Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Clinical Chemistry
Uploaded by
angelwithoutwings3210 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views11 pagesMUST TO KNOW
Original Title
CLINICAL CHEMISTRY
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMUST TO KNOW
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views11 pagesClinical Chemistry
Uploaded by
angelwithoutwings321MUST TO KNOW
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
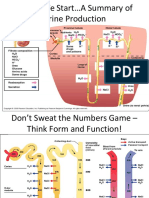
CLINICAL CHEMISTRY Hypothalamus Link between the nervous and endocrine system
Supraoptic/ Paraventricular Hypophyseal hormones
Endocrinology
nuclei
Endocrine system Network of ductless glands that secretes hormones directly to Oxytocin, Vasopressin TRH, Gn-RH, Somatostatin, GH-
the blood RH, PIF
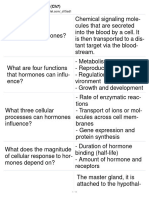
Hormones Chemical signals produced by specialized cells to a target tissue
Infundibulum stalk Connects the hypothalamus to the posterior pituitary gland
Main function of Maintain the constancy of the chemical composition of both the
Pineal Gland Secretes melatonin
hormones: intracellular and extracellular fluids, growth, metabolism and
Pituitary Gland “ Master Gland”
response to stress.
(Hyophysis)
Hormones affected Elderly people secrete less : T3, PTH, cortisol, aldosterone
Sella Turcica / Turkish Location of the pituitary gland
by age
Saddle
Positive Feedback Increased in activity = increased in product
Circadian rhythm All pituitary hormones have _____
e.g thyroid, gonadal, ACTH
Anterior Pituitary “ True endocrine gland”
Negative Feedback Increased in activity = decreased product
Gland “Adenohyophysis”
e.g LH
5 Types of cells by Somatotrophs Secretes GH , most abundant
Hormone Action Endocrine Secreted in one location and binds to specific
Immunochemical Test Lactotrophs Secrete prolactin
receptor
Thyrotrophs Secrete TSH
Paracrine Binds to specific receptor in adjacent cell and
Gonadotrops Secrete FSH, LSH
affect its function
Corticotrophs Secretes POMC
Autocrine Binds to specific receptor on its cell of origin
and affects its function Growth Hormone AKA Somatotropin
Juxtacrine Acts on immediately adjacent cell by direct Secretion is erratic and occurs in a short burst
cell-to-cell contact Major stimulus : deep sleep
Major inhibitor : somatostatin
Intracrine Functions inside the synthesis of origin
GH is structurally Prolactin and HPL
Exocrine Released into lumen of guts
similar to?
Neurocrine Secreted in neurons and released into
Disorders of GH GHD Idiopathic GHD MCC of GHD in
extracellular space
Neuroendocrine Secreted in neurons and released from nerve children
endings; interact with receptor of cells at Pituitary MCC of GHD in
distant site Adenoma adults
Classification of Peptides/ Acromegaly Overproduction of GH ( >50 ng/mL)
Glycoprotein FSH, HCG, TSH, EPO
Hormones Proteins Polypeptides ACTH, ADH, GH, Angiotensin, Diagnostic Tests for For GHD Screening : Exercise Test ( normal : GH
calcitonin, glucagon, insulin, GH Px prep: rest for should elevate)
MSH, PTH, oxytocin, prolactin, 30mins
somatostatin Spx : serum Confirmatory
Water soluble ; not bound to a carrier protein; 1. Insulin Tolerance Test – gold
functions outside of the cell membrane due to their standard
large molec size 2. Arginine stimulation Test –
2nd
Steroids CHOLE = main precursor
Produced by adrenal glands, ovaries, testes,
placenta For Acromegaly Screening : IGF-1 / Somatomedin C
Water insoluble ; bound to a carrier protein **IGF-1 is increased in acromegaly
E.g Aldosterone, cortisol, E2, progesterone
testosterone, activated VD3 Confirmatory : OGTT ( 75g glu)
** Normal = suppression of GH
Amines Derived from AA ; intermediary b/w steroid and
>1ng/mL
protein hormone
** Acromegaly = GH failed to
E.g Epi, Norepi, T3, T4
suppress, increased IGF-1
J.A.M RMT 2024 1
** Exclude Acromegaly = GH failed to 2 types of cells in the 1. Follicular cells = T3 and T4
suppress, Normal IGF-1 Thyroid gland 2. Parafollicular / C cells = Calcitonin
Gonadotropins Important for diagnosing fertility and menstrual cycle disorders Thyroglobulin Preformed matrix ; containing tyrosyl groups; stored in the
FSH Spermatogenesis follicular colloid of the thyroid gland
LH Helps Leydig cells to produce testosterone (male) Iodine Most important element in the biosynthesis of thyroid hormones
Necessary for ovulation and final follicular growth ( Tyrosine + Iodine = MIT and DIT
female) MIT + DIT = T3
Elevated FSH Premature menopause DIT + DIT = T4
Increased FSH and LH Lack of estrogen T3 / 3,5,3 Most active
after menopause Triiodothyronine 75-80% produced from the deiodination of T4
Thyroid Stimulating AKA thyrotropin Better indicator of diagnosis and recurrence of hyperthyroidism
Hormone Main stimulus for the uptake of iodide by the thyroid gland ; T4 / 3,5,3,5 Most abundant
increased the number and size of follicular cells tetraiodothyronine Major fraction of organic iodine in the circulation
LH, FSH, HCG the alpha sub-unit of TSH is similar to ______ Prohormome of T3
Infertility Blood levels of TSH can also be use in the evaluation of ___ Thyroid Hormone Thyroxine Binding Globulin Transports majority of t3
Adenocorticotrophic Produced in response to low cortisol Binding Proteins Thyroxine Binding Albumin Transports t3 ; 10% t4
hormone Diurnal rhythm ( 6am-8am) Thyroxine Binding Transports 15-20% of t4
Increased in Addison’s disease Prealbumin - transthyretin T3 has no affinity for albumin
Spx prep for ACTH Should be collected in a prechilled PLASTIC EDTA TPO Hashimoto’s disease
