Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SHEETS MASTER PLAN
SHEETS MASTER PLAN
Uploaded by
Abhishek WattsOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SHEETS MASTER PLAN
SHEETS MASTER PLAN
Uploaded by
Abhishek WattsCopyright:
Available Formats
GBU 304 : MASTER PLAN (AMRITSAR)
B. PLAN Vth SEM
SESSION : 2021-2022
SUBMITTED TO SUBMITTED BY
Mr.Karamjit Singh Sandhu B. PLAN Vth SEM
GURU RAMDAS SCHOOL OF PLANNING
GURU NANAK DEV UNIVERSITY
AMRITSAR
INTRODUCTION
INTRODUCTION TO EXERCISE
The students of B Plan 5th semester are required to prepare “Master Plan (2021-2041)” of Amritsar as per the course OBJECTIVE
curriculum, the class has to prepare the plan based upon the study conducted earlier exercise “study of town”. In previous o To achieve balanced and organized development best suited for present and future needs.
exercise we have studied different aspects of a town. So, in Master plan, class tried to study all these aspects and find out the
problems and potentials. We tried to eradicate the problems and maximize the use of potential by giving proposals for o To give guidance that should be in scale with population and economic prospects of the community.
present and future population with the help of maps. o To attain conducive living environment by upgrading the undeveloped areas of the city and gradually reconstructing the
developed area of the city with particular attention to blighted section and improper circulation.
INTRODUCTION TO AMRITSAR
Amritsar is the second largest city in the Indian state of Punjab after Ludhiana. It is major cultural and economic centre
o To provide functional relationship between work, place and recreation.
located in the Majha region of Punjab. Amritsar lies about 25km east of the border with Pakistan.
o To provide balanced infrastructural facilities and other services within town. Hence sustainable development and
IMPORTANCE AND NEED
livability is obtained.
o Being a long term plan, it guides future course of development and catering needs of present.
o To achieve integrated and comprehensive development of the area as many projects and programmes will be set up under
the guidance of master plan.
o For the better administration and implementation of development process.
o For guiding the utilisation of present resources efficiently.
o Planning for the each and every class and community of society to upraise the weaker section of society.
o For equally division of the facilities and services with in town.
o Promoting the growth of the existing potential of the town so that economy of the town could enhance.
o To analyze the existing situation of infrastructure and land use development of city.
o To assess required infrastructure for future needs.
o To promote the growth of existing business by identifying and addressing business needs which leads to sustainable
growth.
SCOPE
It is required to solve the planning problems identified earlier, optimum use of the resources, and suggest a suitable plan and
development strategies. The final proposals may include the proposed land use plans, infrastructure requirements and
proposals of the city, phasing, financial measures adopted.
o Housing: Providing affordable housing to EWS and LIG.
o Industrial: Proving more number of industries in order to boost economy.
o Informal : Providing a separate space for street vendors
o Recreational: Increasing recreational area of the area.
Rajneet Kaur Ritik Sharma Neha Bharti Sheet No
B. Plan
Pragyan Galhotra Rydhima Sharma
5th semester
Sachin Sharma Prabhseerat
Session: 2020-21 Kaur Arvind Kumar Verma Kirti Kehra
GBU 304 :MASTER PLAN(AMRITSAR) Guru Ram Das School of Planning
Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
DEFINITIONS OF MASTER PLAN
DERIVED DEFINITION
o According to Charles Abrams has defined master plan as a comprehensive, long-range plan intended to guide the A plan containing policy guidelines to organise the complex relationship between urban landuses taking into consideration the
past, the present and the future (projections and requirements) for the improvement of existing town.
growth and development of a city, town or region, expressing official contemplation on the course its transportation,
housing and community facilities should take, and making proposals for industrial settlement, commerce, population
distribution, and other aspects of growth and development. Contains
policy
guidelines.
o According to S. C. Rangawala ,‖A master plan or a development plan or a town plan may be defined as a general plan
for the future layout of a city showing both the existing and proposed streets or roads, open spaces, public buildings etc.
which aim at controlling the further growth of a town along preconceived and predetermined paths.
o According to URDPFI Guidelines, Development plan is a statutory plan prepared within the framework of approved For improving
Organuse the
complex
MASTER
perspective plan. The objective of a development plan is to provide further necessary details and intended actions in form the present relationship
town. PLAN between urban
of strategies and physical proposals for various policies given in the perspective plan depending upon the economic and landuses.
social needs and aspiration of the people, available resources and priorities.
o According to United Nations publication “Master Plan is a comprehensive long-range plan, including a physical plan
and an explanatory text, providing guidelines for the development of a city, town or region. It defines land-use areas and Considering
the past,
directs location of facilities and transport and utility networks. The term “development plan” is considered parallel to the present and
term master plan. future.
o According to A. Whittick,” A development plan comprises written statements, maps, and are prepared by an authority
CHARACTERSTICS OF MASTER PLAN
responsible for planning. It is based upon a survey including land use, size, composition and distribution of population an
employment together with an analysis of the system of communications. An opportunity is given for the Public to
participate at all stages of the plan-making process. The objective is to satisfy the social and economic desires of the
community by pleasant environment while reconciling Conflicting land use claims.
Characteristics of Master Plan
o According to G.K Hiraskar A master plan is a blueprint of the various proposals that are intended to improve the
existing conditions and to control the future growth of the town in a coordinated manner such a plan may be realistic ,
ideal to be aimed at and preserve the individuality of the town. It is Comprehensive. It is a long range and physical plan.
Master plan is a dynamic long term planning document that provides the conceptual layout to guide future growth and
development. Master planning is about the making connection between the buildings, social setting, and their surrounding
environments. A master plan includes analysis, recommendations, and proposals for a site’s population, economy, housing,
It is a guide to the decision making. It is a statement of public policy.
transportation, community facilities and land use. It is based on public input, surveys, planning initiatives, existing
development, physical characteristics, and social and economic conditions. - The World Bank
Rajneet Kaur Ritik Sharma Neha Bharti Sheet No
B. Plan
Pragyan Galhotra Rydhima Sharma
5th semester
Sachin Sharma Prabhseerat
Session: 2020-21 Kaur Arvind Kumar Verma Kirti Kehra
GBU 304 :MASTER PLAN(AMRITSAR) Guru Ram Das School of Planning
Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar
THEORATICAL FRAMEWORK
Rajneet Kaur Ritik Sharma Neha Bharti Sheet No
B. Plan
Pragyan Galhotra Rydhima Sharma
5th semester
Sachin Sharma Prabhseerat
Session: 2020-21 Kaur Arvind Kumar Verma Kirti Kehra
GBU 304 :MASTER PLAN(AMRITSAR) Guru Ram Das School of Planning
Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar
METHODOLOGY
Rajneet Kaur Ritik Sharma Neha Bharti Sheet No
B. Plan
Pragyan Galhotra Rydhima Sharma
5th semester
Sachin Sharma Prabhseerat
Session: 2020-21 Kaur Arvind Kumar Verma Kirti Kehra
GBU 304 :MASTER PLAN(AMRITSAR) Guru Ram Das School of Planning
Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar
SUMMARY OF THE TOWN
ASPECTS PROBLEMS VISUALS POTENTIALS POLICIES STATUS
FACTS CAUSES IMPLICATIONS
There is always a Amritsar is having a There is no much Amritsar is the second largest city - -
REGIONAL fear of wars & riots locational disadvantage as development in of Punjab and a great center of
SETTING between India and it is present near the Amritsar. learning and literature.
Pakistan which lead international boundary It is connected with National &
to the heavy loss of with Pakistan. State Capitals with National &
human as well as State Highways, giving higher
economy. level of physical accessibility to it.
It has dual broad-gauge railway
Industrial base of Due to its locational It does not contribute track linking national capital &
Amritsar is not very disadvantage as the much to the economy beyond. It has rail connectivity
strong. developers do not feel safe of the city. with Jammu & Kashmir through
to invest in large amount Jammu & Pakistan through
in such areas. Lahore.
