Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sec 4. Mathematics
Uploaded by
huangchasonOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sec 4. Mathematics
Uploaded by
huangchasonCopyright:
Available Formats
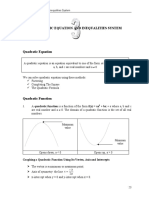
Quadratic Equations Cheat Sheet
When graphed on the coordinate plane, a quadratic equation produces a parabola.
Standard Form: y = ax2 + bx + c
Vertex Form: y = a(x - h)2 + k, where (h, k) is the vertex
Factored Form: y = a(x - r1)(x - r2) where (r1, 0) and (r2, 0) are x-intercepts/solutions
Vertex - The highest or lowest point of a parabola Axis of Symmetry - A vertical line
- Leading coefficient (a)> 0 → vertex is a minimum passing through the vertex that
- Leading coefficient (a) < 0 → vertex is a maximum cuts the parabola in half.
x = −b2a
By Hand In the Calculator
Use x = −b
to find the x Enter the equation into
2a
coordinate, then re-substitute Y=. CALC →
into the original equation to 3: Minimum or
find the corresponding y 4: Maximum
coordinate.
Discriminant - Tells how many solutions a quadratic equation has (i.e. how many times the
parabola crosses the x-axis). d < 0 → no solution
d = b2 – 4ac d > 0 → 2 solutions
d = 0 → 1 solution
Solving Quadratic Equations - X-coordinates at which the parabola crosses the x-axis
Factoring Quadratic Formula Graphing
Factor the equation, then set Enter equation in Y=. Adjust
each binomial equal to zero. window to see all x-intercepts.
−b ± √b2 − 4ac
Solve for x in those two
equations.
x= 2a
CALC → 2: Zero for both
intercepts.
Completing the Square
1. Group the x2 and x terms together in parenthesis.
2 2
2. Add ( b2 ) inside the parenthesis and subtract ( b2 ) behind the parenthesis.
3. Factor the trinomial in the parenthesis to write as a squared binomial.
4. Combine the constants after the squared binomial.
You might also like
- Nogva Marine Gearbox Ver.3.1Document30 pagesNogva Marine Gearbox Ver.3.1cezar frasao67% (3)
- Algebra - Quantitative Aptitude For CAT EBOOKDocument6 pagesAlgebra - Quantitative Aptitude For CAT EBOOKaditya_kumar_me80% (5)
- UsersGuide deltaECDocument285 pagesUsersGuide deltaECHakan AteşNo ratings yet
- PATENT DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS Concept MapDocument2 pagesPATENT DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS Concept MapErika CadawanNo ratings yet
- Post Utme Past Questions and Answers GeneralDocument123 pagesPost Utme Past Questions and Answers GeneralSuccess EzekielNo ratings yet
- A, B, and C Are Real Numbers and A and B Are: C. by Quadratic FormulaDocument2 pagesA, B, and C Are Real Numbers and A and B Are: C. by Quadratic FormulaLean Amara VillarNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICSDocument2 pagesMATHEMATICSLean Amara VillarNo ratings yet
- A, B, and C Are Real Numbers and A and B Are: C. by Quadratic FormulaDocument2 pagesA, B, and C Are Real Numbers and A and B Are: C. by Quadratic FormulaLean Amara VillarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MathematicsDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Mathematicsnjihiawambui29No ratings yet
- 09: Quadratic Equations: Key Terms Concept MapDocument1 page09: Quadratic Equations: Key Terms Concept MapVikas MisraNo ratings yet
- Caie As Level Mathematics 9709 Pure 1 v5Document22 pagesCaie As Level Mathematics 9709 Pure 1 v5Karim OsmanNo ratings yet
- 1432 KamprRuS ResumenecuacionyfuncioncuadraticaDocument8 pages1432 KamprRuS Resumenecuacionyfuncioncuadraticav_149739253No ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations: Square Root MethodDocument8 pagesQuadratic Equations: Square Root MethodMatthew TabucaoNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Additional Mathematics 0606 Theory v2Document7 pagesCaie Igcse Additional Mathematics 0606 Theory v2965161191No ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Additional Mathematics 0606 Theory v2Document8 pagesCaie Igcse Additional Mathematics 0606 Theory v2ballersNo ratings yet
- Middle School Mathematics: 1 Introduction of This ClassDocument9 pagesMiddle School Mathematics: 1 Introduction of This Class01. ZUENo ratings yet
- TwitterDocument4 pagesTwitterAngel Joy ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Brown and White Doodle Creative Kids Workshop Brochure 1Document2 pagesBrown and White Doodle Creative Kids Workshop Brochure 1dhanliecordovezNo ratings yet
