Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DMA Chemical Analysis KO
Uploaded by
qwesghwqedfgCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DMA Chemical Analysis KO
Uploaded by
qwesghwqedfgCopyright:
Available Formats
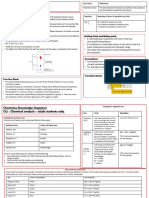
Chemistry Chemical Analysis Y10
Pure Substances Chromatography Required Practical Gas Tests
1 Definition A single element or 1 Chlorine Add damp litmus paper,
compound, not mixed with chlorine bleaches it white.
any other substance.
2 Carbon Bubble through limewater,
2 Using data Pure elements and compounds dioxide carbon dioxide turns in
melt and boil at specific cloudy.
temperatures.
Melting and boiling point data 3 Hydrogen Hold a burning splint at the
can be used to distinguish pure
open end of a test tube.
substances from mixtures.
Hydrogen burns with a
squeaky pop.
3 Melting Pure substances have sharp
and boiling melting/boiling points. 4 Oxygen Insert a glowing splint into a
points test tube. The splint relights in
oxygen.
Formulations Chromatography: Calculating Rf Key Vocabulary
Definition .A mixture that has been 1 Stationary The medium (material) that
1
designed as a useful phase does not move.
product.
2 Mobile phase The liquid that is used to
2 How they Made by mixing the move the sample through
are made components in measured the stationary phase.
quantities to ensure the
product has the desired
3 Solvent front The level reached by the
properties.
top of the moving solvent.
3 Examples Fuels, cleaning products, ,
paints, medicines, alloys, 4 Chromatogram The final result with the
fertilisers and food. substances separated on it.
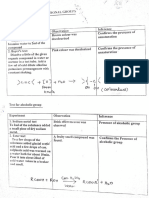
Chemistry Chemical Analysis (Triple Only) Y10
Flame Tests Tests for Metal Hydroxides Chemical Tests
Compound Test Positive Result
1 Lithium Crimson 1 Method Add sodium
2 Sodium Yellow
hydroxide
1 Carbonates 1) React with Limewater turns cloudy
dilute acid 2)
3 Potassium Lilac
Test for
2 Metal Ion Precipitate
4 Calcium Orange-red carbon dioxide
Colour
5 Copper Green
Instrumental Methods a Aluminium, White. 2 Halides Add silver Silver chloride → white
calcium, Only the nitrate precipitate
1 Advantages Accurate, rapid magnesium aluminium solution in the Silver bromide →
and sensitive presence of cream precipitate
hydroxide
dilute nitric Silver iodide → yellow
2 Flame Emission • The sample precipitate acid precipitate
Spectroscopy is put into a
dissolves in
flame and
the light excess NaOH
given out is 3 Sulphates Add barium White precipitate
passed b Copper (III) Blue chloride
through a solution in the
spectroscop presence of
e. dilute
• The line hydrochloric
spectrum c Iron (II) Green acid
produced
can be d Iron (III) Brown
analysed
You might also like
- Organic Chemistry Practical Manual - Compound IdentificationDocument10 pagesOrganic Chemistry Practical Manual - Compound Identificationsp_douglas83% (35)
- Chemistry Project FileDocument17 pagesChemistry Project Fileprithu2170% (20)
- Structural Steel For BridgesDocument9 pagesStructural Steel For Bridgesalucard375No ratings yet
- Testing Methods For Plating BathsDocument3 pagesTesting Methods For Plating BathsR.Subramanian100% (1)
- Philosophers Stone Elixir PDFDocument5 pagesPhilosophers Stone Elixir PDFweber-ellernNo ratings yet
- As and A Level Chemistry Core Practical 7 Inorganic and Organic Unkowns (Student, Teacher, Technician Worksheets)Document7 pagesAs and A Level Chemistry Core Practical 7 Inorganic and Organic Unkowns (Student, Teacher, Technician Worksheets)Namira Shameem67% (3)
- Copper SulphateDocument4 pagesCopper Sulphatesumathi siva50% (2)
- Chem 23Document8 pagesChem 23listerNo ratings yet
- Hot Rolled and Normalized Hot Rolled and Normalized Hot Rolled and Normalized Hot Rolled and NormalizedDocument11 pagesHot Rolled and Normalized Hot Rolled and Normalized Hot Rolled and Normalized Hot Rolled and NormalizedMahmoud Nasr100% (3)
- Trade Atlas - 16-12-2021 - File ID 3663887987Document101 pagesTrade Atlas - 16-12-2021 - File ID 3663887987HCGFH/NNo ratings yet
- 2 - 1. HalogensDocument26 pages2 - 1. HalogensHalil BalNo ratings yet
- Aiigma MembersDocument8 pagesAiigma MembersAsif IqbalNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Transmutation OL2Document33 pagesNuclear Transmutation OL2Shifa ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- PD LABDocument5 pagesPD LABShayden Leslie100% (1)