Domestic and international flights
from International airport,
Rajasansi makes it unique in air
connectivity w. r. t. national and
international links.
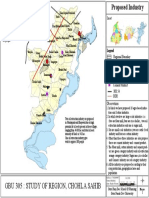
This picture is showing the location of Amritsar.
LOCAL Development Increasing population Facilities available Amritsar is the centre of modern The Punjab Regional and This act is
PLANNING occurred in growth due to migration of within the city are industry and national trade and Town Planning and implemented in
AREA spontaneous, people from villages to the limited. commerce. Development Act, 1995 -To Punjab and it
haphazard and city. As a result of the rapid avoid haphazard and was last
unplanned manner. urbanisation and population unregulated developments. amended in
growth many residential projects 2006.
are going to be established along The Punjab Municipal
the highways or arterial roads Corporation Act, 1976 - For
which results in physical the improvement of areas
expansion of city. and expansion of cities. It
Amritsar city is well connected undertakes schemes for
with the public transport with the general improvement in
surrounding villages. city.
Amritsar is rich in vegetable and
fruit supply so the commodities
can be exported to rest part of
Punjab which can help in
economic development of the
This picture is showing the local planning area. Amritsar.
Rajneet Kaur Ritik Sharma Neha Bharti Sheet No
B. Plan
Pragyan Galhotra Rydhima Sharma
5th semester
Sachin Sharma Prabhseerat
Session: 2020-21 Kaur Arvind Kumar Verma
Kirti Kehra
Guru Ram Das School of Planning
Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar
SUMMARY OF THE TOWN
ASPECTS PROBLEMS VISUALS POTENTIALS POLICIES STATUS
FACTS CAUSES IMPLICATIONS
Historical Amritsar city has Due to presence of tourist It is emerging as major • In earlier time traders Punjab ancient This act is fully implemented in amritsar
historical places and well established tourist destination with were encouraged to monument act 1964
Evolution
significance trade and commerce large flow of tourist both settle in town helping
from India or outside in boosting the
economy. Thus city has
become major
international trade and
commodity centre.
• With presence of
religious places and
other places tourist
increases and economy
boost.
Historical monuments in Amritsar
Rajneet Kaur Ritik Sharma Neha Bharti Sheet No
B. Plan
Pragyan Galhotra Rydhima Sharma
5th semester
Sachin Sharma Prabhseerat Kaur
Session: 2020-21 Arvind Kumar Verma Kirti Kehra
GBU 304 :MASTER PLAN(AMRITSAR) Guru Ram Das School of Planning
Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar
SUMMARY OF THE TOWN
ASPECTS PROBLEMS VISUALS POTENTIALS POLICIES STATUS
FACTS CAUSES IMPLICATIONS
• Physiography • Red category • Maximum wind flows from • Air quality index of Amritsar 1) There are industries in North Eastside. • 4-5 storeys can be easily
industries in the North East to South West. reaches upto 130 ppm. constructed and the number of
windward direction storeys can be increased
(North East to South according to the foundation type
West) are creating the • Amritsar is found as a plain area
problem of air so there is no problem of
pollution development
• Rainfall is decreasing • Temperature of Amritsar is • Ground ater table is • In the western part of Amritsar
so it effects on water increasing. decreasing. course loamy soil is found which
table • As per contour analysis, the is good for agriculture and
• Low lying areas walled city has low lying areas • Creates problems like water vegetation
which is are present having slope downwards as • Sandy soil is good for
which are more prone compared to other areas of
logging, more disaster prone
area. LEGEND construction activities due to
to disaster town. better drainage and infiltration
RESIDENTIAL
capacity. It has a good bearing
OPEN SPACES capacity of 1.00 – 2.54 kg/cm.
INDUSTRIES
• Landuse • Incompatible landuse • There is unplanned • The industries are located 1) Industries located within the residential area • Circulation of town covers 16% National Landuse No ground
in the town which is development in the town within the residential area or of total build –up area which is Policy,1982 implementation is
11 wards out of 65 public. according to standards which Aims to implement and there
wards. could be 15-18%. The town manage the landuse
• Recreational area is • Most of the area is covered by • The children`s play on follows different hierarchy rights and sustainable
only 1.5% of total residential and there no so streets and adults have no according to its width. landuse management
developed area. much space to convert into open spaces to walk so they • Commercial of town covers
parks and green spaces walk on streets 4.72% of total build –up area
which is according to standards
which could be 4-5%.
• The town has good
administrative setup
LEGEND
RESIDENTIAL
OPEN SPACES
INDUSTRIES
Rajneet Kaur Ritik Sharma Neha Sheet No
B. Plan
Bharti Pragyan Galhotra Rydhima
5th semester
Sharma
Session: 2021-22 Sachin Sharma Prabhseerat
GBU 304 :MASTER PLAN(AMRITSAR) Kaur Arvind Kumar Verma Kirti Kehra
Guru Ram Das School of Planning
Guru Nanak Dev University,
Amritsar
SUMMARY OF THE TOWN
ASPECTS PROBLEMS VISUALS POTENTIALS POLICIES STATUS
FACTS CAUSES IMPLICATIONS
Migration rate in City provides the maximum Increasing Urbanization. The study points out that the National Education This policy is not
Demography Amritsar city is very opportunities for the literacy in Amritsar has Policy 2020(Ministry of applied in Amritsar
high. peoples. considerably improved from Human Resource yet. The main
Overcrowding. 69.30% to 75.22% during period Development). target of the policy
Population growth in Due to the Migration. 2001-2011. The overall increase is to enhance the
city is high as compared in literacy rate may be due to education system
to the previous years. improving economic conditions till 2040.
and expansion of educational
facilities in the area.
Dependency ratio in the Less employment resources Financial condition is Marginal workers can be Ayushman Bharat This policy is
Socio-Economic city is high becoming worse. Dependency Ratio
transferred in main worker due Program applied in
33% are workers to a potential of the city . Amritsar. This
and 67% are schemes aims to
non-workers. cover 10 crore
Workers
33%
vulnerable families
with approximately
Non-workers
Workers 50 crores
Non-workers
67%
beneficiaries with
health insurance up
to 5 lakhs.
Financial condition is becoming worse.
Rajneet Kaur Ritik Sharma Neha Bharti Sheet No
B. Plan
Pragyan Galhotra Rydhima Sharma
5th semester
Sachin Sharma Prabhseerat
Session: 2020-21 Kaur Arvind Kumar Verma Kirti Kehra
GBU 304 :MASTER PLAN(AMRITSAR) Guru Ram Das School of Planning
Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar
SUMMARY OF THE TOWN
ASPECTS PROBLEMS VISUALS POTENTIALS POLICIES STATUS
FACTS CAUSES IMPLICATIONS
40.33% i.e. 28.6sqkm. of Due to the absence of Absence of bye laws and Vertical expansion of the cities can Pradhan Mantri Under pradhan mantri
Housing the city residential area is proper directions, development regulation can lead help in catering the future Awas Yojana awas yojna total invested
unplanned, unauthorized management, rule and to increase in unplanned growth population because of lack of vacant amount was 358 crores in
and lacking in basic regulation development viz a viz due to land within the municipal limits for which 103.34 crores
infrastructural facilities. Push or pull factor in unplanned growth, it is further developing the assistance has been
Continuous increase in the search of jobs and for impossible to help during housing. sanctioned under which a
inter state migrants i.e. betterment of lifestyle. disasters in area like walled city. The walled city area covered under total of 40.46 crores
8.5% of the total Leads to increase of housing redevelopment schemes is merely assistance has been
population of the city ( demand ( leads to housing 5.3% of the total walled city area released.
considered in amritsar shortage ) and due to low socio and 4% of the total area developed
master plan 2031 ) is economic condition slum under schemes of Amritsar
109789. population also increase. Improvement Trust.
