Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reviewer in Contemporary World
Uploaded by
Carrie Anne Aquila Garcia0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesContemporary World Midterms
Original Title
REVIEWER IN CONTEMPORARY WORLD
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentContemporary World Midterms
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesReviewer in Contemporary World
Uploaded by
Carrie Anne Aquila GarciaContemporary World Midterms
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
REVIEWER IN opportunities economic the use for
CONTEMPORARY WORLD processes the future
(PRELIM) Growth for Reorganizing ii. Financial – a
countries social processes financial
Globalization – came from the root Development Failure to focus asset that is
word “globalize” which is the of the nations on one’s country used to be
interaction and integration of sold for
companies, people, and government Narrow and Exclusive higher cost
- Internationalization is a new d. Workforce – number
DEFINITIONS OF competitive way to being of people who are
GLOBALIZATION: globalized (Robert Cox) employed and who
Manfred Steger – expansion and - Limited point of view are looking for work
intensification - This usually starts trade wars i. Labor Force
Bauman – time immemorial - Protectionist stand is the age
Thomas Larsson – world shrinkage who are
Martin Khor – colonization ADVANTAGE DISADVANTA working and
S GES are willing to
TYPES OF GLOBALIZATION Focuses on one Trade wars work
ECONOMIC GLOBALIZATION country 4. Liberalization of Import and
- Trade and exchange of Enhancement Limited point of Export System – liberating
resources of policies view import and export system
- Movement of technology, Supported by Failure to 5. Privatization – equalization of
information, services, and people establish distribution by minimizing
capital connections ownership of production and
- Product, finance, markets, Gives distribution
corporations, and labor importance to 6. Increased collaborations –
the people and entrepreneurs collaborate
SOCIAL GLOBALIZATION the cultures 7. Economic Reforms – fiscal
- Human interaction and w/in the and financial reforms
cultural communities country
- Family, religion, work, and MERITS AND DEMERITS OF
education NATURE OF GLOBALIZATION GLOBALIZATION
- Information (meaning this is 1. Liberalization – freedom of MERITS
the fast flow of information entrepreneurs to venture local 1. Peaceful Relations
due to social media and or abroad “removing of 2. Employment
internet) controls” 3. Education
2. Free Trade – free flow trade 4. Product Quality
POLITICAL GLOBALIZATION relations 5. Cheaper price
- Political cooperation where 3. Globalization of Economic 6. Communication
countries unite in trade blocs Activity: 7. Transportation
- TRADE BLOCS – groups of a. International Trades – 8. GDP Increase
countries that provide rules refers to the trade a. Gross Domestic
for trade to all participating between at least two Product are products
countries countries produced within the
i. Import – country
*ENVIRONMENTAL from other b. Gross National
GLOBALIZATION* countries Product products that
- Internationally coordinated ii. Export – to are made outside of
rules and regulations other the country
regarding environmental countries c. Tariff -
protection b. Production – refers to 9. Free Trade – policy where
transforming countries levy taxes, quota,
The purpose of studying globalization intangible and and subsidies
is to understand the differences and tangible materials to 10. Tavel & Tourism
similarities of cultures and how we goods and services 11. External Borrowing
are connected in a separate world. i. Tangible
Inputs – DEMERITS
DEFINING GLOBALIZATION labor, capital, 1. Health Issues
raw a. Chronic Illnesses
Broad and Inclusive materials, b. Environmental
- Borderless World (Ohmae) land Illnesses
