuhurairamunirNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Piston and Jet Engine StudyDocument11 pagesAircraft Piston and Jet Engine StudySuthan RNo ratings yet
- Ame Licence Exam Oct2011Document20 pagesAme Licence Exam Oct2011Aviation WorldNo ratings yet
- Aero Engine - 1504714592213Document75 pagesAero Engine - 1504714592213raviNo ratings yet
- Part1 Q A Marine Engineer PDFDocument10 pagesPart1 Q A Marine Engineer PDFturgut08No ratings yet
- Slow Speed Engine Statement True Crankcase ExplosionDocument2 pagesSlow Speed Engine Statement True Crankcase ExplosiondkpushpdkNo ratings yet
- Lycoming T53-L-1 Turboshaft Engine Technical OverviewDocument3 pagesLycoming T53-L-1 Turboshaft Engine Technical Overviewcecil josef liganNo ratings yet
- Marine Engineering Knowledge (Motor) All CollectionDocument16 pagesMarine Engineering Knowledge (Motor) All CollectionTapan KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Constructing A Turbocharger Turbojet EngineDocument52 pagesConstructing A Turbocharger Turbojet Enginerocketman19911No ratings yet
- Section III. Major Engine SectionsDocument22 pagesSection III. Major Engine SectionsMuddassarNo ratings yet
- 1Document127 pages1Rohan NaikNo ratings yet
- AE 6504 Propulsion II 2 MarksDocument13 pagesAE 6504 Propulsion II 2 Markssrinithims78No ratings yet
- Jet Engine Types & ComponentsDocument1 pageJet Engine Types & ComponentsJohn Gabriel DecenaNo ratings yet
- Ignition System: Aircraft Electrical System ECUDocument32 pagesIgnition System: Aircraft Electrical System ECUJhiGz Llausas de Guzman100% (1)
- Diesel Engine Air Cooler PurposeDocument9 pagesDiesel Engine Air Cooler PurposeMarineroad Vallen AngkasaNo ratings yet
- Basic Document For Oat552Document15 pagesBasic Document For Oat552SivaNo ratings yet
- Mini ProjectDocument37 pagesMini ProjectAmbati ManojNo ratings yet
- A4 EXAMINATION May 2012 Practice TestDocument13 pagesA4 EXAMINATION May 2012 Practice Testegi100% (1)
- 50 Questions and Answers For Marine Engineers Issue 1Document10 pages50 Questions and Answers For Marine Engineers Issue 1severo97100% (1)
- Power Plant: I. Piston Engine II. Turbine Engine Iii. Engine Construction: IV. Engine Systems: V. Auxiliary Power UnitDocument78 pagesPower Plant: I. Piston Engine II. Turbine Engine Iii. Engine Construction: IV. Engine Systems: V. Auxiliary Power UnitNirja ozaNo ratings yet
- Motor FinalDocument72 pagesMotor FinalRamasamy100% (1)
- Airframe Continuation!...Document11 pagesAirframe Continuation!...IdrisNo ratings yet
- Ge Frame 9eDocument22 pagesGe Frame 9eAs C100% (2)
- Basic Helicopter Power Plant ExaminationDocument10 pagesBasic Helicopter Power Plant ExaminationIdrisNo ratings yet
- ME 2351 Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion Unit 4Document14 pagesME 2351 Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion Unit 4Arivukkarasan SundaresanNo ratings yet
- S NssnabDocument4 pagesS NssnabAleksandria Donne D. FernandezNo ratings yet
- 2013 Repeated Objective QuestionsDocument50 pages2013 Repeated Objective QuestionsTanawat SongkroaNo ratings yet
- FICE 1 KeyDocument4 pagesFICE 1 KeyK. Swaminathan Asst Prof - Automobile DeptNo ratings yet
- Eme Ic Engine Module-3 22eme13Document68 pagesEme Ic Engine Module-3 22eme13SHARATH RNo ratings yet
- Lecture #12 Ehsan Roohi Sharif University of Technology Aerospace Engineering DepartmentDocument21 pagesLecture #12 Ehsan Roohi Sharif University of Technology Aerospace Engineering Departmentpsycho_zahranNo ratings yet
- University of Engineering & Technology KSK New CampusDocument9 pagesUniversity of Engineering & Technology KSK New CampusAli RazaNo ratings yet
- 16-Supercharging & TurbochargingDocument31 pages16-Supercharging & Turbochargingxemovi7309No ratings yet
- DASAR TEORI Gas TurbineDocument17 pagesDASAR TEORI Gas TurbineAmirul MukminNo ratings yet
- Aemr Two MarksDocument11 pagesAemr Two MarksRajashree VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Prof. M.S.PATIL: Under The Guidance ofDocument20 pagesProf. M.S.PATIL: Under The Guidance ofAnjanKumarMahantaNo ratings yet
- GTE Note 4 2023Document9 pagesGTE Note 4 2023ibrahim ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Title: Types of Engines General Objective: Specific ObjectivesDocument16 pagesUnit 1: Title: Types of Engines General Objective: Specific ObjectivesAtika MokhtarNo ratings yet
- English For Aircraft Maintenance Engineers ChaptersDocument11 pagesEnglish For Aircraft Maintenance Engineers ChaptersLeila HannaneNo ratings yet
- Turbocharger Characteristics Analysis of 93 KW Marine Diesel EngineDocument6 pagesTurbocharger Characteristics Analysis of 93 KW Marine Diesel EngineFrank ChukwujiNo ratings yet