High rise development is required for
proper utilization of land and to
accommodate the future population by
increasing the FAR of the city.
This picture depicts the condition of walled
city i.e narrow road, high density etc.
Slums 30% of city population Lack of affordable Rapidly increase in slums area By implementing slums schemes , the Valmiki 1400 one room tenements
live in slum. housing. which affects the aesthetic slums must be upgraded to improve ambedkar awas is being conntructed
Vacant plots are used as .Poor solid waste condition of area. the living condition of the slums yojana under VAMBAY scheme
dumping site. management. People are getting sick which dewellers. which costs rs 103000000
27% of the people living Due to contaminated and leads to increase in death rate. Slums should be eradicated and
in the slums area are polluted supply of water. housing should be provided in outer
affected by the water born area having low density and land price
diseases. and have access to all basic
infrastructure
This picture depicts the slums condition i.e.
un-hygiene living condition
Rajneet Kaur Ritik Sharma Neha Bharti Sheet No
B. Plan
Pragyan Galhotra Rydhima Sharma
5th semester
Sachin Sharma Prabhseerat
Session: 2020-21 Kaur Arvind Kumar Verma Kirti Kehra
GBU 304 :MASTER PLAN(AMRITSAR) Guru Ram Das School of Planning
Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar
SUMMARY OF THE TOWN
ASPECTS PROBLEMS VISUALS POTENTIALS POLICIES STATUS
FACTS CAUSES IMPLICATIONS
Industry Unavailability of warehouse Shortage of land Decrease in Amritsar has strong textile MSE Cluster Special
and storage areas production of goods. industries which has the Development funding under
Rising cost of operation . basic need boost in Programme the Punjab
The industrial growth has Shortage of labour This has lead to the economy. industrial
slowed down in the past few process of Credit Guarantee for policy for
years . The growth of deindustrialization Industries have been found Micro & Small improvement
industrial units have been to be the prime movers of Enterprises of industrial
found to be varying between the physical and economic (CGTMSE) infrastructure
0.31% to 1.23%. growth of the urban area.
Absence of filters This table depicts detailed of pollutants caused by industries Pradhan Mantri
Industries produce pollutants Gareeb Kalyan
like sulpjhur dioxide and Yojana.
hydrogen sulphide etc Harmful in nature
Punjab industry
policy 2017.
New vallah mandi is facing These mandis are serving There is no much Shopping and commercial Foreign trade policy The
Trade & Commerce the problem of drainage as such a huge area but facing development of mandis areas reflect the economy or International existing
well as has a improper various problems and are and markets in and the image of city. trade policy. policy was
arrangement of mandis. deficient of infrastructure. Amritsar so it leads to This import and export National trade extended by a
Lack of hygiene. In old market area, there congestion and rise in increases the relation or policy year due to
Abandoned building at old are some of the shop many diseases interaction of Amritsar Covid-19,
vegetable markket serves. keepers which are still The abandoned with other areas which is which was to
doing buildings in this old an important factor of end on March
mandi area which is not development for any city. 31. And the
maintained are serving Amritsar is famous for the government
This picture depicts the drainage problem in Vallah Mandi.
the places for criminals trade of crops mainly for decided to
and druggists. wheat and paddy. further extend
it for 6 more
months.The cu
rrent policy
will now be
valid upto
September 30.
This picture depicts the abandoned buildings near Vallah
Mandi.
Rajneet Kaur Ritik Sharma Neha Bharti Sheet No
B. Plan
Pragyan Galhotra Rydhima Sharma
5th semester
GBU 304 :MASTER PLAN(AMRITSAR) Session: 2020-21
Sachin Sharma Prabhseerat
Kaur Arvind Kumar Verma Kirti Kehra
Guru Ram Das School of Planning
Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar
SUMMARY OF THE TOWN
ASPECTS PROBLEMS VISUALS POTENTIALS POLICIES STATUS
FACTS CAUSES IMPLICATIONS
•Traffic and • Number of private • Poor condition of public • Maximum traffic congestions • High degree of rail, Motor vehicle Act • The act is partially implemented
Transportation vehicles on roads transport system and can be seen in the city road and air Provision: in the city but with low fines as
increasing affordability of people for accessibility with all • To limit speed it did not want to burden on
buying vehicles is increasing major destinations of • Give driving people of the city. To limit the
the country. regulation speed of vehicles only speed
limit signage are provided on
• Ajnala road has • V/C ratio of Ajnala road is 1.2 • Over utilization leads to • NH1- and NH-15 is NH and SH. No signage board
higher traffic volume which is over utilized and these congestion, accidents, delay passing through for speed limit for internal roads
with respect to its roads carry the traffic of all the and pollution. Amritsar making it Punjab road safety provided.
capacity which creates local streets better connectivity rules • Punjab road safety act is also
problems. with other areas. • To impart partially implemented in the city
knowledge of as there is No special provision
VC Ratio at 5 cordon points is there for controlling road
traffic rules and
create awareness accidents. To create awareness
among public. among public few signage and
• Roads are encroached • There is no separate space for •To provide boards are provided adjacent to
• Blocking the path for
by informal sector the informal sector equipment and roads.
pedestrians as well as for
vehicles. vehicles for
enforcement and • NUTP is partially implemented
controlling road in Amritsar because till now no
accidents provision of footpaths in
National urban majority of roads for pedestrian
transport policy and No Intelligent Transport
• Encouraging system is there in the city.
integrated land use
Encroachment by fruit vendors near St.
and transport
Paul Church, Amritsar
planning in order
to reduce distance
• Presence of critical • Absence and non working of • Causes accidents that can be
• Encourage grater
junctions such as traffic signals. injurious or fatal also.
use of public
Kacheri chowk,
transport
Hussianpura chowk
• Introducing
etc.
Intelligent
Transport System
for traffic
management.
Absence of traffic signal at Kacheri
chowk
Rajneet Kaur Ritik Sharma Neha Bharti Sheet No
B. Plan
th Pragyan Galhotra Rydhima Sharma
5 semester
GBU 304 :MASTER PLAN(AMRITSAR) Session: 2020-21
Sachin Sharma Prabhseerat
Kaur Arvind Kumar Verma Kirti Kehra
Guru Ram Das School of Planning
Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar
SUMMARY OF THE TOWN
ASPECTS` PROBLEMS VISUALS POTENTIALS POLICIES STATUS
FACTS CAUSES IMPLICATIONS
Informal sector Improper solid waste Lack of financial management Facilities available within Most of the population is National The National Education
management. ,deficient municipal the city are limited which engaged in commercial activities education policy Policy 2020, outlines the
Lack of infrastructures results in cause of many in Amritsar which acts as a . Formal Non vision of India's new
infrastructure and Insufficient provision of disease . potential for the employment for Formal education education system. The
sitting facilities. development resources and generation. Ministry of policy aims to transform
The disposbles sites inefficiency of develeopment Goods are available at very cheap Labour & India's education system by
and dustbins places. labour as well as poor repair No proper maintaince of rate then the formal sectors Employment 2040.
Poor quality of life- and maintenance. informal sector. It gives the employment and The policy was formulated
lacking edu., health, Poverty, Lack of resources . This picture depicts the solid waste problem in helps in increasing the household with the basic objective of
basic utilities Uncontrolled Peri-urban areas Hall Bazaar. income. suitably rehabilitating the
Housing demand and supply children withdrawn from
gap employment thereby
reducing the incidence of
child labour in areas of
known concentration of
child labour.
This picture depicts the problem of solid waste.
