Professional Documents
Culture Documents
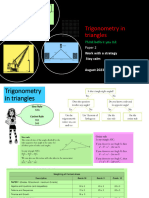
Trigonometry Summary Sheet
Trigonometry Summary Sheet
Uploaded by
vqg4wtjxbhCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Trigonometry Summary Sheet
Trigonometry Summary Sheet
Uploaded by
vqg4wtjxbhCopyright:
Available Formats
Trigonometry Summary Sheet
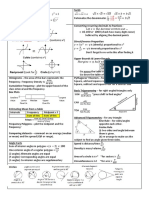
Labelling Triangles
Triangles in General:
Capital letters for angles, and small letters for the opposite sides
Right Angle Triangles:
The adjacent side and opposite side depend on which angle you are using.
Right Angle Triangles Non-Right Angle Triangles
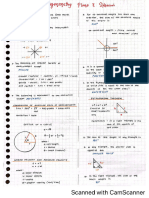
Pythagorean Theorem Cosine Law
a2 = b2 + c2 a2 = b2 + c2 – 2bc cosA
where a is the hypotenuse Used in:
SSS
SAS
Sine Law
Always label your triangle first with Solving for a side:
H, O, A
Solving for an angle:
Used in:
SSA
AAS (whenever you have 2 angles)
If you don’t know the angle, WARNING: Make sure calculator is in degrees.
sin x = 0.722
x = sin-1(0.722)
x = 46°
Sine Law Ambiguous Case:
-occurs when the side opposite to the angle given is smaller than the side adjacent to the
angle.
There are two possible Angle C values, for two different triangles. One of the triangles is
an obtuse triangle, one is an acute.
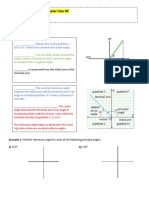
This is an angle of elevation: This is an angle of depression:
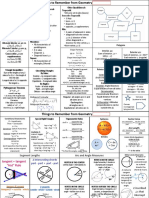
Geometry Theorems: (fill in all the missing ones)
Isosceles Triangle
Parallel Lines
Corresponding Angles Co-interior Angles Alternate Angles
Compass Points (Draw the examples)
S7ºE N10ºW E46ºN W30ºS
(7º East of South) (10º West of North) (46º North of East) (30º South of West)
You might also like
- Ch1 Geometry 2Document47 pagesCh1 Geometry 2trantuanan123No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Key Points: y F (X) + C y F (X) - C y F (X + C) y F (X - C)Document18 pagesChapter 1 Key Points: y F (X) + C y F (X) - C y F (X + C) y F (X - C)Angel Angel100% (1)
- GRade 8 Triangles DemoDocument60 pagesGRade 8 Triangles DemoJoxel GallerNo ratings yet
- Mensuration PDFDocument33 pagesMensuration PDFSudhanshu Kumar100% (1)
- DLP g10 Math 2nd QTR Week 7 FinalDocument13 pagesDLP g10 Math 2nd QTR Week 7 FinalCei-Cei100% (1)
- Spherical Trigonometry Lecture SummaryDocument3 pagesSpherical Trigonometry Lecture SummaryRenderizzah FloraldeNo ratings yet
- Review Module 5 Plane and Solid Geometry Part 1Document2 pagesReview Module 5 Plane and Solid Geometry Part 1YeddaMIlagan100% (1)
- Geometry (2D)Document26 pagesGeometry (2D)mnashish619No ratings yet
- GR 11 Trigonometry in Triangles September 2023Document75 pagesGR 11 Trigonometry in Triangles September 2023zmiqbal786No ratings yet
- A Sum of 360 Degrees 2Document10 pagesA Sum of 360 Degrees 2lam044980No ratings yet
- G11 TrigDocument51 pagesG11 TrigmiwoocyaNo ratings yet
- Geometry: WWW - Percenti Leclasses - in Live - Percentil Eclasses - in Download Mobile APP FromDocument73 pagesGeometry: WWW - Percenti Leclasses - in Live - Percentil Eclasses - in Download Mobile APP FromVIBHANSHU SINGHNo ratings yet
- AnGLES N Triang.sDocument11 pagesAnGLES N Triang.sjayNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument3 pagesTrigonometrycongratsclan7No ratings yet
- Chapter4trigonometry 28versipelajar 29Document18 pagesChapter4trigonometry 28versipelajar 29wan hazirahNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 - Plane Figures Plane Geometry Is Division of Geometry Concerned AboutDocument15 pagesTopic 6 - Plane Figures Plane Geometry Is Division of Geometry Concerned AboutShine100% (1)
- Sec 9.2 042719Document4 pagesSec 9.2 042719efril estradaNo ratings yet
- Quadratic: ST NDDocument8 pagesQuadratic: ST NDtheturfkitchenNo ratings yet
- SAT Math Formulas - Worthington PrepDocument7 pagesSAT Math Formulas - Worthington Prepashrafshehab695No ratings yet
- Review Module 1Document5 pagesReview Module 1aljohnbondad121521No ratings yet
- Using The Sine RuleDocument7 pagesUsing The Sine RuleJoel OkohNo ratings yet
- G09 Week 1 - Q4 - Six Trigonometric RatiosDocument72 pagesG09 Week 1 - Q4 - Six Trigonometric RatiosGladje Fran JerezNo ratings yet
- Lines and AnglesDocument9 pagesLines and AnglesJessie JudithNo ratings yet
