Professional Documents
Culture Documents
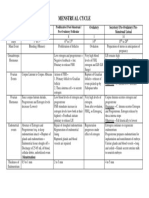
Menstruation
Uploaded by
HazelGraceCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Menstruation
Uploaded by
HazelGraceCopyright:
Available Formats
Maternal 1 Side-notes: Menstruation ⁃ Transport fertilized ovum into
fallopian tubes
Menstruation ⁃ Fluid retention
⁃ 30 to 60cc of blood ⁃ Decreased Hgb and Hct levels
⁃ Bring ovum to maturity ⁃ Increased basal body temperature
⁃ Renew uterine tissue bed ⁃ Corpus luteum
⁃ Conception and implantation of new ⁃ Endometrium implantation
life ⁃ Lactation
⁃ Average length: 28 days ⁃ Decrease GI motility
⁃ From beginning of one menstrual ⁃ Permeability of kidney (lactose and
flow to beginning of next dextrose)
⁃ Color: dark red ⁃ Mood swings
⁃ Mucus and endometrial cells
3rd Day of Cycle
Menstruation Process: ⁃ serum estrogen at lowest level
1. Hypothalamus
2. GnRH (AKA: Luteinizing hormone- Follicle Stimulating Hormone Releasing Factor
releasing hormone) (FSHRF)
3. Anterior pituitary gland ⁃ hypothalamus
⁃ In response to decrease serum
4. Release of Hormones estrogen level
FSH- ovum maturation ⁃ FSH = anterior pituitary gland
LH- ovulation and growth of uterine lining
Primordial follicle
5. Ovary ⁃ immature oocyte
⁃ follicular fluid with high degree of ⁃ Stimulate by FSH to grow
estrogen (mainly estradiol) ⁃ Estrogen to be produced inside
⁃ Small ovum= graafian follicle
⁃ LH = prostaglandin = graafian follicle Graafian Follicle
ruptures ⁃ contains high amounts of estrogen
⁃ Ovum set free = OVULATION ⁃ estrogen inside cause uterine cells
⁃ Ovum proceed to end of fallopian to grow rapidly (8 fold thickness)
tube ⁃ Result: Proliferative or Follicular
Phase
6. Uterus
⁃ uterine changes result of stimulation 13th Day of Cycle
from hormones of ovaries ⁃ Serum progesterone at lowest level
Estrogen Effects Luteinizing Hormone Releasing Factor (LHRF)
⁃ blocks FSH ⁃ In response to decrease
⁃ Hypertrophy and hyperplasia of progesterone
myometrium ⁃ anterior pituitary = LH
⁃ Growth of breast
⁃ Increase cervical mucus LH
(spinnbarkeit test of dilation): 10-13cm ⁃ stimulate ovary to produce
⁃ Regulate fluid and electrolytes progesterone
⁃ Protein synthesis
⁃ Lowers cholesterol level Note:
⁃ Estrogen and progesterone push
Progesterone Effects new mature ovum to surface of ovary until 14th day
⁃ blocks LH ⁃ GF rupture= mature ovum=
ovulation
Ovulation 90 seconds
⁃ GF high in progesterone ⁃ Spermatozoa to reach cervix
⁃ Progesterone = corpus luteum
(yellowish appearance) 5 minutes
⁃ Spermatozoa to reach outer
Progesterone fallopian tube
⁃ uterine endothelium to corkscrew or
twisted in appearance Capacitation
⁃ HORMONE OF PREGNANCY ⁃ Final process of sperm for
⁃ Prevents uterine contraction fertilization
⁃ As sperm move towards ovum
Estrogen ⁃ Change plasma membrane of head
⁃ Hormone of menstrual cycle of sperm
⁃ Reveals sperm binding receptor
Trophoblast sites
⁃ fertilized ovum
⁃ Finger-like projections around Hyaluronidase
blastocyst ⁃ Proteolytic enzyme from sperm
⁃ Implants on surface of uterus ⁃ Dissolves layer of cells protecting
ovum
Note: ⁃ Sperm penetration to ovum
⁃ Ovulation 2 weeks before next ⁃ Dissolves corona cells
menstruation
⁃ 14 days prior to 1st day of next Zygote (46 chromosomes)