- This perspective sees how we ii. Intangible 2. Loss of Culture
can become connected with Inputs – 3. Uneven Wealth Distribution
each other ideas, 4. Environmental Degradation
- Defines the opportunities information, 5. Disparity – bigger companies
- May have political neglect knowledge move to areas where there is
ADVANTAGE DISADVANTA c. Investment – asset or lower cost labor while those
S GES item accrued w/ the who are starting are just
Equal Reshaping of goal of generating getting it for higher rates
opportunities government income and 6. Conflicts
institutions to recognition 7. Cut Throat Competition –
cater everyone i. Economic – the bigger the authority a
Secured Reorganizing purchase for
country has, the louder their c. Difficult to stop other becomes
way of advertising d. Continuous communal
a. Technological fluctuations 3. Ideology
Synergism a. Global Imaginary –
Liquidity and Solidity are two people’s growing
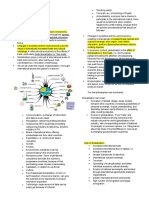
ASPECTS OF GLOBALIZATION interacting forces. Yet, one prevails consciousness that
Cultural Globalization that globalization is liquidity. they are not settled in
- Transmission of ideas, the parameters that
meanings and values FLOWS OF GLOBALIZATION they were placed on
- Common consumption 1. Culture Flows – different b. 6 core domains
relating to the use of social beliefs, music, food, etc. i. Nobody
media and international travel 2. Information Flows – refers to controls
- Spread of language, arts, the exchanges of knowledge globalization
information, food, ideas and and information from ii. Liberalizatio
technology anywhere n and
Economic Globalization integration of
- Economic mixing and CONCEPTS OF markets
interdependence that has flow GLOBALIZATION iii. Inevitable
of goods, services, and 1. Process and
technology a. Globalization – a set irreversible
Industrial Globalization of social processes iv. Benefits
- Specialization – countries that appear to everyone
producing that gives them the transform currently v. Democracy
benefit where they have weakening nationality vi. Requires war
competitive advantage to globality. on terror
- Eg. US specializes in military b. It is a process that is
equipment and Singapore driven by THEORETICAL PARADIGMS
specializes in pharmaceutical international trade WORLD SYSTEMS – views
Financial Globalization that is aided by globalization as a virtual rebirth and
- Emergence of worldwide information spread of world capitalism
financial markets and better technology
access to external financing c. Movement from one The Capitalist World
for corporate, national, and point to another 1. Core – powerful and
sub-national borrowers (Steger) developed
- IMF and the world bank i. Dynamism- 2. Periphery – subordinate to
- Foreign investors fund the Transformati core where they are colonized
projects within the country on- 3. Semi-periphery – either
Informational Globalization movement- moved down or moved up
- Information flows to many desctruction-
geographical areas in the creation THE GLOBAL ECONOMY
world d. Believed to have Economy – interrelated production,
Ecological Globalization existing through the distribution, and consumption;
- Ecological effects beginning of man determines scarcity
Globalization in Politics e. At the end of the 19th o Economic System –
- Resolving the rights and the century production, distribution and
law i. Gregorian consumption
Globalization in Technology Calendar Global Economy – sum of activities
- Communication despite the ii. Prime that take place in between both
distance Meridian countries
Geographical Globalization iii. International Economics – study of how humans
- Exploring different countries Date Line make decisions in the face of scarcity
through migration iv. World Time o Societal, Business, Family,
- MIGRATION zones Individual
2. Condition Scarcity – wants exceeds what is
METAPHORS OF a. Globality – social available
