Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Renal Fabs 1
Uploaded by
sheynmalubay0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views15 pagesOriginal Title
Renal-Fabs-1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views15 pagesRenal Fabs 1
Uploaded by
sheynmalubayCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
Renal Fabs - Antidote:
- Calcium gluconate: Antagonist
Sodium: - Calcium decreases your magnesium
- Purpose: Most important electrolyte of the brain. levels
- Stimulant of the brain
- Hangovers are most likely related to hyponatremia.
- Related to water balance because sodium attracts your
Hypomagnesemia Hypermagnesemia
water.
Potassium Konti depressant (Up Marami depressant (Down
- Most important electrolyte of the heart Symptoms) symptoms)
- Promotes your neuromuscular contractility
I
- Hyperkalemia: Overworking of the heart
Altered LOC (Confusion, Altered LOC (Stupor,
Irritability) Obtunded, Lethargy, Coma)
- It could lead to the possibility of cardiac arrest
Chloride Deep tendon reflexes: Deep tendon reflexes:
- Has the same function as sodium Increased, hyperreflexia Decreased, hyporeflexia
- Not really a priority.
Seizures, Muscles cramps, Muscle weakness
Calcium
Tremors
- For the bones and teeth
- Significantly for the: neuromuscular contractility Insomnia, Increased RR HR Drowsiness, Decreased HR
- Muscles are related to the calcium RR BP
- Hypocalcemia: muscles will not contract
Cause: Alcoholism, Cause: Magnesium sulfate
- Indirectly related to phosphate
decreased intake in the diet toxicity, renal failure (down
Magnesium glomerular filtration rate):
- Depressant Magnesium in diet: Fiber, increased waste and fluids
- OD: Pre-eclampsia grains, legumes, spinach,
- Preeclampsia has a risk for seizures so we can use nuts.
magnesium to prevent it.
MGT: Least to most invasive MGT: Magnesium is
- Magnesium sulfate toxicity must be monitored.
- Oral magnesium rich eliminated via saline diuresis
- Symptoms: foods (urination), we can give
- Decreased tendon reflexes - Oral magnesium diuretics and replace lost
- Heart rate RRBP: Decreased supplements fluid via IV fluid
- Urine output: Decreased
- Hyperkalemia, Hypernatremia,
If magnesium is critically low: Renal failure: decreased
Intravenous functional nephrons: Hypocalcemia, Hyperphosphatemia,
diuretics are no longer Hypermagnesemia
Observe magnesium sulfate effective (Dialysis) - Excessive potassium intake
toxicity - Increased fluid or supplement
Antidote to - Drugs:
hypermagnesemia: Calcium - Potassium sparing drugs
gluconate, will be given via
IV - Spironolactone
- ACE inhibitors
- Lisinopril
Hyperkalemia: - Captopril
- Most important electrolyte in the heart. - NSAIDs
- Cause metabolic acidosis - Take with food because
- “The body CARED too much about K+” they are gastric irritants
- Cellular movement of K+ from intracellular to - Signs and symptoms of Hyperkalemia “MURDER”
extracellular (burns, tissue damage, etc) - Muscle weakness
- The potassium goes out of the cell to the - Too much contraction weakens the
blood. The sodium goes in to the cells muscle.
- Burns: HYPERkalemia - Urine output little or none (renal failure)
- Sodium: HYPOnatremia - Respiratory failure (due to muscle weakness)
- Adrenal insufficiency with Addison’s disease - Strongest respiratory muscle:
- Addison’s disease: Decreased Diaphragm
aldosterone levels (Aldosterone: - It may cause cardiac arrest
promotes water and sodium retention) - Decreased cardiac contractility
- Decreased aldosterone: decreased - Weak pulse or Low HR
sodium leading to HYPOnatremia, - Early: muscle twitches and cramps
leading to HYPERkalemia - Early signs and symptoms causes
- Renal failure: Decreased filtration rate cramps but if late, it gets tired and leads
- Increased electrolytes because blood to muscle weakness
cannot be filtered - Rhythm changes
- Tall peaked T waves, prolonged PR
interval
- Management of critical hyperkalemia - Low potassium in the diet
- Initial management: - Potassium wasting diuretics
- 10% Calcium gluconate: protects - Loop diuretics
myocardium - Thiazide diuretics (Microcide)
- Not related to potassium
- Fastest way to decrease your potassium HYPOKALEMIA
