Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DO Nutrients Double Sided
DO Nutrients Double Sided
Uploaded by
DP ChemOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DO Nutrients Double Sided
DO Nutrients Double Sided
Uploaded by
DP ChemCopyright:
Available Formats
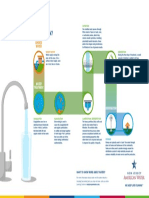
DISSOLVED OXYGEN (DO) STRATIFICATION
Dissolved oxygen, oftentimes abbreviated as DO (dee-oh), What is Dissolved Oxygen? Shelly Krueger
Stratification is when the waterbody has different layers
is the measure of the amount of free oxygen (O2) that is Florida Sea Grant Agent that create a barrier for mixing. These strata develop
dissolved in the water. Fish and invertebrates use their University of Florida IFAS Extension, Monroe County based on the different densities between the water layers
ShellyKrueger@UFL.edu/305-292-4501
gills to breathe oxygen gas underwater, just like humans monroe.ifas.ufl.edu and the general term is pycnocline. Warmer water is
use lungs to breathe oxygen gas from the atmosphere. lighter than cold water, which creates a thermocline.
It is one of the most important water quality indicators, How does oxygen enter the water? Freshwater is lighter than saltwater, so after a rain event
because respiration is fundamental for life. freshwater may sit on top of the denser, saltier water,
Diffusion – Atmospheric O2 via thus creating a halocline. Wind, waves, currents and tides
In general, dissolved oxygen mixing from waves, wind, help these layers to mix. Many of the Keys canals are
values 5 mg/L and above currents, tides and deeper than the basins they are adjacent too, which
support proper metabolism, groundwater means there is really only mixing of the top layers, and
growth and reproduction for oxygen saturation decreases greatly with depth when the
marine animals. Many fish can Photosynthesis – O2 production surface oxygenated layers cannot mix with the bottom
handle very low DO levels, which in the water from seagrasses, layers (Fig. 3). This can lead to very low oxygen
is why we still see pinfish, algae and phytoplankton environments (hypoxia) and even the absence of oxygen
tarpon and mullet in canals with at the bottom (anoxia).
very low DO; however, fish with Artificial – water over a dam,
higher oxygen requirements, like aerators and fountains
grouper, will leave areas with low DECOMPOSITION
Figure 1. Minimum DO levels (mg/L) by species. Credit SCCF DO (Fig. 1). Figure 3. Not all water depths reach 100% saturation. Credit Fondriest Decomposition is the decay of organic matter. When
seagrasses and algae decay the microbes that break them
down consume oxygen through their metabolism, which
TEMPERATURE and SALINITY depletes the water of oxygen. In the absence of oxygen,
The temperature, salinity and atmospheric pressure What Factors Affect Dissolved Oxygen (DO)? the process of decomposition can create hydrogen
determine the amount of oxygen that can physically be Dissolved oxygen (DO) levels vary depending upon a number of physical and biological sulfide, which releases the characteristic “rotten egg”
dissolved into the water. Dissolved oxygen has an inverse factors. DO levels are highest at the poles and lowest at the equator. DO levels are highest smell.
(opposite) relationship with temperature: when the water is cold and lowest when the water is warm. DO levels are higher during the
day and decrease at night. DISSOLVED OXYGEN SATURATION
Temperature Dissolved Oxygen
Dissolved oxygen saturation varies throughout the day
Salinity also effects oxygen saturation. Seawater holds and night. When there is more oxygen consumption by
about 20% less oxygen than freshwater at the same animals, plants and bacteria than oxygen production by
temperature and altitude. When the ocean temperature plants and mixing from the atmosphere, oxygen
is 30⁰C (86⁰F), the oxygen content is 5 milligrams of saturation values naturally go down. The oxygen is being
oxygen per liter (mg/L), which is equivalent to 80% consumed by animals, plants and bacteria faster than it is
dissolved oxygen saturation (Fig. 2). being replenished. DO saturation also declines with
depth (Fig. 3). The highest dissolved oxygen levels tend to
PHOTOSYNTHESIS PHOTOSYNTHESIS be at the surface because oxygen concentrations are
+ +
RESPIRATION RESPIRATION RESPIRATION RESPIRATION higher in the atmosphere and most mixing occurs at the
surface through diffusion. In order to meet Florida
Department of Environmental Protection (FDEP) state
standards for water quality, coastal waters must have a
Figure 4. 24 hour (diel) variations in dissolved oxygen levels due to photosynthesis and respiration. Credit Fondriest diel average at or above 42% DO saturation. Percent
dissolved oxygen saturation is a good calculation for
80% DO Saturation = 5.0 mg/L
DIEL = NIGHT + DAY marine life because it incorporates local conditions for
Diurnal means during the day, and nocturnal means during the night. Diel refers to the 24 temperature, salinity and atmospheric pressure.