GLOBALIZATION condition with tight o Ultimate scarcity is TIME
1. SOLID economic and
a. Barriers that hinder political TWO TYPES OF ECONOMICS
globalization which interconnection and 1. Microeconomics
can be manmade or flow that makes the - Behavior of individual
natural current economic consumers and producers
b. Natural – mountains, boundaries 2. Macroeconomics
natural calamities irrelevant ; future - Overall economies that is
c. Manmade – nine dash social condition ; regional, national,
line, great wall of determines the international
China, berlin wall endpoint that
2. LIQUID precludes any INTERNATIONAL TRADE
a. Ease in flow of development - Exchange of goods across
movement of people, b. This is where borders
things, information globalization has its - Competition and pricing
b. Space and Time are limits that people also - Supports that no country can
crucial elements of be individualistic and supply on its own
globalization competitive while the
ADVANTAGES OF become competitive to lessen products made by citizen abroad and
INTERNATIONAL TRADES reliance on imports domestically
Michael P. Todaro and Stephen C. 4. Export Subsidy
Smith; Lieberman, Marc, & Robert - Financial assistance that is GDP or Gross Domestic Product –
Hall provided by a country to give goods within the country
Benefits to both importers and priority attention to porters
exporters WORLD’S FREE TRADE AREAS
(a) Gains where products are COMPONENTS OF 1. NAFTA
available in regions that lack INTERNATIONAL TRADE - North American free trade
(b) Short specialization gains 1. Import agreement
where production increases 2. Exports - Canada is the best exporter
purchasing power - January 1, 1994
(c) Result of dynamic gains is FACTORS AFFECTING - Three Nations: Canada,
being facilitated with ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT Mexico, US
technology 1. Human Resources 2. AFTA
(d) Political Spin Offs prevent 2. Natural Resources - Association of Southeast
hostilities and conflicts 3. Technological Development Asian Nations Free Trade
(e) Debt relief 4. Social and Political Factors Area
a. DIVISION OF - ORIGINAL MEMBERS:
THEORIES OF INTERNATIONAL LABOR – letting a Brunei, Thailand, Singapore,
TRADES worker focus on Philippines, Malaysia
1. Mercantilism specific tasks - RECENT: Myanmar, Laos,
- Gold and silver accumulation b. Social Factors – Vietnam, Cambodia
is the power and prestige customs, tradition, 3. European Union
- Reduce import and increase and beliefs - Single market
export so that there is increase c. Political factors – - No tariffs, quota or taxes
employment participation of
- Trade Surplus – basis of government FREE TRADE ISSUES
strength where a country d. GEOCULTURE 1. Protectionism – shielding
gains from exports than country’s products from
spending imports CAPITALISM – private ownership competition
2. Comparative Advantage for private profit (gain) 2. Economic Nationalism and
Theory Economic Patriotism –
- Competitive is products are Adam Smith – father of modern emphasized country’s
efficiently produced capitalism and influenced by Francois intervention with tariffs and
- EFFICIENT – lower price, Quesnay restriction
finest product quality, a. Nationalism
responsiveness of the product Francois Quesnay – founder of b. Patriotism
availability physiocratic school and based his
- What you do best giving up doctrines in natural laws, law and INTERNATIONAL
the least orders FINANCIAL INSTITUTION
3. Absolute Advantage Theory - Claimed that natural - International nonprofit
- A country producing products resources are vital in agencies are major financers
that is not available in other economic growth
countries is a total advantage - Argued that commerce and World Bank
4. Purchasing Power Parity industry is ineffective and - Multi national financing
Theory that only agriculture can raise company est. during WWII
- Gustav Cassel states that in wealth for long term capital