- Glucose insulin: stimulate uptake of - Causes
glucose with potassium “Your body is trying to DITCH K+”
- Insulin (Through IV) - Drugs:
- Given for the - Loop diuretics : Wasting
hyperkalemia - Furosemide
- Side effect of insulin: - Laxatives: Wasting
HYPOGLYCEMIA - Inadequate consumption of K+
- Therefore giving glucose to the - Too much water intake
patient to counteract the side - Cushing’s syndrome
effect of the insulin - Endocrine problem
- For DM Type I: Insulin with - Increased aldosterone
Potassium because side effect of - Increased sodium
insulin in patients with DM is - HYPERnatremia causing
hypokalemia. HYPOkalemia
- Sodium bicarbonate (Alkaline in nature) - Heavy fluid loss
- Correct metabolic acidosis to lower - Nasogastric tube suction
plasma K+ - Vomiting
- Metabolic acidosis: Increased - Diarrhea
potassium - Wound drainage
- Renal failure: Metabolic acidosis - Signs and symptoms
- Usually VIA IV drips - Asymptomatic: Late nadedetect
- Kayexelate - 7Ls (7 Lows)
- Via Enema or oral - Lethargic
- Sodium rich - Low shallow respirations…failure
- Sodium potassium exchange - Failure in muscle
- Potassium restriction - Lethal Cardiac dysrhythmias
- ST depression - Has a stimulant effect
- Shallow T wave - Signs and Symptoms of Hypernatremia
- Projecting U wave - Usually caused by dehydration
- Earliest symptom of - FRIED SALT
Hypokalemia - Flushed skin and fever (low grade)
- But cannot be seen by - Restless, irritable, anxious and confused
the naked eye (Up symptoms)
- Needs ECG - Increased blood pressure and fluid
- Lots of urine (Frequent and large retention
amount) - Edema, peripheral and pitting
- Problems with fluid loss - Third spacing (Fluid entered
- Leg cramps interstitial space)
- Limp muscles - Decreased urine output
- Low blood pressure (Severe) - Can be related to dehydration,
- Decreased contractility of heart decreased urine output because
- Management it is conserving fluid
- IV potassium replacement concentration in the blood
- Not more than 10-20 mEq/hr - Skin flushed
- Critically low - Agitation
- Incorporated: mix with IV fluid - Low grade fever
- But if doctor’s order is more than 20, it is - Thirst
required to have Cardiac monitor and - Management:
infusion pump - I/O : Watch out for fluid volume deficit
- High potassium diet - Urine specific gravity:
- Oral potassium replacement concentration of the urine (NV:
- For stable patients 1.010-1.030)
- It should be given with juice to increase - Dehydrated: Concentrated:
palatability Higher SG (>1.025) “Mabigat”
- Monitor cardiac rhythm - Neck veins: Flat
- Weak and thready pulses
SODIUM - Increased HR and RR
- Sodium is the most important electrolyte of the brain - Altered LOC (Up symptoms)
- Anxious - Seizures/Headache
- Weight - Related to severe sodium losses
- Most sensitive indicator of fluid - Stomach cramping
volume - Abdominal discomfort related to nausea
- In case of hypernatremia, there and vomiting
will be weight loss - Management of Hyponatremia
- Dry Mouth/Mucosa - Related to overhydration
- Poor skin turgor - Diluted sodium
- How do we remove sodium? - I/O: Monitor for overhydration
- Via diuresis with replacement of fluid - Specific gravity: <1.010 urine is diluted
- Low sodium diet “Magaan”
- Canned food - Bounding pulses
- Condiments - Distended neck veins
- Instant foods, processed food - BP: Increased BP, HRRR: Increased
- HYPONATREMIA (Vascular resistance)
- Down symptoms - Altered LOC: Down symptoms
- “SALTLOSS” - Weight gain because of
- Stupor overhydrated status
- Anorexia - Sodium tablet
- Nausea and vomiting - 0.9 NaCl PNSS
- Decreased stimulant - Electrolyte drinks
- Lethargy
- Tendon Reflexes CALCIUM
- Limp Muscles HYPERCALCEMIA
- Orthostatic Hypotension “BACKME”
- Drop in DP - Bone pain
- With respect with rapid change in - Arrhythmias
position - Cardiac arrest
- There will be dizziness and risk for falls - Kidney stones
- Management: - Muscle weakness
- Change position slowly, sit at the - Late symptom of late hypercalcemia
bed side because of the increased contractility
- Excessive urination - Hydration to 3000 to 4000 mL to
- Osmotic diuresis flush calcium and to decreased
