Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Coelenterata
Uploaded by
Saba Nazir0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views4 pagesCoelenterata: characteristics and classification
Original Title
Coelenterata.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCoelenterata: characteristics and classification
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views4 pagesCoelenterata
Uploaded by
Saba NazirCoelenterata: characteristics and classification
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
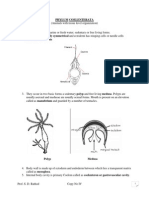
Phylum Coelenterata
Characteristics
• These are the multicellular animals with tissue grade of organization.
• Individuals are radially or bilaterally symmetrical.
• Diploblastic body consisting of outer layer of ectoderm, inner endoderm and
an intermediate of non-cellular gelatinous mesoglea.
• Acoelomate i.e., coelom is absent.
• They are aquatic, mostly marine except a few freshwater forms like Hydra.
• They have a central gastro-vascular cavity called Coelenteron with a single
opening, mouth on hypostome.
• Digestion is intracellular as well as extracellular. Anus is not found.
• Mouth is encircled by short and slender tentacles in one or more whorls.
• The tentacles are meant for capturing food, adhesion and defence.
• Tentacles and the body bears cnidoblasts or cnidocytes which contain the
stinging cells called nematocysts. These are also known as cnidarians.
• Respiratory, circulatory and excretory systems are absent.
• Reproduction takes place by both ways asexually (budding) and sexually (by
formation of gametes).
• Indirect development through a ciliated larva called planula.
• They exhibit polymorphism I.e., the phenomenon of occurrence of different
types of individuals or zooids. Zooids are mainly of two types; Polyps (sessile,
cylindrical form and asexual zooid) like Adamsia and Medusae (free
swimming, umbrella-shaped and sexual zooid) like Aurelia (jellyfish).
• Some cnidarians exhibit Alternation of generation or metagenesis, i.e.,
polyps produce medusae asexually and medusae produce the polyps sexually
e.g., Obelia(sea fur)
Classification (ASH)
CLASS HYDROZOA (Gr., hydra = water; zoios = animal)
• There are two main types of zooids, the polyp and medusa.
• They exhibit polymorphism.
• Many exhibits alteration of generation or metagenesis.
• Coelenteron with gastric filaments and without septa (or mesenteries).
• They are, mostly marine and colonial and some freshwater and solitary.
• Examples: Hydra, Obelia (sea-fur), Millepora (stinging coral), and Physalia
(Portuguese man of war)
CLASS SCYPHOZOA (Gr., skyphos = cup; zoios = animal)
• They are true medusae or large jelly-fishes, polypoid generation absent or
represented by small polyps.
• Medusae are large, bell or umbrella shaped, free swimming and sexual
zooids.
• Coelenteron with gastric filaments and may or may not be divided into four
gastric pouches by mesenteries.
• They are exclusively marine.
• Examples: Chiropsalmus Quadrumanus(four-handed box jellyfish),
Periphylla (helmet jellyfish), Aurelia Aurita (moon jellyfish), Rhizostoma
Pulmo (barrel jellyfish)
CLASS ACTINOZOA (ANTHOZOA) (Gr., anthos = flower; zoios =
animal
• Exclusively polyps, medusoid stage is altogether absent.
• Polyps are cylindrical form, sessile, and asexual zooids.
• Coelenteron is divided into 8 or more compartments by septa or
mesenteries.
• They are exclusively marine.
• Examples: Adamsia (sea anemone), Pennatula (sea pen), Gorgonia (sea-
fan), and Meandrina (brain coral),
You might also like
- CoelenterataDocument10 pagesCoelenteratarudra nayakNo ratings yet
- ZoologyDocument9 pagesZoologymiarrieNo ratings yet
- Animal KingdomDocument16 pagesAnimal KingdomARAÑEZ, Rafael Jr. G.No ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom-1 PDFDocument30 pagesAnimal Kingdom-1 PDFANo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal KingdomDocument9 pagesPlant and Animal KingdomAsim Iftikhar100% (1)
- Repaso Examen Laboratorio ZOOLOGIADocument12 pagesRepaso Examen Laboratorio ZOOLOGIAcaripukisNo ratings yet
- Phylum Coelenterata ClassificationDocument3 pagesPhylum Coelenterata ClassificationSudesh Rathod100% (1)
- Animal Kingdom-Class 11Document6 pagesAnimal Kingdom-Class 11ICSE BOARDNo ratings yet
- The Phylum ADocument9 pagesThe Phylum Airish xNo ratings yet