order to prevail equilibrium - Planning and financing
level between to countries, Laissez Faire – governmental non economic development
there should be one currency interference Purpose:
1. Assist in reconstruction and
REGULATION PLACED ON CHARACTERISTICS OF development
TRADES (as protectionist) CAPITALISM 2. Promote private foreign
1. Tariff 1. Right to own property investment w/ loans
- tax imposed by the 2. Freedom of competition 3. Long range balanced growth
government on foreign goods 3. Freedom of Enterprise and equilibrium in balance
produced abroad and sent 4. Freedom of Cooperation 4. Conduct operations with due
domestically regards to international
- tax imposed only to goods Economic Recession – downturn in investment
traded internationally GNP and a significant decline in 5. Wartime to peacetime
2. Quota economic activity for more than two economy
- Limit on quantity that is quarters
produced and sold at a certain International Monetary Fund
time Economic Depression – is a - Joined by 182 countries
- It is non-tariff that refers to prolonged unemployment, low output - Buying and selling their
limits that good consumes to and investment. A severe recession for currencies
reduce consumption more than three years and decline in - Condition where they do
3. Subsidy GDP of at least 10% economic reforms
- Government gives funds to
domestic producers to limit GNP or Gross National Product –
dependence on imports and products and services turned out for a
makes local producers to certain period of time where these are
You might also like
- WEEK 2 - Parameters of GlobalizationDocument3 pagesWEEK 2 - Parameters of GlobalizationLESLIEJULIA JERUSALEMNo ratings yet
- Trade and Competitiveness Global PracticeFrom EverandTrade and Competitiveness Global PracticeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- ReviewerDocument4 pagesReviewerFerlyn Cariño GundaNo ratings yet
- GlobalizationDocument6 pagesGlobalizationJOHN BEBON YAPNo ratings yet
- Contemporary World - Economic and Technological GlobalizationDocument2 pagesContemporary World - Economic and Technological GlobalizationRika MiyazakiNo ratings yet
- Ipd Midterm Reviewer 2018Document17 pagesIpd Midterm Reviewer 2018Ashley CapcoNo ratings yet
- Contempo (1st Year 1st Sem)Document3 pagesContempo (1st Year 1st Sem)John Edward AliponNo ratings yet
- Ibe Module 1 PDFDocument6 pagesIbe Module 1 PDFJitesh TolaniNo ratings yet
- IBT Reviewer PDFDocument6 pagesIBT Reviewer PDFKekekkeke KekkekekeNo ratings yet
- Ibt ReviewerDocument8 pagesIbt ReviewerHannah RodulfoNo ratings yet
- Summarized Report of Group 1Document5 pagesSummarized Report of Group 1Caryl Relos BasterechiaNo ratings yet
- Class Notes On GlobalizationDocument6 pagesClass Notes On Globalization마스러버No ratings yet
- Notes in TCWDocument13 pagesNotes in TCWMichy DizonNo ratings yet
- Contemporary WorldDocument35 pagesContemporary Worldsir GNo ratings yet
- TNCT 3rd-Periodical-Exam ReviewerDocument2 pagesTNCT 3rd-Periodical-Exam ReviewerCourtney BaguinatNo ratings yet
- Contemporary World ReviewerDocument5 pagesContemporary World ReviewerAugusto RamboyongNo ratings yet
- Summary Marketing InterDocument12 pagesSummary Marketing Interasmara.savira1115No ratings yet
- Module 1-GlobalizationDocument26 pagesModule 1-GlobalizationJeprox MartinezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 What Is GlobalizationDocument17 pagesLesson 1 What Is GlobalizationshaylieeeNo ratings yet
- BBC 1200 Lesson 1 What Is Globalization - 398639958Document17 pagesBBC 1200 Lesson 1 What Is Globalization - 398639958Rafael Capunpon VallejosNo ratings yet
- Introduction To GlobalizationDocument3 pagesIntroduction To GlobalizationLestibournesNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Lesson 6-7Document5 pagesReviewer Lesson 6-7unknownNo ratings yet