hour period of both day and night. Just like the plants and trees on Earth, the plants and
algae in the water produce oxygen, and need oxygen to breathe. When the sun shines, they Literature Cited:
Engineering ToolBox. 2005. “Oxygen Solubility in Fresh Water and Sea Water.”
produce oxygen, but at night, they only consume oxygen – this is why early morning tends to FDEP. 2013. “Derivation of dissolved oxygen criteria to protect aquatic life in Florida’s
have the lowest levels of dissolved oxygen -- until the sun rises, when photosynthesis starts fresh and marine waters.” DEP-SAS-001/13, 232 pp.
Fondriest Environmental, Inc. 2013. “Dissolved Oxygen.” Fundamentals of
again. Afternoon oxygen levels can exceed 100% DO saturation (super-saturated) because Environmental Measurements.
Figure 2. Dissolved oxygen concentrations as temperature increases for freshwater (top line) and saltwater (bottom line). Credit Fondriest
the rate of photosynthesis is high from solar energy (Fig. 4). Sanibel-Captiva Conservation Foundation. 2018. “Hypoxia.”
Funding provided by the EPA South Florida Initiative Grant #00D41115
EUTROPHICATION NITROGEN
Eutrophication (you-trof-eh-cation) is just a really big word What are Nutrients? Shelly Krueger
Nitrogen is an organic element with the atomic symbol N,
for too many nutrients. In the marine environment, when Florida Sea Grant Agent and it is present in all life forms. The majority of the air
we talk about too many nutrients, we are talking about University of Florida IFAS Extension, Monroe County we breathe is nitrogen gas (N2; 78%) followed by oxygen
ShellyKrueger@UFL.edu/305-292-4501
nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P). Just like the fertilizers monroe.ifas.ufl.edu gas (O2; 21%). Nitrogen gas in the atmosphere is inert,
that grow plants on land, N and P stimulate plant and algal and must be converted into a usable form for living
growth in the marine environment. One of the biggest organisms to build amino acids for proteins and nucleic
consequences of too many nutrients = too much acids for DNA and RNA. Nitrogen is taken up by
phytoplankton, followed by low dissolved oxygen in the seagrasses, seaweed and phytoplankton in the form of
water. nitrate (NO3) and ammonium (NH4) and incorporated into
their tissues, which forms the base of the food chain.
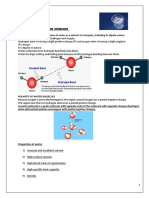
PRIMARY PRODUCERS
Primary producers are plants and algae PHOSPHORUS
that perform photosynthesis to create Phosphorus is an organic element with the atomic symbol
energy and oxygen. Primary producers P, and it is required for aquatic plant growth. Phosphorus
are incredibly important because they Timeline for Eutrophication. Credit BBC Bitesize is a building block for energy. It is also a key element in
form the base of the food chain and Timeline for Eutrophication fertilizer, because it increases plant growth.
produce the oxygen we breathe in the Nutrient Loading: Nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) enter the waterbody from the
atmosphere. Primary producers are the only group that
create their own food; all other organisms on Earth must
1 surrounding watershed from urban runoff, agriculture, fertilizers, detergents, animal When concentrations of N and P are high, it is like a buffet
for phytoplankton, which causes them to multiply
and human waste.
eat to obtain energy for growth and reproduction. There exponentially. The Gulf of Mexico Dead Zone is an
are two types of primary producers in the ocean: Primary producers proliferate: The N and P act like fertilizers, stimulating example of a low oxygen area from too much N and P
seagrasses, which are true plants, and algae. Algae are
divided into two groups: micro-algae and macro-algae.