Rajneet Kaur Ritik Sharma Neha Bharti Sheet No
B. Plan
Pragyan Galhotra Rydhima Sharma
5th semester
GBU 304 :MASTER PLAN(AMRITSAR) Session: 2020-21
Sachin Sharma Prabhseerat
Kaur Arvind Kumar Verma Kirti Kehra
Guru Ram Das School of Planning
Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar
SUMMARY OF THE TOWN
ASPECTS PROBLEMS VISUALS POTENTIALS POLICIES STATUS
FACTS CAUSES IMPLICATIONS
Water supply Wastage of water Unmetered water connection Drop in ground water 80% of population and area is National water
Poor maintenance of service table. covered. policy
20% of area and network. The area which is not served Swachh bharat
population is not The area which is not served includes most of the agricultural abhiyan
covered is generally agricultural land land.
Sewerage Use of drains/water There is no sewerage Water pollution due to National policy on
bodies for disposal treatment plant. disposal of untreated Faecal sludge and
of untreated sullage. Absence of recycling and sullage. separate managment
reuse of waste water
techniques.
Solid waste Bins are not Bins are overutilized or under Health issues due to Solid waste
management maintained properly utilized disposal site surroundings. management rules
Various type of There is no proper
waste gets mixed segregation process.
Land use around Disposal site is over flowing
disposal site is
adversely affected.
Drainage system Outflow of storm Lack of new techniques, such Traffic congestion due to Drainage and
water as rainwater harvesting, water logging. sanitation law and
Only 10% of the which can ultimately help in policy
area is covered by reducing the outflow of storm
drainage network water.
that is Walled City. Water logging problem in
different areas.
Electricity Electricity wires are Poor maintenance of Risk of life. The core area of the town is National electricity
hanging at various electricity network.. completely served with all the policy
places. infrastructure facilities.
There is a direct supply of electricity
to the industries and the surrounding
areas through the electric substation
provided at focal point.
Rajneet Kaur Ritik Sharma Neha Bharti Sheet No
B. Plan
Pragyan Galhotra Rydhima Sharma
5th semester
Sachin Sharma Prabhseerat
Session: 2020-21 Kaur Arvind Kumar Verma Kirti Kehra
GBU 304 :MASTER PLAN(AMRITSAR) Guru Ram Das School of Planning
Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar
SUMMARY OF THE TOWN
ASPECTS PROBLEMS VISUALS POTENTIALS POLICIES STATUS
FACTS CAUSES IMPLICATIONS
Social 75% of the shopkeepers do Low government funding. Public littering. Most of the hospitals and Awaz health
infrastructure not have access to the public . nursing homes are private insurance scheme
toilets in the showrooms, players and they serve the Ayushman bharat
eating outlets etc area beyond the city too. programme
Some hospitals, education Due to narrow streets and Can cause delay to Banks serve 85% of city
facilites are located on narrow on street parking. patients and students. and also the population
streets having mixed landuse, living outside the city.
which create traffic at peak National education
hours because of on street policy 2020
parking of vehicle.
This image deoicts on street parking outside dav public
school.
Amritsar forms segmental Origin of roads is from the Roads are not linear, Ranjit Avenue, Green The Amritsar The new
urban pattern and ring shape. centre of Amritsar. and the city has more Avenue, Lawrence Road Municipal development in
than one exit and entry etc. are well designed Corporation Building the city will be
points. with respect to buildings Bye-Laws, 1997 approved under
Skyline is not uniform in byelaws and zoning this law.
walled city and buildings regulations.
have height of g+1, g+2. Walled city is ancient, It differs the walled city Khalsa College and Guru
planned and not renovated from other urban centre Nanak Dev University, they
except the city walk . . of Amritsar . both are maintained and
Urban design properly landscaped. In
these structure the balance
between mass and voids are
maintained.
a) Inner lanes of walled city
depicting non-uniform
skyline .
Rajneet Kaur Ritik Sharma Neha Bharti Sheet No
B. Plan
Pragyan Galhotra Rydhima Sharma
5th semester
Sachin Sharma Prabhseerat
Session: 2020-21 Kaur Arvind Kumar Verma
Kirti Kehra
Guru Ram Das School of Planning
Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar
SUMMARY OF THE TOWN
ASPECTS PROBLEMS VISUALS POTENTIALS POLICIES STATUS
FACTS CAUSES IMPLICATIONS
Tourism Lack of parking and Due to narrow streets and Contributes to city The city is an important landmark Amritsar cultural and
traffic congestion dead end pattern. economy. when it comes to religious tourism and
cluster of wall city destinations, cultural heritage, development act
national integrity of India and
India’s struggle for independence
from British rule in the early 20th
century.
The tourist spots have a architecture
structure that the tourists attracts,
such as bazaars, kuchas, katra and
mohals which has leads to narrow
street patterns and dead ends of
streets (for safety).
Large number of Tourist inflow
contributes to city economy.
The 12 gates are in No measures are being Quality of the visitor Important Landmarks such as Guru National Heritage The gates are
dilapidated adopted to conserve them and experience decreases. Nanak Dev University, Khalsa City Development under construction
condition. lack of public awareness college, are still in giood condition Augmentation .
due to timely renovations and Yojana (HRIDAY)
Architecture style differs. maintenance. scheme.
Facade features of The city is not looking Amritsar’s rich heritage helps in
old buildings in aesthetically pleasing in maintaining the economy of city.
walled city does not terms of architecture. Various Melas are still in existence
compliment the new and are helping in the conservation
built buildings. of rich culture of Punjab
Heritage and
conservation
b) Gate of walled city under
construction
Rajneet Kaur Ritik Sharma Neha Bharti Sheet No
B. Plan
Pragyan Galhotra Rydhima Sharma
5th semester
Sachin Sharma Prabhseerat
Session: 2020-21 Kaur Arvind Kumar Verma Kirti Kehra
GBU 304 :MASTER PLAN(AMRITSAR) Guru Ram Das School of Planning
Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar
SUMMARY OF THE TOWN
ASPECTS PROBLEMS VISUALS POTENTIALS POLICIES STATUS
FACTS CAUSES IMPLICATIONS
• Disaster Regular occurrence of Non-implementation of fire Cause huge loss to human and 32 wards in the city are under low risk Disaster management This act is fully
Management fire in walled city. safety norms as part of building property life of disaster. The wards are: act,2005 implemented in city.
byelaws. 1,4,5,6,7,15,16,17,31,30,33,34,35,36,3 • For planning and
7,38,39,23,25,29,56,57,58,59,60,61,62 implementation of
,63,64,65,51, disaster plans
• To prevent or mitigate
people from disaster
affected areas
• To respond and
recover from disaster
events
. Fire disaster in walled city
ENVIRONMENT The industries are Due to organic growth of the Creating noise pollution There are some green category Environmental It is implemented
located within the town and violating the bye- and making the land use industries which creates less Protection Act 1986 throughout India.
residential area laws incompatible pollution.
(refer figure 1)
No trees are planted along the Creates air pollution and It is not completely
There is no buffer industries like textile industry. degrades the environment. Swachh Bharat implemented due
zone near the red Program. to lack of support
category industries from government
on Chhehrata road. Presence of solid waste and This picture is showing the industry within residential area. department and
other waste creating land It has lead to health also from the
pollution. problems to about 50,000 people of town.
The dumping ground people living in the locality.
is the source of
many diseases in the
Bhagtanwala dump
site. (refer figure 2)
This picture is showing the land pollution at
Bhagtanwala Site.
Rajneet Kaur Ritik Sharma Neha Bharti Sheet No
B. Plan
th Pragyan Galhotra Rydhima Sharma
5 semester
GBU 304 :MASTER PLAN(AMRITSAR) Session: 2020-21
Sachin Sharma Prabhseerat
Kaur Arvind Kumar Verma Kirti Kehra
Guru Ram Das School of Planning
Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar
VISION AND SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES
VISION SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES
Improving the
condition of
slums under
Rehabilition
VAMBHAY
1. scheme.
Develop Town as
Hub of Trade and
Commerce.
Increasing
2. To increase number of
the
recreational AMRITSAR textile
Promoting industries and
Industries. area in the promoting IT
city. hub.
3.