- With the effort to remove the calcium renal calculi formation
- Parathormone (Katabi ng thyroid) - Synthetic calcitonin can be given to
- Promote calcium balance lower calcium levels
- Promotes bone decalcification or bone - Monitor I and O, vital signs,
resorption (Sisirain ang buto para lumabas ang muscle weakness and heart rate
calcium from the bone to the blood) and rhythm
- Calcitonin: from thyroid - Calcitonin:
- Promotes calcium uptake of the bone - To promote calcium from the
(Pinapapasok si calcium sa boto) blood to the bone
- Calcitonin and Parathormone has opposite HYPOCALCEMIA
effect - Signs and symptoms: “CATS”
- Hyperparathryoidism (Tumor) - Convulsions
- Increased parathormone - Can lead to cerebral edema
- Increased bone decalcification - Decreased contractility
- Increased calcium in the blood - Increased ICP
- Hypercalcemia - Arrhythmias
- That may lead to kidney stones - Decreased calcium leads to decreased
- Increased contractility of the contractility of the heart
heart, causing overworking of the - Tetany
heart that will cause - Numbness and stiffness of the muscles
ARRHYTHMIAS that would lead due to loss of ability to contract
to Cardiac Heart - Stridor and Spams
- Weak brittle bones - Weakness of diaphragm
- Prone to pathologic fracture - Hypoparathyroidism
- Nursing Management for Hypercalcemia - Related to accidental removal of parathyroid
- Promote calcium excretion via the urine (Post thyroidectomy)
- Loop diuretic - Unexpected
- Furosemide - Hypocalcemia is lifetime
- Ethacrynic acid - Malpractice of the doctor
- Calcium is for contractility
- Trousseau’s sign : Severe - Possible mapagod si
- Induction of carpopedal spasms by inflation of a heart if dumami si
sphygmomanometer above SBP for 3 minutes calcium bigla
- Response: - Other Management
- Carpopedal spasms characterized by - IV: Main
- Adduction of thumb - High calcium diet of the
- Flexion of metacarpophalangeal filipinos (Sardines)
joints - High calcium diet of the
- Extension of interphalangeal world (Anchovies)
joints - Vitamin D Supplements
- Flexion of the wrist - Promotes calcium
- Chvotek’s sign absorption
- Contraction of the ipsilateral facial muscle
elicited by tapping the facial nerve just anterior KIDNEYS
to the ear Mnemonic for functions “WET BREAD”
- Response:
- Twitching of the lip to spasm of all facial
Function of the Renal Failure Management
muscles kidney
- Nursing management for Hypocalcemia
- IV: Calcium gluconate Water Balance Hypervolemia : it Fluid restriction (1
- Vesicant solution can cause to 1.5 L/day)
- Irritating to the vein causing cerebral edema,
congestive heart Diet: Low sodium
extravasation (Nasunog ang
failure, portal diet
ugat) hypertension,
- Can lead to Phlebitis pulmonary Diuretics : for
- Management: Use bigger veins hypertension acute renal
- More blood, better failure, reversible,
dilution high percentage of
functioning
- Bleeding gums and mucosa
nephrons
- Calcium is related to your Chronic renal
clotting factors failure:
- Watch out for: Cardiac Monitor
Irreversible, Altered LOC: Renal
decreased Different focusing, Encephalopathy:
functioning of seizures, coma Safety is priority
nephrons,
diuretics are no Uremic Frosts Calamine lotions,
long effective (Acid): Itchy skin antihistamines,
oatmeal bath,
cocoa butter
Electrolyte Hypernatremia Restrict Na in the lotions, cut
balance diet fingernails short,
sodium
Hyperkalemia Insulin with bicarbonate
glucose
Sodium Dialysis
bicarbonate can
be given Blood pressure Hypertension Calcium channel
control because of fluid blockers
Hypocalcemia, Phosphate volume excess Betablockers
Hyperphosphatem binders to
ia decrease
phosphate (Ex. RAAS system: Increased ACE inhibitors-
Alum hydroxide, Renin and aldosterone: causes
Antacids) angiotensin hypernatremia hyperkalemia
aldosterone and hypervolemia ARBS:
Hypermagnesemi Calcium system Angiotensin
a gluconate: Severe receptor blockers
cases Aldosterone: (Sartans):
sodium and water Prevents
Toxin Removal Urea build up Low protein retention aldosterone
Urea (Ntirogen - (Uremia) source from high formation:
byproduct of Nitrogen build up biologic source : Decreased
protein) (Azotemia) Low nitrogen Sodium and water
byproduct, white retention