menstrual cycle ⁃ fusions of spermatozoon and ovum
⁃ Menstrual cycle from day 1 to next ⁃ Sperm: 23 chromosomes
day 1 of next cycle ⁃ Ovum: 23 chromosomes
⁃ 22 autosomes and 1 sex
Fertilization chromosomes
⁃ conception and impregnation
⁃ Union of ovum and spermatozoon Implantation
⁃ Ampulla of fallopian tube ⁃ Complete fertilization
⁃ One ovum will reach maturity ⁃ Zygote migrate to body of uterus
⁃ Mitotic cell division (cleavage
Mature Ovum begins)
⁃ lifespan: 24-48hrs ⁃ 8-10 days after fertilization
⁃ Atrophies and non-functional
⁃ With ring of mucopolysaccharide Mitotic Cell Division
fluid and circle of cells ⁃ 1st cleavage at 24hrs
⁃ Cleavage division 1x q 22hrs
72hrs ⁃ Zygote 16 to 50 cells (Morula Stage)
⁃ critical time for fertilization to be
successful Blastocyst
⁃ Morula stage (bumpy outward
Zona Pellucida-mucopolysaccharide fluid and appearance)
Corona Radiata Circle of Cells ⁃ Morus= mulberry
⁃ Increase bulk of ovum ⁃ Large cells collection
⁃ Protective buffer against injury ⁃ Attaches to uterine endometrium
⁃ Inside cell
Fimbriae (WALIS) ⁃ Invades endometrium to receive
⁃ propelled ovum to fallopian tube nourishment
⁃ Later become EMBRYO ⁃ Ovulation to fertilization
2. Zygote
Trophoblast ⁃ Fertilization to implantation
⁃ cells outer ring 3. Embryo
⁃ Outside cell ⁃ Implantation to 5-8 weeks
⁃ Produces proteolytic enzymes that 4. Fetus
dissolves any tissue ⁃ 5-8 weeks to Term
⁃ Later become PLACENTA
Conceptus
Events of Implantation: ⁃ developing embryo/ fetus and
Implantation placenta throughout pregnancy
⁃ contact of zygote and uterine
endometrium Gametes
⁃ sperm and egg cells
1. Apposition
⁃ zygote brushes against uterine Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HcG)
endometrium ⁃ stimulates estrogen and
⁃ 2nd phase of menstrual cycle progesterone
⁃ Trophoblast tissue and early
2. Adhesion embryos
⁃ attaches to surface of endometrium ⁃ Stimulate corpus luteum to produce
progesterone to maintain pregnancy
3. Invasion
⁃ Settles down into soft folds
Note:
⁃ Zygote implanted = EMBRYO
Time of Ovulation (regular cycle)
⁃ Subtract 16 from number of days in
cycle then add 4
Signs and Symptoms of Ovulation
1. Mittlelschermz
⁃ Abdominal tenderness
⁃ Left or right illiac regions
⁃ Peritoneal irritation from blood
coming out from graafian follicle
2. Spinnbarkeit
⁃ Vaginal secretion clear and
transparent
3. Change vaginal mucus
4. Goodel’s sign
5. Mood changes
6. Breast tenderness
7. Increase progesterone
8. Change basal body temperature
Anterpartal Period:
1. Ovum
You might also like
- Squirting For DummiesDocument31 pagesSquirting For DummiesGustavoCalderin75% (4)
- Ob NotesDocument7 pagesOb NotesAllan Christian AlnNo ratings yet
- All MCN MidtermDocument207 pagesAll MCN MidtermInah SaritaNo ratings yet
- Science5 q2 Mod2 Menstrual-Cycle v4Document14 pagesScience5 q2 Mod2 Menstrual-Cycle v4pot pooot85% (20)
- Reproductive EndocrinologyDocument36 pagesReproductive EndocrinologyswetaNo ratings yet
- Menstrual Cycle: Pepino, Ricalde, Roxas 3PtDocument11 pagesMenstrual Cycle: Pepino, Ricalde, Roxas 3PtAlthea JacobNo ratings yet
- 4. week ovulation, fertilization, implantation (١)Document41 pages4. week ovulation, fertilization, implantation (١)Maisy JohnNo ratings yet
- InfertilityDocument55 pagesInfertilityFedlu SirajNo ratings yet
- Menstrual Cycle: Prepared By: Mrs Bini P S Amuel Assistant Professor, SSRC N, VapiDocument16 pagesMenstrual Cycle: Prepared By: Mrs Bini P S Amuel Assistant Professor, SSRC N, VapiBini Don DanielNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive AnatomyDocument35 pagesFemale Reproductive AnatomySasikala MohanNo ratings yet
- Hormonal Control of GametogenesisDocument37 pagesHormonal Control of GametogenesisZeneishaNo ratings yet
- Three Stages of Fetal DevelopmentDocument4 pagesThree Stages of Fetal DevelopmentmellowlilydeeNo ratings yet
- Menstrual CycleDocument10 pagesMenstrual CycleintanNo ratings yet
- NCM 108 - Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy and Care of The Developing FetusDocument5 pagesNCM 108 - Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy and Care of The Developing FetusKristine BartsNo ratings yet
- Menstrual CycleDocument27 pagesMenstrual CycleBUAHIN JANNANo ratings yet
- OBSTETRIC NURSING Note Taking GuideDocument46 pagesOBSTETRIC NURSING Note Taking GuideJane CuencaNo ratings yet
- 1st Summative Test ADocument3 pages1st Summative Test AJosefina Magadia100% (4)
- MENSTRUATIONDocument3 pagesMENSTRUATIONAdri SinclaireNo ratings yet
- Embryology Lecture Note 2Document19 pagesEmbryology Lecture Note 2jestreametefiaNo ratings yet
- Fetal DevelopmentDocument5 pagesFetal DevelopmentHazelGraceNo ratings yet
- MCHN Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesMCHN Reproductive SystemShaira PacallesNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE Feedback Mechanism in Menstrual CycleDocument6 pagesSCIENCE Feedback Mechanism in Menstrual CycleJasmineNo ratings yet
- (Zerrudo) OB Refresher NotesDocument13 pages(Zerrudo) OB Refresher NotesKatrina CaveNo ratings yet
- Fertilization and Implantation Copy To StudentsDocument40 pagesFertilization and Implantation Copy To StudentsRiya SinghNo ratings yet
- Menstrual Cycle ChartDocument1 pageMenstrual Cycle Chartbkpad026No ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesMale Reproductive SystemRico CawasNo ratings yet
- Handout On ReproDocument4 pagesHandout On ReproJoe JosephNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child EnhancementDocument5 pagesMaternal and Child EnhancementRalph Elvin MacanlalayNo ratings yet
- Ob 1Document28 pagesOb 1Hana Marie AlayonNo ratings yet
- Process of SpermatogenesisDocument3 pagesProcess of SpermatogenesisMarian FloresNo ratings yet
- 5.menstrual CycleDocument62 pages5.menstrual CycleQaiser InayatNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System 1Document36 pagesFemale Reproductive System 1Rahil PatelNo ratings yet
- Hormones of The Reproductive SystemDocument9 pagesHormones of The Reproductive Systemkarthickmech1987No ratings yet
- Premidfin Human RepDocument13 pagesPremidfin Human RepJoymae Olivares TamayoNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Nursing: Note-Taking Guide 2021)Document28 pagesObstetric Nursing: Note-Taking Guide 2021)Benedict James BermasNo ratings yet
- Dasar2 Biomolekuler Repro WanitaDocument51 pagesDasar2 Biomolekuler Repro WanitaFitriaNo ratings yet
- PEDIA-REVIEWER EditedDocument7 pagesPEDIA-REVIEWER EditedTO THE MOONNo ratings yet
- Female ReprodDocument42 pagesFemale Reprodhailu tasheNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument32 pagesReproductive SystemEdwin OkonNo ratings yet