2 exponential phytoplankton (microalgae), seaweed (macroalgae) and seagrass entering the Gulf of Mexico from the Mississippi River
watershed.
growth.
Algae Bloom: The abundance of phytoplankton creates an algae bloom. The
3 phytoplankton may become so thick they can block light to the seagrasses at the
bottom. The water may appear very green or red-brown.
4 Decomposition: The phytoplankton decay, and the decomposition of the organic
matter by microbes removes oxygen from the water.
Very low oxygen levels lead to fish kills. Some phytoplankton blooms cause health
5 effects in humans, and death for dolphins and manatees.
What is Non-Point Source Pollution?
Non-point source pollution is the type of pollution that comes from diffuse sources. The
more impervious surfaces, like parking lots, roads and urban development, the more
Ocean Food Chain. Credit NOAA nonpoint source pollution enters waterways. This is because after a rain event, the rainwater Satellite imagery of chlorophyll A concentrations
literally runs-off into the nearest waterbody – rivers, lakes, estuaries and oceans. When in South Florida. Credit SEAWiFS
• Phytoplankton (Micro-algae) rainfall travels over the ground, it picks up whatever pollutants the water encounters –
Phytoplankton are microscopic, single-celled organisms What is Chlorophyll A?
sediment, fertilizers, pesticides, fossil fuels, animal waste and heavy metals, and carries them Chlorophyll A is the primary photoreceptor used for
that float in the top layers of the Earth’s oceans and through the watershed via gravity to waterways. It is important to educate residents about
produce 40% of the Earth’s oxygen supply. photosynthesis by aquatic plants and algae. Chlorophyll
nonpoint source pollution because we can all prevent pollution entering waterways in the A gives plants and algae their green pigment and it is used
• Seaweed (Macro-algae) first place. as a proxy to estimate the amount of phytoplankton in
Seaweed is the common name for large, visible algae. What is a Harmful Algal Bloom (HAB)? the water column. There are scientific instruments and
Sargassum, halimeda, mermaid’s cups, shaving brushes A proliferation of algae is called an algal bloom. Algal blooms can deplete the water of even satellites that measure the chlorophyll A pigment to
and hair algae are common seaweeds in the Florida Keys. oxygen and cause fish kills. Some phytoplankton species contain toxins that are harmful to estimate the abundance of phytoplankton in the
• Seagrasses (True Plants) humans, which are called Harmful Algal Blooms (HABs). The red tide causing species, environment.
Did you know the Florida Keys are surrounded by one of Karenia brevis, causes respiratory problems in humans, fish kills and dolphin deaths. Drinking
the largest seagrass beds in the world? The three most or inhaling contaminated water from some toxic blooms, or eating contaminated shellfish, Funding provided by the EPA South Florida Initiative Grant
common are turtle grass, manatee grass and shoal grass. can cause liver disease and long-term cognitive dysfunction in humans and marine mammals. #00D41115
You might also like
- Magic Oils PDFDocument5 pagesMagic Oils PDFJennifer Nilson Tyler100% (4)
- 01 PrestoDR 4143 and 3543 Manual MantenimientoDocument350 pages01 PrestoDR 4143 and 3543 Manual Mantenimientojeison100% (3)
- Dissolved Oxygen Fact SheetDocument1 pageDissolved Oxygen Fact SheetDr-Raju AhmedNo ratings yet
- Water (Chemistry)Document10 pagesWater (Chemistry)chrstnmrsgnNo ratings yet
