Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DCNKNQ
DCNKNQ
Uploaded by
J Ali0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesOriginal Title
dcnknq
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesDCNKNQ
DCNKNQ
Uploaded by
J AliCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
elements make up more than 98 percent of the earth’s crust.
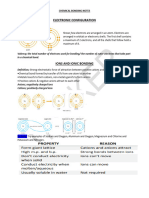
These elements Four types of chemical bonds are found in minerals:
are; Oxygen, Silicon, Aluminum, Iron, Calcium, Magnesium, Potassium and 1. Ionic - Cations and anions are attracted by their opposite electronic charges
Sodium. and thus bond together. This union is called an ionic bond.
2. Covalent - when two or more atoms share their electrons to produce the
STRUCTURE OF AN ATOM effect of filled outer electron shells.
❖ An atom is the basic unit of an element. 3. Metallic - collective sharing of a sea of valence electrons between several
❖ An atom is tiny; the diameter of the average atom is about 10ˉ10 meters. positively charged metal ions
❖ An atom consists of a small, dense, positively charged center called a 4. Van der Waals forces - Weak electrical forces
Nucleus.
❖ The Nucleus contains dense particles with positive electric charge known MATTER AND MINERALS
as Protons. - Most minerals are compounds. Minerals are always electrically
❖ and equally dense particles with neutral electric charges know as neutral
Neutrons.
❖ The nucleus is surrounded by negatively charged Electrons. CRYSTALS - any substance whose atoms are arranged in a regular, periodically
❖ An electron is a fundamental particle; it is not made up of smaller repeated pattern.
components. An electron orbits the nucleus, but not in a clearly. UNIT CELL - small group of atoms, like a single brick in a wall, repeats itself
❖ Atomic weight/mass of an atom is equal to the total number of Neutrons over and over.
+ Protons. CRYSTAL FACE - is a planar surface that develops if a crystal grows freely in
❖ Atomic Number of an atom is equal to its number of Proton or Electron. an uncrowded environment.
❖ A charged atom is called an Ion.
The forces that hold atoms and ions together to form compounds are called
CHEMICAL BONDS.
CHEMICAL BONDS PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF MINERALS
1. CRYSTAL HABIT - is the characteristic shape of a mineral and the
manner in which aggregates of crystals grow.
2. CLEAVAGE - is the tendency of some minerals to break along flat
surfaces.
3. FRACTURE - is the pattern in which a mineral breaks other than along
planes of cleavage.
4. HARDNESS - is the resistance of a mineral to scratching.
5. SPECIFIC GRAVITY - is the weight of a substance in air divided by the
weight of an equal volume of water.
6. COLOR - is the most obvious property of a mineral, but it is commonly
unreliable for identification.
7. STREAK - is the color of a fine powder of a mineral.
8. LUSTER - is the manner in which a mineral reflects light
You might also like
- Crystallography and Mineralogy NotesDocument220 pagesCrystallography and Mineralogy NotesSyed Aquib ShamshadNo ratings yet
- KristMin01 PengantarDocument66 pagesKristMin01 Pengantarmelvinda putriNo ratings yet
- X ICSE Geography 02Document126 pagesX ICSE Geography 02mandar sawant84% (19)
- MineralsDocument28 pagesMineralsraotalha100% (4)
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- An Introduction To BondingDocument14 pagesAn Introduction To BondingDavies MasumbaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Engineering Materials & Properties v1.1 PDFDocument78 pagesTopic 1 Engineering Materials & Properties v1.1 PDFHittossan HitNo ratings yet
