Professional Documents
Culture Documents
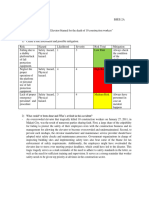
RUELO Assignment#8
Uploaded by
giangianruelo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views6 pagesOriginal Title
RUELO_Assignment#8
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views6 pagesRUELO Assignment#8
Uploaded by
giangianrueloCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Amante Gian L.
Ruelo 12/11/23
BOHS: Assignment#8 BSEE-2A
MIOSHA Regulations Covered in
this Training Session
• Hazard Communication Standard • Anti-discrimination Clause
• Personal Protective Equipment No Discrimination
Standard
• Laboratory Safety Standard - Employees are protected from
discrimination or discharge resulting
from a request for information regarding
hazardous chemicals under the Hazard
Occupational Safety and Health Communication (Right-to-Know) law.
Regulations
Hazardous Chemical List
• Federal Department of Labor
• Federal OSHA Regulations • Include all hazardous chemicals found
• State of Michigan Department of in your work area
Consumer and Industry Services • Maintain up-to-date copy identifying:
• Michigan Occupational Safety ❖ Chemical name
and Health Act (MIOSHA ❖ Maximum potential quantity
❖ Storage location
• Available to employees
Introduction to the Hazard • Can be useful to emergency response
personnel
Communication Standard
Hazardous Chemicals
Purpose of the Hazard Communication
Standard (Right to Know) • Strong Acids and Bases
• Flammable solvents: acetone, ethanol
• To assure that employees are • Toxics: formaldehyde, acetonitrile,
provided with the information ethidium bromide, phenol, silane
they need to handle hazardous • Carcinogens: acrylamide, osmium
materials and equipment safely. tetroxide
Requirements of the Hazard • Compressed gases
Communication Standard Container Labeling
• Written HazCom Program • Manufacturer must label
• Hazardous Chemical Evaluation ❖ Bulk chemical containers
• List and Label Hazardous • Lab personnel must label
Chemicals ❖ Secondary containers
• Chemical Safety Information • Label must include full chemical name,
Available concentration and the primary hazard
• Employee Training
• Recordkeeping
• Deface & triple rinse empty chemical • Substance Identification and Synonyms
containers for disposal • Hazardous Components (if mixture)
• Physical Data: appearance, melting
point
• Fire & Explosion Data: flash-point, LEL
• Toxicity Data: LD50’s, carcinogenicity
• Health Effects & First Aid
• Reactivity: incompatibilities
• Storage & Disposal Procedures
• Spill & Leak Procedures
• Protective Equipment
Health Hazard Definitions
Warning Labels • Carcinogen: Causes cancer
• Corrosive: Causes visible destruction of
living tissue by chemical action
• Irritant: Causes reversible inflammatory
effect on living tissues
• Sensitizer: Causes most people to
develop an allergic reaction after
repeated exposure
• Toxic: Poisonous
What Training is Required?
Target Organ Effects
❖ Baseline Training = this class
• Hepatotoxins: Liver damage
❖ Work Specific Training =
• Neurotoxins: Nervous system damage
instruction you receive from your
supervisor • Nephrotoxins: Kidney damage
• Hematopoietic: Blood
Maintain records for all training function/production damage
• Pulmonary Hazard: Damages the lung
Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS)
• Cutaneous Hazard: Affects or damages
• Primary resource for chemical hazard skin
communication • Ocular hazards: Affects eye or visual
• For every hazardous chemical capacity
• Available online • Reproductive toxins: Affects
• Locator poster required reproductive capabilities
• Standard information required by the ❖ Teratogen: Impacts developing
regulation will be contained in the fetus
MSDS ❖ Mutagen: Impacts DNA
What information will be in the MSDS?
What Factors Affect Chemical Exposure? - To provide employees with appropriate,
reliable and sanitary PPE that is of safe
• Amount and toxicity of chemical design and construction
• Duration and frequency of exposure
• Route of entry What Is Personal Protective Equipment?