** ACTH adheres to glass = falsely decreased TSH receptor Grave’s disease
Prolactin Lactogenic, stress, and a direct effector hormone Symptoms Hyperthyroidism Hypothyroidism
Initiation and maintenance of lactation Tachycardia, weight loss, Bradycardia, weight gain,
Breast tissue development ( estrogen & progesterone) heat intolerance, menstrual coarsened skin, cold
GH The amino acid structure of prolactin is similar to _____ changes intolerance, mental dullness
Dopamine Major inhibitor of prolactin? Hyperthyroidism Primary hyperthyroidism t3, t4 TSH
Hypogonadism Prolactin excess can lead to? Secondary hyperthyroidism T4, TSH
Posterior Pituitary “ Neurohyophysis” Thyrotoxicosis - T3 thyrotoxicosis /
Gland Releases oxytocin ( paraventricular nuclei) and vasopressin Plummer’s dse
(supraoptic) - T4 thyrotoxicosis
Oxytocin Stimulates “ Fergusson reflex” Grave’s dse MCC of thyrotoxicosis
ADH Acts on the DCT and CD of the kidneys Exophthalmos
Regulates water balance / water retention Riedel’s thyroiditis Thyroid turns into a woody /
Increases blood pressure stony hard mass
Affects blood clotting : promotes Factor VII and Factor VIII Subclinical hyperthyroidism No clinical symptoms
Diabetes Insipidus Deficiency of ADH ( 3Ps + normal glucose) TSH , Normal T3, T4
True Diabetes Insipidus Nephrogenic DI De Quervain thyroiditis Neck pain, low grade fever,
(Neurogenic) swings in thyroid function
Nephrogenic DI Normal ADH + Ab ADH tests
receptor Hypothyroidism Primary Def of iodine T4, T3 TSH
Renal resistance to ADH Hypothyroidism Hashimoto’s TPO
Congenital or acquired dse Enlargement of the
Test : Overnight Water Deprivation Test / Concentration Test thyroid
Thyroid Gland Butterfly shaped gland Myxedema Skin becomes
Isthmus The 2 lobes of the thyroid gland is connected by the ___ infiltrated w/
Follicles Fundamental structure of thyroid gland mucopolysaccharides
11 weeks of gestation The thyroid gland starts to produce hormones by ___
J.A.M RMT 2024 2
** myxedema coma = Low PTH can cause Alkalosis
most severe form of Calcium <8mg/dL Tetany, trosseau’s and chvostek’s sign
PH Adrenal Gland Pyramid shape gland located above the kidneys
Secondary Pituitary destruction / pituitary Adrenal Cortex Major site of steroid hormone production
Hypothyroidism adenoma 3 layers of adrenal cortex
T3, T4, TSH Zona glomerulosa Mineralocorticoids
Tertiary Hypothalamic disease Zona fasiculata Glucocorticoid synthesis ; unsulfated
Hypothyroidism T3, T4, TSH DHEA
Congenital Defect in the development of the Zona reticularis Androstenedione and
Hypothyroidism/ thyroid gland dehydroepiandrosterone ( weak
Cretinism Mental and physical retardation androgens)
Subclinical Cortisol Principal glucocorticoid
Hypothyroidism ONLY HORMONE THAT INHIBITS ACTH
Lithium Drug that can cause hypothyroidism Diurnal rhythm
Thyroid Function TRH stimulation test Measure TRH and TSH secretions Transcortin Cortisol is mostly bound to ?
Tests Helpful in confirming Grave’s disease Anti-inflammatory Cortisol is a valuable therapeutic agent due to its?
TSH test Most important to detect clinically and
significant thyroid dysfunction immunosuppressive
RAIU Measures the ability of thyroid to trap actions
iodine Sleep-wake cycle Cortisol affects the?
Thyroglobulin assay Used as a postoperative marker of Disorders of the Cushing’s Syndrome Cortisol and ACTH, aldosterone &
thyroid cancer Cortisol renin ( overuse of corticosteroids)
RT3 3rd major circulating thyroid hormone Obese + thin extremities (buffalo
Identifies px w/ euthyroid sick hump)
syndrome ( RT3) Primary Cortisol ACTH aldosterone
T3 uptake Test for TBG Hyporcortisolism: Primary adrenal insufficiency
TBG Hyperthyroidism vs euthyroidism Addison’s Disease Hypotension, hyponatremia,
Serum Calcitonin Medullary thyroid carcinoma hyperkalemia, hyperpigmentation
Pentagastrin Diagnosis of MTC Due to HIV-AIDS, TB, hemorrhage
Stimulation Test
3rd gen of TSH assays Able to detect thyroid subclinical dse Sec. hypocortisolism : absence of
Parathyroid gland Smallest endocrine gland hyperpigmentation, low ACTH and
Secretes PTH – hypercalcemic hormone cortisol
Disorders of Hyperparathyroidism Congenital Adrenal Deficiency of enzymes necessary for
1 MCC of hypercalcemia
Parathyroid Gland Hyperplasia cortisol synthesis
Parathyroid adenoma
Phosphaturia Types of CAH 21 hydroxylase deficiency Most common ; hirsutism
2 Develops as a response to 11 b-hydroxylase deficiency 2nd most common ;
hypocalcemia hypertension
Severe bone disease 3b-hydroxysteroid Elevated ratio ;
3 Occurs in conjunction dehydrogenase isomerase pseudohermaphroditsim
with 2 deficiency
Calcium phosphates 17 hydroxylase deficiency Cannot convert
deposit in soft tissues HPLC-MS Reference method for measuring urinary free cortisol
Hypoparathyroidsim Usually due to accidental injury to ** 24hr urine free cortisol = most specific and sensitive test for
the neck excess cortisol ( not affected by diurnal rhythm)
Unable to maintain Ca in the blood Urinary metabolites 17-hydroxycorticosteroid Porter Silber method –
without Ca supplement of cortisol yellow
J.A.M RMT 2024 3
17-Ketogenic steroids Zimmermann reaction – Post testicular infertility Disorder of sperm transport
reddish purple and function ~ all markers
Low dose Confirmatory test for hypercortisolism are normal
dexamethasone Estrogen Carbon-18 steroid hormone with a phenol A ring
suppression test Estrogen precursors Testosterone, acetate,cholesterol, progesterone
Insulin tolerance test Confirmatory test for hypocortisolism undetected After menopause, estrogen levels should be ?