- GE 3 The Contemporary World QUIZ 1Document3 pagesGE 3 The Contemporary World QUIZ 1wzialcitaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 & 4Document3 pagesChapter 3 & 4Rhea Lourel Nalam SalapaNo ratings yet
- Course Note 1 - Dang Gia Vung - RA6127378Document6 pagesCourse Note 1 - Dang Gia Vung - RA6127378Gia Vững ĐặngNo ratings yet
- (Notes) GECCON REP1-5Document4 pages(Notes) GECCON REP1-5Alexis PabonNo ratings yet
- TCC 213 ReviewerDocument4 pagesTCC 213 ReviewerSharina DevarasNo ratings yet
- Fin ReviewerDocument24 pagesFin ReviewerESTRADA, Angelica T.No ratings yet
- Ge 3 Contemporary World Prelim 1Document3 pagesGe 3 Contemporary World Prelim 1Amirrah LaurenteNo ratings yet
- Global Business 3e Globalizing Business Emerging Economies Key TermsDocument2 pagesGlobal Business 3e Globalizing Business Emerging Economies Key TermsCassie ParkNo ratings yet
- The Contemporary World PrelimsDocument2 pagesThe Contemporary World PrelimsKC DiazNo ratings yet
- Triptico Alex Nieto-InglesDocument2 pagesTriptico Alex Nieto-Inglescarlos rojasNo ratings yet
- IBT Prelims 1Document8 pagesIBT Prelims 1sah mihNo ratings yet
- BBC 1200 Lesson 1 What Is GlobalizationDocument17 pagesBBC 1200 Lesson 1 What Is GlobalizationMARIANo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 PPT 3Document6 pagesLecture 3 PPT 3mgimogenNo ratings yet
- Contemp 3-5Document20 pagesContemp 3-5ralenedwyerNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document3 pagesLesson 2JuNo ratings yet
- International Business: By: Zahrah., S.P., M.SC BookDocument18 pagesInternational Business: By: Zahrah., S.P., M.SC BookZahra -No ratings yet
- Dwnload Full International Business The Challenges of Globalization 9th Edition Wild Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full International Business The Challenges of Globalization 9th Edition Wild Solutions Manual PDFmorselhurly.qa26100% (9)
- Globalisation and The Indian Economy: Social ScienceDocument4 pagesGlobalisation and The Indian Economy: Social ScienceAnant DwivediNo ratings yet
- UNIT II - Structure of GlobalizationDocument5 pagesUNIT II - Structure of Globalization21-51354No ratings yet
- Gec 103 Reviewer Globalization Global Economy - The Worldwide ExploitationDocument4 pagesGec 103 Reviewer Globalization Global Economy - The Worldwide ExploitationALIENHMBNo ratings yet
- Economic Development 1Document2 pagesEconomic Development 1MitzukiNo ratings yet
- General Education ReviewerDocument10 pagesGeneral Education ReviewerVincentNo ratings yet
- Gec 103Document5 pagesGec 103JANIESAH BALTNo ratings yet
- TRENDSDocument5 pagesTRENDSErica Mae GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing GlobalizationDocument6 pagesFactors Influencing Globalizationryan bhinog100% (1)
- MarketIntegration 3Document11 pagesMarketIntegration 3Franz Althea BasabeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Globalisation SummaryDocument21 pagesChapter 1 Globalisation Summarypink pinkNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Second Half (Globalization, Liberalization, WTO & Its Impact & Consumer Protection)Document35 pagesUnit 2 - Second Half (Globalization, Liberalization, WTO & Its Impact & Consumer Protection)Aneesh DugarNo ratings yet
- Overview of International BusinessDocument7 pagesOverview of International Businesssobashaikh1104No ratings yet
- Prelim - Int'l Business & TradeDocument13 pagesPrelim - Int'l Business & TradeGIGI BODO100% (1)
- 09 Development Experiences in IndiaDocument16 pages09 Development Experiences in IndiaSanket DaveNo ratings yet
- Topic 6Document5 pagesTopic 6KyNo ratings yet
- Con World-Reviewer - Reviewer Con World-Reviewer - ReviewerDocument5 pagesCon World-Reviewer - Reviewer Con World-Reviewer - ReviewerAngelica CalubayNo ratings yet
- What Is Globalization?: Globalization or Globalisation Is The Process of Interaction and Integration Among PeopleDocument2 pagesWhat Is Globalization?: Globalization or Globalisation Is The Process of Interaction and Integration Among PeopleDanielle OnaNo ratings yet