Improving Slums
and Providing
Affordable
Housing. Providing the
infrastructure
to informal
sector.
Rajneet Kaur Ritik Sharma Neha Bharti Sheet No
B. Plan
Pragyan Galhotra Rydhima Sharma
5th semester
Sachin Sharma Prabhseerat
Session: 2020-21 Kaur Arvind Kumar Verma Kirti Kehra
GBU 304 :MASTER PLAN(AMRITSAR) Guru Ram Das School of Planning
Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar
POPULATION PROJECTIONS
LPA PROJECTIONS(2021)
POPULATION PROJECTIONS
Arithmetical Increase Method:-
Year Population Incremental Growth rate This method is used when the population is increasing at the constant rate or the rate of change of
population with the time is constant. PN= P+N * C
1951 336114 - - P=Present population, N= Number of decades
1961 390055 53941 16.04 C= Average increase in population, PN= Future population.
1971 454805 64750 16.60 1). LPA projections for 2021 .
1981 594844 140039 30.79 Year Population Increase in Year Projected
1991 708835 113991 19.16 population (C) population
2001 1003917 295082 41.62 1981 - 2021 (2014626+1*352288)
957761
2011 1132383 128466 12.79 1991 99409 =2366914
1057170
2001 1660466 603296 The LPA population for year
• GEOMETRIC INCREASE METHOD 2011 2014626 354160 2021 according to arithmetical
Population projections with geometric increase method PN=P(1+GR/100)*N increase method =2366914
Total 5390023 352288
Year Projected population Projected growth rate
1132383(1+25.04/100)*1 NOTE: We have calculated local planning are population projections of 2021 by taking 2011 as the
2021 Assuming 25.04 base year.
=1415931.70 =1415932
1415932(1+26.21/100)*1 2). LPA projections of 2041.
2031 Assuming 26.21
=1786507
1786507 (1+27.14/100)*1 Year Population Increase in Year Projected
2041 Assuming 27.14
=2271364.99 = 2271365
population (C) population
NOTE: We have calculated population projections of 2021 by taking 2011 as the base year. 1981 957761 - 2041 (2366914+2*352288)
The projections of 2041 are calculated by taking 2021 and 2031 as the base years. =3071490
1991 1057170 99409
2001 1660466 603296
Basis- population projection The LPA population for year 2041
Due to the development of Amritsar as an industrial hub. 2011 2014626 354160 according to arithmetical increase
method =3071490
Implementation of government policies in housing, industrial and especially in environmental 2021
sector. 2366914 352288
Provision of adequate infrastructural facilities will attract more population. Total 352288
NOTE: The projections of 2041 are calculated by taking 2021 and 2031 as the base years.
Rajneet Kaur Ritik Sharma Neha Bharti Sheet No
B. Plan
Pragyan Galhotra Rydhima Sharma
5th semester
Sachin Sharma Prabhseerat Kaur
Session: 2020-21 Arvind Kumar Verma Kirti Kehra
GBU 304 :MASTER PLAN(AMRITSAR) Guru Ram Das School of Planning
Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar
WORKFORCE PROJECTIONS
WORKFORCE PROJECTION
GEOMETRIC INCREASE METHOD
Workforce projections with geometric increase method.
Year Primary Secondary Tertiary Total Total
Workforce Population
Year Projected Workforce Growth rate
1981 8415 (27.7%) 5376(17.7%) 16531(54.5%) 30322 594844
2021 428364(1+51.78/100)*1 51.78
= 650170
1991 17008(26.6%) 483(0.7%) 46293(72.5%) 63784 708835
2031 650170(1+53.67/100)*1 53.67
2001 7405(2.5%) 12100(4.14%) 272271(93.3%) 291776 1003917 =999116
2011 14044(3.71%) 16710(4.4%) 347352(91.8%) 378106 1132383 2041 999116(1+55.41/100)*1 55.41
= 1207632
Assumed per cent of primary sector: 20%
Therefore, 20/100*1207632=241526 The city has potential of boosting economy both from tertiary and secondary sector as city is
Assumed per cent of secondary sector: 50% because the vision is focusing on increasing industries historical place and has many tourist destination. Around 1lakh tourist (approx) comes to city
Therefore, 50/100*1207632=603816 everyday because of this employment opportunities increases which attract people to do avail
Assumed per cent of tertiary sector: 30%, 30/100*1207632=362289 employment opportunity. Also city has potential regarding industries. By increasing number of
industries (which is our vision) employment opportunities will increase this way the secondary
sector will also increase thus economy of city will boost thus workforce of city will increase.
Year Workforce Increment Growth rate
NOTE: We have calculated workforce projections of 2021 by taking 2011 as the base year.
1981 179282 - The workforce projections of 2041 are calculated by taking 2021 and 2031 as the base years.
1991 213459 34177 19.06
2001 310961 97502 45.67
2011 428364 117403 49.67
Rajneet Kaur Ritik Sharma Neha Bharti Sheet No
B. Plan
Pragyan Galhotra Rydhima Sharma
5th semester
Sachin Sharma Prabhseerat Kaur
Session: 2020-21 Arvind Kumar Verma Kirti Kehra
GBU 304 :MASTER PLAN(AMRITSAR) Guru Ram Das School of Planning
Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar
REQUIREMENTS
Additional U.R.D.P.F.I
2011 2021 Proposed(2041) Area Guidelines
Area Area Area Area
COMPONENTS (Acre) Percentage (Acre) Percentage (Acre) Percentage (Acre) Percentage
Residential 10489 51.79 14527 53.52 26420 63.07 11893 35-40
Commercial 971 4.78 1675 6.17 2900 6.94 1225 4-5
1334
Industrial 1099 5.41 4.91 2228 5.33 894 12-14
Public/Semi-Public 1823 8.9 2211 8.14 2211 5.29 - 14-16
Recreational 306 1.50 691 2.57 1322 3.16 631 20-25
Circulation 3429 16.89 4526 16.7 4526 11 - 15-18
Government Land 2179 10.73 2179 8.02 2179 5.21 -
Total 20296 100 27143 100 41786 100 100
Basis and Assumptions
Residential : Recreational:
• Population increases because the city will grow so adequate housing is required to fulfil the demands of • To give planned open spaces and parks for creating a pleasant environment.
increasing population. Government Land:
• To avoid the scattered development and slums, so enough land has been provided in the residential. • Cantonment area comes under the government land.
• Also provision of housing and housing shortage can be removed.
Commercial: According to our vision we have propose additional area for Residential, Commercial, Industrial and
Recreational.
• City needs a planned informal sector. The percentage of residential area increased from 53.525% to 63.07%, commercial percentage
Industries : increased from 6.17% to 6.94%, percentage for industrial increased from 4.91% to 5.33 whereas
recreational percentage increased from 2.57% to 3.16%
• As per vision, to boost the economy industrial area is proposed.
Rajneet Kaur Ritik Sharma Neha Bharti Sheet No
B. Plan
Pragyan Galhotra Rydhima Sharma
5th semester
GBU 304 :MASTER PLAN(AMRITSAR) Session: 2020-21
Sachin Sharma Prabhseerat
Kaur Arvind Kumar Verma Kirti Kehra
Guru Ram Das School of Planning
Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar
REQUIREMENTS
HOUSING REQUIREMENT
Total housing area = 7944 hec
M.C. Circulation area (18%) = 1430 hec
Total projected population 2271365 Park area (20%) = 1588 hec
Total neighborhood area = 10962 Hectare
Households for projected population 454273
Total houses for projected 454273/1.2= Basics
population(DUR=1.2) 378561 • Proposed high density for lower class and low density for higher class because high class live
Existing houses 279931 in plots and low class live in flats.
• According to the projection,2271365 Population are projected and the family size is
Housing demand 98630
considering 5 according to the town scenario than we calculate the number of household.
