0% found this document useful (0 votes)
585 views15 pagesSurds
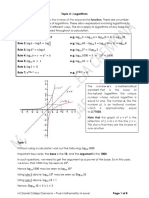
This document discusses laws and properties of surds (roots), working with surds, examples of simplifying and comparing surds, rationalizing denominators, solving surd equations, and examples of solving surd equations. It provides instructions, definitions, examples, and exercises related to working with surds.
Uploaded by
sunbai samuelCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
585 views15 pagesSurds
This document discusses laws and properties of surds (roots), working with surds, examples of simplifying and comparing surds, rationalizing denominators, solving surd equations, and examples of solving surd equations. It provides instructions, definitions, examples, and exercises related to working with surds.
Uploaded by
sunbai samuelCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd