Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Generated File
Generated File
Uploaded by
Vipranshu GuptaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Generated File
Generated File
Uploaded by
Vipranshu GuptaCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
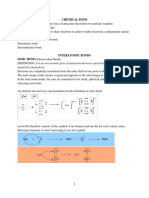
Bonding: Bonding involves the attraction between atoms that allows them to form molecules
or compounds. Types of bonding include covalent, ionic, and metallic. This attraction is due to
the sharing, transfer, or pooling of electrons between atoms. For further study, consider the book
"Chemical Bonding and Molecular Geometry" by David L. Anderson. 2. Covalent Bonding:
Covalent bonding involves the sharing of electrons between atoms to achieve a stable electron
configuration. The strength of a covalent bond is determined by factors such as bond length and
bond order. Understanding the concept of hybridization is crucial in predicting the geometry and
properties of covalent molecules. For in-depth knowledge, refer to "Chemical Bonding" by Mark J.
Winter. 3. Ionic Bonding: Ionic bonding is the transfer of electrons from one atom to another,
resulting in the formation of cations and anions. This type of bonding typically occurs between a
metal and a non-metal. Factors like lattice enthalpy and hydration enthalpy influence the stability
and properties of ionic compounds. To delve deeper into this topic, check out "Ionic Bonding" by
J. A. Plaskett. 4. Coordinate Bonding: Coordinate bonding involves a shared pair of electrons
where both electrons are donated by one atom. This type of bonding is also known as dative
bonding. Understanding coordinate bonding is crucial in explaining the stability and reactivity of
coordination compounds. Delve further into this topic with "Coordination Chemistry" by Vincent
Pecoraro and Peter M. Tebbetts. 5. Resonance: Resonance is a concept in chemistry where
multiple Lewis structures can be drawn for a molecule to represent its actual structure. It occurs
when electron delocalization leads to stabilization of the molecule. Resonance plays a crucial
role in explaining the properties and behavior of molecules like benzene and nitrate ions. For a
detailed exploration of resonance structures, consider "Molecular Themes in Organic Chemistry"
by David Klein.
You might also like
- Chemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.From EverandChemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.No ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument11 pagesOrganic Chemistryzaryabfaraz314No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure PDFDocument56 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Structure PDFAbhishek AgrahariNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Lewis Dot Carbon Hydrogen OxygenDocument17 pagesChemical Bonding: Lewis Dot Carbon Hydrogen OxygenSheila Mae AramanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding MDocument23 pagesChemical Bonding MnewmowneeshNo ratings yet
- St. Patrick School Quezon CityDocument3 pagesSt. Patrick School Quezon CityBigg MacccNo ratings yet
- Definition: What Is A Chemical Bond? Different Types of Chemical Bonds With Examples FaqsDocument33 pagesDefinition: What Is A Chemical Bond? Different Types of Chemical Bonds With Examples FaqsMedakayala Nagasravanthi 20PHD7125No ratings yet
- Chemical BondDocument1 pageChemical Bonddilwale puchNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument53 pagesChemical Bondingpream.s1323No ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Chemical BondingDocument2 pagesBasic Concepts of Chemical BondingHarshal BandkarNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument19 pagesChemistry37 CM3Vijayalaxmi KambleNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 Chemistry As A Central ScienceDocument2 pagesMODULE 1 Chemistry As A Central ScienceEmma Cristie BalahadiaNo ratings yet
- Encyclopedia of Physical Science and TechnologyDocument495 pagesEncyclopedia of Physical Science and TechnologySomethingNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical BondsDocument6 pagesTypes of Chemical BondsjoeldpenosNo ratings yet
- Sci 73A.2Document3 pagesSci 73A.2Andreev ImutanNo ratings yet
- 2Document1 page2Kunai The X GamerNo ratings yet
- Bonding in Solids Definition: Solid State ChemistryDocument9 pagesBonding in Solids Definition: Solid State Chemistryhaimanot yibeltalNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Atomic StructureDocument9 pagesAssignment 1 Atomic StructureAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding - Study NotesDocument15 pagesChemical Bonding - Study NotesTamoghna DeyNo ratings yet