• Hazard controls (Engineering, - Equipment worn to protect workers and
Administrative and PPE) students against hazards in the
Control of Hazards workplace
• Engineering Controls How Does PPE Work?
❖ Substitution - By creating a barrier between the hazard
❖ Isolation and your body
❖ Ventilation
Requirements of PPE Standard
• Administrative Controls
• Conduct hazard assessment
Standard Operating Procedures (SOP)
• Assign and purchase PPE
❖ Duration of exposure • Train employees
• Personal Protective Equipment ❖ use, storage, maintenance
(PPE) • Document everything
❖ Gloves, Glasses, Lab coat • PPE covered: Hand, Eye, Foot, Head
How to Detect a Potential Personal Why Is PPE Important?
Exposure - Every year nearly two million people are
injured on the job One quarter of
• Visual appearance (dust, mist, fume)
disabling work injuries affect the eyes,
• Odor (odor threshold)
face, head, feet or hands Most injuries
• Body signs and symptoms could be prevented with the proper use
❖ (acute vs. chronic effects) of Personal Protective Equipment
• Environmental monitoring
❖ Permissible Exposure Limit (PEL) Who Needs PPE?
Personal Monitoring - Anyone potentially exposed to chemical,
physical, radioactive or biological
Working Safely with Hazardous hazards to the eyes, face, head, feet or
Chemicals hands
• Read labels Protective Eyewear
• Receive chemical specific training
• Stay alert What Type of Eye/Face Protection Do I
• Wear personal protective equipment Need?
• See your supervisor for non-routine
tasks
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Standard
Purpose of the PPE Standard
Minimum PPE Required In All Labs
• Safety Glasses
• Labcoat
• Disposable Gloves
• No shorts or open toe shoes allowed in
labs!!
Are There Limitations? YES!!!
• PPE cannot protect you if…
❖ you do not wear it
❖ you do not wear it properly
Gloves ❖ you do not wear the appropriate
type for the task you are
• Ensure proper equipment is available
performing
• Replace as needed
• INSPECT Your PPE PRIOR To Each
• Do not re-use disposable gloves
Use…
• Remove gloves BEFORE leaving the
• Do NOT Use Damaged Or Defective
work area
PPE!!!
• ALWAYS wash hands after removing
gloves Who Do I Call With Questions?
Don't Wear Protective Gloves Outside the • Your Supervisor
Research Laboratory • Your OSEH Representative
• Gloves may become contaminated Laboratory Safety Standard
during research procedures
• Wearing glove into public areas may Purpose of the Laboratory Safety
lead to cross-contamination Standard
• Transporting specimens
- To reduce or eliminate the risk of
exposure to employees from hazardous
chemicals in the laboratory
Chemical Hygiene Plan (CHP)
• Review before working in the laboratory
• If unavailable please see your supervisor
• Generic CHP is available on-line at:
http://www.umich.edu/~oseh/chp1.html
• Labs must customize the CHP Notebook
section
Laboratory Safety Standard
• Chemical Hygiene Plan (CHP)
Components
Protective Footwear ❖ Chemical List
❖ Standard Operating Procedures
❖ Material Safety Data Sheets • To redistribute unopened chemicals call
❖ Emergency Preparedness OSEH HazMat at 3-4568
❖ General and Specific Training
❖ Specific Waste Disposal
Methods Emergency Preparedness
❖ Personal Protective Equipment
❖ Inspections and Exposure • Rule of thumb - Plan ahead!!
Monitoring ❖ It will explode, catch fire, spill,
or release
Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) • Evacuate the lab
• Written for an individual hazardous • Shut door & post restriction if necessary
chemical or method using that chemical • Activate alarm & call 911
and includes: • Implement emergency response plan for
❖ Hazardous properties of your unit
chemical
Emergency Response
❖ Proper chemical storage
❖ PPE (gloves, glasses, etc.) • Ventilation failures
Proper location to perform • Plumbing leaks
procedure • Power failures
❖ Proper waste disposal • Fires and explosions
❖ Accident and spill reporting
• Spill control and clean-up
❖ Equipment hazards and
• Personal injury and exposure
precautions
Chemical Waste Disposal: What can go
Compressed Gas Cylinders
down the sink?