- C12 - Chemical AnalysisDocument2 pagesC12 - Chemical AnalysisNavdha SachdevaNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemDocument4 pagesOrganic ChemCherry GalamitonNo ratings yet
- Laporan Anorganik Modul 1 KEL.4Document28 pagesLaporan Anorganik Modul 1 KEL.4MonalisausmanNo ratings yet
- Phan111lec FinalsDocument34 pagesPhan111lec FinalsANDREA ROSELLE FULLONANo ratings yet
- 12th Chemistry PracticalDocument2 pages12th Chemistry Practicalsuriya kumarNo ratings yet
- 113L TransesDocument8 pages113L Transesmqdzpmjp2rNo ratings yet
- Title: 1) Preliminary TestsDocument5 pagesTitle: 1) Preliminary TestsAkash PawarNo ratings yet
- Title: 1) Preliminary TestsDocument6 pagesTitle: 1) Preliminary TestsAkash PawarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Index: Name of ExperimentDocument7 pagesChemistry Index: Name of ExperimentR3windNo ratings yet
- Experient Number Test Performed Expected Positive Result Principle OF Reaction Examples of Coumpounds That Give Positive ResultsDocument10 pagesExperient Number Test Performed Expected Positive Result Principle OF Reaction Examples of Coumpounds That Give Positive ResultsErika EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Organic AnalysisDocument15 pagesQualitative Organic Analysisspyzer.x.001No ratings yet
- Teaching DiscussionsDocument16 pagesTeaching DiscussionsRenz Caballero EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Testing Methods For Plating Baths 3 PDFDocument3 pagesTesting Methods For Plating Baths 3 PDFR.SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Reduced 12 TH Organic Salt EMDocument10 pagesReduced 12 TH Organic Salt EM19 Vasanth PurushothamanNo ratings yet
- CHEM181 Experiment4 OxidationReductionReactionsDocument11 pagesCHEM181 Experiment4 OxidationReductionReactionsNeckle JadeNo ratings yet
- Scheme For Organic AnalysisDocument3 pagesScheme For Organic Analysisameenahmed10927No ratings yet
- Pre-Lab Report: Title of The Experiment Experiment No. 8Document15 pagesPre-Lab Report: Title of The Experiment Experiment No. 8Jelo ArtozaNo ratings yet
- Unit Preliminary Qualitative Analysis: StructureDocument12 pagesUnit Preliminary Qualitative Analysis: StructureAnanda VijayasarathyNo ratings yet
- Funtional Group - ChoDocument3 pagesFuntional Group - Choayushanandsingh2309No ratings yet
- Aminopiralid TC - Datos Regulatory Note REG2007-01Document3 pagesAminopiralid TC - Datos Regulatory Note REG2007-01Alfredo MéndezNo ratings yet
- Part I Planet Earth NotesDocument14 pagesPart I Planet Earth NotesHon KwanNo ratings yet
- Determination of Unknown CompoundDocument5 pagesDetermination of Unknown CompoundAzharNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument5 pagesChemistryJaefar ShameemNo ratings yet
- Chemlab - PM3 - Labreport 2Document16 pagesChemlab - PM3 - Labreport 2Jei y’allNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry (Hydrocarbon)Document3 pagesOrganic Chemistry (Hydrocarbon)azzatul amiraNo ratings yet
- Test of Amine & AmideDocument18 pagesTest of Amine & AmideKING RAFINo ratings yet
- Formal Report E3Document6 pagesFormal Report E3Bianca Chellyne AguilarNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 1 Synthesis UHPDocument13 pagesKelompok 1 Synthesis UHPFatmawati KadirNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Properties of Ionic Compounds LabDocument3 pagesWeek 2 Properties of Ionic Compounds LabbaydaaloboudiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8 - Classification Tests For Organic HalidesDocument6 pagesExperiment 8 - Classification Tests For Organic HalidesNICOLE GEA DIVINASFLORESNo ratings yet
- Organic PresentationDocument18 pagesOrganic PresentationJamesShiqNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource WasDocument6 pagesThis Study Resource WasBeatrice GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-04-05 at 12.57.28 AMDocument46 pagesScreenshot 2023-04-05 at 12.57.28 AMOmar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Analysis of The IonsDocument2 pagesAnalysis of The IonsJoanna Carla Marmonejo Estorninos-WalkerNo ratings yet
- Chemical Analysis of Red Lead: Standard Test Methods ofDocument4 pagesChemical Analysis of Red Lead: Standard Test Methods ofAmer AmeryNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem. Lab. M6 ACTIVITY SHEET PCCH103LDocument4 pagesOrganic Chem. Lab. M6 ACTIVITY SHEET PCCH103LPoll DaneNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis of Organic CompoundsDocument10 pagesQualitative Analysis of Organic Compoundspayal_joshi_14No ratings yet