- I.B.Sc - ZoologyEM-18UZO1-Dr.T.PRABU - UNIT - IVDocument18 pagesI.B.Sc - ZoologyEM-18UZO1-Dr.T.PRABU - UNIT - IVAijaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Practical 1Document19 pagesPractical 1Nick YuNo ratings yet
- Phylum ProtozoaDocument123 pagesPhylum Protozoaยุทธพงษ์ สานต์ศิริNo ratings yet
- Evelyn Hone College Lecture 7 2022 Kingdom AnimaliaDocument101 pagesEvelyn Hone College Lecture 7 2022 Kingdom AnimaliaJoyce KapembwaNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom ClassificationDocument6 pagesAnimal Kingdom ClassificationAnjali panikaNo ratings yet
- Phylum Mollusca: Mantle-Is A Dorsal Glandular Fold of The Body Wall. It Is Thick and Muscular and Encloses MantleDocument5 pagesPhylum Mollusca: Mantle-Is A Dorsal Glandular Fold of The Body Wall. It Is Thick and Muscular and Encloses MantleFrenzes PadabocNo ratings yet
- Phylum Cnidaria (Coelenterata)Document112 pagesPhylum Cnidaria (Coelenterata)Silvi valNo ratings yet
- Invertebrateanimals 140331061236 Phpapp02Document17 pagesInvertebrateanimals 140331061236 Phpapp02Cay C. CordovaNo ratings yet
- CnidariaDocument48 pagesCnidariaMafe CabilesNo ratings yet
- CnidariaDocument59 pagesCnidariaMafe CabilesNo ratings yet
- Annelids and MolluscsDocument82 pagesAnnelids and MolluscsHawltu MuluNo ratings yet
- Annelida: The Metameric Body Form: Jasmin Godoy-Dela CruzDocument28 pagesAnnelida: The Metameric Body Form: Jasmin Godoy-Dela Cruzbread genieNo ratings yet
- Phylum Annelida, Mollusca, and ArthropodaDocument20 pagesPhylum Annelida, Mollusca, and ArthropodaElle ManabatNo ratings yet
- Phylum CnidariaDocument26 pagesPhylum CnidariaAbby SangualNo ratings yet
- Kingdom AnimaliaDocument16 pagesKingdom AnimaliaMarese PrietoNo ratings yet
- Phylum CnidariaDocument37 pagesPhylum CnidariaMadhavNo ratings yet
- Practical No 3 FYBSc.Document13 pagesPractical No 3 FYBSc.Vinod SNo ratings yet
- Sokoine University of Agriculture: ClassificationDocument75 pagesSokoine University of Agriculture: ClassificationToke SadockNo ratings yet
- Kindom AnimaliaDocument39 pagesKindom AnimaliaJohnrey CastilloNo ratings yet
- 3 - Cnidaria and CtenophoraDocument42 pages3 - Cnidaria and CtenophoraDwi HardiyantiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: ProtistaDocument8 pagesChapter 4: ProtistaNawal Che IsmailNo ratings yet
- Protista: The First EukaryotesDocument102 pagesProtista: The First EukaryoteshannNo ratings yet
- Animal KingdomDocument16 pagesAnimal KingdomSanchit GautamNo ratings yet
- Animal Diversity NotesDocument11 pagesAnimal Diversity Noteskobe100% (1)
- Helm in TH OlogyDocument49 pagesHelm in TH OlogyRaunaNo ratings yet
- The Lophophorate Phyla: BryozoaDocument20 pagesThe Lophophorate Phyla: BryozoaEthylNo ratings yet
- HydrozoaDocument3 pagesHydrozoaBercia MondialuNo ratings yet
- Kingdo M Animali ADocument29 pagesKingdo M Animali ABaltazar EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Phylum CnidariaDocument3 pagesPhylum CnidariaMA. LYN CASIPENo ratings yet
- Classification Animal Kingdom English 77Document8 pagesClassification Animal Kingdom English 77Aayush MalikNo ratings yet
- Diversity in Living OrganismDocument35 pagesDiversity in Living OrganismEdUcT-VKS100% (1)
- Report BiologyDocument17 pagesReport BiologyChrisjhel EturaldeNo ratings yet
- Lec ReportDocument40 pagesLec ReportmalonesandreagwenethNo ratings yet
- Phylum Ceolenterata: Cnidaria: From A Greek Word "Cnidos" Meaning Stinging ThreadDocument10 pagesPhylum Ceolenterata: Cnidaria: From A Greek Word "Cnidos" Meaning Stinging ThreadJofren MorenoNo ratings yet
- Animal KingdomDocument89 pagesAnimal Kingdom333366998No ratings yet
- Protochordata-Characters & PhylogenyDocument4 pagesProtochordata-Characters & PhylogenyAakash VNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3 Phylum CoelenterataDocument34 pagesExercise 3 Phylum CoelenterataClemence Marie FuentesNo ratings yet
- ChordataDocument39 pagesChordataBlanche Mascarinas LaborteNo ratings yet
- Molluscs New Revised Ppt-1Document41 pagesMolluscs New Revised Ppt-1Issa Avena100% (2)
- Kingdom PlantaeDocument8 pagesKingdom PlantaeSurbhi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Phylum MolluscaDocument36 pagesPhylum MolluscaSheryl Evo Balbutan100% (1)
- Echinodermata PDFDocument57 pagesEchinodermata PDFjerlimanmanalu100% (1)