- Let's Pray!Document45 pagesLet's Pray!HONLETH ROMBLONNo ratings yet
- BiologyyyDocument2 pagesBiologyyyprecious siNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesReproductive SystemHazelGraceNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Non Pregnant FemaleDocument37 pagesPhysiology of Non Pregnant Femalephuyalaryan666No ratings yet
- Applied Endocriology of PregnancyDocument15 pagesApplied Endocriology of PregnancyMARCOS ALEJANDRO CHAMORRO TRUJILLONo ratings yet
- NSVDDocument32 pagesNSVDChris Oliver Kevin Ledesma100% (3)
- Chapter 15 Act 2 GR 12Document13 pagesChapter 15 Act 2 GR 12RSA WalkerNo ratings yet
- General Biology II PDFDocument2 pagesGeneral Biology II PDFColsNo ratings yet
- MCN ReviewerDocument26 pagesMCN ReviewerMary TionNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument61 pagesHuman Reproductionmammuammu005No ratings yet
- 1.5.3.1 - Perkembangan Janin Intrauterin Dan Gangguan Yang Mungkin TimbulDocument54 pages1.5.3.1 - Perkembangan Janin Intrauterin Dan Gangguan Yang Mungkin TimbulMuhammad Fatkhi100% (1)
- Ovulation and Conception - Normal PregnancyDocument8 pagesOvulation and Conception - Normal Pregnancyapi-3705046No ratings yet
- Puberty and Menstrual CycleDocument18 pagesPuberty and Menstrual CycleTheSourLemonNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive System: Mr. LaingDocument66 pagesThe Reproductive System: Mr. LaingTyese DasilvaNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Review LecDocument5 pagesObstetric Review LecKevin PatrickNo ratings yet
- Fertilization, Pregnancy and Lactation: Dedi ArdinataDocument26 pagesFertilization, Pregnancy and Lactation: Dedi ArdinataHalseyNo ratings yet
- Functions of PlacentaDocument8 pagesFunctions of PlacentappsavidalandNo ratings yet
- Good Afternoon: Prepared byDocument102 pagesGood Afternoon: Prepared byKrishna PatelNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument18 pagesScience Reviewer28. Pinera, Yna Angela S.No ratings yet
- Game To GenesisDocument66 pagesGame To GenesisJay PornelaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Reproduction and GrowthDocument11 pagesChapter 4 Reproduction and GrowthDeepa Manogaran100% (5)
- Gametogenesis 1Document10 pagesGametogenesis 1Affie SaikolNo ratings yet
- Fertilization, Pregnancy, and Fetal Development: Paul F. Terranova, PH.DDocument23 pagesFertilization, Pregnancy, and Fetal Development: Paul F. Terranova, PH.DriswanfebriantoNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy - Human ReproductionDocument36 pagesPregnancy - Human ReproductionDICKSONNo ratings yet
- Obstetric NursingDocument14 pagesObstetric NursingreooooNo ratings yet
- Group 9. Presentation. Animal Form and Function 2Document29 pagesGroup 9. Presentation. Animal Form and Function 2Dat HoangNo ratings yet
- Renal FailureDocument5 pagesRenal FailureHazelGraceNo ratings yet
- Developmental Milestones 1Document2 pagesDevelopmental Milestones 1HazelGraceNo ratings yet
- Developmental Milestones 2Document3 pagesDevelopmental Milestones 2HazelGraceNo ratings yet
- Mother and Neonatal ChangesDocument2 pagesMother and Neonatal ChangesHazelGraceNo ratings yet
- Labor and DeliveryDocument6 pagesLabor and DeliveryHazelGraceNo ratings yet