- River Health.: Self-Purification Will Take Less Tim at Hot Temperature Than in WinterDocument4 pagesRiver Health.: Self-Purification Will Take Less Tim at Hot Temperature Than in WinterSrikrishnan DhanajiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Lower Secondary Science Digital Learners Book 7 - Cambridge GODocument1 pageCambridge Lower Secondary Science Digital Learners Book 7 - Cambridge GOkhanhlinh27072012No ratings yet
- Working in Water1Document12 pagesWorking in Water1brufpotNo ratings yet
- Respiration Rate of Fingerlings And: Mus MusculusDocument4 pagesRespiration Rate of Fingerlings And: Mus MusculusRafael VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Ss 52500Document8 pagesSs 52500DP ChemNo ratings yet
- Dissolved Oxygen and The Three S'S: Some DO ChemistryDocument12 pagesDissolved Oxygen and The Three S'S: Some DO ChemistryScience for mindsNo ratings yet
- AquarchDocument30 pagesAquarchGauresh AmbulkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 StructuresDocument10 pagesChapter 1 StructuresVassalyn Su ThatNo ratings yet
- Chapters 3 To 7 Study GuideDocument38 pagesChapters 3 To 7 Study GuideSameh NoorNo ratings yet
- NJAW Water Treatment ProcessDocument1 pageNJAW Water Treatment Processbas haNo ratings yet
- Test 4 Study Page: Tides: Waves: Currents: WaterDocument2 pagesTest 4 Study Page: Tides: Waves: Currents: WaterКагел МагтгиезNo ratings yet
- SPE 65007 Successful Applications of Anti-Agglomerant Hydrate InhibitorsDocument10 pagesSPE 65007 Successful Applications of Anti-Agglomerant Hydrate Inhibitorsaminbm.pt24No ratings yet
- Activity Sheet 4 Properties of WaterDocument14 pagesActivity Sheet 4 Properties of Waterhumptydumpty.elleNo ratings yet
- F Roth F LO A T N TIO: Guided ByDocument49 pagesF Roth F LO A T N TIO: Guided ByGri AvilaNo ratings yet
- Biology AS - Unit 1: Unit 1-1 Chemical Elements Are Joined Together To Form Biological Compounds Inorganic IonsDocument194 pagesBiology AS - Unit 1: Unit 1-1 Chemical Elements Are Joined Together To Form Biological Compounds Inorganic IonsDaKing ZWNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Chemistry of The Environment The Chemistry of WaterDocument19 pagesUnit 4 - Chemistry of The Environment The Chemistry of WaterNiña Viaña BinayNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Engineers (Chem 114E) Bpsu Science ClusterDocument15 pagesChemistry For Engineers (Chem 114E) Bpsu Science ClusterRodelynNo ratings yet
- Sample Brochure About Ecosystem of LakesDocument2 pagesSample Brochure About Ecosystem of LakesFrancis PingulNo ratings yet
- Water: Omar Khayat Faisal Al-Amoudi Abdulaziz Abuldouh Abdullah SejeniDocument7 pagesWater: Omar Khayat Faisal Al-Amoudi Abdulaziz Abuldouh Abdullah Sejenioak-606No ratings yet
- Water ResourcesDocument9 pagesWater Resourcesjo420No ratings yet
- Basic Environmental Engineering (Che4103) : Water and Water Quality ParametersDocument38 pagesBasic Environmental Engineering (Che4103) : Water and Water Quality ParametersNasir Ahmed YusufNo ratings yet
- 9 - Biology Interactive Reading PacketDocument7 pages9 - Biology Interactive Reading Packetapi-375285021No ratings yet
- Candido Gen Bio 2Document4 pagesCandido Gen Bio 2Joash Nimrod CandidoNo ratings yet
- 2-Water ChemistryDocument7 pages2-Water ChemistryHakdog playsNo ratings yet
- Freshwater Biodiversity UNDocument18 pagesFreshwater Biodiversity UNJuan Ignacio FeuerhakeNo ratings yet
- Gas ExchangeDocument3 pagesGas ExchangeDemi Ruth ElenNo ratings yet