ACTH/ Corsyntropin Screening test for hypocortisolism Estrogen derivatives Estrone Most abundant in post menopausal women
Stimulation Test Estradiol Major estrogen
Aldosterone Steroid hormone ; most potent mineralocorticoid Abundant in pre menopausal women
Na retention Estriol Found in maternal urine (pregnancy)
18 hydroxysteroid Enzyme needed for synthesis of aldosterone Progesterone Single best hormone to know if ovulation has occurred
dehydrogenase Prepares the uterus for pregnancy and breast for lactation
RAAS Main controller of aldosterone Progesterone Prime secretory product of ovary
Clinical disorders of Conn’s disease / Primary aldosterone renin Tests for NTBs and Done during the second trimester
Aldosterone hyperaldosteronism Down syndrome
Secondary aldosterone and renin AFP, Inhibin A, HCG, uE3
hyperaldosteronism Pancreas Both an exocrine (synthesis of digestive enzymes) and endocrine
Hypoaldosteronism Deficiency of 21-hydroxylase gland
Hyperkalemia , metabolic Alpha cells Glucagon
acidosis Beta cells Insulin
DHEA Principal adrenal androgen Delta cells Somatostatin
estrone DHEA is converted into? Acinus Functional secretory unit of the pancreas
Chromaffin cells Adrenal medulla is composed primarily? Gastrin Produced by G cells
Catecholamines Adrenal medulla secretes? Diagnostic marker for Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
L-tyrosine Main precursor of catecholamines Serotonin ( 5- From tryptophan
Ratio of Nor:Epi 9:1 hydroxytryptamine) Synthesized by argentaffin cells
Catecholamines Norepinephrine Neurotransmitter both in CNS and SNS Binds to platelets and released during coagulation
Epinephrine / Most abundant medullary hormone 5-HIAA Diagnostic marker for carcinoid syndrome
adrenaline “ fight or flight hormone”
Dopamine From the decarboxylation of 3,4 DOPA ENZYMOLOGY
Major intact catecholamine in the urine Enzymes Hastens chemical reaction
Indwelling catheter Testing for Epinephrine should be collected in the ? Measured in terms of activity ; not concentration
Catecholamine Norepinephrine MHPG – major metabolite in CNS Factors 1. Enzyme concentration
metabolites Epinephrine VMA – major metabolite in urine affecting 2. Substrate concentration
Dopamine HVA Enzymatic 3. Cofactors
Clinical disorders of Pheochromocytoma Overproduction of concentration 4. Inhibitors
Catecholamines catecholamines 5. Isoenzymes
Neuroblastoma Excessive production of 6. Temperature
norepinephrine 7. pH (7-8) (** exrtreme pH can denature the enzyme)
8. Storage
Testosterone Principal androgen in the blood
9. Hemolysis = increase
Most potent male androgen
10. Lactascense/ milky spx = decrease
Testicular Infertility Primary hypogonadism Congenital ( e.g Klinefelter’s
Active site Where substrate binds
( markers : levels of syndrome) ~ decreased
testosterone, FSH, Allosteric site Bind regulator molecules
testosterone w/ increased
LH) LH,FSH Cofactors Coenzymes Organic compound ( NAD, NADP)
Secondary hypogonadism Pituitary lesions ~ normal / Activators Inorganic ions; alters the spatial configuration
decreased markers of enzyme for proper substrate binding
J.A.M RMT 2024 4
Metalloenzymes Inorganic ion attached to a molecule - lung, breast, ovarian and - pancreas, bile duct, pleural
gynecological cancers adenoCA
Inhibitor Competitive Inhibitor Substrate and inhibitor - most heat stable ALP - variant of Regan ALP
compete for the active site - inhibited by phenylalanine - inhibited by L-leucine and
Non-competitive Inhibitor Binds at the allosteric site phenylalanine
Slows the rate of the reaction Placental ALP Most heat stable ALP
Uncompetitive Inhibitor Binds to the ES complex Bone ALP Most heat labile ALP
Prosthetic coenzyme that is tightly bound to an enzyme Liver and Bone Most anodal ALP
group ALP
Zymogen Inactive form Intestinal ALP Least anodal ALP
Holoenzyme Apoenzyme + prosthetic group Neuraminidase, In Electrophoresis, the use of ____ and ____ improves separation of
37C Optimum temp for enzymatic activity wheat germ bone and liver ALP
40-50C Denaturation of enzyme lectin
60-65C Inactivation of enzyme 3M urea Bone ALP is inhibited by ?
-20C Ideal temp for preservation of enzymes Bowers and Mc Most specific method for ALP
2-8C Ideal temp for storage of substrates and coenzymes Comb / Szasz Requires a pH of 10.15 and read at 405 nm
22C or RT Ideal storage for LDH ( LD4 and LD5) modification Substrate : p-nitrophenylphosphate
Classification of Oxidoreductases Removal or addition of electrons Zinc Component of ALP
Enzymes Transferases Transfer of chemical group Mg Enzyme activator of ALP
Hydrolases Hydrolysis or splitting of bond by the Placental ALP Useful tumor marker in serum and CSF for germ cell tumors
addition of water Prostate Major source of ACP ( others: plts, liver,rbcs, bone)
Lyases Removal of groups from substrates w/o Roy and Most specific method for ACP
hydrolysis Hillman Substrate : Thymolphthalein monophosphate
Isomerases Catalyze the intramolecular arrangement of
substrate-compound Transferases ALT/SGPT AST/SGOT
Ligases Joining of two substrate molecules Organ affected Liver Heart
Enzyme Theory 1. Emil-Fischer ~ Lock and Key Theory Substrate Alanine Alpha Aspartic Alpha
2. Kochland’s / Induced fit theory – acceptable theory Ketoglutaric Acid ketoglutaric Acid
Zero order Depends on enzyme concentration End products Glutamic Acid + Glutamic acid +
reaction Pyruvic Acid Oxaloacetic Acid
First order Reaction rate is directly proportional to substrate concentration Color developer 2,4 DNPH 2,4 DNPH
reaction Color intensifier 0.4N NaOH 0.4N NaOH
Liver, Bone, ALP is found in? Methods Reitman and Reitman and
Placenta, Frankel Frankel
Intestine Karmen Method
Liver ALP, Bone Major ALP Acute hepatitis Highest elevations of transferases are seen in ?
ALP End-Stage In_____ there are low levels of transferases due to massive tissue
Blood type A Placental ALP is lower in pregnant women with ____? cirrhosis destruction
and AB De Ritis Ratio >1.0 acute hepatitis
Blood type B Blood types with higher ALP (ALT:AST) >10 alcohol induced
and O Pyridoxal A coenzyme that aminotransferases requires?