Existing shortage of houses 55986
Assumption
Total Housing Demand 154616 • Assumed for HIG 20% and area of plot is 325 sq.m
• Assumed for MIG 50% and area of plot is 225 sq.m
Computed value
• Assumed for LIG 22% and area of flat is 120 sq.m
No .of houses
• Assumed for EWS 8% and area of flat is 75 sq.m
Area of • Dwelling unit ratio is an assumed 1.20 that means the 20% of the population are in joint
one plot Assume Area of family or tenant.
Class Existing % Area
(assumed) d % flat Plots Flats plots Total area
227 % plot of flats • This value is taken with the future prediction because in the future most of the family will get
(sq.m.) % nuclear rather than joint it is only due to the follow of western culture by the Indian people.
HIG 25% 325 20% 100 - 75711 - - 2460 2460 • In Amritsar 55986 housing shortage is there and after all the calculation we will find the
50% housing demand i.e 154616.
MIG 55% 225 100 - 189280 - - 4258 4258
LIG 18% 120 22% - 100 - 83283 999 - 999
EWS 2% 75 8% - 100 - 30284 227 - 227
Computed value
Rajneet Kaur Ritik Sharma Neha Bharti Sheet No
B. Plan
Pragyan Galhotra Rydhima Sharma
5th semester
Sachin Sharma Prabhseerat Kaur
Session: 2020-21 Arvind Kumar Verma Kirti Kehra
GBU 304 :MASTER PLAN(AMRITSAR) Guru Ram Das School of Planning
Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar
INDUSTRY REQUIREMENT REQUIREMENTS
Industry Percentage Percentage Proposed
of existing of proposed area (Acre) RECREATIONAL REQUIREMENTS
industry industry
Proposed Recreational Area
Red 54% 40% 622
industry Recreational Components Components in Number Total Area
Orange 5.80% 5% 135 Neighbourhood Play Area 2 7.4 Acre
industry Parks and Playgrounds 2 4.9 Acre
Green 39.4% 6% 147 District Park 2 123 Acre
industry
Sub City Park 2 494 Acre
Total Area 894
Year Projected Workforce Growth Total 8 631 Acre
rate
2021 428364(1+51.78/100)* 51.78
1= 650170 Existing recreational
• Existing recreational area of Amritsar is 691 Acre which is 2.57% of total build up area which mean the
2031 650170(1+53.67/100)* 53.67
city lacks in the provision of recreational spaces, which requires attention
1=999116 • There are mainly three recreational spaces in the city, namely, Ram Bagh Garden located in the north of
2041 999116(1+55.41/100)* 55.41 the city, Gol Bagh and Saktri Bagh in the south of the city.
1= 1207632 • There is one stadium commonly known as Gandhi Ground present in the city located on M.M. Malviya
Road. Apart from these, there are small parks/ playgrounds located within the planned residential
Basis: colonies/areas of the city
• According to standards we need 20-25% of recreational area because Amritsar have more than 10 lakh
Since 1991 about 200 units have been already closed down leaving more than 8000 workers jobless in population so Amritsar is considered as Metropolitan city.
industries , it is estimated that another 175 units may also close down due to import of clothes and Covid-19.
Proposed recreational area
That’s why we proposing more of textile and I.T industry • All recreational area proposed is within the M.C. limit.
•Textile industry : Textile industry primarily concerned with design, production and distribution of clothes, • Proposed recreational area for 2041 is 630 Acre. After proposed recreational area would be 1332 Acre.
• One sub city park of cultural and sports has been proposed near Verka bypass road.
yarn and clothing. Because of the high tourist inflow and demand of traditional clothing in Amritsar, so we • One sub city park has been proposed near Gurudwara Bohri road passing through Haripura main road.
will propose these industry.
•I.T industry : I.T industry is comprised of companies that produce software, hardware, or semiconductor
equipment or companies that provide internet or related services. I.T sector is considered to be a major factor
for economic development, in the addition , it also helps in growth of service sector and provide employment to
innumerable men and women.
Rajneet Kaur Ritik Sharma Neha Bharti Sheet No
B. Plan
Pragyan Galhotra Rydhima Sharma
5th semester
Sachin Sharma Prabhseerat Kaur
Session: 2020-21 Arvind Kumar Verma Kirti Kehra
GBU 304 :MASTER PLAN(AMRITSAR) Guru Ram Das School of Planning
Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar
SOCIAL INFRASTRUCTURE REQUIREMENTS
Rajneet Kaur Ritik Sharma Neha Bharti Sheet No
B. Plan
Pragyan Galhotra Rydhima Sharma
5th semester
Sachin Sharma Prabhseerat
Session: 2020-21 Kaur Arvind Kumar Verma Kirti Kehra
GBU 304 :MASTER PLAN(AMRITSAR) Guru Ram Das School of Planning
Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar
SUMMARY OF THE TOWN
COMPONENTS PROPOSALS TOTAL AREA (ACRE) FINANCIAL AND GOVERNMENT POLICIES
ORGANIZATIONAL STRATEGIES
RESIDENTIAL To provide affordable housing to EWS and LIG 11893 Finance: MC funds, funding from Pradhan Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana, Valmiki ambedkar
mantri awas yojna. awas yojana,
Organization: Municipal corporation, Amritsar
development authority.
COMMERCIAL Setting up of informal sector 1225 Finance: Municipal corporation Street vendor policy.
Organization: Municipal corporation
INUSTRIES Setting up of new textile industries and 894 Finance : Private authorities MSE Cluster Development Programme,Credit
information technology park in Amritsar. Organization: Private authorities Guarantee for Micro & Small Enterprises
(CGTMSE) ,Pradhan Mantri Gareeb Kalyan
Yojana.,Punjab industry policy 2017.
RECREATIONAL a. Neighbourhood Play Area 631 Finance: Funds from the state government. National landuse policy.
b. Parks and Playgrounds Organization: Amritsar Development Authority
c. District Park
d. Sub City Park
TRAFFIC AND TRANSPORTATION a. Improving the intersection of Kacheri Finance: MC own sources which include Punjab road safety rules
chowk: The intersection will be improved by property taxes, advertisement taxes. Additionally
providing signage boards, traffic signals in municipal development fund can be utilised as • To impart knowledge of traffic rules and create
all the sub stretches that are included in this well awareness among public.
road Organization: Amritsar municipal corporation
b. Redesign of Ajnala road: The redesign of • To provide equipment and vehicles for
cross section of Ajnala road is proposed Finance: enforcement and controlling road accidents
which includes the parking on both sides and MC own sources which include property taxes,
length of footpath is increased by 2m on both advertisement taxes. Additionally municipal
sides. development fund can be utilised as well
Organization:
Amritsar municipal corporation
.
Rajneet Kaur Ritik Sharma Neha Bharti Sheet No
B. Plan
Pragyan Galhotra Rydhima Sharma
5th semester
GBU 304 :MASTER PLAN(AMRITSAR) Session: 2021-22
Sachin Sharma Prabhseerat
Kaur Arvind Kumar Verma Kirti Kehra
Guru Ram Das School of Planning
Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar
REQUIREMENTS
Rajneet Kaur Ritik Sharma Neha Bharti Sheet No
B. Plan
Pragyan Galhotra Rydhima Sharma
5th semester
Sachin Sharma Prabhseerat Kaur
Session: 2020-21 Arvind Kumar Verma Kirti Kehra
GBU 304 :MASTER PLAN(AMRITSAR) Guru Ram Das School of Planning
Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar
REQUIREMENTS
Rajneet Kaur Ritik Sharma Neha Bharti Sheet No
B. Plan
Pragyan Galhotra Rydhima Sharma
5th semester
Sachin Sharma Prabhseerat Kaur
Session: 2020-21 Arvind Kumar Verma Kirti Kehra
GBU 304 :MASTER PLAN(AMRITSAR) Guru Ram Das School of Planning
Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar
PHASING
Phase I – 2021-2026
Phase II – 2026-2031
Phase III – 2031-2036
Phase IV – 2036-2041
PHASE I (2021-2026)
In phase I of the plan is fully dedicated to the development and improvement of road infrastructure such as traffic signals and for providing a separate place for street
vendors.It is always in first place to improve the basic infrastructure for any settlement to attain good living environment. For the same matter following proposals to be
attained in the first phase;
Traffic signals will be provided.