Urea build up: can meat, Poultry,
cause renal Dairy, Tofu
encephalopathy: Erythropoietin : Decreased Synthetic
Stimulates RBC erythropoietin: erythropoietin :
production Decreased RBC stimulates RBC Hypertension
production production
(Decrease DM: decreased blood flow
oxygenation, easy because viscous
fatigability, activity
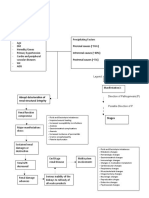
intolerance) Intrarenal failure: Inside the Glomerulonephritis,
kidneys nephrotoxic drugs,
Acid balance Hyperkalemia Sodium Nephron, glomerular, tubular dye/contrast medium:
causes metabolic bicarbonate drip damage : Decreased Tubular necrosis (Tissue
acidosis : Cardiac filtration rate, decreased death)
arrest urine production Tubular sclerosis (Tissue
scarring)
D- Vitamin D : Hypocalcemia : Vitamin D
promotes Hyperphosphatem supplements Post renal failure (After the > Renal calculi
absorption of ia kidneys), with urine > Benign prostatic
calcium production but hyperplasia
OBSTRUCTED > Bladder cancer > Bladder
failure
Causes:
- Acute renal failure
- High reversible in nature
Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease
- Goal: to preserve kidney functioning
- Stage 1: Kidney damage with normal or increased
- Acute renal failure would cause chronic renal failure
EGFR
- Chronic renal failure: Irreversible
- Normal EGFR: 90 to 125mL/min
- Stage 2: Mild
- Weakness
Causes of Renal Failure Examples - Nausea and vomitin
- Stage 3: Moderate
Prerenal failure (before the Decreased cardiac output or
kidneys), decreased related to heart future - Stage 4: Severe
perfusion status - decreased - Stage 5: Kidney failure
filtration status - little to none Hemorrhage
urine production Renal transplant: High risk for rejection
Sepsis - By the immune system
- Management: immunosuppressants
Uses dialyzer to filter blood Dialysate: high in glucose
- Ex. Azathioprine, steroids, cyclosporine and remove waste (More that would cause
- High risk for infection efficient) hyperglycemic,
- Symptom of kidney rejection hyperosmolar ultrafiltration
- Oliguria
- Flank pain Access points: AV fistula Access point: Peritoneum
(takes 3 months to be (Between umbilicus and
- Renal encephalopathy
prepared), if not yet suprapubic area)
available, intrajugular
DIALYSIS catheter (More accessible)
- Hemodialysis
- Dialyzer serves as the kidney For severe cases with For young, milder cases,
- Peritoneal decreased renal functioning ambulatory with high renal
functioning
- Dialysate : high in glucose
- Osmosis: from lower to higher concentration AV fistula care: Keep it clean Dialysate: rich in glucose,
and dry, avoid BP taking, watch out for hyperglycemia
phlebotomy, at the affected
site
Check patency: Present bruit
> (Aucultate: Whooshing
sound) and thrill (palpate :
machine like vibrations)
Prio complication: Prio complication: Peritonitis
- Disequilibrium syndrome
Clinical symptoms: Rigid
WHAT: It offers you cerebral boardlike abdomen, fever,
Hemodialysis Vs. Peritoneal dialysis edema - increased ICP - increased HR RR
Altered LOC, BP decreased, Why? Dialysate -Rich in
HRRR increased, possible glucose - attracts infection
for coma and seizures
Hemodialysis Peritoneal dialysis WHY:Rapid removal of Management: Report,
nitrogen waste related to medical emergency, it may
- Decreased albumin, down oncotic pressure,
rapid rate of HD lead to septic shock
third spacing (Edema, Ascites, Anasarca)
Management: Stop, report Patient home based - Cause:
- Infections
Teach sterile technique - Post GABS (Group A Beta
hemolytic Strep) : history of strep
AV Fistula: Large blood Peritoneum: risk of bowel
throat infection or rarely impetigo
vessels, high chance of perforation
bleeding - Bacterial endocarditis
- Viral:HIV hepa B, Hepa C
WOF: Muscle cramps. That - Autoimmune disorders
is caused by rapid removal - SLE: Systemic lupus
of fluid and sodium erythematosus
- Systemic inflammation
Management: administer
fluid and sodium (PNSS) - Good pasture’s syndrome
- Mimics pneumonia,
causes bleeding in the
lungs or glomerulus
GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
- With secretions
- Inflammation of glomerulus inside the nephron
- IgA nephropathy
- Usually caused by Staphylococcus spp.