- Lecture2. Globalization 2021Document27 pagesLecture2. Globalization 2021hoang anhNo ratings yet
- T Globalization: An: ObjectivesDocument7 pagesT Globalization: An: ObjectivesRakesh SainiNo ratings yet
- Uniform Motion WorksheetDocument8 pagesUniform Motion Worksheetnikhil patro100% (1)
- CL Honours Report NamanDocument11 pagesCL Honours Report NamanNaman VermaNo ratings yet
- Sabian Aspect OrbsDocument8 pagesSabian Aspect Orbsellaella13100% (2)
- SDS ERSA Rev 0Document156 pagesSDS ERSA Rev 0EdgarVelosoCastroNo ratings yet
- Man Bni PNT XXX 105 Z015 I17 Dok 886160 03 000Document36 pagesMan Bni PNT XXX 105 Z015 I17 Dok 886160 03 000Eozz JaorNo ratings yet
- Analisis Kebutuhan Bahan Ajar Berbasis EDocument9 pagesAnalisis Kebutuhan Bahan Ajar Berbasis ENur Hanisah AiniNo ratings yet
- Philo Q2 Lesson 5Document4 pagesPhilo Q2 Lesson 5Julliana Patrice Angeles STEM 11 RUBYNo ratings yet
- The Pneumatics of Hero of AlexandriaDocument5 pagesThe Pneumatics of Hero of Alexandriaapi-302781094No ratings yet
- Banking Ombudsman 58Document4 pagesBanking Ombudsman 58Sahil GauravNo ratings yet
- Internal Resistance To Corrosion in SHS - To Go On WebsiteDocument48 pagesInternal Resistance To Corrosion in SHS - To Go On WebsitetheodorebayuNo ratings yet
- Jinivefsiti: Sultan LorisDocument13 pagesJinivefsiti: Sultan LorisSITI HAJAR BINTI MOHD LATEPINo ratings yet
- E7d61 139.new Directions in Race Ethnicity and CrimeDocument208 pagesE7d61 139.new Directions in Race Ethnicity and CrimeFlia Rincon Garcia SoyGabyNo ratings yet
- Abnt NBR 16868 1 Alvenaria Estrutural ProjetoDocument77 pagesAbnt NBR 16868 1 Alvenaria Estrutural ProjetoGIOVANNI BRUNO COELHO DE PAULANo ratings yet
- L 11Document3 pagesL 11trangNo ratings yet
- CPD - SampleDocument3 pagesCPD - SampleLe Anh DungNo ratings yet
- Daftar ObatDocument18 pagesDaftar Obatyuyun hanakoNo ratings yet
- RH-A Catalog PDFDocument1 pageRH-A Catalog PDFAchmad KNo ratings yet
- Keeping Track of Your Time: Keep Track Challenge Welcome GuideDocument1 pageKeeping Track of Your Time: Keep Track Challenge Welcome GuideRizky NurdiansyahNo ratings yet
- Resume - James MathewsDocument2 pagesResume - James Mathewsapi-610738092No ratings yet
- Puma PypDocument20 pagesPuma PypPrashanshaBahetiNo ratings yet
- EPW, Vol.58, Issue No.44, 04 Nov 2023Document66 pagesEPW, Vol.58, Issue No.44, 04 Nov 2023akashupscmadeeaseNo ratings yet
- Regulasi KampenDocument81 pagesRegulasi KampenIrWaN Dompu100% (2)
- Amity School of Business:, Semester IV Research Methodology and Report Preparation Dr. Deepa KapoorDocument23 pagesAmity School of Business:, Semester IV Research Methodology and Report Preparation Dr. Deepa KapoorMayank TayalNo ratings yet
- A202 KBK3043 - Assignment Individual (20%) Review LiteratureDocument5 pagesA202 KBK3043 - Assignment Individual (20%) Review LiteratureAlfie AliNo ratings yet
- Transfert de Chaleur AngDocument10 pagesTransfert de Chaleur Angsouhir gritliNo ratings yet
- Configuration Guide - Interface Management (V300R007C00 - 02)Document117 pagesConfiguration Guide - Interface Management (V300R007C00 - 02)Dikdik PribadiNo ratings yet
- Pitch DeckDocument21 pagesPitch DeckIANo ratings yet
- Sheet-Metal Forming Processes: Group 9 PresentationDocument90 pagesSheet-Metal Forming Processes: Group 9 PresentationjssrikantamurthyNo ratings yet
- Saflex-Dg - 41 Data SheetDocument5 pagesSaflex-Dg - 41 Data SheetrasheedgotzNo ratings yet
- Department of Ece, Adhiparasakthi College of Engineering, KalavaiDocument31 pagesDepartment of Ece, Adhiparasakthi College of Engineering, KalavaiGiri PrasadNo ratings yet