A separate informal sector will be laid.
These proposals are done in these schemes given below
Street vendors policy.
PHASE II (2026-2031)
This phase has been decided on the basis of generate economy for future development and to provide affordable housing, improving the Following goals is to be met in the
second phase of the plan;
Providing affordable housing for LIG and EWS group.
Laying down of a textile industry
These proposals are done in these schemes given below
VAMBAY scheme
PHASE III (2031-2036)
In the third phase the attention will be given towards open spaces and recreational area.In the third phase of the plan following goals are to be met;
Providing recreational area and open spaces.
These proposals are done in these schemes given below
Land use act
PHASE IV (2036-2041)
In the last five years’ rest of the development will take place comprising of new industries Again, in fourth phase these following goals are to be met which are
Laying down of Information technology park.
Rajneet Kaur Ritik Sharma Neha Bharti Sheet No
B. Plan
Pragyan Galhotra Rydhima Sharma
5th semester
Sachin Sharma Prabhseerat
Session: 2020-21 Kaur Arvind Kumar Verma Kirti Kehra
GBU 304 :MASTER PLAN(AMRITSAR) Guru Ram Das School of Planning
Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar
REQUIREMENTS
Rajneet Kaur Ritik Sharma Neha Bharti Sheet No
B. Plan
Pragyan Galhotra Rydhima Sharma
5th semester
Sachin Sharma Prabhseerat
Session: 2020-21 Kaur Arvind Kumar Verma Kirti Kehra
GBU 304 :MASTER PLAN(AMRITSAR) Guru Ram Das School of Planning
Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar
You might also like
- Master PlanDocument4 pagesMaster PlanSachin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Urban Planning and Development Practices of AUDADocument86 pagesUrban Planning and Development Practices of AUDAHarneet KaurNo ratings yet
- (Hortonworks University) HDP Developer Apache SparkDocument66 pages(Hortonworks University) HDP Developer Apache SparkHimanshu Sekhar Paul100% (1)
- Coefficients of Form - Ship's Waterplane, Block, Midship and Prismatic CoefficientDocument5 pagesCoefficients of Form - Ship's Waterplane, Block, Midship and Prismatic CoefficientGiorgi KandelakiNo ratings yet
- Creating A Painting RubricDocument1 pageCreating A Painting Rubricapi-376050083No ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument14 pagesAssignmentNasir HussainNo ratings yet
- Visakhapatnam Urban Development Authority: Revised Master Plan For Visakhapatnam Metropolitan Region - 2021Document348 pagesVisakhapatnam Urban Development Authority: Revised Master Plan For Visakhapatnam Metropolitan Region - 2021Vullapu sai sesidhar100% (2)
- Maharashtra Regional Town Planning Act 1Document42 pagesMaharashtra Regional Town Planning Act 1Upsc AspirantNo ratings yet
- Singapore Tax System and Tax RatesDocument10 pagesSingapore Tax System and Tax RatesshafirasrjNo ratings yet
- Revised Master Plan Mysore NanjangudDocument213 pagesRevised Master Plan Mysore NanjangudPruthvi Prakasha0% (1)
- DP 2030 PlanningDocument100 pagesDP 2030 PlanningSandip ShahNo ratings yet
- Day 1 - Dr. Morales - Praxis - May 2017Document77 pagesDay 1 - Dr. Morales - Praxis - May 2017BobbetLopezMolasNo ratings yet
- HRIDAY - Draft DPR - Jaipur Road Precinct-Compressed PDFDocument134 pagesHRIDAY - Draft DPR - Jaipur Road Precinct-Compressed PDF2018 mcoNo ratings yet
- Lecture Population EcologyDocument75 pagesLecture Population Ecologyrkv100% (3)
- Phonetic 1Document10 pagesPhonetic 1John Viondi MendozaNo ratings yet
- Training Presentation - Mandeep KaurDocument15 pagesTraining Presentation - Mandeep Kauralankrit sharmaNo ratings yet
- ProjectionsDocument7 pagesProjectionsوشال VISHALNo ratings yet
- Tender PDFDocument34 pagesTender PDFvatsalbu89No ratings yet
- Land Reservations For The Urban Poor The Case of Town Planning Schemes in AhmedabadDocument18 pagesLand Reservations For The Urban Poor The Case of Town Planning Schemes in AhmedabadAnkita VinchoorkarNo ratings yet
- Redevelopment of Machhabhaudi, Dharan, Sunsari: Project ProposalDocument10 pagesRedevelopment of Machhabhaudi, Dharan, Sunsari: Project Proposaldiwas baralNo ratings yet
- Rohit BharambeDocument2 pagesRohit BharambeRohit BharambeNo ratings yet
- +91 2227899484 (R) E-Mail:: Kedarnath Rao Ghorpade Tel: (Mobile) : +91 9967014432Document10 pages+91 2227899484 (R) E-Mail:: Kedarnath Rao Ghorpade Tel: (Mobile) : +91 9967014432srishyamdasNo ratings yet
- CRP Inception SriperumbudurDocument67 pagesCRP Inception SriperumbudurSudharsanamurthy PunniamurthyNo ratings yet
- GURPREET ReportDocument55 pagesGURPREET ReportChaudharies Creativity MindNo ratings yet
- Ring RoadDocument7 pagesRing Roaddhruv2222No ratings yet
- Final ReportDocument57 pagesFinal Reportmansi rawatNo ratings yet
- U19ce009 - Week 1 ReportDocument2 pagesU19ce009 - Week 1 ReportJanviNo ratings yet
- Mysore Master Plan Vol 2Document100 pagesMysore Master Plan Vol 2shahimabdu50% (2)
- Vishal Jain - Urband & Transport Planning PortfolioDocument10 pagesVishal Jain - Urband & Transport Planning PortfolioVishal JainNo ratings yet
- Informal Sector in Ludhiana: 2.1. Theoretical FrameworkDocument6 pagesInformal Sector in Ludhiana: 2.1. Theoretical FrameworkanandNo ratings yet
- ICETDACE 2020 - International Conference On Emerging Trends in Design, Architecture and Civil EngineeringDocument391 pagesICETDACE 2020 - International Conference On Emerging Trends in Design, Architecture and Civil EngineeringSVS ICNo ratings yet
- AdhvaryuB 2011 TheAhmedabadurbanDevelopmentPlan-makingprocess - Acriticalreview PlanningPracticeandResearch262229250Document24 pagesAdhvaryuB 2011 TheAhmedabadurbanDevelopmentPlan-makingprocess - Acriticalreview PlanningPracticeandResearch262229250aslamfathima.20No ratings yet
- The Ahmedabad Urban Development Plan-Making Process: A Critical ReviewDocument24 pagesThe Ahmedabad Urban Development Plan-Making Process: A Critical ReviewBhaskar BhatiaNo ratings yet
- 6Document28 pages6sumitNo ratings yet
- GUU/GIU-561:Planning Studio Master Plan For Indore M. Planning (Urban/Infrastructure) 2 SemesterDocument27 pagesGUU/GIU-561:Planning Studio Master Plan For Indore M. Planning (Urban/Infrastructure) 2 Semesterوشال VISHALNo ratings yet
- Chaitanya G SaiDocument6 pagesChaitanya G SaivasaganeshNo ratings yet
- Smart Highway, Smart CityDocument21 pagesSmart Highway, Smart Citytannu singhNo ratings yet
- Sustainable City-Amravati EditedDocument23 pagesSustainable City-Amravati EditedMoeez Hasan Nawab100% (1)
- Bridges Specs 10.11.14Document300 pagesBridges Specs 10.11.14Saurabh PednekarNo ratings yet
- CV Mohaneesh Feb 2020 GenDocument3 pagesCV Mohaneesh Feb 2020 GenMohaneeshNo ratings yet