- 6 Geometry 01apr2009 PDFDocument1 page6 Geometry 01apr2009 PDFNarenNo ratings yet
- Geometry and TrigonometryDocument15 pagesGeometry and Trigonometryahmedghazali5No ratings yet
- Circle TheoremsDocument18 pagesCircle TheoremsSamuel MalileNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Mathematics Quarter 4Document25 pagesGrade 9 Mathematics Quarter 4DgkNo ratings yet
- Trig Ratios For Angles Greater Than 90 Degrees Lesson NOTEDocument3 pagesTrig Ratios For Angles Greater Than 90 Degrees Lesson NOTE970637No ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument86 pagesTrigonometryOlha ShyikoNo ratings yet
- OriginalDocument28 pagesOriginalTushar BadheNo ratings yet
- L2s - Ratios For Angles Greater Than 90Document5 pagesL2s - Ratios For Angles Greater Than 90YoviNo ratings yet
- Triangles: Here, Ab Ac B CDocument1 pageTriangles: Here, Ab Ac B CDavidkumar MoramNo ratings yet
- TRIG FUNCTIONS Lesson Solving Right TrianglesDocument52 pagesTRIG FUNCTIONS Lesson Solving Right TrianglesRudi BerlianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Organizer Right Triangles and TrigDocument9 pagesChapter 9 Organizer Right Triangles and TrigCristina BilogNo ratings yet
- Handout 1 - Sine Rule and Cosine RuleDocument4 pagesHandout 1 - Sine Rule and Cosine Ruledam damNo ratings yet
- Topic 2: Trigonometry I: Part A: Angle MeasuresDocument10 pagesTopic 2: Trigonometry I: Part A: Angle MeasuresNjoka Samuel K100% (1)
- Trigo NotesDocument7 pagesTrigo NotesFaith Rezza Mahalia F. BETORIONo ratings yet
- Cambridge Standard 12 Chapter 4Document11 pagesCambridge Standard 12 Chapter 4Raymond Zhu100% (1)
- Short Notes For Geometry - PrintDocument8 pagesShort Notes For Geometry - PrintAvinash GudainiyanNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument28 pagesGeometryASHWIN .A.S.No ratings yet
- Geometry Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesGeometry Cheat Sheetsweta_123No ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument20 pagesTrigonometryLeanelle ReynoNo ratings yet
- PreCal 2nd Periodical ReviewerDocument9 pagesPreCal 2nd Periodical ReviewerCastillo Kiefer AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Review Module - Plane & Solid Geometry - N2023Document3 pagesReview Module - Plane & Solid Geometry - N2023Mina, KhristineNo ratings yet
- Triangle Congruence PostulateDocument12 pagesTriangle Congruence PostulateShania Deidre GamayanNo ratings yet
- Angles Facts, Parallel Lines, Angle ProofsDocument68 pagesAngles Facts, Parallel Lines, Angle ProofsPeter GanzNo ratings yet
- Maths Holiday Homework (Trigonometric Ratios) X-A Roll No 3Document11 pagesMaths Holiday Homework (Trigonometric Ratios) X-A Roll No 3daxe ytNo ratings yet
- Geometry 12 ReviewerDocument8 pagesGeometry 12 ReviewerBlanche Iris Estrel SiapnoNo ratings yet
- PHYS2614 Year 2023Document243 pagesPHYS2614 Year 2023Lesego MogoaneNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Quarter 4 Week 7-Ms. TimaDocument7 pagesMath 9 Quarter 4 Week 7-Ms. TimaJuvy Rose TimaNo ratings yet
- Finals ModuleDocument22 pagesFinals ModuleTin MhudzNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Chapter 5Document30 pagesTrigonometry Chapter 5Luisa Mae N. MahenerNo ratings yet
- GCSE CheatSheet v2 - JORDocument2 pagesGCSE CheatSheet v2 - JORHelp GloPosNetNo ratings yet
- 2 MathDocument5 pages2 MathAlexandra EscalonaNo ratings yet
- Topic 6-Introduction To TrigonometryDocument26 pagesTopic 6-Introduction To Trigonometryshaunjali21No ratings yet
- Geometry and TrigonometryDocument6 pagesGeometry and TrigonometryAbhay SoniNo ratings yet
- Triangle Congruence PDFDocument28 pagesTriangle Congruence PDFLA AlmznNo ratings yet
- Right Angled TriangleDocument5 pagesRight Angled TriangleMana GargiNo ratings yet
- MCR3U CH 5 Notes - Filled In-3Document28 pagesMCR3U CH 5 Notes - Filled In-3vqg4wtjxbhNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 2d ProblemsDocument1 pageLesson 8 2d Problemsvqg4wtjxbhNo ratings yet
- Solving 3d DiagramsDocument2 pagesSolving 3d Diagramsvqg4wtjxbhNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Intro To Periodic Functions - Notebook November 14, 2016: Nov 14 12:20 PMDocument1 page5.1 Intro To Periodic Functions - Notebook November 14, 2016: Nov 14 12:20 PMvqg4wtjxbhNo ratings yet