• Always secure in an upright position
• Only…
• Use valve protection caps
❖ Bleach and other disinfectants
• Properly label cylinder
❖ Blood and blood-products
❖ Name of gas
❖ Detergent and other cleaners
❖ Type of gas (Oxidizer,
❖ Buffers, isotonic saline
Flammable, etc.)
solutions, or non-hazardous
❖ Current status "Full or Empty"
liquid media, acids/bases with a
• Do not store flammable gasses near
pH between 5-10
ignition sources or oxidizers
• Do not block access to cylinders Hazardous Chemical Waste Management
• Do not run hoses throughout lab
• Properly store compatible waste
Safe Chemical Storage • Use secondary containment when > 10
gallons
• Separate stored chemicals by • Pack in a suitable container for
compatibility: (acid, base, flammable, transportation
oxidizer)
• Affix completed “Hazardous Waste”
• Store bulk flammable liquids in a
label listing chemicals in the container
Flammable Liquid Storage Cabinet
• Make sure the container is closed and
• Refrigerate flammable chemicals only in
sealed
a unit designed for that purpose
Hazardous Chemical Waste Labeling
• EPA ID Number: • Frequent hand washing recommended
❖ MI0000052852 • Do Not block access to emergency
• Manifest Number showers and eyewash stations
• Generator Information
• Chemical Description of Hazardous
Waste
• Accumulation Start Date
• Label ALL hazardous waste containers
Call OSEH HazMat (734-763-4568) for
assistance
Hazardous Waste Manifest
*See handout for explanation of numbers
Tips for Fume Hood Use
• Check that the hood is operating
correctly
• Use the sash to protect yourself
• Keep sash at the certification mark
• Do not use for chemical storage
• Be aware of ignition sources when using
flammables (multiple users of a hood)
• Keep the work surface neat
• Close the sash when not in use
Additional Safety Precautions
• Know location of Emergency Shower
and Eyewash (100 feet/10 second rule)
• Know location of Fire Response
Equipment
• No eating or drinking in laboratories
• Do NOT store food in laboratory
refrigerators; label with appropriate sign
You might also like
- Haz Com 2010Document57 pagesHaz Com 2010Mohammad AshpakNo ratings yet
- PMLS 6 LABORATORY SAFETY Converted 1Document9 pagesPMLS 6 LABORATORY SAFETY Converted 1seaynNo ratings yet
- Laboratory SafetyDocument42 pagesLaboratory SafetyIrizz LlagasNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Safety Safety Documentation & Records: - Sample ContentsDocument8 pagesLaboratory Safety Safety Documentation & Records: - Sample ContentsGraceNo ratings yet
- Aubf LabDocument99 pagesAubf Labhinata shoyoNo ratings yet
- 01 Laboratory Regulations + Post LabDocument6 pages01 Laboratory Regulations + Post LabCARLA MAY MACATANGAYNo ratings yet
- SPDX Lab-SafetyDocument7 pagesSPDX Lab-Safetydumppotato24No ratings yet
- Laboratory Safety Safety Documentation & Records: - Sample ContentsDocument8 pagesLaboratory Safety Safety Documentation & Records: - Sample ContentsGraceNo ratings yet
- MDR With Brexit - How The Combination Is Impacting The European Medical Device Industry - NelsonDocument26 pagesMDR With Brexit - How The Combination Is Impacting The European Medical Device Industry - Nelsonliesbeth albertsNo ratings yet
- Pmls 5-Laboratory SafetyDocument8 pagesPmls 5-Laboratory SafetySheena ChanNo ratings yet