- Proceeding MGEI 2016Document134 pagesProceeding MGEI 2016Slh100% (3)
- Basic Concepts in Electronics ServicingDocument13 pagesBasic Concepts in Electronics ServicingBenjamin FalletNo ratings yet
- Physical Geology - Earle 2nd EditionDocument824 pagesPhysical Geology - Earle 2nd Editionowen sherry100% (1)
- Atomic Bonding (Metallic, Ionic, Covalent, and Van Der Waals Bonds)Document5 pagesAtomic Bonding (Metallic, Ionic, Covalent, and Van Der Waals Bonds)Aris YusepNo ratings yet
- KgekDocument5 pagesKgekJ AliNo ratings yet
- Igneous Rocks Formation of The Solar SystemDocument8 pagesIgneous Rocks Formation of The Solar SystemJ AliNo ratings yet
- Defining RockDocument24 pagesDefining Rockgeneabi012No ratings yet
- NAME Aneela Aftab Semester Second Subject Fiber Science Submitted To Sir Muhammad QasimDocument22 pagesNAME Aneela Aftab Semester Second Subject Fiber Science Submitted To Sir Muhammad QasimAnila AftabNo ratings yet
- CeramicsDocument103 pagesCeramicsTamil SelvanNo ratings yet
- Science Q2 ReviewerDocument7 pagesScience Q2 ReviewerSherra Mariel PintorNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atoms and Molecules: Bohr's Atomic ModelDocument4 pagesStructure of Atoms and Molecules: Bohr's Atomic ModelChristianNo ratings yet
- Geo Week 4 Powerpoint Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesGeo Week 4 Powerpoint Lecture NotesGil GameshNo ratings yet
- The Solids Have Definite Volume and Definite Shape) Model of An AtomDocument5 pagesThe Solids Have Definite Volume and Definite Shape) Model of An AtomKat OrcinoNo ratings yet
- BondingDocument33 pagesBondingNathaniel WhyteNo ratings yet
- Mse Group 2Document100 pagesMse Group 2Nicko CortoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 MineralsDocument5 pagesChapter 2 MineralsPrincess Lourdes CarinNo ratings yet
- Atomic BondsDocument4 pagesAtomic Bondsfatiman333333No ratings yet
- The Structure of Solids: RK ChowdaryDocument27 pagesThe Structure of Solids: RK Chowdaryrkchowdary007No ratings yet
- Bonding in Solids Definition: Solid State ChemistryDocument9 pagesBonding in Solids Definition: Solid State Chemistryhaimanot yibeltalNo ratings yet
- Kimia Kristal - 1Document37 pagesKimia Kristal - 1Wana KimhanbinNo ratings yet
- Mod 2 Book 1 PhysicsDocument41 pagesMod 2 Book 1 Physicsranjit prasadNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Topic 4 Bonding and StructureDocument7 pagesEdexcel Topic 4 Bonding and Structurekmoiz427No ratings yet
- MSM R19 - Unit-1Document62 pagesMSM R19 - Unit-1Madheswaran DharmapuriNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding NotesDocument5 pagesChemical Bonding NotesShaswat PattnayakNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondsDocument36 pagesChemical BondsicelleNo ratings yet
- Material Science MotivationDocument18 pagesMaterial Science MotivationPrateek BayalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To GeologyDocument21 pagesIntroduction To GeologyDelmae ToledoNo ratings yet
- Reviewers-In-Science (Atomic Theory)Document3 pagesReviewers-In-Science (Atomic Theory)HelloNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument40 pagesChemical BondingabuhurairabscNo ratings yet
- Dental Biomaterial Book (61-71)Document146 pagesDental Biomaterial Book (61-71)Abdelruhman SobhyNo ratings yet
- Chem 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical BondingDocument2 pagesChem 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical BondingKuo SarongNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of LifeDocument14 pagesChemistry of LifeRebecca TercianoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of LifeDocument14 pagesChemistry of LifeBayramNo ratings yet