- As Math - Pure 1 - ZnotesDocument22 pagesAs Math - Pure 1 - ZnotesYossef AmrNo ratings yet
- Math9 (Pivot)Document24 pagesMath9 (Pivot)Patrick MorgadoNo ratings yet
- EE C222/ME C237 - Spring'18 - Lecture 3 Notes: Murat Arcak January 24 2018Document5 pagesEE C222/ME C237 - Spring'18 - Lecture 3 Notes: Murat Arcak January 24 2018SBNo ratings yet
- Calc II ReviewDocument7 pagesCalc II ReviewPablo KhilopNo ratings yet
- Math NotesDocument1 pageMath NotesCesal100% (1)
- Mathematics Formula Sheets (Class-X)Document34 pagesMathematics Formula Sheets (Class-X)Mansi RajputNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation and Inequalities SystemDocument14 pagesQuadratic Equation and Inequalities Systemmintchoco98No ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations: Lecture-1 Solving Polynomial EquationsDocument5 pagesQuadratic Equations: Lecture-1 Solving Polynomial EquationsSoham RaneNo ratings yet
- An Equation of The Second Degree in X Is Called A QUADRATIC EQUATION and Is Written in TheDocument3 pagesAn Equation of The Second Degree in X Is Called A QUADRATIC EQUATION and Is Written in TheizumiNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Math Q1 M1Document12 pagesGrade 9 Math Q1 M1Renny Romero Luzada100% (2)
- Caie As Level Maths 9709 Pure 1 v2Document22 pagesCaie As Level Maths 9709 Pure 1 v2Daniel LiuNo ratings yet
- Solving Neq1Document6 pagesSolving Neq1SAYID MABRUR RABBANI AL BABNo ratings yet
- Solve Quadratic Inequalities: Learning ObjectivesDocument10 pagesSolve Quadratic Inequalities: Learning ObjectivesNSHANJI BrandonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 PDFDocument60 pagesChapter 3 PDFBrishti AroraNo ratings yet
- Polynomial Equation Quadratic EquationDocument1 pagePolynomial Equation Quadratic EquationJaswant SubudhiNo ratings yet
- The Graph of y Ax 2 - BX - C (Algebra 1, Quadratic Equations) - MathplanetDocument5 pagesThe Graph of y Ax 2 - BX - C (Algebra 1, Quadratic Equations) - MathplanetArlin SisonNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Lesson NotesDocument22 pagesUnit 9 Lesson Notesapi-291793268No ratings yet
- Ecuaciones de 2do GradoDocument17 pagesEcuaciones de 2do GradoCARLOS LEONEL BARRERA GAMBOANo ratings yet
- Different Forms of Quadratic FunctionsDocument3 pagesDifferent Forms of Quadratic FunctionsCharalampidis Dimitris0% (1)
- Algebra FormulasDocument12 pagesAlgebra FormulasLuis Fernando De AlvarengaNo ratings yet
- A1 c9 Study Guide and Review Worked Out Solution KeyDocument31 pagesA1 c9 Study Guide and Review Worked Out Solution KeyLiezl CanlasNo ratings yet
- Solutions 2: Vector FieldDocument12 pagesSolutions 2: Vector FieldAnnas FauzyNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument32 pagesMathsnour mohammedNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Formula ProjectDocument6 pagesQuadratic Formula ProjectCameron TomNo ratings yet
- AmathDocument9 pagesAmathAnnette ChiangNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Add Maths 0606 Theory v1Document8 pagesCaie Igcse Add Maths 0606 Theory v1vivianlangzhaoNo ratings yet
- Linear Equation-X CheatsheetDocument5 pagesLinear Equation-X CheatsheetJd AnimationNo ratings yet
- Applications of Equalities and InequalitiesDocument14 pagesApplications of Equalities and Inequalities鄭仲抗No ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics (Formulas)Document2 pagesAdditional Mathematics (Formulas)Yousuf MemonNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics: Formula That Are Within The Syllabus and Which Need To Be LearntDocument2 pagesAdditional Mathematics: Formula That Are Within The Syllabus and Which Need To Be LearntJames SimNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Quadratic EquationiiiDocument9 pagesWorksheet Quadratic EquationiiiKartik AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Lezione 3Document17 pagesLezione 3blackwoodsam3No ratings yet
- Math 9 Module 1Document7 pagesMath 9 Module 1Lance GabrielNo ratings yet
- Esempio LezioneDocument2 pagesEsempio LezionePaolaNo ratings yet
- Algebra Formulas: Log Formulas: Quadratic Equations: General FormDocument2 pagesAlgebra Formulas: Log Formulas: Quadratic Equations: General FormJerome MansibangNo ratings yet