- Hazard Communication and Chemical SafetyDocument18 pagesHazard Communication and Chemical SafetyJerahMaligayaNo ratings yet
- 2 1industrialhygieneDocument33 pages2 1industrialhygieneAizm DinaniNo ratings yet
- IG2 Element 7Document84 pagesIG2 Element 7Shabry SamoonNo ratings yet
- Industrial Hygiene: by - Iram Danish SEMT-48Document33 pagesIndustrial Hygiene: by - Iram Danish SEMT-48Ultrapure AnalytichemNo ratings yet
- HEMA Lab PRELIMSDocument29 pagesHEMA Lab PRELIMSBARBIE CORONELNo ratings yet
- ChemicalDocument82 pagesChemicalTonyo LinaNo ratings yet
- HLTWHS001 - Risk Management and AssessmentDocument9 pagesHLTWHS001 - Risk Management and AssessmentkinyzoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Safety 2019Document42 pagesChemical Safety 2019Maria OzaoNo ratings yet
- Afa12 FP Q3 W1 SLMDocument6 pagesAfa12 FP Q3 W1 SLMwhite kiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 - General Provision On Toxic - Dec 2020Document43 pagesCHAPTER 4 - General Provision On Toxic - Dec 2020Adam Zachary Mohd FaizalNo ratings yet
- Health, Safety, and The Environment: Thrust 4: Responsible NanomanufacturingDocument5 pagesHealth, Safety, and The Environment: Thrust 4: Responsible NanomanufacturingMaterials Research Institute0% (1)
- Effective Health and Safety Committees - Part OneDocument22 pagesEffective Health and Safety Committees - Part OneIwueke Cynthia EzinneNo ratings yet
- Hirarc PDFDocument97 pagesHirarc PDFWan ZahirNo ratings yet
- Hazard Identification and Risk AssessmentDocument20 pagesHazard Identification and Risk AssessmentSaraansh SinghNo ratings yet
- KH Enviornment of Care PhysiciansDocument2 pagesKH Enviornment of Care PhysiciansAngelo Russel LazagaNo ratings yet
- A Delay in MDR Where Are We Now GreenDocument19 pagesA Delay in MDR Where Are We Now GreenmedjtouhNo ratings yet
- Webinarslides HazComDocument22 pagesWebinarslides HazComhuzaifa.safdarNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To COSHH: Control of Substances Hazardous To Health Regulations, 2004)Document118 pagesAn Introduction To COSHH: Control of Substances Hazardous To Health Regulations, 2004)Parthasarathy VadapalliNo ratings yet
- 03 Hazard CommunicationsDocument29 pages03 Hazard Communicationssemeneh haileNo ratings yet
- Chemical SafetyDocument27 pagesChemical SafetyVina May LaurioNo ratings yet
- 5 - CHRA in Plantation - PN MariniDocument33 pages5 - CHRA in Plantation - PN Marininona_supergirl9No ratings yet
- WMSU Lec5 OHealthDocument63 pagesWMSU Lec5 OHealthKaiser CarloNo ratings yet
- Chp. 4 - Hazards Identification: Faculty of Chemical Engineering Universiti Teknologi MARADocument39 pagesChp. 4 - Hazards Identification: Faculty of Chemical Engineering Universiti Teknologi MARACaratsSVTNo ratings yet
- SH5108 - 1 Chemical Hazard Management - PrinciplesDocument24 pagesSH5108 - 1 Chemical Hazard Management - Principlestaaouicha mujahidNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document27 pagesLec 2Syeda Wardah NoorNo ratings yet
- Practical 1 - SafetyDocument8 pagesPractical 1 - SafetyMona JayNo ratings yet
- Sheila Mae C. Dauz Donna C. SardeñolaDocument15 pagesSheila Mae C. Dauz Donna C. SardeñolastoopiidgurlNo ratings yet
- Occupational Health & Safety Programs: IacucDocument10 pagesOccupational Health & Safety Programs: IacucIrish Joy CachaperoNo ratings yet