Obstructive Highest elevation of ALP phosphate (
jaundice VB6)
Paget’s disease Highest elevation of Bone ALP pH 7.5 , 340 nm The pH and nm in Karmen method for AST
B1x Found in serum of dialysis patients, it is also used to study low BMD AST in AMI Begins to rise at 6-8hrs, peaks at 24 hrs, normalizes within 5 days
Carcinoplacenta Regan ALP Nagao ALP Amylase Catalyzes breakdown of starch and glycogen
l ALP Earliest pancreatic marker
J.A.M RMT 2024 5
Freely filtered by the glomerulus ; can be seen in the urine LD2 Most abundant LD isoenzyme
Isoenzymes of P type (amylopsin) (p3 – most predominant in acute pancreatitis) LD6 Alcohol dehydrogenase enzyme
AMY S type ( ptyalin) Seen in obstructive jaundice and drug hepatoxicity ( conversion of
starch Considered to be a substrate for all methods methanol and ethylene glycol to toxic compounds)
Methods for Saccharogenic Reference method ; expressed in Somogyi Methods for LD Wacker Method Forward reaction
AMY units Most commonly used ( not affected by
Measures the amount of reducing sugars inhibition)
produced by the hydrolysis of starch Preferred by LD1
Amyloclastic Degradation of starch ; measures amylase Ph 8.8 @ 340 nm
activity by the decrease in substrate Pyruvate + NADH --→ Lactate + NAD
concentration Wrobleuski La Reverse Reaction
Chromogenic Measures AMY by the increase in color due Preferred by LD5
intensity Ph 7.2
Coupled-Enzyme Measures AMY by continuous monitoring Lactate + NAD --→ Pyruvate + NADH
technique LD5 Cold labile LD isoenzyme
Wheat germ Salivary AMY is inhibited by? Creatine Kinase Catalyzes the transfer of phosphate group b/w creatine phosphate and
lectin ADP
AMY: CREA Normal 1%:4% Duchenne Highest elevation of CK
AP >4% Muscle
Lipase Most specific pancreatic marker Dystrophy
Catalyzes the hydrolysis of ester linkages of fats to produce OH and CK isoenzymes CK-BB most anodal
fatty acids CK-MB
Pancreatic AMYLASE LIPASE CK-MM Most abundant and least anodal
Markers Begins to rise 2-12hrs 6-8hrs Methods for CK Tanzer Gilbarg Assay pH 9.0 @ 340 nm
Peak 24hrs 24hrs Oliver-Rosalki Most commonly used
Normalizes 5 days 8-14 days Ph 6.8 @ 340 nm
Methods for Cherry - Crandal Reference method 5’nucleotidase Marker for hepatobiliary disease and infiltrative lesions of the liver
Lipase Substrate : 50% Olive oil GGT Sensitive indicator for alcoholism
Incubate for 24hrs at 37C Increased in individuals takin warfarin, phenytoin, phenobarbitals
End product : Fatty acids PcHE Marker for insecticide / pesticide poisoning
Peroxidase Most commonly used “ antixenobiotic enzyme”
Coupling Does not use olive oil ACE Possible indicator of neuronal dysfunction ( Alzheimer’s dse)
Lactate Catalyzes the interconversion of lactic and pyruvic acids Diagnosis and monitoring of Sarcoidosis
Dehydrogenase Uses NAD as coenzyme Critical target for inhibitory drugs -blood pressure
Highest source is from the breakdown of RBCs and platelets Ceruloplasmin Marker for wilson’s disease
Pernicious Highest elevations of LD G6PD Maintains NADPH in its reduced form in RBCs
Anemia , Newborn screening marker
Hemolytic Deficiency can lead to DIHA
disorders AMI Markers MyTROPICAL
LD1 > LD2 “flipped pattern” Myoglobin Trop CK-MB AST LD
Seen in MI and hemolytic anemia I
LD isoenzymes LD 1 HHHH begins 4-8hrs 6-8hrs 12-24hrs
LD 2 MMMH Peaks 12-24hrs 24 hrs 48-72hrs
normalizes 48-72hrs 5 days 7-14days
LD 3 MMHH
LD 4 MMMH
LD 5 MMMM
J.A.M RMT 2024 6
LIVER FUNCTION TESTS A1 flat curve Juvenile Cirrhosis / Pulmonary
Liver Chief metabolic organ Emphysema
2 types of cells Kupffer cells Phagocytic cells Spikes of a1. A2. beta inflammation
in the liver Hepatocytes Makes up the 80% of the total volume of the liver Small spikes in B2 IDA
Responsible for the regenerative properties of the ** Fibrinogen causes b-gamma bridging that’s why plasma should
liver never be use
Lobules Anatomic unit of the liver Prothrombin Differentiates intrahepatic (prolonged) vs. extrahepatic liver disorder
The 2 lobes are separated via falciform ligament time (normal)
Hepatic Artery Oxygen rich blood ** Vit K = 10 mg daily for 1- 3 days
25% of total blood supply Protein Dyes BCG MC used. Affected by penicillin ( false
Portal Vein Nutrient rich blood decrease in albumin)
75% of total blood supply BCP Most specific
Functions of 1. Synthetic – albumin (12g daily) Methyl Orange
the liver 2. Conjugation - bilirubin Hydroxyazobenzene Affected by hyperbilirubinemia
3. Detoxification and Drug metabolism – Cytochrome p450 benzoic acid (HABA)
enzymes ** BCG and BCP are cationic dyes = not affected by bilirubin and
4. Excretory and Secretory function hemolyzed samples
5. Storage function – fat soluble, water soluble vitamins ( Vit A, Prolonged Cause of artifactual hyperalbuminemia