- D/T recurrent episodes of
- Decreased EGFR: will cause increased fluid and waste
blood in the urine, can be
- Acute renal failure (Irreversible)
asymptomatic for years
- Long term, it will lead to chronic renal failure
- Beurger’s disease:
- Headache and lethargy: renal encephalopathy
cola-colored urine :
(increased urea)
hematuria
- Urea: highly toxic to your brain
- Other conditions
- Hypertension and Edema
- High BP
- Related to fluid retention
- Diabetic nephropathy
- Fever
- Focal segmental
- Related to inflammatory responses
glomerulosclerosis: scattered
- Proteinuria
scarring of glomeruli either
pathologic or idiopathic
- Intraproblem
- Diagnostics:
- Urine: presence of RBCs, red cell casts,
WBCs, elevated creatinine and urea
- Blood tests: Elevated BUN and
Creatinine
- Kidney UTz, Xray, CT scan
- Kidney biopsy
- Treatment
- General goal is to treat underlying cause
and preserve kidney function
- To prevent the progression to chronic
renal failure
- For GABS - Collection of symptoms
- Might improve without treatment, - Nephritic syndrome:
antibiotics can also be used - Inflammation of the glomerulus
- For autoimmune DO - HIHO
- Corticosteroid or - HTN
immunosuppressants - Inflammation of glomerulus
- For DM - Hematuria
- Blood sugar control via insulin or - Oliguria
OHA - Nephrotic syndrome
- For hypertension - Hypoalbuminemia: oncotic pressure problem >
- Sodium restriction and loop Third spacing,
diuretics - Ascites
- Dietary protein and potassium restriction - Hyperlipidemia
for BUN elevation, carbohydrates given - Cholesterol
liberally - Oh my god! Ang taas ng cholesterol!
- Fluid balance is utmost priority - Oil or Olesterol
- Proteinuria
NEPHROTIC VS NEPHRITIC SYNDROME - Foamy urine
- OEdema
- Weight gain - Blood tests for albumin, cholesterol and
- Periorbital trigly
- Causes of nephrotic syndrome - Kidney biopsy
- DM - Management
- Chronic GN - Objective is to preserve renal function
- SLE and prevent complications
- Multiple myeloma - Diuretics , ACE inhibitors, ARBS : To
- Cancer of the plasma decrease BP
- Causes an abnormal globulins - Antineoplastics : Multiple myeloma
- Amyloidosis of the kidneys - Immunosuppressants : Autoimmune
- Accumulation of amyloid proteins disorders
in the kidney - Corticosteroid: Autoimmune disorders
- Renal vein thrombosis - Blood thinners: Prevents risk of clots
- Emboli formation - Low sodium diet
- Infections (HIV, Hepa B and C, Malaria) - Dietary restrictions of protein and
- Complications cholesterol
- Blood clots: due to poor filtration that
leads to loss of protein needed to Nephritic Syndrome
prevent clotting - Inflammation of glomerulus
- Aspirin or anticoagulants - Down GFR
- High BP and triglycerides: loss of - Acute
albumin stimulates liver to produce - Major cause of Beurger’s disease
albumin and produce cholesterol and - Diagnostics
trigly consequently - Urine tests for hematuria, dark colored urine
- Poor nutrition - Blood tests for uremia or azotemia
- Acute kidney injury - Uremia: increased urea in the blood
- Chronic kidney disease - Azotemia: increased nitrogen in the
- Higher risk of infection blood
- Diagnostics - Kidney biopsy
- Urine test for albumin levels: Low, - Treatment
hypoalbuminemia - Bed rest
- A diet that is restricted in salt, potassium and - Manageable
fluid - Management
- Medication to control BP - Alpha blockers: relax bladder neck
- Medication to reduce inflammation muscles and muscle fibers of prostate,
- Medication to remove fluids from the body making urination easier
- Dialysis to replace kidney function in severe - Examples: alfuzosin, doxazosin,
cases tamsulosin, and silodosin
- Side effects: dizziness and
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia harmless condition in which
- FUN-WISE semen goes back into the
- Irritative symptoms bladder instead out of the tip of
- Frequency the penis (Retrograde
- Urgency ejaculation)
- Nocturia - Priority is safety
- Obstructive symptoms - 5-alpha reductase inhibitors
- Weak stream - Shrink your prostate by
- Intermittency preventing hormonal changes
- Straining that cause prostate growth
- Emptying incomplete - Examples: Finasteride and
- Prostate gland: produces glucose and fluid for the dutasteride
sperm to survive - Side effect: Retrograde