- Brandi Kissel - Risk Assessment For New DisinfectantsDocument22 pagesBrandi Kissel - Risk Assessment For New DisinfectantsmohamedNo ratings yet
- Lab Safety 5Document30 pagesLab Safety 5S Lin Ong100% (2)
- 01 All-Hazards Threat Overview v3 JAB FINALDocument33 pages01 All-Hazards Threat Overview v3 JAB FINALLuka KoloskiNo ratings yet
- Occupational Health Hazards: Raymond Gomez BlancoDocument113 pagesOccupational Health Hazards: Raymond Gomez BlancoAviects Avie JaroNo ratings yet
- FDA Perspectives On Human Factors in Device DevelopmentDocument46 pagesFDA Perspectives On Human Factors in Device DevelopmentsachinNo ratings yet
- Sterilization and DisinfectionDocument9 pagesSterilization and DisinfectionFrances Lau Yee ChinNo ratings yet
- Chemical Hazard and Biological HazardDocument16 pagesChemical Hazard and Biological HazardPrimelift Safety Resources LimitedNo ratings yet
- COSH Module 2 - 2B Medical Surveilance (Synerquest) - CompressedDocument54 pagesCOSH Module 2 - 2B Medical Surveilance (Synerquest) - Compressedalmiraraiza bustamanteNo ratings yet
- Chemical Management Plan (Revised)Document25 pagesChemical Management Plan (Revised)Crizaldo Mempin67% (3)
- Lifting Plan and MaintenanceDocument21 pagesLifting Plan and MaintenanceMuhamad arifNo ratings yet
- Introduction Applicable Regulatory Req v3Document52 pagesIntroduction Applicable Regulatory Req v3mercentNo ratings yet
- General Workplace SafetyDocument43 pagesGeneral Workplace SafetySivaraman Pillai100% (3)
- Good Health Is Good BusinessDocument67 pagesGood Health Is Good BusinessNaba majeadNo ratings yet
- Labman Week 4Document5 pagesLabman Week 4tuamicaiiiNo ratings yet
- .Archivetempunit GC2 Element 7 - InternationalDocument98 pages.Archivetempunit GC2 Element 7 - Internationalaqib.aliNo ratings yet
- School Report Chemical HazardsDocument22 pagesSchool Report Chemical HazardsoatcookiesNo ratings yet
- Hazard and Risk Management - Yadav Pooja.S.Document30 pagesHazard and Risk Management - Yadav Pooja.S.Shivali PatilNo ratings yet
- Biological Laboratory SafetyDocument14 pagesBiological Laboratory Safetykhalid najjarNo ratings yet
- HEMA311LABWEEK2Document4 pagesHEMA311LABWEEK2Daphlene Kayt A. MapoyNo ratings yet
- Safety Guidelines For Recombinant DNA ResearchDocument29 pagesSafety Guidelines For Recombinant DNA ResearchNikhil Kumar - 35No ratings yet
- Fundamental of Process Safety Management System (PSM)Document41 pagesFundamental of Process Safety Management System (PSM)Basaci AbdelghaffarNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Materials Characterization: Evaluation Methods, Procedures, and ConsiderationsFrom EverandHazardous Materials Characterization: Evaluation Methods, Procedures, and ConsiderationsNo ratings yet
- Report MFDocument11 pagesReport MFgiangianrueloNo ratings yet
- RUELO Assignment#6Document1 pageRUELO Assignment#6giangianrueloNo ratings yet
- Idoy MalakiDocument1 pageIdoy MalakigiangianrueloNo ratings yet
- Idoy DakoDocument2 pagesIdoy DakogiangianrueloNo ratings yet
- BOMMI-PRD-07.0013-Rev.00 - Anchor Handling and Towing OperationsDocument10 pagesBOMMI-PRD-07.0013-Rev.00 - Anchor Handling and Towing Operationsfundatia_gaudeamus100% (3)
- Eisenberg ModelDocument9 pagesEisenberg ModelJesusNo ratings yet
- Userguide SW-MC V2 2015-W45 EN S034308Document131 pagesUserguide SW-MC V2 2015-W45 EN S034308ReneNo ratings yet