- Lo5 1) Chemical BondsDocument9 pagesLo5 1) Chemical BondsabdogamreNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondsDocument7 pagesChemical BondsRakibul HassanNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument5 pagesChemical BondingStellaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledManureet SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond TypeDocument8 pagesChemical Bond TypeShabbir TamboliNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Notes Ch04 Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument4 pages11 Chemistry Notes Ch04 Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureAkhed100% (1)
- Chemical BondingDocument19 pagesChemical BondingAnjali Rakhyani0% (1)
- Notes Chemistry - ch4 - 11Document17 pagesNotes Chemistry - ch4 - 11VikramNo ratings yet
- Ichem Module 5Document4 pagesIchem Module 5Bin BinNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument36 pagesChemical BondingDarwin Cruz100% (1)
- Defintion 3Document2 pagesDefintion 3shueNo ratings yet
- Primary and Secondary BondingDocument6 pagesPrimary and Secondary BondingosmondNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond 21Document16 pagesChemical Bond 21Thanks OdoiNo ratings yet
- Module 2, Chemistry, PDFDocument11 pagesModule 2, Chemistry, PDFMARIA CORAZON CONTANTENo ratings yet
- Test 3 Bonding Review Sheet-Final VersionDocument7 pagesTest 3 Bonding Review Sheet-Final VersionJuventie PrimastutiNo ratings yet
- Bonding Essay: IFP Engineering and Science January IntakeDocument6 pagesBonding Essay: IFP Engineering and Science January IntakeGhassan MousaNo ratings yet
- Dental Biomaterial Book (61-71)Document146 pagesDental Biomaterial Book (61-71)Abdelruhman SobhyNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Sem 1Document20 pagesBiochemistry Sem 1baroque.nacNo ratings yet
- Concept Review With Key TermsDocument4 pagesConcept Review With Key TermsWaqar AhmedNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Notes - Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - AglaSem SchoolsDocument14 pagesCBSE Class 11 Chemistry Notes - Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - AglaSem SchoolsAswar ShaileshNo ratings yet
- CH 01Document201 pagesCH 01Khaled OsmanNo ratings yet
- CHAP 4-5 GPT PromptDocument4 pagesCHAP 4-5 GPT PromptHanz Josiah Balatero SerranoNo ratings yet
- Bonding in Solids Tanish, Rudar, Devansh, HarshDocument14 pagesBonding in Solids Tanish, Rudar, Devansh, HarshtanishbadyalsharmaNo ratings yet
- Notes On Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument17 pagesNotes On Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDeepti KashyapNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Supramolecular ChemistryDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Supramolecular ChemistrySaidul Islam RupokNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument16 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureSancia SamNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding NotesDocument5 pagesChemical Bonding NotesShaswat PattnayakNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding (Engineering Chemistry Lecture)Document13 pagesChemical Bonding (Engineering Chemistry Lecture)kiana Jessica MonroeNo ratings yet
- MELC 7 Chemical Bonding 1Document32 pagesMELC 7 Chemical Bonding 1A Dee YoungNo ratings yet
- Ionic and Covalent BondsDocument2 pagesIonic and Covalent BondsMeg Dianne V. CañedaNo ratings yet
- Class 10th Chemistry NotesDocument4 pagesClass 10th Chemistry NotesRehan KhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture #2. Contact Between Solids. Solid Surfaces. Roughness of Surfaces. Characterization of Surface TopographyDocument10 pagesLecture #2. Contact Between Solids. Solid Surfaces. Roughness of Surfaces. Characterization of Surface TopographyAbdulla CamalNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding: What Is An Ionic or Covalent Bond?Document2 pagesCovalent Bonding: What Is An Ionic or Covalent Bond?M3xobNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Handout Chapter 4Document17 pages11 Chemistry Handout Chapter 4Erreneo100% (1)
- By AdithyaDocument35 pagesBy AdithyaA SQUARE GAMING DEVIL L7ADILHYANo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class 11 Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument18 pagesChemistry Class 11 Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureAnurag Singh Tomar50% (2)
- Covalent Bond: "Covalent" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeDocument15 pagesCovalent Bond: "Covalent" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeekhadijabugtiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document19 pagesChapter 2Melanie AquinoNo ratings yet
- 化学考点Document1 page化学考点Long Eks XuNo ratings yet
- Islamic University, Kushtia-7003: Department of PharmacyDocument29 pagesIslamic University, Kushtia-7003: Department of PharmacyRayhanuzzaman ShazibNo ratings yet
- PPAR Lecture Guide - Forces of Attraction-1Document4 pagesPPAR Lecture Guide - Forces of Attraction-1Michelle Elisha CartanoNo ratings yet