- Eg208 Topic 2-Mineralogy P1 28052020Document29 pagesEg208 Topic 2-Mineralogy P1 28052020Lionel MessiNo ratings yet
- Minerals Are The Building Blocks of RocksDocument8 pagesMinerals Are The Building Blocks of RocksC A M I L ANo ratings yet
- Chemical BondsDocument6 pagesChemical BondsARDIUZNo ratings yet
- Material Chapter 2 Atomic Structure and BondingDocument19 pagesMaterial Chapter 2 Atomic Structure and BondingÇãłl Mê MęlkãNo ratings yet
- Bonding & Structure NotesDocument11 pagesBonding & Structure NotesKamran TajbakhshNo ratings yet
- Read and Annotate! I Want To See Notes and Highlights and Underlines On This Paper!Document7 pagesRead and Annotate! I Want To See Notes and Highlights and Underlines On This Paper!api-344880038No ratings yet
- Kangwon ProjectDocument2 pagesKangwon ProjectJhastine Mhae De VeraNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Notes by ThinkerDocument5 pagesChemical Bonding Notes by ThinkerIshmael TynoeNo ratings yet
- Ayena Semiconductor DevicesDocument2 pagesAyena Semiconductor DevicesAceng PikriNo ratings yet
- The Cristal Structure of Metals, Basic Phase Diagrams, and The Metallografic Sample Preparation LabolatoryDocument6 pagesThe Cristal Structure of Metals, Basic Phase Diagrams, and The Metallografic Sample Preparation LabolatoryZack WijayaNo ratings yet
- Class Atomic Structure-1Document45 pagesClass Atomic Structure-1Dj chemzoneNo ratings yet
- GEOLOGY 101 Sections 519-527 Spring 2014 Class 3Document44 pagesGEOLOGY 101 Sections 519-527 Spring 2014 Class 3Tyler MroskoNo ratings yet
- Atoms 1Document30 pagesAtoms 1poorv1235570No ratings yet
- Chemical Bond Notes by TouhidDocument23 pagesChemical Bond Notes by Touhidnabilnakib0077No ratings yet
- Forces of AttractionDocument21 pagesForces of AttractionDoveNo ratings yet
- Three Types of Chemical BondingDocument97 pagesThree Types of Chemical Bondingriza loveresNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument5 pagesChemical BondingStellaNo ratings yet
- Bonding and Naming CompoundsDocument10 pagesBonding and Naming CompoundsDaniel BerryNo ratings yet
- EMD Module 1Document69 pagesEMD Module 1Amirtha Abirami RajuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes For Form 2Document70 pagesChemistry Notes For Form 2Charles OtienoNo ratings yet
- Bonding and Structure: Group: Hammad Rashid Luqman Arshad Moeed AliDocument11 pagesBonding and Structure: Group: Hammad Rashid Luqman Arshad Moeed AliPro IdiotNo ratings yet
- Chem Lec ReviewerDocument42 pagesChem Lec ReviewerMaryashlyn NableaNo ratings yet
- KgekDocument5 pagesKgekJ AliNo ratings yet
- Igneous Rocks Formation of The Solar SystemDocument8 pagesIgneous Rocks Formation of The Solar SystemJ AliNo ratings yet
- Magnets and Magnetism Science Quiz Presentation in A Orange Blue and Gray Collage StyleDocument45 pagesMagnets and Magnetism Science Quiz Presentation in A Orange Blue and Gray Collage StyleJ AliNo ratings yet
- ReviewetDocument22 pagesReviewetJ AliNo ratings yet
- General Orientation ReviewerDocument12 pagesGeneral Orientation ReviewerJ AliNo ratings yet
- 02.matter and MineralsDocument33 pages02.matter and MineralsJ AliNo ratings yet
- Ge Fest Volleyball PDFDocument2 pagesGe Fest Volleyball PDFJ AliNo ratings yet
- Narrative PDFDocument1 pageNarrative PDFJ AliNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 2.1 - Roilo2BSVT-BDocument3 pagesActivity No. 2.1 - Roilo2BSVT-BJ AliNo ratings yet
- Secular Variation in Seawater Chemistry and The Origin of Calcium Chloride Basinal BrinesDocument5 pagesSecular Variation in Seawater Chemistry and The Origin of Calcium Chloride Basinal BrinesAnonymous PdzpkUNo ratings yet