- Lawson Products, Inc - Non-Flammable Penetrating OilDocument4 pagesLawson Products, Inc - Non-Flammable Penetrating Oiljaredf@jfelectric.comNo ratings yet
- Exam NIOSH Paper 3Document12 pagesExam NIOSH Paper 3Ahmad FarisNo ratings yet
- Hospital Emergency Incident Command SystemDocument32 pagesHospital Emergency Incident Command SystemIzar Ramil Carlyl YbañezNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment 5Document28 pagesRisk Assessment 5Shivaraman ShankarNo ratings yet
- Level 2 Risk Assessment Form - UTTM - Rev0Document2 pagesLevel 2 Risk Assessment Form - UTTM - Rev0Raznan RamliNo ratings yet
- Stonproof CT5 Product Data - en - USDocument2 pagesStonproof CT5 Product Data - en - USVentas ExpertisNo ratings yet
- BiosafetyMicroBiomedicalLab5th 2007Document413 pagesBiosafetyMicroBiomedicalLab5th 2007Lâm Thái ThànhNo ratings yet
- S1 - Preliminaries (Jan 2013)Document64 pagesS1 - Preliminaries (Jan 2013)msyan1965No ratings yet
- JSA - Paintng in Confined SpaceDocument6 pagesJSA - Paintng in Confined SpaceJohnNo ratings yet
- Nalco Msds Ec 1021aDocument10 pagesNalco Msds Ec 1021aMuhammad SulemanNo ratings yet
- Front Side Silver Paste 653G SDS - GENERAL - TEXANOL (English Version) V2.7 (PB)Document6 pagesFront Side Silver Paste 653G SDS - GENERAL - TEXANOL (English Version) V2.7 (PB)Desheng ChewNo ratings yet
- MAN - AirPackDocument150 pagesMAN - AirPackhardevNo ratings yet
- Q1 Module 1 TVL-Plumbing12ModulesDocument63 pagesQ1 Module 1 TVL-Plumbing12ModulesMARLA RUBY PAZ YTING100% (1)
- Quarter 4 - Module 1: Computer Systems ServicingDocument12 pagesQuarter 4 - Module 1: Computer Systems ServicingRHAYAN DAQUIZNo ratings yet
- 720 Msds-Dromus BDocument8 pages720 Msds-Dromus Bmsjadm MegasuplindoNo ratings yet
- NFPA 1072 Ops Skills For StudentsDocument19 pagesNFPA 1072 Ops Skills For StudentsVictor Hugo CabralNo ratings yet
- Helmet: Safety Is No More An Option It Is An Imperative. - SnsDocument19 pagesHelmet: Safety Is No More An Option It Is An Imperative. - SnsRajanbabuNo ratings yet
- 23 Case Studies For Falling From HeightsDocument65 pages23 Case Studies For Falling From HeightsAejaz MujawarNo ratings yet
- 7 - Pile Cutting & HackingDocument2 pages7 - Pile Cutting & HackingRafee Pie93% (14)
- MXJ-1100 Training Doc 1Document37 pagesMXJ-1100 Training Doc 1marcos marquez100% (1)
- JSS-DSB-TAWAU-MOS-018 - Drainage - Rev 00Document7 pagesJSS-DSB-TAWAU-MOS-018 - Drainage - Rev 00Masar Abdul RakmanNo ratings yet
- Ceramic Polymer STP Ep HV Part B - V 1,03 - 2016!02!19 - GB en CP 90 B - NeuDocument12 pagesCeramic Polymer STP Ep HV Part B - V 1,03 - 2016!02!19 - GB en CP 90 B - NeuhainguyenbkvhvNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Pile Head TreatmentDocument7 pagesMethod Statement For Pile Head TreatmentJoe Ps100% (1)
- Endozime - Sponge - Mini SDS 345MINI Rev02Document2 pagesEndozime - Sponge - Mini SDS 345MINI Rev02carlos andres calderon torresNo ratings yet
- 1.1. Hse Key Management StandardDocument26 pages1.1. Hse Key Management StandardagumsyahNo ratings yet
- HITACHI - EX1200-6 - Workshop Manual - W18J-E-00 PDFDocument590 pagesHITACHI - EX1200-6 - Workshop Manual - W18J-E-00 PDFGeorge Zormpas100% (3)
- SM - wx145 - Wx185 Tier3 - enDocument788 pagesSM - wx145 - Wx185 Tier3 - enhassan hamdyNo ratings yet