- Identification of Ions and GasesDocument5 pagesIdentification of Ions and GasesJobelle Aleli Perez EhinaNo ratings yet
- 12 Salt Analysics EMDocument20 pages12 Salt Analysics EMUma SaravananNo ratings yet
- Class-XII (Chemistry Practical) : ObjectDocument22 pagesClass-XII (Chemistry Practical) : ObjectsaberNo ratings yet
- 10-REDOX TitrationsDocument23 pages10-REDOX TitrationsnidsNo ratings yet
- 5 - Volatile Poisons in Simulated Gastric ContentDocument7 pages5 - Volatile Poisons in Simulated Gastric ContentMedSure PharmacyNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Functional Groups and Lewis StructureDocument6 pagesActivity 1 Functional Groups and Lewis StructurePearl NecoleNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Inorganic and Organic ChemistryDocument57 pagesLab Manual Inorganic and Organic ChemistryKashif NazirNo ratings yet
- Precipitation Titration by SiteshDocument17 pagesPrecipitation Titration by Siteshsanjeev khanalNo ratings yet
- Galata Chemicals Produces Bulk MMP in The United States. at 99.9% PurityDocument3 pagesGalata Chemicals Produces Bulk MMP in The United States. at 99.9% PurityvenkNo ratings yet
- Chemical Analysis of Yellow, Orange, Red, and Brown Pigments Containing Iron and ManganeseDocument5 pagesChemical Analysis of Yellow, Orange, Red, and Brown Pigments Containing Iron and ManganeseAmer AmeryNo ratings yet
- Experiment-4 Group-8Document5 pagesExperiment-4 Group-8ROSE ANN JAWADNo ratings yet
- Distinction Test (Organic Chemistry)Document14 pagesDistinction Test (Organic Chemistry)Ashish Kumar100% (3)
- Functional Group and Food StuffDocument6 pagesFunctional Group and Food StuffNandana MNo ratings yet
- N-Levels: 2014 Chemistry Notes For Secondary School Combined ChemistryDocument44 pagesN-Levels: 2014 Chemistry Notes For Secondary School Combined ChemistryAnnie Tan100% (1)
- Semi-Scientific Lab Report Ex. 2Document6 pagesSemi-Scientific Lab Report Ex. 2MARY FLOR CANADALLANo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry of Organic Halogen Compounds: International Series in Analytical ChemistryFrom EverandAnalytical Chemistry of Organic Halogen Compounds: International Series in Analytical ChemistryNo ratings yet
- Product Certificate Welding Wire-ModelDocument1 pageProduct Certificate Welding Wire-ModelRamona CrangasNo ratings yet
- Purchase Order FormatDocument2 pagesPurchase Order Formatmini p shendeNo ratings yet
- Volumetric Analysis - Class Assignment Part 01 PDFDocument2 pagesVolumetric Analysis - Class Assignment Part 01 PDFyug agarwalNo ratings yet
- Class Test Metals and NonmetalsDocument1 pageClass Test Metals and NonmetalsSania AbidNo ratings yet
- Analysis of TalcDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Talcalexander_suarez_19No ratings yet
- Observation of Cation and Anion TestDocument6 pagesObservation of Cation and Anion Testsshyam3No ratings yet
- ReveDocument48 pagesReveJunel AlapaNo ratings yet
- Metal Ring Joint GasketsDocument2 pagesMetal Ring Joint Gasketswaseemiqbal133No ratings yet
- Formula SprayDocument3 pagesFormula SprayW MegaNo ratings yet
- Cutting Tool Applications: by George Schneider, Jr. CmfgeDocument9 pagesCutting Tool Applications: by George Schneider, Jr. CmfgeyvanNo ratings yet
- Metal and Non MetalDocument4 pagesMetal and Non MetalphygoNo ratings yet
- Quiz #2-MidtermDocument2 pagesQuiz #2-MidtermeeeearllNo ratings yet
- PDF Ebooks - Org 1516978367 654Document54 pagesPDF Ebooks - Org 1516978367 654sryh2012No ratings yet
- Xi Salt Analysis em PDFDocument3 pagesXi Salt Analysis em PDFvvn natrajNo ratings yet
- Module I Seminar Skor A Chemistry SPM 2010Document9 pagesModule I Seminar Skor A Chemistry SPM 2010Suriati Bt A RashidNo ratings yet
- Molar Ionization Energies of The ElementsDocument8 pagesMolar Ionization Energies of The ElementsYourMotherNo ratings yet
- Solubility Curve Worksheet P4Document2 pagesSolubility Curve Worksheet P4Kalina DimovNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument4 pagesRedox Reactionsronique sanchoNo ratings yet
- Valve Summary AS2473.3Document4 pagesValve Summary AS2473.3Time To Use BrainNo ratings yet
- CHEM 26.1 Finals ReviewerDocument1 pageCHEM 26.1 Finals ReviewerClara Mirabueno100% (1)
- Mole Concept (PQRS)Document11 pagesMole Concept (PQRS)Raju SinghNo ratings yet