- KINGDOM ANIMALIA CompressedDocument266 pagesKINGDOM ANIMALIA CompressedDiana Jean Alo-adNo ratings yet
- Kingdom AnimaliaDocument41 pagesKingdom Animaliababaaijaz01No ratings yet
- Unit 8. InvertebratesDocument142 pagesUnit 8. InvertebratesPika PiNo ratings yet
- Animal KingdomDocument252 pagesAnimal KingdomBiju MylachalNo ratings yet
- 10 Kingdom Animalia..Document189 pages10 Kingdom Animalia..Tooba MarjanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1&2 - Intro, Protozoa, Por If EraDocument60 pagesLecture 1&2 - Intro, Protozoa, Por If Eraapi-3827285No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 The Pseudocoelomate Body PlanDocument39 pagesChapter 11 The Pseudocoelomate Body PlancontactrafiakhuramNo ratings yet
- Freshwater Aquariums in Your LifeFrom EverandFreshwater Aquariums in Your LifeAmanda PisaniNo ratings yet
- Woods Ho!e Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole, MassachusettsDocument18 pagesWoods Ho!e Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole, MassachusettsRizky Aulia DewiNo ratings yet
- Co-Existence and Interactions of Pest With Bee-Wax Baited Gmelina Arborea (Roxb.) Woodhives in Abeokuta, NigeriaDocument5 pagesCo-Existence and Interactions of Pest With Bee-Wax Baited Gmelina Arborea (Roxb.) Woodhives in Abeokuta, NigeriaInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- Birds of Sri Lanka A Pictorial Guide and Checklist: Gehan de Silva WijeyeratneDocument20 pagesBirds of Sri Lanka A Pictorial Guide and Checklist: Gehan de Silva WijeyeratneDilip SirisenaNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom Phylum - ChordataDocument11 pagesAnimal Kingdom Phylum - ChordatamalavikaNo ratings yet
- ST-18 The Ape Girl by Author UnknownDocument56 pagesST-18 The Ape Girl by Author Unknownsorin61100% (2)
- Animal Crossing Season Guide For FishDocument2 pagesAnimal Crossing Season Guide For FishKatie DeeNo ratings yet
- Colony MorphologyDocument9 pagesColony MorphologyKirk AdderleyNo ratings yet
- Fixed Protista WorksheetDocument4 pagesFixed Protista WorksheetcandraNo ratings yet
- PNAS 2011 Bilsborough 3424 9Document29 pagesPNAS 2011 Bilsborough 3424 9Vlad PredaNo ratings yet
- DNAMethodsforHLATyping WorkbookDocument81 pagesDNAMethodsforHLATyping WorkbookithilaminNo ratings yet
- Polygenic TraitsDocument14 pagesPolygenic Traitsherzchen123No ratings yet
- Jurassic World The Game Bosses (Autosaved)Document15 pagesJurassic World The Game Bosses (Autosaved)CHAN KWOK VINN Moe0% (1)
- III.1 Dino IntroductionDocument10 pagesIII.1 Dino IntroductionCesar Alarcon ZapataNo ratings yet
- Cephalometric Analysis PGDocument114 pagesCephalometric Analysis PGaung NaingmyoNo ratings yet
- Temple Fay: Marco Aurelio Elias RuizDocument8 pagesTemple Fay: Marco Aurelio Elias RuizRuiz MarkiNo ratings yet
- Etextbook PDF For Invertebrates 3rd Edition by Richard C BruscaDocument61 pagesEtextbook PDF For Invertebrates 3rd Edition by Richard C Bruscabeverly.bustos487100% (43)
- Genetika PopulasiDocument48 pagesGenetika PopulasiRoy SinagaNo ratings yet
- Report Text About Panda (1)Document2 pagesReport Text About Panda (1)hanumsaavNo ratings yet
- AnthropometryDocument172 pagesAnthropometryAntonio C. Keith100% (1)
- Stem Cell Technology and Bioceramics: From Cell To Gene EngineeringDocument15 pagesStem Cell Technology and Bioceramics: From Cell To Gene Engineeringcobram1No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Bugs Week 2Document2 pagesLesson Plan Bugs Week 2api-314832142No ratings yet
- Anatomical Landmarks - MaxillaDocument5 pagesAnatomical Landmarks - MaxillaAdarsh A SNo ratings yet
- BIOLAB FROG Organ HistologyDocument7 pagesBIOLAB FROG Organ HistologyCloie Anne Rabinetas100% (1)
- Radiate AnimalsDocument58 pagesRadiate AnimalsBudi AfriyansyahNo ratings yet
- Blg1502 Exam Prep Doc - Part 1&2Document18 pagesBlg1502 Exam Prep Doc - Part 1&2Pasipanodya MuzendaNo ratings yet
- Dias Et Al 2008Document8 pagesDias Et Al 2008Fru Toosie PaloozaNo ratings yet
- OrnithologyDocument13 pagesOrnithologySaraah GhoriNo ratings yet
- Soluzioni Esercizi Del LibroDocument8 pagesSoluzioni Esercizi Del Librofeysalnur100% (1)
- Arthropods: Surviving The Frost: Charmayne Roanna L. GalangDocument2 pagesArthropods: Surviving The Frost: Charmayne Roanna L. GalangBabes-Rose GalangNo ratings yet
- Ielts Writing Task 1Document1 pageIelts Writing Task 1Họ Tên100% (1)