D, E, K) tourniquet
Serum albumin Most useful indicator for assessing severity of liver diseases application
and Vit K Analbuminemia Hereditary absence of albumin / unable to synthesize albumin
dependent Bisalbuminemi Presence of 2 albumin bands in SPE
factors a Can be due to excess therapeutic drugs in the serum ( e.g penicillin)
Kjedahl Reference method Bilirubin From breakdown of rbc , principal pigment in bile
Method Based on the nitrogen component of protein 2 types of Unconjugated Conjugated
1 g nitrogen = 6.54 g of protein bilirubin Indirect Direct
Rgt = H2SO4 Water insoluble Water soluble
EP = ammonia Hemobilirubin Cholebilirubin
Biuret Method Most commonly used Slow reacting Prompt bilirubin
Based on the no. of peptide bonds @545nm
Prehepatic bilirubin Post hepatic bilirubin / hepatic /
Rgt : R,A,N
obstructive
EP : violet colored complex
Delta Bilirubin conjugated bilirubin bound to albumin seen in biliary obstruction
Folic Ciocalteu Highest analytical sensitivity
TB-DB+IB
/ Lowry Rgt : phenol reagent / phosphotungstic molybdic acid
AKA biliprotein
Method EP : deep blue color due to the oxidation of T, T, H
Jaundice AKA hyperbilirubinemia , Icterus
Ultraviolet Absorbance of peptide bonds @ 210 nm
>2mg/dl of TB
Absorption
Yellowing of the skin, sclera and mucus membranes
Method
Classification of Pre-Hepatic Excessive RBC destruction B1
SPE Albumin Fastest band
Jaundice Hepatic Hepatocyte injury caused by viruses,
A1 Alpha 1-antitrypsin, TBG. AAG
parasites, and alcohol B1, B2
A2 A2-macroglobulin, haptoglobin, CEU
Post-Hepatic Failure of bile to flow to the intestine B2
Beta Transferrin, Hemopexin, C3, C4
Gamma Immunoglobulins, CRP Derangements Gilbert’s syndrome Impaired cellular uptake of bilirubin
in Bilirubin Crigler Najjar UDPGT problem
Abnormal SPE Gamma spike Multiple Myeloma
metabolism * Type 1 = complete absence ( kernicterus)
patterns Beta gamma bridging Hepatic Cirrhosis
* Type 2 = partial deficiency ( small amounts
A2 spike Nephrotic Syndrome
of B2 are produced)
J.A.M RMT 2024 7
Dubin Johnson, Defective excretion of B2 Clearance Removal of substance from plasma into urine over a fixed time (
Rotor syndrome (+) intense dark pigmentation of liver ~ ml/min)
lipofuscin
Lucey-Driscoll Circulating inhibitor of bilirubin conjugation Formula = U/P x Volume / Min (1440) x 1.73/A
Liley’s test @ Used to monitor the degree and progression of fetal hemolytic disease
450 nm Inulin Clearance Reference Method
Cholelithiasis MCC of hyperbilirubinemia in adults Disadv : necessity for continuous IV infusion
Bilirubin Assay Evelyn and Malloy Jendrassik-Grof and timed urine collection
Accelerator 50% Methanol Caffeine-Sodium Creatinine Clearance Estimate the amount of plasma that must
Benzoate have flowed to the kidney/minute
pH Alkaline ( due to alkaline Measures the completeness of 24hr urine
tartrate solution) Not affected by diet
Principle Diazo salt + bilirubin = Urea Clearance Demonstrate progression of renal disease
azobilirubin and response to therapy
End-result Pink-purple Blue azobilirubin Cystatin C / Indirect Used to assess GFR among pediatric,
azobilirubin GFR test geriatric and renal transplant patients
Presence of it in the urine, significantly
Jendrassik and Not affected by pH changes and Hgb up to 750 mg/dL
means tubular damage ( because it is
Grof
completely reabsorbed in the PCT)
Ascorbic Acid In Jendrassik and Grof, _____ terminates the initial reaction and
B-trace protein Isolated primarily from the CSF
destroys excess diazo reagent
Increased in renal disease
Urobilinogen Colorless end product of bilirubin metabolism, oxidized by intestinal
bacteria
1-4mg – Urine Blood Urea Major end product of protein and amino acid catabolism
50-150 mg - feces Nitrogen First to elevate and easily removed by dialysis
Ehrlich’s Method for urobilinogen Ornithine / [ LIVER] Ammonia → (CO2) -→ Urea
Method ( p- Krebs Henseleit
DABA) Cycle
Caraway Method for Ammonia determination via microdiffusion 10:1 – 20:1 BUN:CREA ratio
Method 2.14 To obtain urea from bun multiply it by ____
Reye’s Increased ammonia Fluoride or Do not use _____ for BUN determination ( inhibits urease)
Syndrome Occurs in children due to the intake of aspirin after viral infection citrate
BUN methods Diacetyl Monoxime Method Yellow Diazine Method [ chemical]
Urease Enzyme method
KIDNEY FUNCTION TESTS Urea + Urease → NH3 + CO2
Nephrons Functional units of kidneys
Creatinine End product of muscle metabolism, derived from creatine
NPNs Compound Approx. Plasma Approx. Urine Concentration Not affected by diet, not easily removed by dialysis
Concentration ( % of ( % Excreted Nitrogen) Used to evaluate fetal kidney maturity
total NPN) Methionine, Crea is derived from what amino acids?