- Postpartum CareDocument4 pagesPostpartum CareHazelGraceNo ratings yet
- What Is The Follicular Phase?: Good To KnowDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Follicular Phase?: Good To KnowNancy SinghNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument35 pagesHuman ReproductionMERYL SALOMINA FRANCISCONo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - Human Sexual Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesChapter 16 - Human Sexual Reproductive SystemChaw Wei HengNo ratings yet
- 1a ReproductiveAndSexualHealthDocument2 pages1a ReproductiveAndSexualHealthKenjie Palaganas CentenoNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi HaidDocument3 pagesFisiologi HaidAndi Farid ANo ratings yet
- SCIENCE FORM 3 Chapter 4 ExerciseDocument7 pagesSCIENCE FORM 3 Chapter 4 ExerciseWan Shuhaimi Wan Ali100% (1)
- Disectie AnatomieDocument908 pagesDisectie AnatomieMircea SimionNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Science ReviewerDocument25 pagesGrade 10 Science ReviewertinaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Anatomy: Chapter 34 Lesson 1 Page 958Document13 pagesReproductive Anatomy: Chapter 34 Lesson 1 Page 958JanaNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human ReproductionDocument5 pagesNcert Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human ReproductionR.A creationNo ratings yet
- Congenital and Acquired Malformations in Vulva and Vagina - Pediatric AgeDocument2 pagesCongenital and Acquired Malformations in Vulva and Vagina - Pediatric AgePramedicaPerdanaPutraNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science VDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science VEric Glenn CalingaNo ratings yet
- Laporan SPH 2 Sistem ReproduksiDocument4 pagesLaporan SPH 2 Sistem ReproduksiAghits LailyNo ratings yet
- Fallopian Tube BlockageDocument11 pagesFallopian Tube Blockagesimran kaurNo ratings yet
- Daftar Alat-Alat Skill Lab: No Nama Alat No - Katalog - Merk Gambar Total Harga (RP) Qty Harga Satuan (RP)Document4 pagesDaftar Alat-Alat Skill Lab: No Nama Alat No - Katalog - Merk Gambar Total Harga (RP) Qty Harga Satuan (RP)fk unramNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument121 pagesMale Reproductive SystemProf Lina RamliNo ratings yet
- Endometriosis Older Julia 1941 1st PBK Ed New York Annas ArchiveDocument244 pagesEndometriosis Older Julia 1941 1st PBK Ed New York Annas Archivenathanford1No ratings yet
- Reproduction WorksheetDocument5 pagesReproduction WorksheetJENY VEV GAYOMANo ratings yet
- Jurnal Robekan Jalan LahirDocument6 pagesJurnal Robekan Jalan Lahiryuli aprilia100% (1)
- Kuliah ST Reproduksi WanitaDocument103 pagesKuliah ST Reproduksi Wanitaanon_88598530100% (1)
- Soal Ujian Tengah Semester GanjilDocument5 pagesSoal Ujian Tengah Semester GanjilNovia FaizatiwahidaNo ratings yet
- COT Lesson Plan in Science 5Document9 pagesCOT Lesson Plan in Science 5ChAd Surmion HisanzaNo ratings yet
- Case of Hymen Imperforata in Adolescents: Ade Triansyah, Muh Ardi Munir, Daniel SarangaDocument6 pagesCase of Hymen Imperforata in Adolescents: Ade Triansyah, Muh Ardi Munir, Daniel Sarangafabiola umbohNo ratings yet
- H-Mole Chapter I-VDocument103 pagesH-Mole Chapter I-VJoevence Gazo CuaresmaNo ratings yet