- Matter Cycles Through Ecosystems.: Do Plants Release Water?Document5 pagesMatter Cycles Through Ecosystems.: Do Plants Release Water?Mr ShrekNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Aquatic Ecology - Barnes - Mann - 1991-8-31Document24 pagesFundamental of Aquatic Ecology - Barnes - Mann - 1991-8-31Lizeth Maria lizarazoNo ratings yet
- Wiki Water PDFDocument25 pagesWiki Water PDFAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- Give Two Ways of Determining The Genotypes (Height) of The Pawpaw Plant ShownDocument246 pagesGive Two Ways of Determining The Genotypes (Height) of The Pawpaw Plant ShownAbigail ChepkuruiNo ratings yet
- 5 Impending Signs of Landslides and Sinkholes Continuation... Feb. 8 2021Document23 pages5 Impending Signs of Landslides and Sinkholes Continuation... Feb. 8 2021Shiela Jean H. RescoNo ratings yet
- Fish - FINS GlossaryDocument7 pagesFish - FINS GlossaryTadej GornjecNo ratings yet
- G5 - LSR - 2Y - 5.07 Earths WaterDocument14 pagesG5 - LSR - 2Y - 5.07 Earths WaterJohn DavissonNo ratings yet
- Hot - Sour - and BreathlessDocument6 pagesHot - Sour - and BreathlessCatarina FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Water: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument26 pagesWater: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaZurneva RosyNo ratings yet
- Water Chemistry: CHM 001 Chemistry For EngineersDocument33 pagesWater Chemistry: CHM 001 Chemistry For EngineersEjay CabangcalaNo ratings yet
- Explanation Text - PassiveDocument12 pagesExplanation Text - Passivepd9hw7qzm9No ratings yet
- Unit 1Document196 pagesUnit 1No NameNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Biological Molecules: WaterDocument15 pagesChapter 1: Biological Molecules: WaterChong Hyen100% (1)
- EarthDocument9 pagesEarthSHERYN REANA A/P KUMARASAMY MoeNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange, Transport, Circulation PeTaDocument3 pagesGas Exchange, Transport, Circulation PeTaHarold James OrdonezNo ratings yet
- Water: Water Is A Transparent, Tasteless, Odorless, and Nearly Colorless ChemicalDocument31 pagesWater: Water Is A Transparent, Tasteless, Odorless, and Nearly Colorless ChemicalJonathan OtadoraNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 5-TranspirasiDocument8 pagesPertemuan 5-Transpirasieva febrianiNo ratings yet
- Unit 4. Lesson 3.: Cycles of MatterDocument8 pagesUnit 4. Lesson 3.: Cycles of MatterGabriela BolañosNo ratings yet
- Hydrologic CycleDocument2 pagesHydrologic CycleSonny Mae TuboNo ratings yet
- Earth Sheryn ReanaDocument10 pagesEarth Sheryn ReanaSHERYN REANA A/P KUMARASAMY MoeNo ratings yet
- Aqa Biology Unit b3 Revision GuideDocument23 pagesAqa Biology Unit b3 Revision Guide111222333ANo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of EcologyDocument9 pagesFundamentals of EcologyIssa AvenaNo ratings yet
- Water ChemDocument18 pagesWater Chemalysha100% (1)
- Lesson 1: Aquatic Ecosystems: Neighborhood Water QualityDocument12 pagesLesson 1: Aquatic Ecosystems: Neighborhood Water QualityVainapriya RNo ratings yet
- Dissolved Oxygen For Fish ProductionDocument3 pagesDissolved Oxygen For Fish ProductionLydia HasnaNo ratings yet
- Chemicals of Life 1 3Document30 pagesChemicals of Life 1 3kitderoger_391648570No ratings yet
- Exp SC 3 - Chapter 11Document10 pagesExp SC 3 - Chapter 11megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Water and Waste MGMTDocument7 pagesWater and Waste MGMTSATUR LABRADURNo ratings yet