- Metro Region DP PDFDocument627 pagesMetro Region DP PDFpushpak navandarNo ratings yet
- Mughal Medieval CitiesDocument38 pagesMughal Medieval Citiesvivedaa100% (1)
- Comprehensive StrategiesDocument94 pagesComprehensive StrategiesShreyas SrivatsaNo ratings yet
- AMT RPT 2011 PDFDocument319 pagesAMT RPT 2011 PDFGurnoor Singh100% (1)
- Pravin B. Masalge: ObjectiveDocument3 pagesPravin B. Masalge: ObjectivePravin MasalgeNo ratings yet
- Final Report On City Development and Slum Upgradation Strategy of BengaluruDocument64 pagesFinal Report On City Development and Slum Upgradation Strategy of BengaluruKavya KaladharanNo ratings yet
- Ankur ResumeDocument3 pagesAnkur ResumeSarthak PunyarthiNo ratings yet
- Once More FinalDocument89 pagesOnce More FinaljhuggfdNo ratings yet
- AP Major City InfoDocument138 pagesAP Major City InfoAryaJyothiNo ratings yet
- Assistant Bridge Engineer: Krishna JangidDocument5 pagesAssistant Bridge Engineer: Krishna JangidAayush AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Draft Report Submission Sonali Hadke 2021mud021Document21 pagesDraft Report Submission Sonali Hadke 2021mud021SPIRITUAL CREATIVENo ratings yet
- CDP VasaivirarDocument194 pagesCDP VasaivirarKruti ShahNo ratings yet
- Ahmed Sadeed CVDocument3 pagesAhmed Sadeed CVTeam CUNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Management B.R.A.Biharuniversity, Muzaffarpur in The Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement For The Degree ofDocument56 pagesFaculty of Management B.R.A.Biharuniversity, Muzaffarpur in The Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement For The Degree ofHarsh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- DSRDocument210 pagesDSRwasim ahmedNo ratings yet
- BS (20BAR070) Week-2Document3 pagesBS (20BAR070) Week-2Stuti ParikhNo ratings yet
- 076MSurP006 ManishDocument92 pages076MSurP006 ManishAashutosh Raj TimilsenaNo ratings yet
- RCD - Receiving Letter - MuzaffarpurDocument1 pageRCD - Receiving Letter - MuzaffarpurPrabhat RanjanNo ratings yet
- MPSC Coep Online Training MRTP Act - TP Entr Exam PDFDocument148 pagesMPSC Coep Online Training MRTP Act - TP Entr Exam PDFShatrughna Bansi SangleNo ratings yet
- Orientation Training Programme IALADocument280 pagesOrientation Training Programme IALARaghuNo ratings yet
- Assessing Urban Open Spaces in Township PlanningDocument13 pagesAssessing Urban Open Spaces in Township PlanningInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- MUPG FlyerDocument1 pageMUPG FlyerShreya SinghaNo ratings yet
- Report ChandigarhDocument126 pagesReport ChandigarhAtul DevNo ratings yet
- Resume Haricharan 04062019Document3 pagesResume Haricharan 04062019Hari CharanNo ratings yet
- Gearing Up for Competitiveness: The Role of Planning, Governance, and Finance in Small and Medium-sized Cities in South AsiaFrom EverandGearing Up for Competitiveness: The Role of Planning, Governance, and Finance in Small and Medium-sized Cities in South AsiaNo ratings yet
- Master Plan Report AmritsarDocument64 pagesMaster Plan Report AmritsarAbhishek WattsNo ratings yet
- Rainwater HarvestingDocument52 pagesRainwater HarvestingAbhishek WattsNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Case StudyDocument24 pagesAnalysis and Case StudyAbhishek WattsNo ratings yet
- ADFEC FS Final SignedDocument98 pagesADFEC FS Final SignedAbhishek WattsNo ratings yet
- Amritsar Press ReleaseDocument3 pagesAmritsar Press ReleaseAbhishek WattsNo ratings yet
- Oil Extraction IndustryDocument1 pageOil Extraction IndustryAbhishek WattsNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction KineticsDocument4 pagesChemical Reaction KineticsMichaela BorjaNo ratings yet
- 05thjan Assignment Abroad TimesDocument8 pages05thjan Assignment Abroad TimesSameer ShaikNo ratings yet
- Delovio PDS ReclaDocument4 pagesDelovio PDS ReclaRene DelovioNo ratings yet
- P1 TransportationNepal SahadevDocument15 pagesP1 TransportationNepal SahadevRam Chandra GhimireNo ratings yet
- Abbott, Don Paul - Splendor and Misery - Semiotics and The End of RhetoricDocument22 pagesAbbott, Don Paul - Splendor and Misery - Semiotics and The End of RhetoricHonorato LoboNo ratings yet
- Immunity ProjectDocument9 pagesImmunity ProjectAditi ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Tarbuck 14th Edition Test BankDocument24 pagesEarth Science Tarbuck 14th Edition Test BankMichaelRobertskneda100% (27)
- How-To Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesHow-To Lesson Planapi-276590409No ratings yet
- Audit Fee Lowballing, Determinants, Recovery, and Future Audit QualityDocument24 pagesAudit Fee Lowballing, Determinants, Recovery, and Future Audit QualityErlisa AgustinaNo ratings yet
- Teaching English in The K To 12Document28 pagesTeaching English in The K To 12Rusty PadrequilNo ratings yet
- Icici PoDocument5 pagesIcici Potanujchopra1No ratings yet
- H800-1050HD/S SERIES Technical GuideDocument6 pagesH800-1050HD/S SERIES Technical GuideRaduNo ratings yet
- Overview of Modeling Studies in HDS, HDN, HDO CatalysisDocument16 pagesOverview of Modeling Studies in HDS, HDN, HDO Catalysisnguyennha1211No ratings yet
- The MailboxesDocument4 pagesThe MailboxesDayanaNo ratings yet
- Rockwell and Brinell Hardness of Metallic Materials by Portable Hardness TestersDocument5 pagesRockwell and Brinell Hardness of Metallic Materials by Portable Hardness TestersJones Pereira NetoNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Management On Indian Railways Through Knowledge PortalDocument20 pagesKnowledge Management On Indian Railways Through Knowledge PortalIndian Railways Knowledge PortalNo ratings yet
- RPP + LKS (Bagian 2)Document11 pagesRPP + LKS (Bagian 2)Mega Cries AceceNo ratings yet
- Updated - Actual Listening Test Vol 2 PDFDocument125 pagesUpdated - Actual Listening Test Vol 2 PDFFandi SaputraNo ratings yet
- HTTPS:WWW Ncbi NLM Nih gov:pmc:articles:PMC4804599:pdf:IDOJ-7-77Document10 pagesHTTPS:WWW Ncbi NLM Nih gov:pmc:articles:PMC4804599:pdf:IDOJ-7-77Riefka Ananda ZulfaNo ratings yet
- FeverDocument0 pagesFeverRegina SeptianiNo ratings yet
- "Probability": Arun Kumar, Ravindra Gokhale, and Nagarajan KrishnamurthyDocument53 pages"Probability": Arun Kumar, Ravindra Gokhale, and Nagarajan KrishnamurthyNirmal SasidharanNo ratings yet
- APB COT 2 2printDocument14 pagesAPB COT 2 2printanjelyka BNo ratings yet
- Package and Libraries: Cpe 487: Digital System DesignDocument14 pagesPackage and Libraries: Cpe 487: Digital System Designlakka273No ratings yet
- Body Composition Analysis of Animals - A Handbook of Non-Destructive MethodsDocument252 pagesBody Composition Analysis of Animals - A Handbook of Non-Destructive MethodsRogelio Avila100% (1)