- Algebraiic Expressions, Equations and Quadratic EquationsDocument37 pagesAlgebraiic Expressions, Equations and Quadratic EquationsNaomi NyambasoNo ratings yet
- QE - 11th (2019C) - EDocument36 pagesQE - 11th (2019C) - EAlbertNo ratings yet
- Unit 18 - Curved Graphs - DerivativeDocument5 pagesUnit 18 - Curved Graphs - DerivativeRaffaella LaxaldeNo ratings yet
- SUSTECH MathDocument24 pagesSUSTECH Matht0xic.369xNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations 4: Polynomial EquationDocument16 pagesQuadratic Equations 4: Polynomial EquationRithin NagarajNo ratings yet
- Algebra FormulasDocument12 pagesAlgebra FormulasAmir MustakimNo ratings yet
- Mathematics9 QuadraticfunctionsDocument14 pagesMathematics9 Quadraticfunctionswilliam FELISILDANo ratings yet
- Simultaneous Equations, Indices, Surds, Logarithms: Additional Mathematics SA2 Overall Revision NotesDocument8 pagesSimultaneous Equations, Indices, Surds, Logarithms: Additional Mathematics SA2 Overall Revision NotesVikas PatelNo ratings yet
- Solving Cubic Polynomials: 1.1 The General Solution To The Quadratic EquationDocument8 pagesSolving Cubic Polynomials: 1.1 The General Solution To The Quadratic Equationjohndo3No ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Vrindavana Bhajana by Srila PrabhupadaDocument7 pagesVrindavana Bhajana by Srila PrabhupadaPrabhatSinghNo ratings yet
- Gul in SpaceDocument22 pagesGul in SpaceJAN OVE CLAUNANo ratings yet
- For Your Local Distributor VisitDocument4 pagesFor Your Local Distributor VisitninaNo ratings yet
- AWC NDS SUPP - National Design Specification For Wood ConstructionDocument3 pagesAWC NDS SUPP - National Design Specification For Wood ConstructionMichaelNo ratings yet
- Come On ManDocument48 pagesCome On ManSami Arts100% (2)
- Chemistry 2019Document17 pagesChemistry 2019Amr Khaled Amar Mohamed salh عمرو خالد عمار محمود صالحNo ratings yet
- Amul STP: MissionDocument3 pagesAmul STP: MissionKhushi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- DEP 31.40.60.11-Gen. Rev. Sep 2002Document19 pagesDEP 31.40.60.11-Gen. Rev. Sep 2002Subbu AbuNo ratings yet
- Transport Phenomena 2Document9 pagesTransport Phenomena 2Kaify PeshmergaNo ratings yet
- Quality Evaluation of Jaggery Chocolate Under VariDocument7 pagesQuality Evaluation of Jaggery Chocolate Under VariAbhinit SinhaNo ratings yet
- IDIN-3 DTV3 Extra Grammar Exercises I PARTIALDocument4 pagesIDIN-3 DTV3 Extra Grammar Exercises I PARTIALrobert martinezNo ratings yet
- Futura 001-100Document11 pagesFutura 001-100z0rankNo ratings yet
- Reliable Detection of Downed and Broken ConductorsDocument5 pagesReliable Detection of Downed and Broken Conductorsprathikgala2324234No ratings yet
- Infectious or Communicable Diseases: TuberculosisDocument7 pagesInfectious or Communicable Diseases: TuberculosischandraNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-09-18 at 11.25.28 AMDocument49 pagesScreenshot 2023-09-18 at 11.25.28 AMVishwa OzaNo ratings yet
- HPLC Determination of Active Diterpene Lactones From Andrographis Paniculata Nees Planted in Various Seasons and Regions in ThailandDocument10 pagesHPLC Determination of Active Diterpene Lactones From Andrographis Paniculata Nees Planted in Various Seasons and Regions in ThailandAlil MaqdizaNo ratings yet
- Switchgear Manufacturing Company Pvt. LTD Smc-454-Rev-0Document62 pagesSwitchgear Manufacturing Company Pvt. LTD Smc-454-Rev-0Suvendu Sekhar SabatNo ratings yet
- Dow Corning 791Document3 pagesDow Corning 791Trung Nguyễn Ngọc100% (1)
- BEE SafetyManualDocument196 pagesBEE SafetyManualAmeenudeenNo ratings yet
- KaranthDocument9 pagesKaranthRakesh KhannaNo ratings yet
- Matt Zwier - Freelance - Metropolitan Radiation Oncology BrochureDocument2 pagesMatt Zwier - Freelance - Metropolitan Radiation Oncology BrochureMattNo ratings yet
- Session-2021-22 Assignment On:-: IgkvraipurDocument31 pagesSession-2021-22 Assignment On:-: IgkvraipurBHUPENDRA RANANo ratings yet
- NW June P1 2019 MemoDocument6 pagesNW June P1 2019 MemoAsandaNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and ElectromagnetismDocument19 pagesMagnetism and ElectromagnetismRyan A. RamosNo ratings yet
- KBS Series Piezo BuzzersDocument1 pageKBS Series Piezo BuzzersBenjamín Varela UmbralNo ratings yet
- FactoringDocument1 pageFactoringGary NugasNo ratings yet