- The Major Chemical and Physical Properties of Water AreDocument5 pagesThe Major Chemical and Physical Properties of Water AreApeksha BagchiNo ratings yet
- A1.1.4 Adhesion of Water To Materials That Are Polar or Charged and Impacts For Organisms.Document10 pagesA1.1.4 Adhesion of Water To Materials That Are Polar or Charged and Impacts For Organisms.taiga.aisaka14404No ratings yet
- List of MaterialsDocument5 pagesList of MaterialsNONI ZERIMARNo ratings yet
- Batty About Bats!Document25 pagesBatty About Bats!Chris CorralesNo ratings yet
- GFDGFDGDocument32 pagesGFDGFDGKelli Moura Kimarrison SouzaNo ratings yet
- The MailboxesDocument4 pagesThe MailboxesDayanaNo ratings yet
- ROSS 708: Performance ObjectivesDocument16 pagesROSS 708: Performance ObjectivesSafet FejzicNo ratings yet
- Study of Different Refrigerant Control Lab ManualDocument4 pagesStudy of Different Refrigerant Control Lab ManualMohdQasimNo ratings yet
- Stone VesselsDocument42 pagesStone VesselsVesna MatićNo ratings yet
- Josh Moulin - Covert Entry TacticsDocument5 pagesJosh Moulin - Covert Entry TacticsJosh MoulinNo ratings yet
- Quantum CryptographyDocument8 pagesQuantum Cryptographyapi-3777036No ratings yet
- EIN 3390 Chap 12 Expendable-Mold Cast B Spring - 2012Document51 pagesEIN 3390 Chap 12 Expendable-Mold Cast B Spring - 2012Deepak SharmaNo ratings yet
- LV RV FailureDocument118 pagesLV RV FailureMirza Thaariq HapsitoNo ratings yet
- English 4 Summative Test I-1Document19 pagesEnglish 4 Summative Test I-1CatfaldasNo ratings yet
- Packed Tower Internals PDFDocument32 pagesPacked Tower Internals PDFmehul10941No ratings yet
- Lucy, The Amazing Astronaut With An Incredible Dream: A) Follow The LinesDocument2 pagesLucy, The Amazing Astronaut With An Incredible Dream: A) Follow The LinesMaria Raquel RamirezNo ratings yet
- Hotel Navrang Liquor NON-1Document6 pagesHotel Navrang Liquor NON-1gourav.damadeNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word For Beginners: Training@health - Ufl.eduDocument17 pagesMicrosoft Word For Beginners: Training@health - Ufl.eduArvin Anthony Sabido AranetaNo ratings yet
- 438 TimetableDocument34 pages438 Timetablechubbylover5350% (2)
- Catalog of Coolmay 2018 V 5.4Document23 pagesCatalog of Coolmay 2018 V 5.4Amir MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Sap S4hana FicaDocument23 pagesSap S4hana FicaSurani shaiNo ratings yet
- TS 3 2022 MFP1Document2 pagesTS 3 2022 MFP1Goloo yadavNo ratings yet
- ASTM A789 Stainless Steel TubingDocument6 pagesASTM A789 Stainless Steel TubingPlinio PazosNo ratings yet
- Avigilon - 4.0c-H5a-Bo2-Ir-Camara BulletDocument11 pagesAvigilon - 4.0c-H5a-Bo2-Ir-Camara BulletLuisDonairesNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument3 pagesExamSidraGhafoorNo ratings yet
- The Perception of Bus Rapid Transit: A Passenger Survey From Beijing Southern Axis BRT Line 1Document21 pagesThe Perception of Bus Rapid Transit: A Passenger Survey From Beijing Southern Axis BRT Line 1Edmer FloresNo ratings yet
- Prodelin 1.8m 1184 Assembly Manual PDFDocument24 pagesProdelin 1.8m 1184 Assembly Manual PDFMario SegoviaNo ratings yet
- PartnershipsDocument35 pagesPartnershipspavithran selvamNo ratings yet
- Body Composition Analysis of Animals - A Handbook of Non-Destructive MethodsDocument252 pagesBody Composition Analysis of Animals - A Handbook of Non-Destructive MethodsRogelio Avila100% (1)
- Test Bank For Investments Analysis and Management 12th Edition JonesDocument10 pagesTest Bank For Investments Analysis and Management 12th Edition Jonesverityfelixl6e40No ratings yet