- Chemistry and Engineering of The Clinkerization Process PDFDocument18 pagesChemistry and Engineering of The Clinkerization Process PDFAnonymous NxpnI6jC100% (1)
- Aspden Et Al., 1992a Regional Type S PDFDocument10 pagesAspden Et Al., 1992a Regional Type S PDFErnestoNo ratings yet
- Mineral Stations LabDocument5 pagesMineral Stations Labapi-315557948No ratings yet
- Introduction To PetrologyDocument53 pagesIntroduction To Petrologyaaaaaa123456aaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Student Rock Sets Content ListsDocument3 pagesStudent Rock Sets Content ListsdsopranoNo ratings yet
- B SC - II-10Document84 pagesB SC - II-10vishal jamnekarNo ratings yet
- Ore Geology Reviews: Fan Yang, Jingwen Mao, Weidong Ren, Zesheng Qian, Chao Li, Gilby JepsonDocument15 pagesOre Geology Reviews: Fan Yang, Jingwen Mao, Weidong Ren, Zesheng Qian, Chao Li, Gilby Jepsonyuri tagawaNo ratings yet
- MineralsDocument2 pagesMineralsKevin Fernandez MendioroNo ratings yet
- SST3005 Basic Soil ScienceDocument29 pagesSST3005 Basic Soil ScienceSleeping BeautyNo ratings yet
- Oxide Mineralization at The Radomiro Tomic Porphyry Copper Deposit, Northern ChileDocument14 pagesOxide Mineralization at The Radomiro Tomic Porphyry Copper Deposit, Northern Chilejunior.geologiaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Rocks and Minerals GoodDocument5 pagesLesson 1 - Rocks and Minerals Goodapi-314775182No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Grade 7 ScienceDocument8 pagesLesson Plan in Grade 7 ScienceThricia SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Application of Superconducting High Gradient Magnetic Separation Technology On Silica Extraction From Iron Ore BeneDocument7 pagesApplication of Superconducting High Gradient Magnetic Separation Technology On Silica Extraction From Iron Ore BeneLuanna MouraNo ratings yet
- Wang 2020Document13 pagesWang 2020JULIO JEAN CONDEZO AGUILARNo ratings yet
- MineralogyDocument9 pagesMineralogyVarun ShahNo ratings yet
- Structure System and It Controls To Mineralization of Primary Tin Deposit, Airdibi Area, Jebus Subdistrict, West Bangka, Bangka and BelitungDocument5 pagesStructure System and It Controls To Mineralization of Primary Tin Deposit, Airdibi Area, Jebus Subdistrict, West Bangka, Bangka and BelitungSaifullah FatahNo ratings yet
- Sulfuric Acid Caves of Italy - A ReviewDocument18 pagesSulfuric Acid Caves of Italy - A ReviewFilipe CruzNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science Level/Year: Grade 7 I. Learning ObjectivesDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in Science Level/Year: Grade 7 I. Learning ObjectivesJacquelyn MendozaNo ratings yet
- Crystal SystemsDocument99 pagesCrystal SystemsTristram KeatsNo ratings yet
- Unu GTP 1998 18 PDFDocument78 pagesUnu GTP 1998 18 PDFFirdausNo ratings yet
- Materials and Design: Nailia R. Rakhimova, Ravil Z. RakhimovDocument8 pagesMaterials and Design: Nailia R. Rakhimova, Ravil Z. RakhimovApoorva AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Earth 2 2nd Edition Hendrix Solutions ManualDocument4 pagesEarth 2 2nd Edition Hendrix Solutions ManualVernon Hilton100% (28)
- The Role of Clay Minerals IN Influencing Porosity AND Permeability Characteristics in The Bridport Sands of Wytch Farm, DorsetDocument14 pagesThe Role of Clay Minerals IN Influencing Porosity AND Permeability Characteristics in The Bridport Sands of Wytch Farm, DorsetDaniel Mauricio Rojas CaroNo ratings yet
- Alflarsenite Mineral Data1Document3 pagesAlflarsenite Mineral Data1BlacksacerdoteNo ratings yet
- Advanced of Geology of Ore MineralDocument9 pagesAdvanced of Geology of Ore MineralNarith Somalin Reaksa MealikaNo ratings yet