- Aging men: decreased sexual practice ejaculation
- BPH: causes obstruction of urine - Tadalafil
- Postrenal failure - Studies suggest this medication
- Increased frequency and urgency to void - Often used to treat erectile
- Diagnostics dysfunction
- Digital Rectal Exam - Can also treat prostate
- 1 finger, gloved with lubricant enlargement
- Poc: left side lying, with knees - Sildenafil: Purpose: Vasodilator
flexed/Sim lateral position, straighten the - To decrease BP
colon - SE: Penis erection
- PSA - WOF: Hypotension
- Surgical procedures: Prostatectomy - Flush out clots and electrolytes
- TURP: Transurethral resection of - Normal within 24 hours
prostate gland (No incision) - Pinkish red because there is still
- Faster recovery bleeding (Increased flow rate)
- Risk for bladder clots and - Normal after 24 to 48 hrs
bleeding - Clear na dapat (Decreased flow rate)
- Perform cystoclysis/
continuous bladder
irrigation
- Radical prostatectomy
- With incision
- Via the rectum
- Slower recovery
Cystoclysis
- Three way foley catheter
- Inflow port
- Outflow port
- Anchor
- Urobag:
- Below the bladder because it works via gravity
- Solution
- Ideally PNSS (with sodium)
- Equal concentration with bladder as
bladder has sodium
- Prevents water toxicity
- No osmosis (no movement of water)
- If distilled water, without sodium (Lower conc)
- There will be osmosis
- Promotes water toxicity
- Priority
- Patent system
You might also like
- Diana's Renal DiseasesDocument9 pagesDiana's Renal DiseasesdhyltonNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Condition NCM 112Document10 pagesCardiac Condition NCM 112Irish Eunice FelixNo ratings yet
- PathoPhysiology of Renal Failure (Overview)Document7 pagesPathoPhysiology of Renal Failure (Overview)Tiger Knee100% (3)
- Obsessive Compulsive Disorder: Patient Treatment ManualDocument20 pagesObsessive Compulsive Disorder: Patient Treatment ManualJay DraperNo ratings yet
- Potassium (Hyperkalaemia and Hypokalaemia) - Armando HasudunganDocument4 pagesPotassium (Hyperkalaemia and Hypokalaemia) - Armando HasudunganDr.Snehal100% (1)
- English User Manual of JHF-53 (HIFU)Document17 pagesEnglish User Manual of JHF-53 (HIFU)dfdfdfdfdfdf100% (1)
- An Investigatory Project ProposalDocument13 pagesAn Investigatory Project ProposalJeg B. Israel Jr.No ratings yet
- Hypermagnesemia: Lim - Madalan - Madelo - MagalitDocument17 pagesHypermagnesemia: Lim - Madalan - Madelo - MagalitKyle De Sagun Oteda100% (1)
- Renal Fabs NotesDocument9 pagesRenal Fabs NotesLucky GomezNo ratings yet
- PharmaDocument3 pagesPharmaConcepcion NazaredoNo ratings yet
- SIADH/DIDocument7 pagesSIADH/DIKimberly Louise LopezNo ratings yet
- Doria. 30emergency DrugsDocument7 pagesDoria. 30emergency DrugsAbegail Bautista DoriaNo ratings yet
- Diuretic Theraphy and Drugs For Renal FailureDocument2 pagesDiuretic Theraphy and Drugs For Renal Failurerenz bartolomeNo ratings yet
- ElectrolyteDocument4 pagesElectrolyteRon Vien'sNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Values: ElectrolytesDocument5 pagesLaboratory Values: ElectrolytesLauren Agatha ManipolNo ratings yet
- Hypokalemia and Hyperkalemia: Normal Value: 3.5-5 Meq/L Hypokalemia HyperkalemiaDocument7 pagesHypokalemia and Hyperkalemia: Normal Value: 3.5-5 Meq/L Hypokalemia HyperkalemiaSyimah UmarNo ratings yet
- Doria. 30emergency DrugsDocument7 pagesDoria. 30emergency DrugsAbegail Bautista DoriaNo ratings yet
- CC Lec Mod 3Document13 pagesCC Lec Mod 38wgmhh9ks9No ratings yet
- Ammonia Manganese: AstrocytesDocument2 pagesAmmonia Manganese: AstrocytesJULIUS ART VINCENT A. PADINITNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte Imbalances 103123Document14 pagesElectrolyte Imbalances 103123grazelantonette.calubNo ratings yet
- Fluids PDFDocument26 pagesFluids PDFLeogalvez BedanoNo ratings yet
- Viii. Pathophysiology A. Overview of The Disease HypokalemiaDocument4 pagesViii. Pathophysiology A. Overview of The Disease HypokalemiaCleo Joyce C. CristalNo ratings yet
- Fluids & Electrolytes 5Document14 pagesFluids & Electrolytes 5Justin Angelo SildoraNo ratings yet