Urea 45-50 (most 86.0 ( most abundant Arginine, Lysine
abundant) organic component in urine) Cephalosporins Interference in the Jaffe reaction [ falsely increases the crea]
AA 25 - CREATININE Direct Jaffe Creatinine + alkaline picrate = red-orange
Uric Acid 10 1.7 Methods Kinetic Jaffe Serum + alkaline picrate = rate of absorbance is
Creatinine 5 4.5 measured
Creatine 1-2 - Enzymatic 1. Creatinine amidohydrolase-CK method
Ammonia 0.2 2.8 Method 2. Creatinine Hydrogen Peorxide method )
Glomerular Best overall indicator of kidney function no interference from cephalosporins)
Filtration Rate Alkaline Picrate 1. Saturated Picric Acid
J.A.M RMT 2024 8
2. 10% NaOH LIPIDS AND LIPOPROTEINS
Low BUN:CREA 1. Low protein diet Major lipids 1. Phospholipids
ratio 2. Acute Tubular necrosis 2. TAG
3. Repeated dialysis 3. CHOLE
4. Hepatic disease 4. Fatty Acids
High ratio 1. Pre renal azotemia 5. Fat Soluble Vitamins ( ADEK)
BUN:CREA ( 2. Dehydration Phospholipid Most abundant, derived from phosphatidic acid
normal crea) 3. Catabolic stress From the conjugation of 2 FA + glycerol
4. GI Hemorrhage Amphipathic lipid
5. High Protein diet Saturated FA Independent risk factor for atherosclerosis
High ratio 1. Pre renal and post renal azotemia Type II In the lungs, phospholipids are produced by the ______, in the form
BUN:CREA ( 2. Renal failure pneumocytes of lamellar bodies
increased) Forms of 1. Lecithin / Phosphatidyl choline – 70%
BUA Major product of adenine and guanine catabolism phospholipids 2. Sphingomyelin – 20%
Final breakdown of nucleic acid catabolism 3. Cephalin – 10%
Monosodium Uric acid is 95% exists as ___ Sphingomyelin Not derived from glycerol . derived from AA [ sphingosine]
Urate Essential component of cell membrane
Tophi If monosodium urate is deposited in the tissues Accumulates in the liver and spleen in Niemann pick disease
Gout Found in males Lecithin/ Status of FLM
“birefringent crystals in the synovial fluid” Sphingomyelin Pulmonary surfactant measured in the amniotic fluid
Lesch-Nyhan Deficiency of HGPRT ratio Can be measured through chromatography or microviscosity by
syndrome fluorescence polarization
Fanconi’s Renal type of aminoaciduria > 2 = mature fetal lung
syndrome Cholesterol is a 1. Progestins
Uricase Enzymatic method for BUA, routinely used and specific precursor of 2. Glucocorticoids
Method 3. Mineralocorticoids
293 nm Uric acid has an absorbance peak at? 4. Androgens
Azotemia Elevated concentrations of NPNs in the blood 5. Estrogen
Types of Pre-Renal Diminished GFR w/ normal renal function Forms of Cholesterol Ester Bound to FA
Azotemia Decreased renal blood flow cholesterol Neutral lipid – not found in the surface
E.g dehydration, CHF, shock Esterified by LCAT
Renal Damaged within the kidneys, can cause coma and Free CHOLE Polar nonesterified alcohol produced by
neuropsychiatric changes lysosomal hydrolysis
Post Renal Due to urinary tract obstruction LCAT Enables HDL to accumulate CHOLE as CE
Potassium Do not use ____ for BUA determination Apo-A1 Activator of LCAT
Oxalate Methods for Chemical Methods
Ascorbic acid, Major interferences in NPNs determination CHOLE Liebermann-Burchardt Cholestadienyl monosulfonic acid –
Bilirubin determination green
Isotope Reference Method for NPNs Salkowski Cholestadienyl monosulfonic acid – red
Dilution Mass Cholesterol Oxidase Enzymatic Method
Spectrometry Abell, Levy and Brodie CDC reference method
Seebeck effect An increase in osmolality decreases the freezing point and vapor General Methods One-step Colorimetry – Pearson, Stern, Mac Gavack
pressure for CHOLE Two-step Colorimetry + Extraction – Bloors
Osmolal gap Sensitive indicator of alcohol or drug abuse Three-step Colorimetry + Extraction + saponification – Abell-
Kendall
J.A.M RMT 2024 9
Four-step Colorimetry + Extraction + saponification + Found in type 3 hyperlipoproteinemia or
precipitation – Schoenheimer, Sperry, Parekh, dysbetalipoproteinemia
Jung “ VLDL rich in chole”
Triglyceride 3 FA + 1 glycerol linked via ester bonds Methods for LPP Ultracentrifugation Reference Method
Hydrophobic ; main storage of lipid in man determination Expressed in Svedberg units
TAG and CHOLE Most important lipids for management for CAD Electrophoresis Chylo = origin
Methods for TAG Chemical Methods VLDL = pre B ( a2)
Determination Van Handel & Zilversmith Colorimetric method ~ blue LDL = beta
Hantzsch Condensation Fluorometric method HDL = alpha
Glycerol Kinase Enzymatic Method ~ routine ** uses agarose gel
Modified Van Handel & CDC reference method Chemical Precipitation
Zilversmith HDL Homogenous assays – most popular
Fatty Acids Mainly found as constituents of phospholipids and TAG method for HDL-C
Mostly bound to albumin Uses dextran sulfate w/ magnesium
Saturated FA = w/o double bonds LDL Beta quantification = ultracentrifugation +
Unsaturated FA = w/ double bonds chemical precipitation
Lipoproteins Transport TAG and cholesterol to the sites of energy storage Uses polyanions = removes apo-B
Apolipoprotein Helps in the solubilization of lipids [ helps lipids to stay in the containing LPP
solution]
Has an “amphipathic helix” [ ability of protein to bind lipids] LDL-C formula TC – HDL-VLDL
Major Chylomicrons Largest and least dense Apo-B48
Lipoproteins Transports exogenous TAG to liver VLDL
and muscles Friedewald = mmol = TAG/2.175
VLDL Transports endogenous TAG from Apo-B100 Mg/dL = TAG/5
the liver to the msucles
HDL Smallest and most dense Apo-A1 De Long = mmol = TAG/2.825
Reverse cholesterol transport Mg/dL = TAG/6.5
LDL Major end product from the Apo-B100 Apo-CII Activates lipoprotein lipase
catabolism of VLDL Disorders of Familial Defective/ deficient LDL receptors
Most abundant LPP Lipids and LPP Hypercholesterolemia [+] xanthelasma & planar xanthomas
Most CHOLE rich Familial “Type 3 Hyperlipoproteinemia”
Most atherogenic Dysbetalipoproteinemia B-VLDL
Primary marker for CHD risk Accumulation of VLDL rich in chole
Minor IDL VLDL remnant Apo- and chylomicron remnants
Lipoproteins Subclass of LDL B100 Assc. with apo E2 – rare form of apo-
Migrates in either B or pre-B in E
electrophoresis Abetalipoproteinemia “ Bassen-Kornzweig Syndrome”
Lp(a) Similar to LDL ( density and composition) Apo- VLDL,LDL, CHYLO – not found in
Electrophoretic mobility = VLDL B100 plasma
Sinking pre-B lipoprotein TAG and CHOLE – decreased levels
Similar to plasminogen – independent risk Deficient fat soluble vitamins
factor for atherosclerosis Defective apo-B synthesis
[+] acanthocytosis, cerebellar ataxia,
Abnormal LpX Found in obstructive jaundice and LCAT deficiency
malabsorption
Lipoproteins Specific and sensitive indicator of cholelithiasis
Hypobetalipoproteinemia Deficient apo-B
Contains Apo-C and albumin
Niemann-Pick Disease Sphingomyelin accumulation
B-VLDL Abnormally migrating B-VLDL
Tangier Disease Complete absence of HDL due to
ABCA1 mutation
J.A.M RMT 2024 10
Increased HDL catabolism
Low blood CHOLE
[+] orange / yellow discoloration of
the tonsils and pharynx
LPL Deficiency Presents in childhood w/ abdominal
pain and pancreatitis
Deficiency in Apo-CII
Do not develop to premature CHD
LCAT deficiency Mutation in the LCAT gene
[+] corneal opacities, normochromic
anemia, renal failure in young adults
Tay-Sachs disease Deficiency in hexosaminidase A
Anderson’s disease Chylomicron retention disease
Defective apo-b48
Deficiency in VitE
Sitosterolemia Sterols accumulate in plasma and
peripheral tissues
J.A.M RMT 2024 11
You might also like
- The Art of Increasing Testosterone Naturally - Anabolic Health - V1 March 2020Document647 pagesThe Art of Increasing Testosterone Naturally - Anabolic Health - V1 March 2020Tom W83% (6)
- A Simple Guide to The Pineal Gland (The Third Eye) And Its FunctionFrom EverandA Simple Guide to The Pineal Gland (The Third Eye) And Its FunctionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Biochemistry of HormonesIDocument24 pagesBiochemistry of HormonesIStephie GhassanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System - Part 1 (Robbins)Document28 pagesEndocrine System - Part 1 (Robbins)sarguss14100% (2)
- Drugs Affecting The Endocrine SystemDocument43 pagesDrugs Affecting The Endocrine SystemJustine Vens G. AgustinNo ratings yet
- EndocrinologyDocument12 pagesEndocrinologyNathaniel Derige AndesNo ratings yet
- ADRENALSDocument60 pagesADRENALSJyoti ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument59 pagesEndocrine SystemCharm Angeles100% (3)
- Clinical Chemistry 3: EndocrinologyDocument21 pagesClinical Chemistry 3: EndocrinologyRomie Solacito100% (3)
- Chapter 34 - Introduction To The Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesChapter 34 - Introduction To The Endocrine Systemkdayeon018No ratings yet
- CC 2Document4 pagesCC 2Mary Kaye Yvonne OtillaNo ratings yet
- Business: Reminder: Study For Quiz #2Document43 pagesBusiness: Reminder: Study For Quiz #2Melanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Harliansyah Dept Biochemistry University of YARSIDocument26 pagesEndocrine System: Harliansyah Dept Biochemistry University of YARSIAnonymous 7r6o3g4jNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Lec 1Document26 pagesEndocrine System Lec 1Fadli IlhamNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology PDFDocument15 pagesEndocrinology PDFJanneth MendozaNo ratings yet
- MUST To KNOW in BacteriologyDocument3 pagesMUST To KNOW in BacteriologySam CatanghalNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Chemical ControlDocument36 pagesEndocrine System: Chemical ControlGary VlaicuNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Day 1 TemplateDocument17 pagesEndocrine Day 1 TemplateMikeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Endocrine SystemDocument9 pagesChapter 9 - Endocrine SystemrishellemaepilonesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Endocrine SystemDocument9 pagesChapter 9 - Endocrine SystemRishelle Mae Miñoza PilonesNo ratings yet
- Review of Endocrine SystemDocument32 pagesReview of Endocrine SystemJames FNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument14 pagesChemical Coordination and Integrationadityaaggarwal821No ratings yet
- Pcol Lec Book FinalsDocument61 pagesPcol Lec Book FinalsMarco Sta AnaNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Endocrine Systems-0Document14 pagesAP Biology Endocrine Systems-0Aamer AlmansourNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Classification of GlandsDocument5 pagesThe Endocrine System: Classification of GlandsGlenn BanlaygasNo ratings yet
- CC3 - Introduction To Hormones Endocrinology HormoneDocument4 pagesCC3 - Introduction To Hormones Endocrinology HormonecasijyhdiqweNo ratings yet
- Endocrine GM Eng 2020Document32 pagesEndocrine GM Eng 2020snowrose2609No ratings yet
- Coordination: GlandsDocument11 pagesCoordination: Glandskashish joshiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine PhysiologyDocument7 pagesEndocrine PhysiologyLomongo ChristianNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM-Molecular Endocrinology 1Document14 pagesBIOCHEM-Molecular Endocrinology 1Std DlshsiNo ratings yet
- Male ReproductiveDocument10 pagesMale ReproductivevivekNo ratings yet
- Describe Hormones and Their CompositionDocument7 pagesDescribe Hormones and Their CompositionShahzaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Endocrine System PDFDocument55 pagesChapter 7 - Endocrine System PDFDanial JuniorNo ratings yet
- EndocrinologyDocument2 pagesEndocrinologyJoanna Ella Kim MontañoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System - SheepDocument1 pageEndocrine System - SheepmilumvzNo ratings yet
- Multiple-Choice QuizDocument6 pagesMultiple-Choice QuizHUAWEI HUAWEI100% (1)
- Endocrine System: EndocrinologyDocument10 pagesEndocrine System: EndocrinologyAnya IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Capitulo Eje PDFDocument15 pagesCapitulo Eje PDFMilena ArdilaNo ratings yet
- Article 12Document10 pagesArticle 12WPRN RanasingheNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics Trans EndoDocument6 pagesPediatrics Trans EndoyayayanizaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument14 pagesEndocrine SystemElaine Victoria ElizanNo ratings yet
- 2.signal Transduction-2Document26 pages2.signal Transduction-2Ragdha MehdawiNo ratings yet
- Endokrinologi DasarDocument33 pagesEndokrinologi DasarwadejackNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument25 pagesThe Endocrine SystemFritz MirandaNo ratings yet