- PPL Exam Secrets Guide: Aircraft General & Principles of FlightFrom EverandPPL Exam Secrets Guide: Aircraft General & Principles of FlightRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Oral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseFrom EverandOral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseNo ratings yet
- Operator's Guide to General Purpose Steam Turbines: An Overview of Operating Principles, Construction, Best Practices, and TroubleshootingFrom EverandOperator's Guide to General Purpose Steam Turbines: An Overview of Operating Principles, Construction, Best Practices, and TroubleshootingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 1-11Document6 pages1-11Luis AlonsoNo ratings yet
- 181-190Document1 page181-190Luis AlonsoNo ratings yet
- 161-170Document1 page161-170Luis AlonsoNo ratings yet
- 91-100Document1 page91-100Luis AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Power For FutureDocument28 pagesSustainable Power For Futureasim.infniteNo ratings yet
- Government Policy Statement - President Ranil Wickremesinghe - 07 Feb 2024Document11 pagesGovernment Policy Statement - President Ranil Wickremesinghe - 07 Feb 2024Adaderana OnlineNo ratings yet
- Cita Bentley Bim Overview PDFDocument41 pagesCita Bentley Bim Overview PDFPedro FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Trial Exam 2014 PT3 ScienceDocument9 pagesTrial Exam 2014 PT3 ScienceNor Shuhada100% (1)
- AUHF TS001 A6 Lineator AUHF Typical SpecificationDocument2 pagesAUHF TS001 A6 Lineator AUHF Typical SpecificationSlick72No ratings yet
- P & P - QuestionsDocument125 pagesP & P - QuestionsShariq RaoNo ratings yet
- Manual de Partes Maverick 4750hspDocument5 pagesManual de Partes Maverick 4750hspAbelardo PinaNo ratings yet
- CBIP Substation Manual 2006 PDFDocument122 pagesCBIP Substation Manual 2006 PDFPravin Narkhede83% (18)
- Effect of Heater Geometry On The High Temperature Distribution On A MEMS Micro-HotplateDocument6 pagesEffect of Heater Geometry On The High Temperature Distribution On A MEMS Micro-HotplateJorge GuerreroNo ratings yet
- How power grids deliver electricity from plants to homesDocument17 pagesHow power grids deliver electricity from plants to homesNitz Fajilan PaulasaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Heat Pump Analysis Of A Supercritical Water-cooled Nuclear Reactor And Hydrogen Production CycleDocument36 pagesChemical Heat Pump Analysis Of A Supercritical Water-cooled Nuclear Reactor And Hydrogen Production Cyclepisces1985No ratings yet
- Form 4 Physics Chapter 4 - Teacher'sDocument9 pagesForm 4 Physics Chapter 4 - Teacher'sPavithiran50% (2)
- Siemens Bullet Train Feasibility Report For PakistanDocument153 pagesSiemens Bullet Train Feasibility Report For Pakistansyed usman wazirNo ratings yet
- Interview Guidance by S K MondalDocument16 pagesInterview Guidance by S K MondaljishnuNo ratings yet
- Governor ReplacementDocument2 pagesGovernor ReplacementabdullahNo ratings yet
- Light Intensity Control Using Diac and Triac 1Document12 pagesLight Intensity Control Using Diac and Triac 1Prathamesh KaleNo ratings yet
- Green Hydrogen AgreementsDocument3 pagesGreen Hydrogen Agreementsishika VermaNo ratings yet
- Epa Chemical Compatibility ChartDocument3 pagesEpa Chemical Compatibility ChartMohamedNo ratings yet
- HhidraulicDocument60 pagesHhidraulicapi-26356646No ratings yet
- Answers Exam 21jan 2015Document14 pagesAnswers Exam 21jan 2015Mark HinsterNo ratings yet
- Work Report On Automated Hydraulic Jack SystemDocument20 pagesWork Report On Automated Hydraulic Jack Systemcoolrohitkumar666100% (2)
- Sustainable Bio Kerosene: Process Routes and Industrial Demonstration Activities in Aviation BiofuelsDocument9 pagesSustainable Bio Kerosene: Process Routes and Industrial Demonstration Activities in Aviation BiofuelsJaymar JaminNo ratings yet
- 4 Tec Troubleshooting ChartDocument11 pages4 Tec Troubleshooting ChartnelsoncoNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory TimelineDocument17 pagesAtomic Theory TimelineAngelo Julius Nuque100% (3)
- Exercise 4 (Chromatography)Document6 pagesExercise 4 (Chromatography)Wendell Kim LlanetaNo ratings yet
- Mawa 10Document2 pagesMawa 10Hemant RasamNo ratings yet
- Case Expension - LVDT SensorDocument6 pagesCase Expension - LVDT Sensortrung2iNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Integrity Inspection ExchangerDocument7 pagesMechanical Integrity Inspection ExchangerSyed Faraz RazaNo ratings yet
- Current Transformers 03-06Document12 pagesCurrent Transformers 03-06noonbcc130No ratings yet
- Smart Grid Communication and Co-Simulation: Vincenzo Liberatore, Member, IEEE Computer, Ahmad Al-HammouriDocument5 pagesSmart Grid Communication and Co-Simulation: Vincenzo Liberatore, Member, IEEE Computer, Ahmad Al-HammouriLahcen AmiriNo ratings yet