- Felixcharlie Electrolyte Homeostasis Part 3Document3 pagesFelixcharlie Electrolyte Homeostasis Part 3Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- NCM 112-Mod4Document2 pagesNCM 112-Mod4Samantha BolanteNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes LecDocument4 pagesElectrolytes LecMichelle San Miguel FeguroNo ratings yet
- Zalameda - Thiazides Loop Diuretics Osmotic Diuretics Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Potassium SparingDocument16 pagesZalameda - Thiazides Loop Diuretics Osmotic Diuretics Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Potassium SparingNicole ObispoNo ratings yet
- Ncmb316 Lec: BSN 3Rd Year 2Nd Semester Final 2023: Parkinson'S Disease, Multiple Sclerosis, and Myasthenia GravisDocument31 pagesNcmb316 Lec: BSN 3Rd Year 2Nd Semester Final 2023: Parkinson'S Disease, Multiple Sclerosis, and Myasthenia GravisGideon Mercado UmlasNo ratings yet
- Introduction & Epidemiology Clinical Features: End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD)Document2 pagesIntroduction & Epidemiology Clinical Features: End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD)Nikki VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Wk8 - Electrolyte Imbalances & Acid-Base ImbalancesDocument65 pagesWk8 - Electrolyte Imbalances & Acid-Base ImbalancesPotato PceeNo ratings yet
- SodiumDocument3 pagesSodiumEmily FernandezNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System-Ms3-Maam RioDocument5 pagesEndocrine System-Ms3-Maam RioLovely Hope LugatimanNo ratings yet
- Fe Finals NotesDocument23 pagesFe Finals NoteshanhananicasNo ratings yet
- Glomerulonephritis vs. NephrosisDocument1 pageGlomerulonephritis vs. NephrosisHailey ReeseNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Electrolytes (Concentration and Composition Changes)Document6 pagesFluids and Electrolytes (Concentration and Composition Changes)Kristin SaberonNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes Na, MG, Ca, KDocument10 pagesFluid and Electrolytes Na, MG, Ca, Kfile downloadNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Part 2 DRAFTDocument6 pagesEndocrine Part 2 DRAFTPreeti Joan BuxaniNo ratings yet
- Eelectrolyte DisordersDocument14 pagesEelectrolyte DisordersarianNo ratings yet
- PHS CVSDocument25 pagesPHS CVStewogbadeomobuwajo005No ratings yet
- Sodium CompatibleDocument2 pagesSodium CompatiblesherikeeNo ratings yet
- Fe 2Document26 pagesFe 2api-3697326No ratings yet
- Mark Billy L. Perpetua, Man RN: Fluids, Electrolytes andDocument96 pagesMark Billy L. Perpetua, Man RN: Fluids, Electrolytes andMaica LectanaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument4 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseImnot YouNo ratings yet
- MedicationDocument3 pagesMedicationmurphy 1087No ratings yet
- Sodium Imbalances (Hyponatremia Vs Hypernatremia)Document17 pagesSodium Imbalances (Hyponatremia Vs Hypernatremia)Angel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- LP3 NCM 112 Electrolytes2021 UpdatedDocument57 pagesLP3 NCM 112 Electrolytes2021 UpdatedJade CentinoNo ratings yet
- Furosemide Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFurosemide Drug StudyNoah Kent MojicaNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Cardiovascular DisordersDocument6 pagesDrugs For Cardiovascular DisordersAirha Mhae HomoNo ratings yet
- Pedia - Intensive PhaseDocument2 pagesPedia - Intensive Phasepasabay270No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument7 pagesCardiovascular SystemLeigh Maxenne IcoNo ratings yet
- Magnesium Sulfate 250 500 MG Metoclopramide Drug StudyDocument4 pagesMagnesium Sulfate 250 500 MG Metoclopramide Drug Studyprog.ecleo.swuNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology NotesDocument22 pagesPharmacology NotesAlexia OwenNo ratings yet
- Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Side Effects/ Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: Brand Name: Classifications: DoseDocument1 pageDrug Mechanism of Action Indications Side Effects/ Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: Brand Name: Classifications: DoseRAFNo ratings yet
- Activity On Pituitary Disorders and Diabetes MellitusDocument8 pagesActivity On Pituitary Disorders and Diabetes MellitusSherlyn Miranda GarcesNo ratings yet