- Endocine System Physiology 20-4-2020Document61 pagesEndocine System Physiology 20-4-2020Farah AljayyousiNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamus Pituitary and Gonad AxisDocument6 pagesHypothalamus Pituitary and Gonad Axisalok nayakNo ratings yet
- Responsible For The Direct Control of The Endocrine System Through The Pituitary GlandDocument4 pagesResponsible For The Direct Control of The Endocrine System Through The Pituitary GlandJessa Mae BanquirigNo ratings yet
- CCHM Lecture QuizzesDocument3 pagesCCHM Lecture QuizzesGrace GasconNo ratings yet
- PCOL - Hormonal AgentsDocument7 pagesPCOL - Hormonal AgentsTerepe CrimsonNo ratings yet
- Cc2 l5 EndocrinologyDocument4 pagesCc2 l5 EndocrinologyRose Denisse EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 17 PhysiologyDocument49 pagesChapter - 17 PhysiologyAhsanullah PathanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System (Ch7)Document15 pagesEndocrine System (Ch7)moepiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine 1 PageDocument3 pagesEndocrine 1 PagetimbitNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Endocrine System: BSPT (Cebu Doctors' University) BSPT (Cebu Doctors' University)Document13 pagesEndocrine System Endocrine System: BSPT (Cebu Doctors' University) BSPT (Cebu Doctors' University)Carina DaduloNo ratings yet
- Physio 1Document6 pagesPhysio 1amjadNo ratings yet
- NCM 116 Case Analysis 2Document9 pagesNCM 116 Case Analysis 2Dominic DegraciaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Respiratory Reproductive Excretory Urinary Nervous Immune SysytemDocument185 pagesEndocrine Respiratory Reproductive Excretory Urinary Nervous Immune SysytemEms TeopeNo ratings yet
- 10 - The Endocrine SystemDocument56 pages10 - The Endocrine SystemNickson OnchokaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Reproductive EndocrinologyDocument5 pagesLecture 2 Reproductive EndocrinologyCharisse Angelica MacedaNo ratings yet
- Mcqs of Endocrine SystemDocument25 pagesMcqs of Endocrine SystemkajuNo ratings yet
- 10-17-2019 Neuroendocrinology in Mental Health An UpdateDocument44 pages10-17-2019 Neuroendocrinology in Mental Health An UpdatehelalNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesEndocrine SystemJames CastroNo ratings yet
- ADVIA Centaur Parametros AnalisadosDocument2 pagesADVIA Centaur Parametros AnalisadosSara MacedoNo ratings yet
- Uso de Esteroides en AnestesiaDocument7 pagesUso de Esteroides en AnestesiatitinodeNo ratings yet
- Rosenfield2015 PDFDocument27 pagesRosenfield2015 PDFdanilacezaraalinaNo ratings yet
- Sglt2 Inhibitor - PDF 25Document7 pagesSglt2 Inhibitor - PDF 25JaganNo ratings yet
- BrochureDocument2 pagesBrochureapi-583829374No ratings yet
- Studi Litelatur Analisis Penanganan Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS) Pada Remaja PutriDocument8 pagesStudi Litelatur Analisis Penanganan Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS) Pada Remaja PutriReyin RahmanNo ratings yet
- NCP Diabetes MellitusDocument2 pagesNCP Diabetes MellitusrhueneisenNo ratings yet
- 2010 Endocrine System ChartDocument3 pages2010 Endocrine System ChartAlexander QianNo ratings yet
- IBÁÑEZ Et Al., 2011Document4 pagesIBÁÑEZ Et Al., 2011Luana BarrosNo ratings yet
- Bimtek PTM & Keswa: Puskesmas Pujon 2022Document12 pagesBimtek PTM & Keswa: Puskesmas Pujon 2022fenny novianaNo ratings yet
- Alopecia Unapproved Treatmentes or IndicationsDocument10 pagesAlopecia Unapproved Treatmentes or IndicationsdanizituNo ratings yet
- Biology - Human ReproductionDocument21 pagesBiology - Human Reproductionsgw67No ratings yet
- Water Balance Grade 12 BioDocument27 pagesWater Balance Grade 12 BioAllan AnthiahNo ratings yet
- About Thyroid Cancer: Overview and TypesDocument12 pagesAbout Thyroid Cancer: Overview and Typesumaima rizwanNo ratings yet
- Asm 2380Document2 pagesAsm 2380Aryaan LaskarNo ratings yet
- DFGHJKDocument3 pagesDFGHJKcliffwinskyNo ratings yet
- A Review of Endocrine Disorders in ThalassaemiaDocument10 pagesA Review of Endocrine Disorders in ThalassaemiaNiken RositaNo ratings yet
- 1st Summatve 2nd RatingDocument26 pages1st Summatve 2nd RatingLea ManambayNo ratings yet
- SCE Nephrology Book 20106Document210 pagesSCE Nephrology Book 20106Sagvan HajaniNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction - DPP 10 (Of Lecture 14) - Lakshya NEET 2024Document3 pagesHuman Reproduction - DPP 10 (Of Lecture 14) - Lakshya NEET 2024Ankit BhartiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of Thyroid GlandDocument5 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of Thyroid GlandJohnpaul DelapenaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Review: Management of Hyperkalemia With Insulin and Glucose: Pearls For The Emergency ClinicianDocument7 pagesClinical Review: Management of Hyperkalemia With Insulin and Glucose: Pearls For The Emergency ClinicianJulio Castro pinedoNo ratings yet
- SNDT Women's University Syllabus - Bachelors in PharmacyDocument101 pagesSNDT Women's University Syllabus - Bachelors in Pharmacysunil_vaman_joshiNo ratings yet
- Chiari - Frommel Syndrome - Sexual Dysfunction, Sexual Intercourse Discomfort & Loss of Sexual Desire Related To Dryness in The Vagina Secondary To Gal Actor RheaDocument3 pagesChiari - Frommel Syndrome - Sexual Dysfunction, Sexual Intercourse Discomfort & Loss of Sexual Desire Related To Dryness in The Vagina Secondary To Gal Actor RheaLoord Vie Lu MondigoNo ratings yet
- Tugas Kuliah: Membuat Makalah Interaksi Obat Dan MakananDocument3 pagesTugas Kuliah: Membuat Makalah Interaksi Obat Dan MakananNovi AzzaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3, PersonalityDocument25 pagesChapter-3, PersonalityDweep BajajNo ratings yet
- Journal of Endocrinology Androgens and Ovarian Function - Translation From Basic Discovery Research To Clinical ImpactDocument28 pagesJournal of Endocrinology Androgens and Ovarian Function - Translation From Basic Discovery Research To Clinical ImpactHong Ngoc PhamNo ratings yet
- Manifestasi Kulit DAN HipotiroidDocument26 pagesManifestasi Kulit DAN HipotiroidAa SsNo ratings yet