- A History of the United States in Five Crashes: Stock Market Meltdowns That Defined a NationFrom EverandA History of the United States in Five Crashes: Stock Market Meltdowns That Defined a NationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Look Again: The Power of Noticing What Was Always ThereFrom EverandLook Again: The Power of Noticing What Was Always ThereRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Financial Literacy for All: Disrupting Struggle, Advancing Financial Freedom, and Building a New American Middle ClassFrom EverandFinancial Literacy for All: Disrupting Struggle, Advancing Financial Freedom, and Building a New American Middle ClassNo ratings yet
- Narrative Economics: How Stories Go Viral and Drive Major Economic EventsFrom EverandNarrative Economics: How Stories Go Viral and Drive Major Economic EventsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (94)
- The Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationFrom EverandThe Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (46)
- The Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumFrom EverandThe Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (12)
- The Trillion-Dollar Conspiracy: How the New World Order, Man-Made Diseases, and Zombie Banks Are Destroying AmericaFrom EverandThe Trillion-Dollar Conspiracy: How the New World Order, Man-Made Diseases, and Zombie Banks Are Destroying AmericaNo ratings yet
- The New Elite: Inside the Minds of the Truly WealthyFrom EverandThe New Elite: Inside the Minds of the Truly WealthyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- The War Below: Lithium, Copper, and the Global Battle to Power Our LivesFrom EverandThe War Below: Lithium, Copper, and the Global Battle to Power Our LivesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- University of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingFrom EverandUniversity of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (97)
- Vulture Capitalism: Corporate Crimes, Backdoor Bailouts, and the Death of FreedomFrom EverandVulture Capitalism: Corporate Crimes, Backdoor Bailouts, and the Death of FreedomNo ratings yet
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyFrom EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (227)
- Economics 101: How the World WorksFrom EverandEconomics 101: How the World WorksRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (34)
- The Meth Lunches: Food and Longing in an American CityFrom EverandThe Meth Lunches: Food and Longing in an American CityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Principles for Dealing with the Changing World Order: Why Nations Succeed or FailFrom EverandPrinciples for Dealing with the Changing World Order: Why Nations Succeed or FailRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (237)
- Poor Economics: A Radical Rethinking of the Way to Fight Global PovertyFrom EverandPoor Economics: A Radical Rethinking of the Way to Fight Global PovertyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (263)
- The Sovereign Individual: Mastering the Transition to the Information AgeFrom EverandThe Sovereign Individual: Mastering the Transition to the Information AgeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (89)
- Doughnut Economics: Seven Ways to Think Like a 21st-Century EconomistFrom EverandDoughnut Economics: Seven Ways to Think Like a 21st-Century EconomistRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (37)
- The Myth of the Rational Market: A History of Risk, Reward, and Delusion on Wall StreetFrom EverandThe Myth of the Rational Market: A History of Risk, Reward, and Delusion on Wall StreetNo ratings yet
- Nudge: The Final Edition: Improving Decisions About Money, Health, And The EnvironmentFrom EverandNudge: The Final Edition: Improving Decisions About Money, Health, And The EnvironmentRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (92)
- Rewired: The McKinsey Guide to Outcompeting in the Age of Digital and AIFrom EverandRewired: The McKinsey Guide to Outcompeting in the Age of Digital and AIRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)