- Medici Di Makati College 1061 Metropolitan Avenue, San Antonio Village, Makati City, Philippines 1200Document18 pagesMedici Di Makati College 1061 Metropolitan Avenue, San Antonio Village, Makati City, Philippines 1200Andee SalegonNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes: Dr. Nupur SarkarDocument24 pagesFluid and Electrolytes: Dr. Nupur SarkarNupurshinjiniNo ratings yet
- Pathognomonic SignsDocument11 pagesPathognomonic Signscheskahortelano08No ratings yet
- Fluids and Renal DisorderDocument139 pagesFluids and Renal DisorderLhara MañoNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances Part 2Document46 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Imbalances Part 2Gabrielle Frances FernandezNo ratings yet
- HypoparathyroidismDocument2 pagesHypoparathyroidismLorelyn Santos CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical NursingDocument11 pagesMedical Surgical NursingMaria TagubaNo ratings yet
- ElectrolytesDocument2 pagesElectrolytestentenNo ratings yet
- Ramesh Chandra Agarwal Vs Regency Hospital LTD SC 2009 Expert Opinion Can Not Be Accepted Without ExaminationDocument18 pagesRamesh Chandra Agarwal Vs Regency Hospital LTD SC 2009 Expert Opinion Can Not Be Accepted Without ExaminationYatn BangadNo ratings yet
- Radiology ContrastDocument4 pagesRadiology ContrastsreekaasamNo ratings yet
- Allergy Clinic Policy and ProceduresDocument4 pagesAllergy Clinic Policy and ProceduresMiselonNo ratings yet
- 2019 Lateral Extra-Articular Tenodesis With ACL Reconstruction Demonstrates Better Patient-Reported Outcomes Compared To ACL Reconstruction Alone at 2 Years Minimum Follow-UpDocument9 pages2019 Lateral Extra-Articular Tenodesis With ACL Reconstruction Demonstrates Better Patient-Reported Outcomes Compared To ACL Reconstruction Alone at 2 Years Minimum Follow-Upsumon.huqNo ratings yet
- Phaseolus VulgarisDocument25 pagesPhaseolus VulgarisMueen mohsinNo ratings yet
- Living With A Tracheostomy: Patient EducationDocument2 pagesLiving With A Tracheostomy: Patient EducationJack Supramaniam100% (1)
- MohammediaDocument3 pagesMohammediasetata7128No ratings yet
- The Critical-Care Pain Observation Tool (CPOT) : Indicator Score DescriptionDocument6 pagesThe Critical-Care Pain Observation Tool (CPOT) : Indicator Score DescriptioncignalNo ratings yet
- ST 11 Juni-1Document38 pagesST 11 Juni-1yunannegariNo ratings yet
- Differences in Left Ventricular and Left Atrial FuDocument10 pagesDifferences in Left Ventricular and Left Atrial FueugeniaNo ratings yet
- Oral Contributions: JACC March 9, 2010 ABSTRACTS: Cardiac Arrhythmias A1Document217 pagesOral Contributions: JACC March 9, 2010 ABSTRACTS: Cardiac Arrhythmias A1Apner Calvin SuNo ratings yet
- Muscular System FunctionDocument2 pagesMuscular System FunctionLachlan PalmerNo ratings yet
- Final PhysicalDocument409 pagesFinal PhysicalAbhishiktaAbhiNo ratings yet
- Pharma Prelim ExamDocument6 pagesPharma Prelim ExamMelody DoriaNo ratings yet
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Jodhpur: WebsiteDocument4 pagesAll India Institute of Medical Sciences, Jodhpur: WebsiteTai ManuNo ratings yet
- Daily Inspiration: Powered by Crystallive™Document8 pagesDaily Inspiration: Powered by Crystallive™douglaszimbaNo ratings yet
- 2020 Using Sildenafilto Treata Dogwithidiopathic MegaesophagusDocument7 pages2020 Using Sildenafilto Treata Dogwithidiopathic MegaesophagusEduardo SantamaríaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Plan For PidDocument5 pagesTeaching Plan For PidokaciaNo ratings yet
- J1-T5 Anemia FerropénicaDocument12 pagesJ1-T5 Anemia FerropénicaGoblin HunterNo ratings yet
- Alajar - Act9 - Biol 015Document3 pagesAlajar - Act9 - Biol 015jarrettrayke14No ratings yet
- Personalized Acute Kidney Injury TreatmentDocument8 pagesPersonalized Acute Kidney Injury TreatmentGabriela PachecoNo ratings yet
- VACCINESDocument8 pagesVACCINESzilikajainNo ratings yet
- Pham Ngoc Thach University of Medicine DUOC2019Document109 pagesPham Ngoc Thach University of Medicine DUOC2019Nhung PhamNo ratings yet
- Tarife AnalizeDocument1 pageTarife AnalizeVincze Alina ClaudiaNo ratings yet
- Hinoguin, Jocelyn Patana 1851114785Document3 pagesHinoguin, Jocelyn Patana 1851114785Paulline Joyce HinoguinNo ratings yet
- Case Study SampleDocument4 pagesCase Study SamplenivienneNo ratings yet
- Case Obsos SellyDocument24 pagesCase Obsos SellyDwi CahyaNo ratings yet